Direct repair mechanisms US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Direct repair mechanisms. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Direct repair mechanisms US Medical PG Question 1: A 17-year-old patient presents to the emergency department with left wrist pain after falling off of his bike and landing on his left hand. On physical exam the thenar eminence is red, swollen, and tender to palpation, so a radiograph is ordered. The patient is worried because he learned in biology class that radiography can cause cancer through damaging DNA but the physician reassures him that radiographs give a very minor dose of radiation. What is the most common mechanism by which ionizing radiation damages DNA?
- A. Strand breakage (Correct Answer)
- B. Thymidine dimer formation
- C. Microsatellite instability
- D. Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer formation
- E. Cytosine deamination
Direct repair mechanisms Explanation: ***Strand breakage***
- Ionizing radiation, such as X-rays, directly or indirectly causes **breaks in the phosphodiester backbone** of DNA, resulting in single or double-strand breaks.
- **Double-strand breaks** are particularly dangerous as they are difficult to repair and can lead to chromosomal rearrangements and cell death or malignant transformation.
*Thymidine dimer formation*
- This is primarily caused by **ultraviolet (UV) radiation**, not ionizing radiation like X-rays.
- **UV radiation** causes covalent bonds between adjacent pyrimidine bases, particularly thymine, leading to the formation of thymine dimers.
*Microsatellite instability*
- This is a hallmark of defects in **DNA mismatch repair pathways**, often associated with hereditary disorders like Lynch syndrome or certain sporadic cancers.
- It involves changes in the length of **microsatellites** (short, repetitive DNA sequences) due to insertion or deletion errors, not direct radiation damage.
*Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer formation*
- Similar to thymidine dimers, **cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs)** are the most common photoproducts formed in DNA after exposure to **UV radiation**.
- These dimers distort the DNA helix and interfere with replication and transcription, but are not characteristic of ionizing radiation damage.
*Cytosine deamination*
- This is a spontaneous chemical reaction where a **cytosine base (C)** loses its amino group and is converted to **uracil (U)**.
- It is a common endogenous DNA lesion that can lead to C-to-T transition mutations if not repaired, but it is not directly induced by ionizing radiation.
Direct repair mechanisms US Medical PG Question 2: A 71-year-old man with colorectal cancer comes to the physician for follow-up examination after undergoing a sigmoid colectomy. The physician recommends adjuvant chemotherapy with an agent that results in single-stranded DNA breaks. This chemotherapeutic agent most likely has an effect on which of the following enzymes?
- A. DNA polymerase III
- B. Topoisomerase I (Correct Answer)
- C. Helicase
- D. Telomerase
- E. Topoisomerase II
Direct repair mechanisms Explanation: ***Topoisomerase I***
- **Topoisomerase I** creates **single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) breaks** to relieve torsional stress during DNA replication and transcription.
- Many chemotherapeutic agents, such as camptothecin and its derivatives (e.g., irinotecan, topotecan), target topoisomerase I, leading to DNA damage and apoptosis in cancer cells.
*DNA polymerase III*
- **DNA polymerase III** is primarily involved in bacterial DNA replication, synthesizing new DNA strands in a 5' to 3' direction.
- While essential for bacterial survival, it is not the target of chemotherapeutic agents that induce single-stranded DNA breaks in human cells.
*Helicase*
- **Helicase** is responsible for unwinding the DNA double helix during replication and transcription, separating the two strands.
- While its function is critical for DNA processes, it does not directly create DNA breaks as its primary mechanism of action.
*Telomerase*
- **Telomerase** is an enzyme that maintains telomere length at the ends of chromosomes, particularly active in cancer cells.
- Inhibitors of telomerase aim to shorten telomeres, leading to cellular senescence or apoptosis, but they do not primarily cause single-stranded DNA breaks.
*Topoisomerase II*
- **Topoisomerase II** creates **double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) breaks** to untangle and decatenate DNA.
- Though also a target for chemotherapy (e.g., etoposide, doxorubicin), its mechanism involves double-stranded breaks, not single-stranded breaks as specified in the question.
Direct repair mechanisms US Medical PG Question 3: A 3-year-old male child is found to have a disease involving DNA repair. Specifically, he is found to have a defect in the endonucleases involved in the nucleotide excision repair of pyrimidine dimers. Which of the following is a unique late-stage complication of this child's disease?
- A. Telangiectasia
- B. Colorectal cancer
- C. Malignant melanoma (Correct Answer)
- D. Lymphomas
- E. Endometrial cancer
Direct repair mechanisms Explanation: **Malignant melanoma**
- The described condition is **xeroderma pigmentosum**, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by a defect in **nucleotide excision repair (NER)**, specifically the inability to remove **pyrimidine dimers** caused by **UV radiation**.
- This severely impaired DNA repair leads to an extreme predisposition to **UV-induced skin cancers**, including basal cell carcinomas, squamous cell carcinomas, and, most aggressively, **malignant melanoma**, which is a unique and life-threatening late-stage complication.
*Telangiectasia*
- **Telangiectasias** are dilated small blood vessels that appear on the skin or mucous membranes and can be associated with various conditions.
- While skin abnormalities are prevalent in xeroderma pigmentosum due to sun damage, **melanoma** is a more specific and severe late-stage complication directly resulting from the DNA repair defect.
*Colorectal cancer*
- **Colorectal cancer** is typically associated with other DNA repair defects, such as those in the **mismatch repair system**, as seen in conditions like **Lynch syndrome**.
- It is not a primary or most significant late-stage complication of xeroderma pigmentosum, which is primarily characterized by skin cancers.
*Lymphomas*
- **Lymphomas** are cancers of the lymphatic system, often linked to immune deficiencies or specific genetic translocations.
- While individuals with genetic syndromes can have increased cancer risks, **lymphoma** is not the hallmark late-stage complication of xeroderma pigmentosum; skin cancers are the predominant concern.
*Endometrial cancer*
- **Endometrial cancer** is a gynecological cancer often associated with hormonal factors or genetic predispositions like Lynch syndrome, which involves mismatch repair defects.
- This type of cancer is not a characteristic or unique late-stage complication of xeroderma pigmentosum, whose pathology is centered on **UV-induced DNA damage** and subsequent skin malignancies.
Direct repair mechanisms US Medical PG Question 4: An investigator is studying the biology of human sperm cells. She isolates spermatogonia obtained on a testicular biopsy from a group of healthy male volunteers. She finds that the DNA of spermatogonia obtained from these men show a large number of TTAGGG sequence repeats. This finding can best be explained by increased activity of an enzyme with which of the following functions?
- A. Ligation of Okazaki fragments
- B. Proofreading of synthesized daughter strands
- C. RNA-dependent synthesis of DNA (Correct Answer)
- D. Production of short RNA sequences
- E. Hemimethylation of DNA strand
Direct repair mechanisms Explanation: ***RNA-dependent synthesis of DNA***
- The TTAGGG sequence repeats are **telomeric sequences**, which are maintained by **telomerase**, an enzyme that synthesizes DNA from an RNA template.
- **Spermatogonia** are germline stem cells that express high levels of telomerase to maintain telomere length across generations.
*Ligation of Okazaki fragments*
- This function is carried out by **DNA ligase**, which joins discontinuous DNA fragments during replication on the lagging strand.
- This process is essential for general DNA replication but is not specific to the formation or maintenance of telomeric repeats.
*Proofreading of synthesized daughter strands*
- This is a function of **DNA polymerase exonuclease activity**, which corrects errors during DNA replication.
- While important for genetic fidelity, it does not explain the presence or increase of specific TTAGGG repeat sequences at telomeres.
*Production of short RNA sequences*
- This function is performed by **primase**, which synthesizes RNA primers necessary to initiate DNA synthesis during replication.
- These RNA primers are later removed and replaced with DNA, and this process is not directly responsible for generating or extending telomeric repeats.
*Hemimethylation of DNA strand*
- Hemimethylation occurs during **DNA replication** when new DNA strands are unmethylated while parental strands are methylated.
- This phenomenon is involved in DNA repair and gene regulation but is unrelated to the synthesis or regulation of telomeric sequences.
Direct repair mechanisms US Medical PG Question 5: A 7-month-old boy presents to the family physician with extensive scaliness and pigmentation of sun-exposed skin areas. His mother says that these symptoms were absent until mid-spring and then became significantly worse after their trip to California in the summer. The child was born in December to a consanguineous couple after an uncomplicated pregnancy. He is breastfed and receives mashed potatoes, bananas, and carrots as complementary foods. His weight is 8.5 kg (18.7 lb) and length is 70 cm (2 ft 96 in). The patient’s vital signs are within normal limits for his age. On physical examination, there is freckling, scaling, and erythema on the sunlight-exposed areas of the face, trunk, and upper and lower extremities. No blistering, scarring, hypertrichosis, or alopecia is noted. The rest of the exam is unremarkable. Which process is most likely disrupted in this patient?
- A. Nucleotide-excision DNA repair (Correct Answer)
- B. Base-excision DNA repair
- C. Hydroxylation of proline and lysine in the procollagen molecule
- D. Conversion of uroporphyrinogen III to coproporphyrinogen III
- E. NAD production
Direct repair mechanisms Explanation: ***Nucleotide-excision DNA repair***
- The patient's symptoms (extensive scaliness, pigmentation, freckling, scaling, and erythema on sun-exposed areas) that worsen with sun exposure are characteristic of **xeroderma pigmentosum**.
- This condition is caused by a defect in **nucleotide-excision repair (NER)**, which is essential for repairing DNA damage, particularly from UV radiation.
*Base-excision DNA repair*
- **Base-excision repair (BER)** primarily addresses single-base damage, like oxidized or alkylated bases, not the bulky adducts formed by UV light.
- Defects in BER are associated with conditions like colorectal cancer, but not the specific photosensitivity seen here.
*Hydroxylation of proline and lysine in the procollagen molecule*
- This process is essential for proper collagen synthesis; defects lead to disorders like **Ehlers-Danlos syndrome** or **scurvy**.
- These conditions manifest with skin fragility, bruising, and joint hypermobility, not the prominent photosensitivity observed.
*Conversion of uroporphyrinogen III to coproporphyrinogen III*
- This step is involved in **heme synthesis**; defects can lead to **porphyrias**, which often cause photosensitivity and blistering.
- However, the patient's presentation of scaling, freckling, and erythema without blistering or scarring is less typical for porphyria.
*NAD production*
- **NAD (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)** is a crucial coenzyme in many metabolic pathways; its deficiency can lead to pellagra-like symptoms (dermatitis, diarrhea, dementia).
- While pellagra can involve sun-exposed skin, it typically involves a more diffuse, symmetrically inflamed rash with hyperpigmentation and thickening, rather than the discrete freckling and scaling described.
Direct repair mechanisms US Medical PG Question 6: DNA replication is a highly complex process where replication occurs on both strands of DNA. On the leading strand of DNA, replication occurs uninterrupted, but on the lagging strand, replication is interrupted and occurs in fragments called Okazaki fragments. These fragments need to be joined, which of the following enzymes is involved in the penultimate step before ligation can occur?
- A. DNA gyrase
- B. DNA ligase
- C. DNA helicase
- D. DNA polymerase I (Correct Answer)
- E. DNA polymerase III
Direct repair mechanisms Explanation: **DNA polymerase I**
- **DNA polymerase I** plays a crucial role in removing the **RNA primers** from the Okazaki fragments on the lagging strand.
- After primer removal, it fills the resulting gaps with **deoxyribonucleotides** before DNA ligase seals the nicks.
*DNA gyrase*
- **DNA gyrase** (a type of **topoisomerase**) is involved in relieving **supercoiling** ahead of the replication fork.
- It does not directly participate in the joining of Okazaki fragments, but rather in maintaining DNA topology during replication.
*DNA ligase*
- **DNA ligase** is responsible for the **final sealing** of the nicks between adjacent Okazaki fragments.
- It forms a **phosphodiester bond** between the 3'-hydroxyl end of one fragment and the 5'-phosphate end of the next, following primer removal and gap filling.
*DNA helicase*
- **DNA helicase** unwinds the double-stranded DNA helix, separating the two strands at the **replication fork**.
- This enzyme is essential for initiating replication but does not participate in processing Okazaki fragments.
*DNA polymerase III*
- **DNA polymerase III** is the primary enzyme responsible for the **elongation of new DNA strands** in both leading and lagging strand synthesis.
- It synthesizes the actual Okazaki fragments but does not directly remove primers or fill the gaps.
Direct repair mechanisms US Medical PG Question 7: A group of microbiological investigators is studying bacterial DNA replication in E. coli colonies. While the cells are actively proliferating, the investigators stop the bacterial cell cycle during S phase and isolate an enzyme involved in DNA replication. An assay of the enzyme's exonuclease activity determines that it is active on both intact and demethylated thymine nucleotides. Which of the following enzymes have the investigators most likely isolated?
- A. DNA ligase
- B. Telomerase
- C. Primase
- D. DNA topoisomerase
- E. DNA polymerase I (Correct Answer)
Direct repair mechanisms Explanation: ***DNA polymerase I***
- **DNA polymerase I** possesses **5' to 3' exonuclease activity**, which is crucial for removing **RNA primers** (intact nucleotides) laid down by primase during DNA replication.
- This 5' to 3' exonuclease activity also allows it to excise damaged DNA, including DNA containing **demethylated thymine nucleotides**.
- It also has 3' to 5' exonuclease activity for proofreading.
- **Key distinction:** While DNA polymerase III (the main replicative enzyme) only has 3' to 5' exonuclease activity, DNA polymerase I has **both** 3' to 5' and 5' to 3' exonuclease activities, making it essential for primer removal and DNA repair.
*DNA ligase*
- **DNA ligase** functions to form a **phosphodiester bond** between adjacent nucleotides to seal nicks in the DNA backbone, but it does not have exonuclease activity.
- Its primary role is in joining Okazaki fragments and repairing single-strand breaks.
*Telomerase*
- **Telomerase** is a specialized reverse transcriptase that extends the telomeres at the ends of eukaryotic chromosomes, but is not present in prokaryotes like *E. coli*.
- It uses an RNA template to synthesize DNA, and it lacks exonuclease activity.
*Primase*
- **Primase** is an RNA polymerase that synthesizes short **RNA primers** on the DNA template, providing a starting point for DNA synthesis.
- It is involved in synthesizing primers, not in removing or excising nucleotides, and has no exonuclease activity.
*DNA topoisomerase*
- **DNA topoisomerases** relieve supercoiling in DNA during replication and transcription by cutting and rejoining DNA strands.
- While they act on DNA, their function is to manage topological stress, and they do not exhibit exonuclease activity on nucleotides.
Direct repair mechanisms US Medical PG Question 8: A 62-year-old man with small cell lung cancer undergoes radiation therapy. His oncologist explains that radiation causes DNA damage and double strand breaks and this damage stops the cancer cells from growing because they can no longer replicate their DNA. One key mediator of this process is a cell cycle regulator called P53, which is upregulated after DNA damage and helps to trigger cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. One mechanism by which P53 activity is increased is a certain chromatin modification that loosens DNA coiling allowing for greater transcription of the proteins within that region of DNA. Which of the following enzymes most likely causes the chromatin modification described in this case?
- A. Histone deacetylase
- B. Histone acetyltransferase (Correct Answer)
- C. Histone methyltransferase
- D. DNA methyltransferase
- E. Xist
Direct repair mechanisms Explanation: ***Histone acetyltransferase***
- This enzyme **acetylates histone proteins**, neutralizing their positive charge and thereby weakening their interaction with negatively charged DNA.
- This modification leads to a more **relaxed chromatin structure (euchromatin)**, making DNA more accessible for **transcription**, which is consistent with the upregulation of P53.
*Histone deacetylase*
- This enzyme **removes acetyl groups from histones**, making them more positively charged and increasing their affinity for DNA.
- This results in **condensed chromatin (heterochromatin)**, which generally **represses gene transcription**.
*Histone methyltransferase*
- This enzyme **adds methyl groups to histones**, which can either activate or repress gene transcription depending on the specific **lysine or arginine residue** methylated and the number of methyl groups added.
- While methylation is a chromatin modification, the question specifically describes a process of **loosening DNA coiling for greater transcription**, which is more characteristic of acetylation.
*DNA methyltransferase*
- This enzyme **adds methyl groups directly to DNA**, typically at **CpG sites**, leading to **gene silencing** by hindering transcription factor binding or recruiting repressor complexes.
- This modification primarily affects DNA directly, not histone proteins, and generally **inhibits gene expression**.
*Xist*
- **Xist (X-inactive specific transcript)** is a **long non-coding RNA** that plays a crucial role in **X-chromosome inactivation** in females.
- It functions by coating one of the X chromosomes, leading to its transcriptional silencing, rather than directly modifying chromatin for general gene upregulation.
Direct repair mechanisms US Medical PG Question 9: A 5-month-old male infant from a consanguineous marriage presents with severe sunburns and freckling in sun exposed areas. The mother explains that the infant experiences these sunburns every time the infant goes outside despite applying copious amounts of sunscreen. Which of the following DNA repair mechanisms is defective in this child?
- A. Non-homologous end joining
- B. Homologous recombination
- C. Base excision repair
- D. Mismatch repair
- E. Nucleotide excision repair (Correct Answer)
Direct repair mechanisms Explanation: ***Nucleotide excision repair***
- The symptoms of **severe sunburns** and **freckling in sun-exposed areas** are classic manifestations of **Xeroderma Pigmentosum (XP)**.
- XP is caused by a defect in **nucleotide excision repair (NER)**, which is crucial for removing **UV-induced DNA damage**, such as **pyrimidine dimers**.
*Non-homologous end joining*
- This mechanism repairs **double-strand DNA breaks** by directly ligating the broken ends, often with some loss of genetic information.
- Defects in non-homologous end joining are associated with conditions like **immunodeficiency** and increased cancer risk, but not with UV sensitivity like XP.
*Homologous recombination*
- This high-fidelity repair pathway uses a **homologous DNA template** to accurately repair **double-strand breaks** and interstrand crosslinks.
- Impaired homologous recombination is linked to conditions like **Fanconi anemia** and increased risk of certain cancers, but not primarily to UV hypersensitivity.
*Base excision repair*
- **Base excision repair (BER)** is responsible for removing **damaged or modified bases** from DNA, such as oxidized or alkylated bases.
- Defects in BER can lead to increased spontaneous mutagenesis and cancer, but do not explain the specific sensitivity to UV light seen in this infant.
*Mismatch repair*
- **Mismatch repair (MMR)** corrects errors that occur during DNA replication, such as **base mismatches** or small insertions/deletions.
- Defective MMR is strongly associated with **hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer (Lynch syndrome)**, but not with severe reactions to sun exposure.
Direct repair mechanisms US Medical PG Question 10: A 58-year-old obese male has noticed the gradual development of a soft bulge on his right groin that has been present over the past year and occasionally becomes very tender. He notices that it comes out when he coughs and strains during bowel movements. He is able to push the bulge back in without issue. After examination, you realize that he has an inguinal hernia and recommend open repair with mesh placement. After surgery, the patient returns to clinic and complains of numbness and tingling in the upper part of the scrotum and base of the penis. What nerve was most likely injured during the procedure?
- A. Ilioinguinal nerve (Correct Answer)
- B. Iliohypogastric nerve
- C. Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
- D. Obturator nerve
- E. Genitofemoral nerve
Direct repair mechanisms Explanation: **Ilioinguinal nerve**
- The **ilioinguinal nerve** supplies sensory innervation to the skin of the **scrotum** (or labia majora in females), the medial thigh, and the base of the penis.
- Injury to this nerve during an open inguinal hernia repair can cause **numbness and tingling** in these specific areas, consistent with the patient's symptoms.
*Iliohypogastric nerve*
- The **iliohypogastric nerve** primarily provides sensation to the skin over the **suprapubic region** and a small part of the buttock.
- Damage to this nerve would not typically result in numbness of the scrotum or base of the penis.
*Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve*
- This nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the **lateral aspect of the thigh**.
- Its injury would lead to symptoms of numbness or pain on the lateral thigh (**meralgia paresthetica**), not the scrotum or penis.
*Obturator nerve*
- The **obturator nerve** is a motor nerve that innervates the **adductor muscles of the thigh** and provides sensory innervation to a small area of the medial thigh.
- Damage to this nerve would result in **adductor weakness** and sensory loss in the medial thigh, which does not match the patient's complaints.
*Genitofemoral nerve*
- The **genitofemoral nerve** has two branches: the genital branch (supplies the cremaster muscle and scrotal skin) and the femoral branch (supplies skin of the anterior thigh).
- While the genital branch does innervate the scrotum, injury to this nerve more commonly causes **cremasteric reflex loss** or pain radiating to the anterior thigh, and the described symptoms (base of penis) are more characteristic of ilioinguinal nerve involvement.
More Direct repair mechanisms US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.
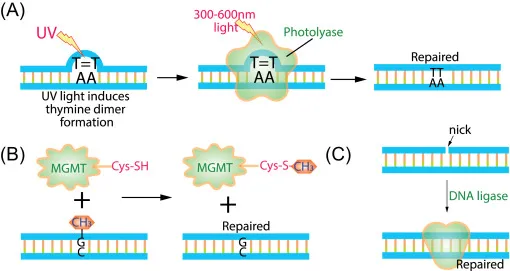
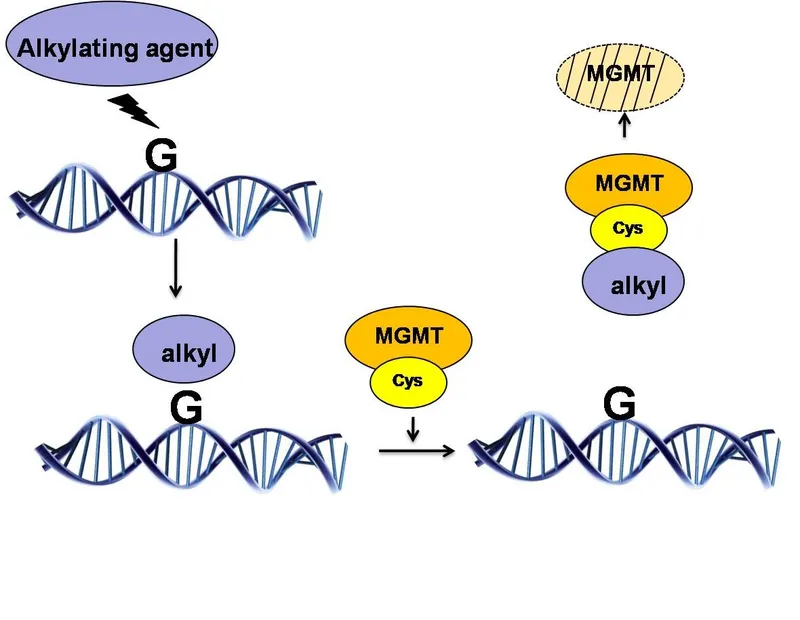 suicide mechanism repairing DNA alkylation damage)
suicide mechanism repairing DNA alkylation damage)
