DNA repair deficiency syndromes US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for DNA repair deficiency syndromes. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
DNA repair deficiency syndromes US Medical PG Question 1: A 24-year-old man comes to the physician because his vision has worsened rapidly over the last 2 months. His maternal uncle lost his vision suddenly over a period of 3 months at 26 years of age. The patient's wife and 1-year-old son have normal vision. Funduscopic examination of the patient shows bilateral circumpapillary telangiectasia. Genetic testing shows a missense mutation in one of the genes of the electron transport chain complexes. The probability that this patient's son will be affected by the same disease is closest to which of the following?
- A. 33%
- B. 100%
- C. 0% (Correct Answer)
- D. 25%
- E. 50%
DNA repair deficiency syndromes Explanation: ***0%***
- This condition, **Leber's Hereditary Optic Neuropathy (LHON)**, is caused by a mutation in **mitochondrial DNA**.
- **Mitochondrial DNA** is exclusively inherited from the mother, meaning the father cannot pass it on to his children.
*33%*
- This percentage does not align with any known pattern of Mendelian inheritance or mitochondrial inheritance.
- It would be too low for a dominant mitochondrial disorder and too high for a recessive one if the mother were a carrier.
*100%*
- While all children of an affected mother would inherit the disease, the patient is a male, and mitochondria are inherited maternally.
- Therefore, the father cannot pass on his **mitochondrial DNA** to his son.
*25%*
- This percentage is typically associated with **autosomal recessive inheritance**, where both parents are carriers.
- LHON follows a **mitochondrial inheritance pattern**, which is distinct from autosomal inheritance.
*50%*
- This percentage is characteristic of **autosomal dominant inheritance** or X-linked recessive inheritance where the mother is a carrier.
- Since this is a **mitochondrial disorder**, the father's genes are not involved in transmission to his son.
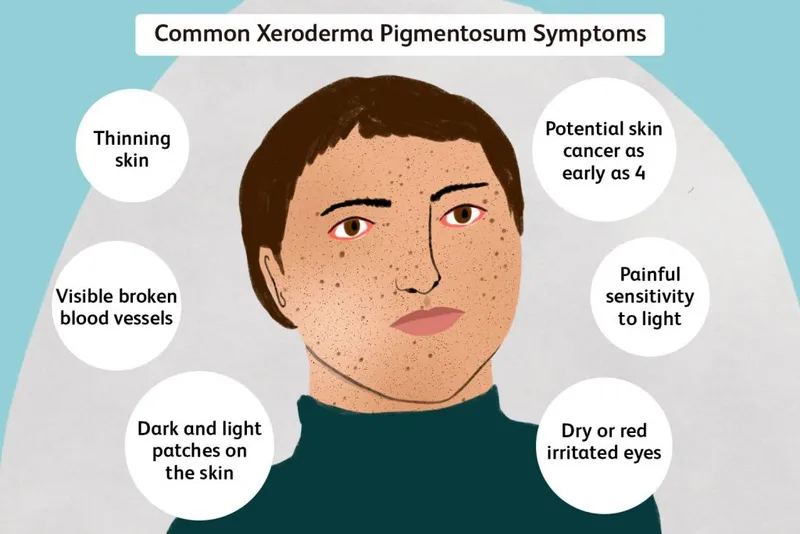
DNA repair deficiency syndromes US Medical PG Question 2: A 7-month-old boy presents to the family physician with extensive scaliness and pigmentation of sun-exposed skin areas. His mother says that these symptoms were absent until mid-spring and then became significantly worse after their trip to California in the summer. The child was born in December to a consanguineous couple after an uncomplicated pregnancy. He is breastfed and receives mashed potatoes, bananas, and carrots as complementary foods. His weight is 8.5 kg (18.7 lb) and length is 70 cm (2 ft 96 in). The patient’s vital signs are within normal limits for his age. On physical examination, there is freckling, scaling, and erythema on the sunlight-exposed areas of the face, trunk, and upper and lower extremities. No blistering, scarring, hypertrichosis, or alopecia is noted. The rest of the exam is unremarkable. Which process is most likely disrupted in this patient?
- A. Nucleotide-excision DNA repair (Correct Answer)
- B. Base-excision DNA repair
- C. Hydroxylation of proline and lysine in the procollagen molecule
- D. Conversion of uroporphyrinogen III to coproporphyrinogen III
- E. NAD production
DNA repair deficiency syndromes Explanation: ***Nucleotide-excision DNA repair***
- The patient's symptoms (extensive scaliness, pigmentation, freckling, scaling, and erythema on sun-exposed areas) that worsen with sun exposure are characteristic of **xeroderma pigmentosum**.
- This condition is caused by a defect in **nucleotide-excision repair (NER)**, which is essential for repairing DNA damage, particularly from UV radiation.
*Base-excision DNA repair*
- **Base-excision repair (BER)** primarily addresses single-base damage, like oxidized or alkylated bases, not the bulky adducts formed by UV light.
- Defects in BER are associated with conditions like colorectal cancer, but not the specific photosensitivity seen here.
*Hydroxylation of proline and lysine in the procollagen molecule*
- This process is essential for proper collagen synthesis; defects lead to disorders like **Ehlers-Danlos syndrome** or **scurvy**.
- These conditions manifest with skin fragility, bruising, and joint hypermobility, not the prominent photosensitivity observed.
*Conversion of uroporphyrinogen III to coproporphyrinogen III*
- This step is involved in **heme synthesis**; defects can lead to **porphyrias**, which often cause photosensitivity and blistering.
- However, the patient's presentation of scaling, freckling, and erythema without blistering or scarring is less typical for porphyria.
*NAD production*
- **NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)** is a crucial coenzyme in many metabolic pathways; its deficiency can lead to pellagra-like symptoms (dermatitis, diarrhea, dementia).
- While pellagra can involve sun-exposed skin, it typically involves a more diffuse, symmetrically inflamed rash with hyperpigmentation and thickening, rather than the discrete freckling and scaling described.
DNA repair deficiency syndromes US Medical PG Question 3: A 47-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for fatigue. Over the past 3 months, his tiredness has impacted his ability to work as a corporate lawyer. He denies any changes to his diet, exercise regimen, bowel movements, or urinary frequency. His past medical history is notable for obesity, type II diabetes mellitus, and hypertension. He takes metformin and enalapril. His family history is notable for colorectal cancer in his father and paternal grandfather and endometrial cancer in his paternal aunt. He has a 20-pack-year smoking history and drinks one 6-pack of beer a week. His temperature is 98.8°F (37.1°C), blood pressure is 129/71 mmHg, pulse is 82/min, and respirations are 17/min. On exam, he has conjunctival pallor. A stool sample is positive for occult blood. A colonoscopy reveals a small hemorrhagic mass at the junction of the ascending and transverse colon. Which of the following processes is likely impaired in this patient?
- A. Mismatch repair (Correct Answer)
- B. Homologous recombination
- C. Non-homologous end joining
- D. Nucleotide excision repair
- E. Base excision repair
DNA repair deficiency syndromes Explanation: ***Mismatch repair***
- The patient's presentation with **colorectal cancer** at a relatively young age and a strong family history of various cancers (colorectal, endometrial) in **first-degree and second-degree relatives** suggests Lynch syndrome (Hereditary Nonpolyposis Colorectal Cancer).
- **Lynch syndrome** is caused by inherited mutations in genes responsible for **DNA mismatch repair**, leading to an accumulation of errors and increased cancer risk.
*Homologous recombination*
- This repair mechanism is crucial for fixing **double-strand DNA breaks** using a homologous DNA template, important for genetic stability and primarily associated with genes like BRCA1/2.
- While defects in homologous recombination can lead to cancer (e.g., **breast and ovarian cancers**), it is not the primary mechanism implicated in Lynch syndrome or the patient's specific presentation of colorectal and endometrial cancer families.
*Non-homologous end joining*
- This is another major pathway for repairing **double-strand DNA breaks**, but it does so by directly ligating the broken ends, often with some loss of genetic information, and does not rely on a homologous template.
- Defects in non-homologous end joining are not typically linked to the specific spectrum of cancers seen in **Lynch syndrome**.
*Nucleotide excision repair*
- This pathway is responsible for removing bulky DNA lesions, such as those caused by **UV light (e.g., pyrimidine dimers)** or certain chemical mutagens, and its defects are associated with conditions like xeroderma pigmentosum.
- The clinical picture and family history are not characteristic of disorders related to impaired **nucleotide excision repair**.
*Base excision repair*
- This repair pathway primarily corrects small, non-bulky DNA lesions, such as **oxidized, alkylated, or deaminated bases**, that do not distort the DNA helix.
- While important for maintaining genomic integrity, defects in base excision repair are typically associated with different cancer susceptibilities and not the specific features of **Lynch syndrome**.
DNA repair deficiency syndromes US Medical PG Question 4: While performing a Western blot, a graduate student spilled a small amount of the radiolabeled antibody on her left forearm. Although very little harm was done to the skin, the radiation did cause minor damage to the DNA of the exposed skin by severing covalent bonds between the nitrogenous bases and the deoxyribose sugar, leaving several apurinic/apyrimidinic sites. Damaged cells would most likely repair these sites by which of the following mechanisms?
- A. Nucleotide excision repair
- B. Nonhomologous end joining repair
- C. Homologous recombination
- D. Mismatch repair
- E. Base excision repair (Correct Answer)
DNA repair deficiency syndromes Explanation: **Base excision repair**
- This mechanism is specifically involved in correcting **single-base DNA damage** or **modified bases**, such as **apurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) sites**.
- It involves removing the damaged base by a **DNA glycosylase**, creating an AP site, which is then processed by an **AP endonuclease** to cleave the phosphodiester backbone, followed by DNA polymerase and ligase.
*Nucleotide excision repair*
- Primarily repairs **bulky DNA lesions**, such as **thymine dimers** caused by UV radiation, or damage from chemical adducts that distort the DNA helix.
- It involves excising a larger oligonucleotide containing the damage, not just a single base.
*Nonhomologous end joining repair*
- This pathway is used to repair **double-strand DNA breaks**, where both strands of the DNA molecule are broken.
- It is a "quick-and-dirty" repair mechanism that ligates the broken ends together, often leading to small insertions or deletions.
*Homologous recombination*
- A repair mechanism for **double-strand DNA breaks** that uses a homologous DNA template (e.g., sister chromatid) to accurately repair the break.
- This process is highly accurate but occurs only when a homologous template is available, typically during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle.
*Mismatch repair*
- Corrects **base-pair mismatches** and **small insertions/deletions** that occur during DNA replication, which were not corrected by DNA polymerase proofreading.
- It targets newly synthesized DNA strands based on methylation patterns in the parental strand.
DNA repair deficiency syndromes US Medical PG Question 5: A 44-year-old man comes to the physician because of fatigue and increased straining during defecation for 3 months. During this time, he has lost 5 kg (12 lb) despite no change in appetite. He has a family history of colon cancer in his maternal uncle and maternal grandfather. His mother died of ovarian cancer at the age of 46. Physical examination shows conjunctival pallor. His hemoglobin concentration is 11.2 g/dL, hematocrit is 34%, and mean corpuscular volume is 76 μm3. Colonoscopy shows an exophytic mass in the ascending colon. Pathologic examination of the resected mass shows a poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. Genetic analysis shows a mutation in the MSH2 gene. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Familial adenomatous polyposis
- B. Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
- C. Turcot syndrome
- D. Lynch syndrome (Correct Answer)
- E. Gardner syndrome
DNA repair deficiency syndromes Explanation: ***Lynch syndrome***
- The patient's **poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma** in the ascending colon, coupled with the **family history of colon and ovarian cancer** (early onset, diverse cancer types), and the **MSH2 gene mutation**, strongly indicates Lynch syndrome (hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer).
- **Lynch syndrome** is caused by germline mutations in **DNA mismatch repair (MMR) genes** (e.g., MSH2, MLH1, MSH6, PMS2), leading to an increased risk of colorectal, ovarian, endometrial, and other cancers, often at a younger age and predominantly in the **right colon**.
*Familial adenomatous polyposis*
- This syndrome is characterized by the development of **hundreds to thousands of colorectal adenomatous polyps** during adolescence or early adulthood, a feature not mentioned in the patient's presentation.
- It is caused by a germline mutation in the **APC gene**, not MSH2, leading to an almost 100% lifetime risk of colorectal cancer if untreated.
*Peutz-Jeghers syndrome*
- This syndrome is characterized by **hamartomatous polyps** throughout the gastrointestinal tract and **mucocutaneous melanin pigmentation** (dark spots on lips, buccal mucosa, fingers/toes).
- It is associated with mutations in the **STK11 gene** and an increased risk of various cancers, but the clinical presentation and genetic mutation do not match.
*Turcot syndrome*
- Turcot syndrome is a rare condition characterized by the coexistence of **colorectal polyposis** (either FAP-like or Lynch-like) and **central nervous system tumors** (e.g., medulloblastoma, glioblastoma).
- While it can involve MMR gene mutations in some cases, the prominent feature of CNS tumors is absent in this patient's history.
*Gardner syndrome*
- This is a subtype of FAP, characterized by colorectal polyps along with **extra-intestinal manifestations** such as **osteomas** (especially in the mandible or skull), **epidermoid cysts**, and **desmoid tumors**.
- Like FAP, it is caused by mutations in the **APC gene**, and the characteristic extra-intestinal features are not described in the patient.
DNA repair deficiency syndromes US Medical PG Question 6: Two healthy adults have only one child. He has Friedreich ataxia (FA). They are considering having more children, but are uncertain of their risk of having another child with the condition. What should they do?
- A. Proceed with conception; risk of having another child with FA is unpredictable
- B. See a genetic counselor; risk of having another child with FA is 66%
- C. See a genetic counselor; risk of having another child with FA is 25% (Correct Answer)
- D. Proceed with conception; risk of having another child with FA is 0%
- E. See a genetic counselor; risk of having another child with FA is 50%
DNA repair deficiency syndromes Explanation: ***See a genetic counselor; risk of having another child with FA is 25%***
- **Friedreich ataxia (FA)** is an **autosomal recessive** disorder. For a child to inherit an autosomal recessive disorder, both parents must be carriers of the recessive allele, and the child must inherit one copy from each parent.
- Since their first child has FA, both parents must be **heterozygous carriers**. In this scenario, the probability of each subsequent child inheriting two recessive alleles (one from each carrier parent) is **25%** (1 in 4). A genetic counselor can provide precise risk assessment and discuss options.
*Proceed with conception; risk of having another child with FA is unpredictable*
- The risk is **predictable** as FA follows an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern.
- Parents who are both carriers have a consistent 25% chance of having an affected child with each pregnancy.
*See a genetic counselor; risk of having another child with FA is 66%*
- A 66% risk is not associated with an autosomal recessive inheritance pattern for subsequent children once carrier status is established for both parents.
- This percentage might refer to the probability of an unaffected sibling being a carrier (2/3 chance), but not the risk of having an affected child.
*Proceed with conception; risk of having another child with FA is 0%*
- This statement is incorrect because both parents are confirmed carriers, meaning there is always a **25% chance** of having another child with FA.
- The disease has already manifested in a previous child, confirming the genetic risk.
*See a genetic counselor; risk of having another child with FA is 50%*
- A **50% risk** is characteristic of an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern, where only one affected parent passes on the gene, or if one parent is a carrier for a recessive disease and the other parent is affected.
- This scenario does not apply to two healthy parents who are both carriers for an **autosomal recessive** condition.
DNA repair deficiency syndromes US Medical PG Question 7: A 54-year-old woman with breast cancer comes to the physician because of redness and pain in the right breast. She has been undergoing ionizing radiation therapy daily for the past 2 weeks as adjuvant treatment for her breast cancer. Physical examination shows erythema, edema, and superficial desquamation of the skin along the right breast at the site of radiation. Sensation to light touch is intact. Which of the following is the primary mechanism of DNA repair responsible for preventing radiation-induced damage to neighboring neurons?
- A. Homology-directed repair
- B. Base excision repair
- C. Nonhomologous end joining repair (Correct Answer)
- D. DNA mismatch repair
- E. Nucleotide excision repair
DNA repair deficiency syndromes Explanation: ***Nonhomologous end joining repair***
- This pathway is crucial for repairing **double-strand DNA breaks**, which are a major form of damage caused by **ionizing radiation**.
- It directly ligates the broken DNA ends without requiring a homologous template, making it an efficient but potentially error-prone repair mechanism.
*Homology-directed repair*
- This pathway is also used to repair **double-strand DNA breaks** but requires a **homologous DNA template** (usually a sister chromatid) for accurate repair.
- While highly accurate, it is typically active during the S and G2 phases of the cell cycle and is generally slower and less dominant than NHEJ for immediate radiation-induced damage in non-dividing cells like neurons.
*Base excision repair*
- This mechanism primarily corrects damage to individual DNA bases, such as **oxidative damage**, alkylation, or deamination.
- It is not the primary mechanism for repairing the **double-strand breaks** induced by ionizing radiation.
*DNA mismatch repair*
- This pathway corrects errors that arise during **DNA replication**, specifically mismatched base pairs or small insertions/deletions.
- It is not involved in repairing radiation-induced DNA damage like **double-strand breaks**.
*Nucleotide excision repair*
- This pathway repairs bulky DNA lesions, such as those caused by **UV radiation** (e.g., pyrimidine dimers) or chemical mutagens.
- It removes a segment of DNA containing the damage but is not the primary repair mechanism for **double-strand breaks** caused by ionizing radiation.
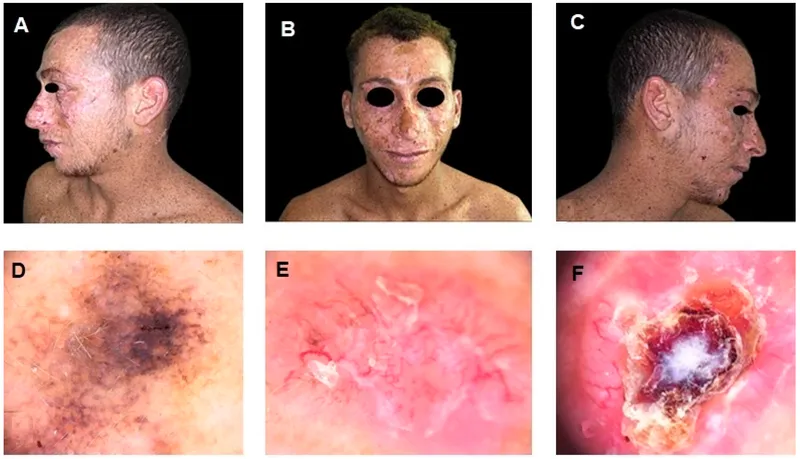
DNA repair deficiency syndromes US Medical PG Question 8: A 5-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her mother because of a 1-month history of a painful ulcer on her face. She has developed painful sunburns in the past with minimal UV exposure. Examination of the skin shows a 2-cm ulcerated nodule on the left cheek. There are scaly, hyperpigmented papules and plaques over the skin of the entire body. Ophthalmologic examination shows decreased visual acuity, clouded corneas, and limbal injection. Examination of a biopsy specimen from the facial lesion shows poorly-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma. Impairment of which of the following proteins is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Rb nuclear protein
- B. Base-specific glycosylase
- C. Excision endonuclease (Correct Answer)
- D. ATM serine/threonine kinase
- E. DNA helicase
DNA repair deficiency syndromes Explanation: ***Excision endonuclease***
- This patient's presentation with **painful sunburns**, **early-onset squamous cell carcinoma** on the face, and **ocular abnormalities (clouded corneas, decreased visual acuity)** is highly suggestive of **xeroderma pigmentosum (XP)**.
- XP is an autosomal recessive disorder caused by a defect in **nucleotide excision repair (NER)**, which is responsible for removing DNA damage primarily induced by **UV radiation**. **Excision endonucleases** are key enzymes in the initiation phase of NER, recognizing and excising the damaged DNA segment.
*Rb nuclear protein*
- The **Rb nuclear protein** is a tumor suppressor involved in cell cycle regulation (G1/S checkpoint).
- Impairment of Rb is associated with **retinoblastoma** and several other cancers, but not typically with this specific constellation of light sensitivity, skin cancer, and ocular damage seen in XP.
*Base-specific glycosylase*
- **Base-specific glycosylases** are involved in **base excision repair (BER)**, which primarily corrects small, non-helix-distorting base lesions (e.g., deaminated or alkylated bases).
- While important for DNA repair, defects in BER would not explain the extreme UV sensitivity and subsequent skin cancers characteristic of xeroderma pigmentosum, as these are primarily linked to UV-induced pyrimidine dimers.
*ATM serine/threonine kinase*
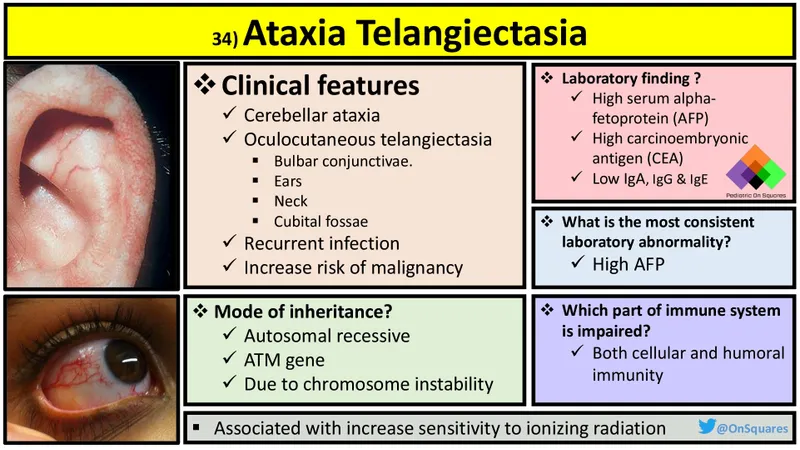
- **ATM (ataxia-telangiectasia mutated) kinase** is a critical protein involved in initiating the cellular response to **DNA double-strand breaks**.
- Defects in ATM cause **ataxia-telangiectasia**, characterized by cerebellar ataxia, immunodeficiency, and a predisposition to lymphoid malignancies, but not the specific skin and eye findings of XP.
*DNA helicase*
- **DNA helicases** are enzymes that unwind DNA and are involved in various DNA processes, including replication, recombination, and repair.
- While critical for many functions, a general defect in **DNA helicase** would lead to a broader range of severe developmental and cellular defects, and is not specifically linked to the clinical phenotype of xeroderma pigmentosum which results from specific NER pathway defects.
DNA repair deficiency syndromes US Medical PG Question 9: A 3-year-old male child is found to have a disease involving DNA repair. Specifically, he is found to have a defect in the endonucleases involved in the nucleotide excision repair of pyrimidine dimers. Which of the following is a unique late-stage complication of this child's disease?
- A. Telangiectasia
- B. Colorectal cancer
- C. Malignant melanoma (Correct Answer)
- D. Lymphomas
- E. Endometrial cancer
DNA repair deficiency syndromes Explanation: **Malignant melanoma**
- The described condition is **xeroderma pigmentosum**, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by a defect in **nucleotide excision repair (NER)**, specifically the inability to remove **pyrimidine dimers** caused by **UV radiation**.
- This severely impaired DNA repair leads to an extreme predisposition to **UV-induced skin cancers**, including basal cell carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas, and, most aggressively, **malignant melanoma**, which is a unique and life-threatening late-stage complication.
*Telangiectasia*
- **Telangiectasias** are dilated small blood vessels that appear on the skin or mucous membranes and can be associated with various conditions.
- While skin abnormalities are prevalent in xeroderma pigmentosum due to sun damage, **melanoma** is a more specific and severe late-stage complication directly resulting from the DNA repair defect.
*Colorectal cancer*
- **Colorectal cancer** is typically associated with other DNA repair defects, such as those in the **mismatch repair system**, as seen in conditions like **Lynch syndrome**.
- It is not a primary or most significant late-stage complication of xeroderma pigmentosum, which is primarily characterized by skin cancers.
*Lymphomas*
- **Lymphomas** are cancers of the lymphatic system, often linked to immune deficiencies or specific genetic translocations.
- While individuals with genetic syndromes can have increased cancer risks, **lymphoma** is not the hallmark late-stage complication of xeroderma pigmentosum; skin cancers are the predominant concern.
*Endometrial cancer*
- **Endometrial cancer** is a gynecological cancer often associated with hormonal factors or genetic predispositions like Lynch syndrome, which involves mismatch repair defects.
- This type of cancer is not a characteristic or unique late-stage complication of xeroderma pigmentosum, whose pathology is centered on **UV-induced DNA damage** and subsequent skin malignancies.
DNA repair deficiency syndromes US Medical PG Question 10: An investigator studying DNA mutation mechanisms isolates single-stranded DNA from a recombinant bacteriophage and sequences it. The investigator then mixes it with a buffer solution and incubates the resulting mixture at 70°C for 16 hours. Subsequent DNA resequencing shows that 3.7 per 1,000 cytosine residues have mutated to uracil. Which of the following best describes the role of the enzyme that is responsible for the initial step in repairing these types of mutations in living cells?
- A. Connecting the phosphodiester backbone
- B. Cleavage of the phosphodiester bond 3' of damaged site
- C. Creation of abasic site (Correct Answer)
- D. Release of the damaged nucleotide
- E. Addition of free nucleotides to 3' end
DNA repair deficiency syndromes Explanation: ***Creation of abasic site***
- The mutation of **cytosine to uracil** is an example of **deamination**, which is repaired by the **base excision repair (BER)** pathway.
- The initial step in BER involves **DNA glycosylase**, which *removes* the damaged base (uracil) from the sugar-phosphate backbone by hydrolyzing the **N-glycosidic bond**, creating an **abasic site**.
*Connecting the phosphodiester backbone*
- This is the function of **DNA ligase**, which acts at the *final step* of DNA repair pathways to seal the nicks in the backbone.
- It does not initiate the repair process for deaminated bases.
*Cleavage of the phosphodiester bond 3' of damaged site*
- This is typically performed by an **AP endonuclease (APE1)** after the abasic site has been created.
- It is a *subsequent step* in BER, not the initial one for removing the damaged base itself.
*Release of the damaged nucleotide*
- While the damaged base is eventually *released*, the initial enzyme (DNA glycosylase) specifically removes the **base**, leaving the sugar and phosphate intact.
- The entire nucleotide (base, sugar, and phosphate) is typically removed later by an **AP lyase** or APE1, after the initial glycosylase action.
*Addition of free nucleotides to 3' end*
- This is the function of **DNA polymerase**, which fills in the gap after the damaged nucleotide and surrounding region have been excised.
- This occurs *after* the initial recognition and removal of the damaged base, not as the primary repair step.
More DNA repair deficiency syndromes US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.