Urea cycle disorders US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Urea cycle disorders. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
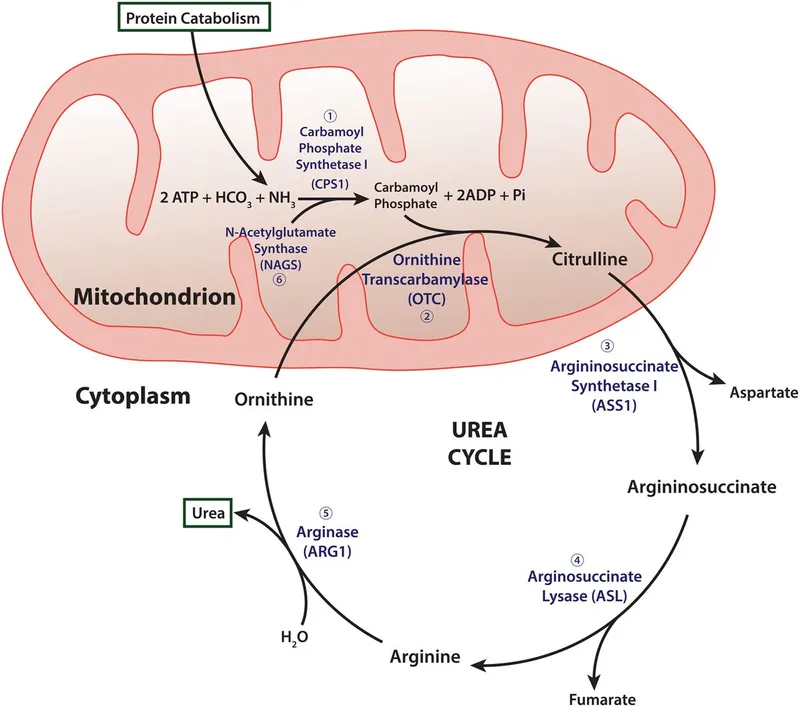
Urea cycle disorders US Medical PG Question 1: A 4-day-old male newborn delivered at 39 weeks' gestation is evaluated because of poor feeding, recurrent vomiting, and lethargy. Physical examination shows tachypnea with subcostal retractions. An enzyme assay performed on a liver biopsy specimen shows decreased activity of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I. This enzyme plays an important role in the breakdown and excretion of amino groups that result from protein digestion. Which of the following is an immediate substrate for the synthesis of the molecule needed for the excretion of amino groups?
- A. N-acetylglutamate
- B. Homocysteine
- C. Phenylalanine
- D. Valine
- E. Aspartate (Correct Answer)
Urea cycle disorders Explanation: ***Aspartate***
- The question describes a case of **carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)** deficiency, which leads to **hyperammonemia** due to impaired urea cycle function.
- The urea cycle is responsible for excreting **amino groups** as urea; one of the key molecules directly incorporated into the urea molecule is **aspartate**, which donates an amino group to form **argininosuccinate**.
*N-acetylglutamate*
- **N-acetylglutamate** is an essential activator of **carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)**, the enzyme deficient in this patient.
- While crucial for the urea cycle's regulation, it is an **allosteric activator** rather than a direct substrate for the synthesis of molecules needed for amino group excretion.
*Homocysteine*
- **Homocysteine** is an intermediate in **methionine metabolism** and is primarily associated with cardiovascular disease and neurological issues when elevated.
- It plays no direct role as a substrate in the urea cycle for the excretion of amino groups.
*Phenylalanine*
- **Phenylalanine** is an **essential amino acid** that is a precursor to tyrosine and neurotransmitters.
- Its metabolism is separate from the urea cycle, and it is not a direct substrate for ammonia excretion in this pathway.
*Valine*
- **Valine** is a **branched-chain amino acid (BCAA)** primarily catabolized in muscles and used for energy.
- It is not a direct substrate in the urea cycle, which processes nitrogen from various amino acids into urea for excretion.
Urea cycle disorders US Medical PG Question 2: A 56-year-old woman with a history of alcoholic cirrhosis and recurrent esophageal varices who recently underwent transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) placement is brought to the emergency room by her daughter due to confusion and agitation. Starting this morning, the patient has appeared sleepy, difficult to arouse, and slow to respond to questions. Her temperature is 97.6°F (36.4°C), blood pressure is 122/81 mmHg, pulse is 130/min, respirations are 22/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. She repeatedly falls asleep and is combative during the exam. Laboratory values are notable for a potassium of 3.0 mEq/L. The patient is given normal saline with potassium. Which of the following is the most appropriate treatment for this patient?
- A. Rifaximin
- B. Lactulose (Correct Answer)
- C. Nadolol
- D. Ciprofloxacin
- E. Protein-restricted diet
Urea cycle disorders Explanation: ***Lactulose***
- The patient's symptoms (confusion, agitation, somnolence) following **TIPS placement** and with a history of **cirrhosis** are highly suggestive of **hepatic encephalopathy**. Lactulose is a first-line treatment as it acidifies the colon, converting ammonia (a neurotoxin) to ammonium, which is then trapped and excreted.
- Additionally, this patient has **hypokalemia**, which can exacerbate hepatic encephalopathy by increasing renal ammonia production due to intracellular potassium shifts. Correcting hypokalemia is crucial alongside lactulose therapy.
*Rifaximin*
- Rifaximin is a non-absorbable antibiotic that can be used as an **adjunctive therapy** in hepatic encephalopathy, particularly in patients who do not respond adequately to lactulose or in whom lactulose is contraindicated.
- It works by reducing the number of **ammonia-producing bacteria** in the gut, but it is not the primary or initial treatment of choice for acute hepatic encephalopathy and is typically used after lactulose.
*Nadolol*
- Nadolol is a **non-selective beta-blocker** primarily used to prevent rebleeding from esophageal varices by reducing portal pressure.
- It does not directly treat or improve the symptoms of **hepatic encephalopathy** and is not indicated for the acute management of this condition.
*Ciprofloxacin*
- Ciprofloxacin is an antibiotic sometimes used to prevent **spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP)** in patients with cirrhosis and ascites, or for the treatment of **bacterial infections**.
- While infections can precipitate hepatic encephalopathy, ciprofloxacin is not a direct treatment for encephalopathy itself, nor is there evidence of active infection here (e.g., fever, leukocytosis) that would necessitate its use over lactulose.
*Protein-restricted diet*
- In the past, protein restriction was a common recommendation for hepatic encephalopathy to reduce ammonia production from protein catabolism. However, severe protein restriction can lead to **malnutrition and sarcopenia**, which are detrimental in cirrhotic patients.
- Current guidelines recommend maintaining adequate protein intake and only briefly restricting protein (if at all) in severe, refractory cases, as it is generally not helpful for acute management and can worsen patient outcomes in the long term.
Urea cycle disorders US Medical PG Question 3: A 3-week old boy is brought to the physician for the evaluation of lethargy, recurrent vomiting, and poor weight gain since birth. Physical examination shows decreased skin turgor and a bulging frontal fontanelle. Serum studies show an ammonia concentration of 170 μmol/L (N < 30) and low serum citrulline levels. The oral intake of which of the following nutrients should be restricted in this patient?
- A. Gluten
- B. Lactose
- C. Fructose
- D. Protein (Correct Answer)
- E. Vitamin A
Urea cycle disorders Explanation: ***Protein***
- Elevated **ammonia** and low **citrulline** levels indicate a **urea cycle disorder**, which impairs the body's ability to excrete nitrogenous waste from protein metabolism.
- Restricting **protein intake** limits the production of ammonia, thereby reducing the toxic burden on the system and preventing further neurological damage.
*Gluten*
- **Gluten restriction** is primarily indicated for **celiac disease**, which presents with gastrointestinal symptoms like diarrhea, malabsorption, and poor weight gain, but not directly with hyperammonemia or urea cycle dysfunction.
- While malabsorption can cause poor weight gain, the specific metabolic derangements here point away from celiac disease.
*Lactose*
- **Lactose intolerance** or **galactosemia** would necessitate **lactose restriction**. Symptoms usually include vomiting, diarrhea, and failure to thrive, but they do not typically present with the extreme hyperammonemia seen here.
- Galactosemia specifically would show elevated galactose and galactose-1-phosphate, not ammonia.
*Fructose*
- **Hereditary fructose intolerance** requires **fructose restriction**. It generally presents with vomiting, hypoglycemia, and liver dysfunction (jaundice, hepatomegaly) upon exposure to fructose, not primarily with hyperammonemia.
- The metabolic pathway for fructose metabolism does not directly generate ammonia in the quantities seen with urea cycle disorders.
*Vitamin A*
- **Vitamin A restriction** is not a primary treatment for any known inborn error of metabolism or hyperammonemia.
- While deficiencies or toxicities of vitamins can occur, they do not present with the specific metabolic profile described (high ammonia, low citrulline).
Urea cycle disorders US Medical PG Question 4: A 2-day-old male is seen in the newborn nursery for repeated emesis and lethargy. He was born at 39 weeks to a 24-year-old mother following an uncomplicated pregnancy and birth. He has been breastfeeding every 2 hours and has 10 wet diapers per day. His father has a history of beta-thalassemia minor. Laboratory results are as follows:
Hemoglobin: 12 g/dL
Platelet count: 200,000/mm³
Mean corpuscular volume: 95 µm³
Reticulocyte count: 0.5%
Leukocyte count: 5,000/mm³ with normal differential
Serum:
Na+: 134 mEq/L
Cl-: 100 mEq/L
K+: 3.3 mEq/L
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen: 1 mg/dL
Creatinine: 0.6 mg/dL
Ammonia: 150 µmol/L (normal: 50-80 µmol/L)
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Phenylketonuria
- B. Orotic aciduria
- C. Alkaptonuria
- D. Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency (Correct Answer)
- E. Beta-thalassemia minor
Urea cycle disorders Explanation: ***Ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency***
- The combination of **lethargy**, vomiting (emesis), and **significantly elevated ammonia levels** in a neonate strongly points to a **urea cycle disorder**, with ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency being the most common.
- This X-linked disorder leads to a buildup of ammonia due to the inability to convert carbamoyl phosphate and ornithine into citrulline, a crucial step in the urea cycle.
*Phenylketonuria*
- Characterized by the inability to metabolize **phenylalanine**, leading to its accumulation and neurological damage if untreated.
- Typically presents with developmental delay, seizures, and a musty odor, not acute hyperammonemia and vomiting in the neonatal period.
*Orotic aciduria*
- A rare metabolic disorder caused by a defect in **pyrimidine synthesis**, leading to accumulation of **orotic acid**.
- Presents with megaloblastic anemia, developmental delay, and failure to thrive, but not typically with severe neonatal hyperammonemia.
*Alkaptonuria*
- An autosomal recessive disorder of **tyrosine metabolism** where homogentisic acid oxidase is deficient, leading to a buildup of **homogentisic acid**.
- Characterized by dark urine when exposed to air, ochronosis (bluish-black pigmentation of cartilage), and early-onset osteoarthritis; it does not cause acute neonatal illness with hyperammonemia.
*Beta-thalassemia minor*
- This is an **inherited blood disorder** causing mild anemia, often asymptomatic, due to reduced or absent beta-globin chain production.
- While the father has this condition, the infant's symptoms of lethargy, vomiting, and hyperammonemia are **not consistent** with beta-thalassemia minor.
Urea cycle disorders US Medical PG Question 5: A 56-year-old male with a history of hepatitis C cirrhosis status post TIPS procedure is brought in by his wife to the emergency department because he has been acting disoriented, slurring his speech, and sleeping throughout the day. On arrival the patient is afebrile and his vital signs are pulse is 87/min, blood pressure is 137/93 mmHg, and respirations are 12/min with shallow breaths. Examination reveals a jaundiced male who appears older than stated age. Abdominal exam is positive for a fluid wave and shifting dullness to percussion. You note enlarged breasts, decreased facial hair, 3+ patellar reflexes bilaterally, and the following in the upper extremity (Image A). Paracentesis reveals ascitic fluid with neutrophil counts of < 100 cells/mcL. Serum creatinine is 1.0 and BUN is 15. Which of the following is the next best step in management?
- A. Administer neomycin and glucose
- B. IV albumin and antibiotic therapy with cefotaxime
- C. Administer rifaximin and glucose
- D. Administer lactulose (Correct Answer)
- E. Liver transplantation
Urea cycle disorders Explanation: ***Administer lactulose***
- The patient exhibits classic symptoms of **hepatic encephalopathy** (disorientation, slurred speech, somnolence, asterixis as demonstrated by Image A), combined with findings consistent with **cirrhosis** (jaundice, ascites, gynecomastia, decreased facial hair, history of hepatitis C and TIPS).
- **Lactulose** is the first-line treatment for hepatic encephalopathy as it acidifies the colon, promoting the conversion of ammonia (a neurotoxin) to ammonium, which is then trapped and excreted in the feces.
*Administer neomycin and glucose*
- **Neomycin** is an antibiotic that can reduce ammonia-producing bacteria in the gut but is generally considered a second-line agent due to potential side effects like **ototoxicity** and **nephrotoxicity**.
- **Glucose** administration is not a primary treatment for hepatic encephalopathy; it would only be indicated if the patient were hypoglycemic, which is not suggested by the clinical picture.
*IV albumin and antibiotic therapy with cefotaxime*
- **IV albumin** is primarily used in **spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP)** to prevent hepatorenal syndrome, and the paracentesis finding of < 100 cells/mcL neutrophils suggests SBP is unlikely.
- **Cefotaxime** is an appropriate antibiotic for **SBP**, but the patient's presentation is more consistent with hepatic encephalopathy, not an active infection.
*Administer rifaximin and glucose*
- **Rifaximin** is a non-absorbable antibiotic used to reduce ammonia-producing bacteria in the gut, often as an add-on or alternative to lactulose for maintenance therapy or in cases unresponsive to lactulose alone. It is not generally the initial monotherapy for an acute, severe encephalopathy episode.
- As mentioned, **glucose** is not a primary treatment for hepatic encephalopathy.
*Liver transplantation*
- **Liver transplantation** is a definitive treatment for end-stage liver disease, but it is not the **next best step** for acute management of hepatic encephalopathy.
- The immediate priority is to address the acute encephalopathy episode pharmacologically before considering long-term solutions like transplantation, which has a complex workup and waiting list.
Urea cycle disorders US Medical PG Question 6: A 20-year-old male presents with confusion, asterixis, and odd behavior. Very early in the morning, his mother found him urinating on the floor of his bedroom. A detailed history taken from the mother revealed that he has been a vegetarian his entire life but decided to "bulk up" by working out and consuming whey protein several times a day. A blood test revealed increased levels of ammonia and orotic acid but a decreased BUN. The patient began hemodialysis and was given oral sodium benzoate and phenylbutyrate, which improved his condition. Gene therapy of the enzyme producing which product would correct his condition?
- A. Citrulline (Correct Answer)
- B. Fructose-1-phosphate
- C. Homocysteine
- D. Phenylalanine
- E. Uridine monophosphate
Urea cycle disorders Explanation: ***Citrulline***
- The clinical presentation (confusion, asterixis, bizarre behavior, high ammonia, low BUN, high orotic acid, improvement with sodium benzoate and phenylbutyrate) is classic for a **urea cycle disorder**, specifically **ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency**.
- OTC catalyzes the conversion of ornithine and carbamoyl phosphate to citrulline. A deficiency in OTC leads to a buildup of carbamoyl phosphate, which is then shunted to the pyrimidine synthesis pathway, leading to increased orotic acid. Therefore, gene therapy for the enzyme producing citrulline (OTC) would address the underlying defect.
*Fructose-1-phosphate*
- This is an intermediate in **fructose metabolism**. Disorders related to this, such as **hereditary fructose intolerance**, are not associated with hyperammonemia or orotic aciduria in this manner.
- Symptoms typically involve hypoglycemia, vomiting, and liver dysfunction upon fructose ingestion.
*Homocysteine*
- Elevated homocysteine levels are characteristic of **homocystinuria**, which is due to defects in methionine metabolism, often involving **cystathionine beta-synthase** or enzymes in the folate/B12 pathways.
- Homocystinuria presents with developmental delay, skeletal abnormalities, and thromboembolic events, distinct from the patient's symptoms.
*Phenylalanine*
- Elevated phenylalanine is the hallmark of **phenylketonuria (PKU)**, an inherited disorder of amino acid metabolism where the body cannot process **phenylalanine**.
- PKU primarily causes neurological issues if untreated, but not typically hyperammonemia or orotic aciduria.
*Uridine monophosphate*
- While orotic acid is a precursor to uridine monophosphate in pyrimidine synthesis, a direct gene therapy for the enzyme producing uridine monophosphate is not the primary intervention for the underlying urea cycle disorder.
- The high orotic acid is a consequence of the urea cycle blockade, not the primary defect itself.
Urea cycle disorders US Medical PG Question 7: A 4-day-old boy is brought to the physician because of somnolence, poor feeding, and vomiting after his first few breast feedings. He appears lethargic. His respiratory rate is 73/min. Serum ammonia is markedly increased. Genetic analysis shows deficiency in N-acetylglutamate synthase. The activity of which of the following enzymes is most likely directly affected by this genetic defect?
- A. Ornithine translocase
- B. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (Correct Answer)
- C. Argininosuccinase
- D. Argininosuccinate synthetase
- E. Arginase
Urea cycle disorders Explanation: ***Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I***
- **N-acetylglutamate** (NAG) is an essential allosteric activator of **carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPS I)**, the rate-limiting enzyme of the urea cycle.
- A deficiency in **N-acetylglutamate synthase** directly leads to a lack of NAG, significantly impairing CPS I activity and causing severe hyperammonemia.
*Ornithine translocase*
- This enzyme is responsible for transporting **ornithine** into the mitochondria for the urea cycle.
- While a defect in **ornithine translocase** also causes hyperammonemia, it is due to accumulation of ornithine and upstream substrates, not a defect in N-acetylglutamate synthase.
*Argininosuccinase*
- Also known as **argininosuccinate lyase**, this enzyme cleaves argininosuccinate into arginine and fumarate.
- A deficiency would lead to accumulation of **argininosuccinate**, and while it is a urea cycle disorder, it is not directly affected by N-acetylglutamate synthase deficiency.
*Argininosuccinate synthetase*
- This enzyme catalyzes the condensation of **citrulline** and **aspartate** to form argininosuccinate.
- A defect in **argininosuccinate synthetase** causes citrullinemia but is not directly regulated by N-acetylglutamate.
*Arginase*
- **Arginase** is the final enzyme in the urea cycle, hydrolyzing arginine to form urea and ornithine.
- A deficiency would lead to hyperargininemia, which typically presents later in childhood and is not directly affected by N-acetylglutamate.
Urea cycle disorders US Medical PG Question 8: A 2-week-old boy presents to the emergency department because of unusual irritability and lethargy. The patient is admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit and minutes later develops metabolic encephalopathy. This progressed to a coma, followed by death before any laboratory tests are completed. The infant was born at home via vaginal delivery at 39 weeks' of gestation. His mother says that the symptoms started since the infant was 4-days-old, but since he only seemed ‘tired’, she decided not to seek medical attention. Further testing during autopsy shows hyperammonemia, low citrulline, and increased orotic acid. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase
- B. Propionyl-CoA carboxylase
- C. Homogentisic acid dioxygenase
- D. Ornithine transcarbamylase (Correct Answer)
- E. Cystathionine beta-synthase
Urea cycle disorders Explanation: **Ornithine transcarbamylase**
- **Hyperammonemia**, **low citrulline**, and **increased orotic acid** are classic findings in **Ornithine Transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency**. OTC is an X-linked urea cycle disorder.
- The rapid progression to **metabolic encephalopathy** and death in a neonate with these laboratory findings is highly characteristic of severe OTC deficiency, often presenting in the first few days of life.
*Branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes **Maple Syrup Urine Disease**, characterized by elevated **branched-chain amino acids** and their corresponding ketoacids in blood and urine.
- While it can cause neurological symptoms, it does not typically present with the specific constellation of **hyperammonemia**, low citrulline, and high orotic acid.
*Propionyl-CoA carboxylase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme leads to **Propionic acidemia**, a type of organic acidemia, characterized by **propionic acid accumulation** and often **metabolic acidosis**, ketosis, and hyperammonemia.
- However, it would not typically cause **low citrulline** or isolated **elevated orotic acid** as seen in urea cycle disorders.
*Homogentisic acid dioxygenase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes **Alkaptonuria**, an inborn error of metabolism characterized by the accumulation of **homogentisic acid**.
- This condition is usually benign in infancy, with symptoms appearing later in life such as **dark urine** on standing and **ochronosis** (darkening of cartilage). It does not present with acute hyperammonemia or metabolic encephalopathy.
*Cystathionine beta-synthase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes **homocystinuria**, an inborn error of methionine metabolism, leading to elevated **homocysteine** and methionine.
- Clinical features include **ectopia lentis**, skeletal abnormalities, and intellectual disability, but not usually acute neonatal hyperammonemia or the specific findings of low citrulline and high orotic acid.
Urea cycle disorders US Medical PG Question 9: A 7-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of sudden-onset abdominal pain that began 1 hour ago. Three days ago, he was diagnosed with a urinary tract infection and was treated with nitrofurantoin. There is no personal history of serious illness. His parents emigrated from Kenya before he was born. Examination shows diffuse abdominal tenderness, mild splenomegaly, and scleral icterus. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 9.8 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume 88 μm3
Reticulocyte count 3.1%
Serum
Bilirubin
Total 3.8 mg/dL
Direct 0.6 mg/dL
Haptoglobin 16 mg/dL (N=41–165 mg/dL)
Lactate dehydrogenase 179 U/L
Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Defective red blood cell membrane proteins
- B. Lead poisoning
- C. Defect in orotic acid metabolism
- D. Absent hemoglobin beta chain
- E. Enzyme deficiency in red blood cells (Correct Answer)
Urea cycle disorders Explanation: ***Enzyme deficiency in red blood cells***
- The patient's symptoms (abdominal pain, scleral icterus, mild splenomegaly, anemia, elevated reticulocyte count, increased unconjugated bilirubin, low haptoglobin, and elevated LDH) are consistent with **hemolytic anemia**. The recent use of **nitrofurantoin**, an oxidative stressor, in a patient of African descent, strongly suggests a diagnosis of **Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency**.
- G6PD deficiency is an **X-linked recessive** inherited enzyme defect causing red blood cells to be susceptible to oxidative damage, leading to hemolysis when exposed to certain drugs (like nitrofurantoin) or infections.
*Defective red blood cell membrane proteins*
- This describes conditions like **hereditary spherocytosis** or **hereditary elliptocytosis**. While these cause hemolytic anemia, the acute onset triggered by a drug (nitrofurantoin) is less typical.
- Hereditary spherocytosis is characterized by **microspherocytes** on a peripheral smear and is usually diagnosed earlier in life or has a chronic course, often without an acute precipitating drug.
*Lead poisoning*
- Lead poisoning typically causes **microcytic anemia** with **basophilic stippling** and neurological symptoms, not the type of hemolytic anemia and jaundice described.
- It does not present as an acute hemolytic crisis triggered by an oxidative drug.
*Defect in orotic acid metabolism*
- This can lead to conditions like **hereditary orotic aciduria**, which presents with **megaloblastic anemia** (without B12 or folate deficiency) and developmental delay.
- It is not associated with acute hemolytic episodes triggered by oxidative drugs or the specific lab findings seen here.
*Absent hemoglobin beta chain*
- This refers to **beta-thalassemia major**, which causes **microcytic hypochromic anemia** that is typically chronic and presents early in childhood with severe anemia requiring regular transfusions.
- Beta-thalassemia does not present as an acute hemolytic crisis triggered by nitrofurantoin, and the MCV in this patient is normal (88 μm³), not microcytic.
Urea cycle disorders US Medical PG Question 10: A 23-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician due to amenorrhea. The patient states that historically she has her period once every three months but recently has not had it at all. Otherwise, she has no other complaints. The patient recently started college and is a varsity athlete for the track team. She works part time in a coffee shop and is doing well in school. The patient is not sexually active and does not drink alcohol, use illicit drugs, or smoke. She has no significant past medical history and occasionally takes ibuprofen for headaches. Her temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 100/55 mmHg, pulse is 50/min, respirations are 10/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. On physical exam, you note a young, lean, muscular woman in no acute distress. Which of the following is the most likely long-term outcome in this patient?
- A. Osteoarthritis
- B. Infertility
- C. Endometrial cancer
- D. Anorexia nervosa
- E. Osteoporosis (Correct Answer)
Urea cycle disorders Explanation: ***Osteoporosis***
- This patient likely has **functional hypothalamic amenorrhea (FHA)** due to her athletic activity, low body weight, and stress, leading to low **estrogen** levels.
- **Chronic hypoestrogenism** is a significant risk factor for **decreased bone mineral density** and subsequent **osteoporosis** and stress fractures.
*Osteoarthritis*
- **Osteoarthritis** is a degenerative joint disease typically associated with aging, obesity, or joint injury, none of which are primary features in this patient's presentation.
- While intense athletic activity can contribute to joint wear over time, it is not a direct long-term consequence of the amenorrhea and hypoestrogenic state.
*Infertility*
- While **functional hypothalamic amenorrhea (FHA)** can cause temporary infertility as long as menstruation is suppressed, ovulation can resume once the underlying causes (e.g., intense exercise, low body weight, stress) are addressed.
- Therefore, infertility is not necessarily a permanent long-term outcome if the condition is managed.
*Endometrial cancer*
- Amenorrhea, particularly **anovulatory cycles** with prolonged estrogen exposure *without* progesterone withdrawal (as seen in PCOS), can increase the risk of endometrial hyperplasia and cancer.
- However, in **functional hypothalamic amenorrhea (FHA)**, low estrogen levels typically lead to a **thinner endometrium**, which *reduces* rather than increases the risk of endometrial cancer.
*Anorexia nervosa*
- Although **anorexia nervosa** can cause amenorrhea due to extremely low body weight and nutritional deficiencies, this patient's history and physical exam do not suggest an eating disorder.
- She is described as lean and muscular from athletic activity, not emaciated or exhibiting other signs of anorexia nervosa.
More Urea cycle disorders US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.