One-carbon metabolism US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for One-carbon metabolism. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
One-carbon metabolism US Medical PG Question 1: A 54-year-old woman with metastatic breast cancer comes to the physician for a follow-up examination. She had a mastectomy 6 months ago and received chemotherapy with doxorubicin and paclitaxel. A CT scan of the chest shows new metastases in the lungs and liver. Adjuvant therapy is initiated with a drug that inhibits the formation of deoxythymidine monophosphate and results in the accumulation of deoxyuridine triphosphate. The patient is advised to avoid folic acid supplementation while receiving this drug in order to prevent the toxic effects of this drug. Which of the following drugs was most likely given?
- A. Leflunomide
- B. Capecitabine (Correct Answer)
- C. Mycophenolate mofetil
- D. Hydroxyurea
- E. Azathioprine
One-carbon metabolism Explanation: Capecitabine
- Capecitabine is a **prodrug of 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)**, which inhibits **thymidylate synthase**, thereby blocking the formation of **deoxythymidine monophosphate (dTMP)** from deoxyuridine monophosphate (dUMP) [1], [2].
- This leads to the accumulation of **deoxyuridine triphosphate (dUTP)** and depletion of deoxythymidine triphosphate (dTTP), disrupting DNA synthesis [2].
- The instruction to avoid **folic acid supplementation** is important because excessive folate can potentially reduce the drug's efficacy by providing alternative pathways for nucleotide synthesis, though leucovorin (folinic acid) is sometimes given WITH 5-FU to enhance its binding to thymidylate synthase in certain chemotherapy regimens [1], [2].
- Commonly used in **metastatic breast cancer** and colorectal cancer [3].
*Hydroxyurea*
- Inhibits **ribonucleotide reductase**, preventing the conversion of ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides needed for DNA synthesis.
- Affects all deoxyribonucleotides (not specifically dTMP), and does not cause dUTP accumulation.
- Used in **sickle cell disease**, chronic myeloid leukemia, and polycythemia vera.
*Mycophenolate mofetil*
- An **immunosuppressant** that inhibits **inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase (IMPDH)**, blocking de novo **guanine nucleotide synthesis**.
- Does not affect thymidylate synthase or pyrimidine metabolism.
- Used to prevent **organ transplant rejection** and in autoimmune diseases.
*Leflunomide*
- An **immunosuppressant** that inhibits **dihydroorotate dehydrogenase**, blocking de novo **pyrimidine synthesis** at an earlier step than thymidylate synthase.
- Does not specifically inhibit dTMP formation or cause dUTP accumulation.
- Primarily used in **rheumatoid arthritis**.
*Azathioprine*
- An **immunosuppressant** that acts as a prodrug for 6-mercaptopurine, interfering with **purine synthesis** (adenine and guanine pathways).
- Does not affect pyrimidine metabolism or thymidylate synthase.
- Used in transplant recipients and autoimmune diseases.
One-carbon metabolism US Medical PG Question 2: A 35-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 1-day history of swelling and pain in the left leg. Two days ago, she returned from a business trip on a long-distance flight. She has alcohol use disorder. Physical examination shows a tender, swollen, and warm left calf. Serum studies show an increased homocysteine concentration and a methylmalonic acid concentration within the reference range. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following serum findings?
- A. Decreased cobalamin concentration
- B. Decreased protein C concentration
- C. Increased fibrinogen concentration
- D. Decreased folate concentration (Correct Answer)
- E. Increased pyridoxine concentration
One-carbon metabolism Explanation: ***Decreased folate concentration***
- The patient's presentation with **pain and swelling in the left leg following a long flight** suggests a **deep vein thrombosis (DVT)**. Increased homocysteine levels are a risk factor for DVT.
- Alcohol use disorder often leads to **malabsorption and poor nutritional intake**, profoundly affecting **folate metabolism** and leading to **folate deficiency**. This deficiency is a common cause of **hyperhomocysteinemia**, especially when methylmalonic acid levels are normal (ruling out B12 deficiency as the primary cause of hyperhomocysteinemia).
*Decreased cobalamin concentration*
- While alcohol use disorder can decrease **cobalamin (vitamin B12) concentration**, the **normal methylmalonic acid (MMA) concentration** in this patient makes a significant B12 deficiency unlikely to be the cause of the elevated homocysteine.
- Elevated MMA is a more specific indicator of **cobalamin deficiency**, as B12 is a cofactor for the enzyme that converts methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA.
*Decreased protein C concentration*
- Decreased protein C concentration is a **thrombophilic condition** that increases the risk of DVT, but there is no direct evidence in the patient's history or lab results pointing specifically to this deficiency.
- While hereditary thrombophilias can contribute, a **primary nutritional deficiency** explains the constellation of findings better in this context.
*Increased fibrinogen concentration*
- **Fibrinogen** is an **acute-phase reactant** and would likely be elevated in the context of inflammation or thrombosis, but it is not directly linked to the patient's hyperhomocysteinemia due to alcohol use disorder.
- Elevated fibrinogen is a **consequence** of the thrombotic process, not typically a direct cause of the hyperhomocysteinemia in this scenario.
*Increased pyridoxine concentration*
- **Pyridoxine (vitamin B6) levels** are generally not increased in individuals with alcohol use disorder; in fact, chronic alcohol abuse can lead to **pyridoxine deficiency**.
- Pyridoxine is a cofactor in homocysteine metabolism, and deficiency can lead to elevated homocysteine, but an *increase* is not expected.
One-carbon metabolism US Medical PG Question 3: A 9-month-old boy is brought to the pediatrician because he cannot sit on his own without support and has involuntary movements. He was born vaginally with no complications at full term. There is no history of consanguinity among parents. On physical examination, it was noticed that he is a stunted infant with generalized hypotonia and severe generalized dystonic movements. The mother says that she has noticed the presence of orange sand in his diapers many times. Laboratory evaluation revealed elevated uric acid levels in both blood and urine. Which of the following enzymes is deficient in this patient?
- A. Ribonucleotide reductase
- B. Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase
- C. Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase
- D. Dihydrofolate reductase
- E. Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (Correct Answer)
One-carbon metabolism Explanation: ***Hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase (HGPRT)***
- The clinical presentation describes classic **Lesch-Nyhan syndrome**: developmental delay, dystonia, hyperuricemia, and orange crystals (uric acid) in diapers.
- Lesch-Nyhan syndrome is caused by **deficiency of HGPRT**, an enzyme in the **purine salvage pathway**.
- HGPRT normally converts hypoxanthine to IMP and guanine to GMP, recycling purine bases.
- Without HGPRT, purines cannot be salvaged and are degraded to uric acid, causing hyperuricemia.
- Treatment includes allopurinol (xanthine oxidase inhibitor) to reduce uric acid production.
- X-linked recessive inheritance affects males primarily.
*Ribonucleotide reductase*
- This enzyme converts ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides for DNA synthesis.
- Not involved in purine salvage or degradation pathways.
- Deficiency would affect DNA synthesis globally, not specifically purine metabolism.
*Inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase*
- Converts IMP to XMP in the de novo purine synthesis pathway.
- Inhibited by mycophenolate (immunosuppressant), not deficient in Lesch-Nyhan syndrome.
*Orotate phosphoribosyltransferase*
- Enzyme in de novo pyrimidine synthesis pathway.
- Deficiency causes orotic aciduria with megaloblastic anemia and developmental delay, but not hyperuricemia or dystonia.
*Dihydrofolate reductase*
- Essential for tetrahydrofolate synthesis, required for purine and pyrimidine synthesis.
- Target of methotrexate, not deficient in this condition.
One-carbon metabolism US Medical PG Question 4: A 43-year-old woman visits her primary care provider complaining of fatigue. Although she has had it for several months, her fatigue has been worsening over the past few weeks. She has no other symptoms. Past medical history is significant for hypertension. She takes chlorthalidone, an oral contraceptive pill, and a multivitamin every day. Family history is noncontributory. She drinks about 1 bottle of wine every day and started taking a shot or two of whisky or vodka every morning before work to “clear out the cobwebs”. She was recently fired from her job. Today, her heart rate is 90/min, respiratory rate is 17/min, blood pressure is 110/65 mm Hg, and temperature is 36.7°C (98.1°F). On physical exam, she appears malnourished and anxious. Her conjunctiva are pale, and glossitis is noted on oral exam. Her heart has a regular rate and rhythm and her lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally. She has no gait or balance abnormalities. Lab results show a hemoglobin of 10 g/dL, with a mean corpuscular volume (MCV) of 108 fl. Elevated level of which of the following will most likely to be found in this patient?
- A. Methionine
- B. Phenylalanine
- C. Cysteine
- D. Homocysteine
- E. Methylmalonic acid (Correct Answer)
One-carbon metabolism Explanation: ***Methylmalonic acid***
- The patient's presentation with **macrocytic anemia** (MCV 108 fl, Hb 10 g/dL), **glossitis**, and **fatigue** suggests a **vitamin B12 deficiency**.
- **Elevated methylmalonic acid (MMA)** is a sensitive and specific marker for **vitamin B12 deficiency**, as **B12** acts as a cofactor for the enzyme **methylmalonyl-CoA mutase**, which converts MMA to succinyl-CoA.
*Methionine*
- **Methionine** is an essential amino acid, and its levels are not directly elevated in **vitamin B12 deficiency**; rather, **B12** is involved in the conversion of **homocysteine to methionine**.
- In **B12 deficiency**, the conversion of **homocysteine to methionine** is impaired, leading to **elevated homocysteine**, not necessarily methionine.
*Phenylalanine*
- **Phenylalanine** is an essential amino acid whose metabolism is primarily linked to **phenylketonuria (PKU)** if its levels are elevated due to deficient **phenylalanine hydroxylase**, which is unrelated to **vitamin B12 deficiency**.
- Elevated phenylalanine would not be an expected finding in this patient's clinical scenario.
*Cysteine*
- **Cysteine** is a non-essential amino acid, and its levels are not typically elevated as a direct consequence or marker of **vitamin B12 deficiency**.
- While involved in various metabolic pathways, it doesn't serve as a diagnostic indicator for B12 status.
*Homocysteine*
- While **homocysteine levels are elevated in vitamin B12 deficiency**, as B12 is a cofactor for **methionine synthase**, which converts homocysteine to methionine, **methylmalonic acid** is a more specific marker for **B12 deficiency**.
- **Elevated homocysteine** can also be caused by **folate deficiency** or **vitamin B6 deficiency**, making it less specific than **MMA** for isolating B12 deficiency.
One-carbon metabolism US Medical PG Question 5: A 4-year-old boy presents to the ophthalmologist for a down- and inward dislocation of the lens in his left eye. On physical exam, the boy has a marfanoid habitus and intellectual disability. Biochemical tests were performed to locate the exact defect in this boy. It was found that there was a significant deficiency in cystathionine beta-synthase activity with elevated homocysteine levels. Which of the following is the diagnosis?
- A. Marfan syndrome
- B. Homocystinuria (Correct Answer)
- C. Alkaptonuria
- D. Phenylketonuria
- E. Maple syrup urine disease
One-carbon metabolism Explanation: ***Homocystinuria***
- The combination of **ectopia lentis** (lens dislocation), **marfanoid habitus**, and **intellectual disability** is characteristic of homocystinuria.
- The **deficiency in cystathionine beta-synthase** leading to **elevated homocysteine levels** is the biochemical hallmark of this disorder.
*Marfan syndrome*
- While it presents with **marfanoid habitus** and **ectopia lentis**, the lens dislocation is typically **upward and outward**, unlike the down- and inward dislocation seen here.
- Marfan syndrome is caused by a defect in **fibrillin-1**, and biochemical tests would not show elevated homocysteine.
*Alkaptonuria*
- This disorder is characterized by **dark urine** upon standing, **ochronosis** (darkening of cartilage and connective tissue), and **arthropathy**.
- It results from a deficiency in **homogentisate oxidase** and does not present with lens dislocation or intellectual disability.
*Phenylketonuria*
- PKU is caused by a deficiency in **phenylalanine hydroxylase**, leading to an accumulation of phenylalanine.
- It primarily causes **severe intellectual disability**, seizures, and a musty odor, but not ectopia lentis or marfanoid habitus.
*Maple syrup urine disease*
- This is a metabolic disorder affecting the metabolism of **branched-chain amino acids** (leucine, isoleucine, valine).
- It presents with a characteristic **maple syrup odor** in urine, poor feeding, lethargy, and developmental delay, but not the specific features seen in this case.
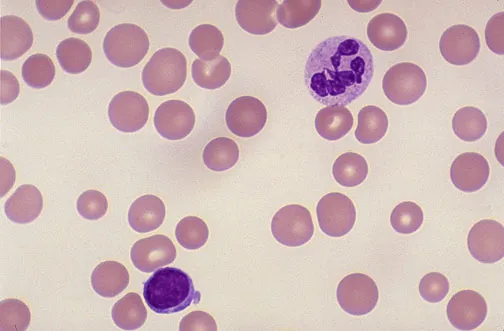
One-carbon metabolism US Medical PG Question 6: A 51-year-old gentleman presents with new onset bilateral paresthesias of his feet. He also admits that he has not been able to exercise as much as previously and his friends have commented that he looks pale. Upon physical exam you find that he has conjunctival pallor and mildly decreased sensation and proprioception on his feet bilaterally. Based on your suspicions you decide to obtain a blood smear where you see megaloblasts as well as hypersegmented neutrophils. Given these findings you decide to investigate the cause of his disorder by injecting an intramuscular vitamin, then feeding him a radiolabeled version of the same vitamin orally. After waiting 24 hours you see that no radiolabeled vitamin appears in the urine so you repeat the test with intrinsic factor added to the oral mixture, at which point 20% of the radiolabeled vitamin appears in the urine. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this gentleman's symptoms?
- A. Bacterial overgrowth
- B. Pancreatic insufficiency
- C. Insufficient vitamin intake
- D. Pernicious anemia (Correct Answer)
- E. Folate deficiency
One-carbon metabolism Explanation: ***Pernicious anemia***
- The combination of **neurological symptoms** (paresthesias, decreased proprioception), **anemia symptoms** (pallor, fatigue), **megaloblastic anemia** on blood smear (megaloblasts, hypersegmented neutrophils), and the specific Schilling test results (vitamin B12 malabsorption corrected by added **intrinsic factor**) is diagnostic for pernicious anemia.
- Pernicious anemia is an autoimmune condition targeting **gastric parietal cells** or **intrinsic factor** itself, leading to **vitamin B12 deficiency** due to impaired absorption.
*Bacterial overgrowth*
- **Bacterial overgrowth in the small intestine** can consume vitamin B12, leading to deficiency, but the Schilling test would show improvement with **antibiotics**, not intrinsic factor.
- While it can cause B12 deficiency and megaloblastic anemia, improvement upon adding intrinsic factor points away from this diagnosis.
*Pancreatic insufficiency*
- **Pancreatic enzymes** are required to cleave vitamin B12 from its binding proteins, but the **Schilling test** would show improvement with **pancreatic enzyme supplements**, not intrinsic factor.
- While pancreatic insufficiency can lead to B12 malabsorption, the specific Schillings test results rule it out.
*Insufficient vitamin intake*
- **Insufficient dietary intake** of vitamin B12 would lead to B12 deficiency, but in such a case, the **Schilling test** would show normal absorption of radiolabeled B12 even without intrinsic factor in the second stage.
- The initial B12 malabsorption indicates an absorption problem, not solely a dietary lack.
*Folate deficiency*
- **Folate deficiency** also causes **megaloblastic anemia** and can present with fatigue and pallor, but it does **not cause neurological symptoms** like paresthesias or proprioception deficits.
- The Schilling test specifically evaluates **vitamin B12 absorption**, not folate levels, so it would be irrelevant for diagnosing pure folate deficiency.
One-carbon metabolism US Medical PG Question 7: A 38-year-old, working, first-time mother brings her 9-month-old male infant to the pediatrician for "wounds that simply won't heal" and bleeding gums. She exclaims, "I have been extra careful with him making sure to not let him get dirty, I boil his baby formula for 15 minutes each morning before I leave for work to give to the caregiver, and he has gotten all of his vaccinations." This infant is deficient in a molecule that is also an essential co-factor for which of the following reactions?
- A. Conversion of homocysteine to methionine
- B. Conversion of alpha ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA
- C. Conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine (Correct Answer)
- D. Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA
- E. Conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate
One-carbon metabolism Explanation: ***Conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine***
- The infant's symptoms of "wounds that simply won't heal" and **bleeding gums** are classic signs of **scurvy**, caused by a deficiency in **vitamin C (ascorbic acid)**.
- **Vitamin C** is an essential cofactor for **dopamine beta-hydroxylase**, the enzyme responsible for converting **dopamine to norepinephrine**.
*Conversion of homocysteine to methionine*
- This reaction is catalyzed by **methionine synthase**, which requires **vitamin B12** (cobalamin) and **folate (vitamin B9)** as cofactors.
- Deficiency in these vitamins would lead to **megaloblastic anemia** and neurological symptoms, not delayed wound healing and bleeding gums.
*Conversion of alpha ketoglutarate to succinyl-CoA*
- This step in the **Krebs cycle** is catalyzed by **alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase**, which requires **thiamine (vitamin B1)**, **lipoic acid**, **Mg2+**, **NAD+**, and **FAD** as cofactors.
- Thiamine deficiency can cause **beriberi** or **Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome**, not scurvy symptoms.
*Conversion of pyruvate to acetyl-CoA*
- This reaction is catalyzed by the **pyruvate dehydrogenase complex**, which requires **thiamine (vitamin B1)**, **lipoic acid**, **coenzyme A**, **FAD**, and **NAD+** as cofactors.
- A deficiency in any of these, particularly thiamine, leads to impaired carbohydrate metabolism and lactic acidosis.
*Conversion of pyruvate to oxaloacetate*
- This reaction is catalyzed by **pyruvate carboxylase**, which requires **biotin (vitamin B7)** as a cofactor and is essential for **gluconeogenesis**.
- Biotin deficiency is rare and can present with dermatitis, hair loss, and neurological symptoms, not the classic signs of scurvy.
One-carbon metabolism US Medical PG Question 8: A 30-year-old man is brought to the emergency room by ambulance after being found unconscious in his car parked in his garage with the engine running. His wife arrives and reveals that his past medical history is significant for severe depression treated with fluoxetine. He is now disoriented to person, place, and time. His temperature is 37.8 deg C (100.0 deg F), blood pressure is 100/50 mmHg, heart rate is 100/min, respiratory rate is 10/min, and SaO2 is 100%. On physical exam, there is no evidence of burn wounds. He has moist mucous membranes and no abnormalities on cardiac and pulmonary auscultation. His respirations are slow but spontaneous. His capillary refill time is 4 seconds. He is started on 100% supplemental oxygen by non-rebreather mask. His preliminary laboratory results are as follows:
Arterial blood pH 7.20, PaO2 102 mm Hg, PaCO2 23 mm Hg, HCO3 10 mm Hg, WBC count 9.2/µL, Hb 14 mg/dL, platelets 200,000/µL, sodium 137 mEq/L, potassium 5.0 mEq/L, chloride 96 mEq/L, BUN 28 mg/dL, creatinine 1.0 mg/dL, and glucose 120 mg/dL. Which of the following is the cause of this patient's acid-base abnormality?
- A. Decreased oxygen delivery to tissues (Correct Answer)
- B. Decreased ability for the tissues to use oxygen
- C. Increased anions from toxic ingestion
- D. Increased metabolic rate
- E. Decreased minute ventilation
One-carbon metabolism Explanation: ***Decreased oxygen delivery to tissues***
- The patient's presentation in a running car in a garage suggests **carbon monoxide (CO) poisoning**. CO binds to hemoglobin with higher affinity than oxygen, forming **carboxyhemoglobin (COHb)**, which impairs oxygen delivery to tissues despite normal PaO2.
- The **metabolic acidosis (pH 7.20, HCO3 10)** with an elevated anion gap (Na - (Cl + HCO3) = 137 - (96 + 10) = 31) and altered mental status are consistent with widespread tissue hypoxia due to decreased oxygen delivery, leading to **lactic acid accumulation**.
*Decreased ability for the tissues to use oxygen*
- This scenario typically occurs in conditions like **cyanide poisoning**, where cellular metabolism is inhibited, preventing oxygen utilization despite adequate delivery.
- Cyanide poisoning often presents with a narrower or normal anion gap metabolic acidosis and a **"cherry red" skin color**, which are not specifically noted here.
*Increased anions from toxic ingestion*
- While there is an **elevated anion gap metabolic acidosis**, merely stating "increased anions from toxic ingestion" is less precise than identifying the underlying mechanism of oxygen deprivation.
- Many toxins can cause an elevated anion gap, but the specific context of **CO poisoning** points to tissue hypoxia as the primary driver of acidosis, not just the presence of other toxic anions.
*Increased metabolic rate*
- An increased metabolic rate, as seen in conditions like **sepsis** or hyperthyroidism, can lead to increased acid production and metabolic acidosis.
- However, in this case, the **depressed respiratory rate** and context of CO exposure point away from a primary state of hypermetabolism.
*Decreased minute ventilation*
- **Decreased minute ventilation** would primarily lead to **respiratory acidosis** (elevated PaCO2) due to CO2 retention.
- The patient's lab results show a **low PaCO2 (23 mmHg)**, indicating respiratory compensation for a metabolic acidosis, not a primary respiratory problem.
One-carbon metabolism US Medical PG Question 9: A 6-day-old female newborn is brought to the physician because of yellowish discoloration of her eyes and body, vomiting, and poor feeding for 3 days. She has had diarrhea for the past 2 days. She was born at 38 weeks' gestation and the antenatal period was uncomplicated. She appears lethargic. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows jaundice of the skin and conjunctivae. Bilateral cataracts are present. The abdomen is soft and nontender. The liver is palpated 4-cm below the right costal margin; there is no splenomegaly. Muscle tone is decreased in all extremities. Serum glucose concentration is 37 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most appropriate recommendation to prevent long-term complications of this illness?
- A. Phototherapy
- B. Thiamine therapy
- C. Levothyroxine therapy
- D. Frequent glucose feeds
- E. Stop milk feeds (Correct Answer)
One-carbon metabolism Explanation: ***Stop milk feeds***
- The constellation of **jaundice**, **vomiting**, **diarrhea**, **lethargy**, **hepatomegaly**, **hypoglycemia**, **decreased muscle tone**, and **bilateral cataracts** in a newborn is highly suggestive of **galactosemia**.
- **Stopping milk feeds** (specifically those containing lactose and galactose) is the primary and most crucial intervention to prevent long-term complications such as intellectual disability, liver damage, and kidney failure.
*Phototherapy*
- While phototherapy is used to treat **neonatal jaundice**, it addresses only the symptom of hyperbilirubinemia, not the underlying cause in galactosemia.
- It would not prevent the systemic devastating effects on other organs caused by galactose and its metabolites.
*Thiamine therapy*
- **Thiamine therapy** is indicated for conditions like **Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome** or **thiamine-dependent metabolic disorders**, which do not align with the presented symptoms.
- There is no evidence to support its use in galactosemia.
*Levothyroxine therapy*
- **Levothyroxine therapy** is used for **hypothyroidism**, a condition characterized by feeding problems, jaundice, and lethargy but typically lacks the specific findings of cataracts, vomiting/diarrhea in this acute presentation, and hepatomegaly, as seen in this clinical picture.
- The combination of symptoms described points more specifically to a metabolic disorder affecting galactose metabolism.
*Frequent glucose feeds*
- While the newborn has **hypoglycemia**, simply providing frequent glucose feeds addresses **only a symptom** and does not resolve the underlying metabolic defect in galactosemia.
- Continuing milk feeds would worsen the primary disease, despite potentially correcting blood glucose temporarily.
One-carbon metabolism US Medical PG Question 10: A 9-month-old infant presents to your office for a check-up. Exam reveals developmental delay, microcephaly, and a mousy odor to his breath. You should be concerned that the infant may have which of the following?
- A. Excess tetrahydrobiopterin cofactor
- B. Deficit of porphobilinogen deaminase activity
- C. Deficit of tyrosine hydroxylase activity
- D. Excess phenylalanine hydroxylase activity
- E. Deficit of phenylalanine hydroxylase activity (Correct Answer)
One-carbon metabolism Explanation: ***Deficit of phenylalanine hydroxylase activity***
- The combination of **developmental delay**, **microcephaly**, and a **mousy odor** is characteristic of **phenylketonuria (PKU)**.
- PKU is caused by a deficient **phenylalanine hydroxylase** enzyme, leading to a buildup of phenylalanine and its metabolites, which are toxic to the developing brain.
*Excess tetrahydrobiopterin cofactor*
- This condition (**BH4 excess**) is rare and does not typically present with the classic signs of PKU; rather, it often involves neurological symptoms due to other metabolic imbalances.
- An excess of the BH4 cofactor would theoretically enhance rather than inhibit phenylalanine hydroxylase activity, if the enzyme itself were functional.
*Deficit of porphobilinogen deaminase activity*
- A deficit in **porphobilinogen deaminase** is associated with **Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP)**, which presents with acute neurovisceral attacks.
- Symptoms of AIP include severe abdominal pain, psychiatric disturbances, and neurological deficits, but not developmental delay or a mousy odor.
*Deficit of tyrosine hydroxylase activity*
- A deficiency in **tyrosine hydroxylase** affects the synthesis of **dopamine** and other catecholamines, leading to neurological disorders, including **dystonia** and **Parkinsonian symptoms**.
- While it can cause developmental delay, it does not typically present with a mousy odor or microcephaly, and its primary symptoms relate to motor control.
*Excess phenylalanine hydroxylase activity*
- An **excess** of phenylalanine hydroxylase activity would lead to increased breakdown of phenylalanine, preventing its buildup.
- This would not cause the symptoms described; instead, it would likely result in lower-than-normal phenylalanine levels, which is generally not problematic.
More One-carbon metabolism US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.