Aromatic amino acid metabolism US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Aromatic amino acid metabolism. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
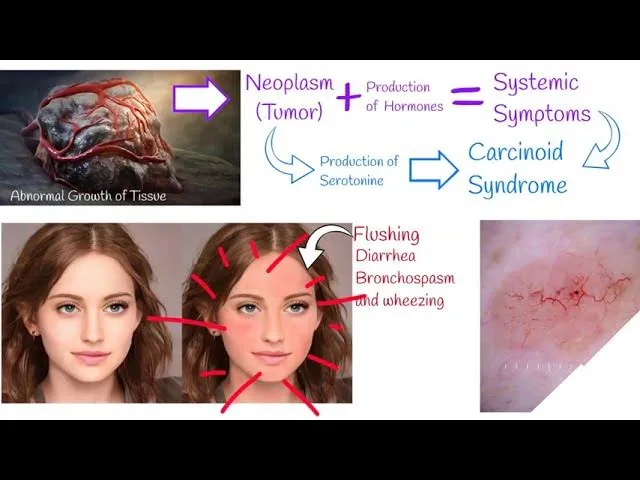
Aromatic amino acid metabolism US Medical PG Question 1: A 34-year-old man comes to the physician because of palpitations, shortness of breath, diarrhea, and abdominal cramps for 2 months. Physical examination shows cutaneous flushing of the face. Auscultation of the chest shows bilateral wheezing. A 24-hour urine collection shows increased 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid (5-HIAA) concentration. A contrast-enhanced CT scan of the abdomen shows an intestinal tumor with extensive metastasis to the liver. A diagnosis of an inoperable disease is made and the patient is started on treatment with octreotide. Six weeks later, the patient's symptoms have improved except for his abdominal pain and frequent loose stools. The physician suggests enrolling the patient in a trial to test additional treatment with a new drug that has been shown to improve symptoms in other patients with the same condition. The expected beneficial effect of this new drug is most likely caused by inhibition of which of the following?
- A. Histidine decarboxylase
- B. Plasma kallikrein
- C. Vasoactive intestinal peptide
- D. Tryptophan hydroxylase (Correct Answer)
- E. Dopamine β-hydroxylase
Aromatic amino acid metabolism Explanation: ***Tryptophan hydroxylase***
- This patient presents with symptoms consistent with **carcinoid syndrome** from an intestinal neuroendocrine tumor with liver metastases. The increased urinary **5-HIAA** confirms serotonin overproduction.
- While existing treatment with **octreotide** (a somatostatin analog) controls most symptoms, persistent abdominal pain and diarrhea suggest continued serotonin effects. A new drug targeting **tryptophan hydroxylase** would inhibit the rate-limiting step in serotonin synthesis, thus reducing serotonin levels.
*Histidine decarboxylase*
- This enzyme converts **histidine to histamine**. While histamine can contribute to flushing in some carcinoid tumors, it is not the primary mediator of the systemic symptoms in this case.
- The main issue here is serotonin overproduction, not histamine.
*Plasma kallikrein*
- **Plasma kallikrein** is involved in the kinin-kallikrein system, which produces **bradykinin**, a potent vasodilator. While bradykinin can cause flushing, it is not primarily responsible for the GI symptoms or serotonin overproduction seen in carcinoid syndrome.
- Inhibiting plasma kallikrein would not address the fundamental problem of excess serotonin.
*Vasoactive intestinal peptide*
- **VIP (Vasoactive Intestinal Peptide)** is a neuroendocrine peptide that can cause watery diarrhea and flushing, often associated with **VIPomas**.
- However, the patient's elevated **5-HIAA** strongly points towards serotonin overproduction from a carcinoid tumor, not a VIPoma.
*Dopamine β-hydroxylase*
- This enzyme converts **dopamine to norepinephrine**. This pathway is relevant to catecholamine synthesis, not serotonin.
- This enzyme would be targeted in conditions involving excess catecholamines (e.g., pheochromocytoma), which is not the case here.
Aromatic amino acid metabolism US Medical PG Question 2: You are examining a 3-day-old newborn who was delivered vaginally without any complications. The newborn presents with vomiting, hyperventilation, lethargy, and seizures. Blood work demonstrates hyperammonemia, elevated glutamine levels, and decreased blood urea nitrogen. A CT scan demonstrates cerebral edema. Defects in which of the following enzymes would result in a clinical presentation similar to this infant?
- A. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (Correct Answer)
- B. Homogentisate oxidase
- C. Cystathionine synthase
- D. Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase
- E. Phenylalanine hydroxylase
Aromatic amino acid metabolism Explanation: **Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I**
- **Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPSI)** deficiency is a severe **urea cycle disorder** that typically presents in the neonatal period with **hyperammonemia**, **vomiting**, **lethargy**, **seizures**, and **hyperventilation**.
- The enzyme CPSI catalyzes the first step of the urea cycle, which is crucial for detoxifying ammonia, leading to **elevated glutamine** and **decreased blood urea nitrogen** when defective.
*Homogentisate oxidase*
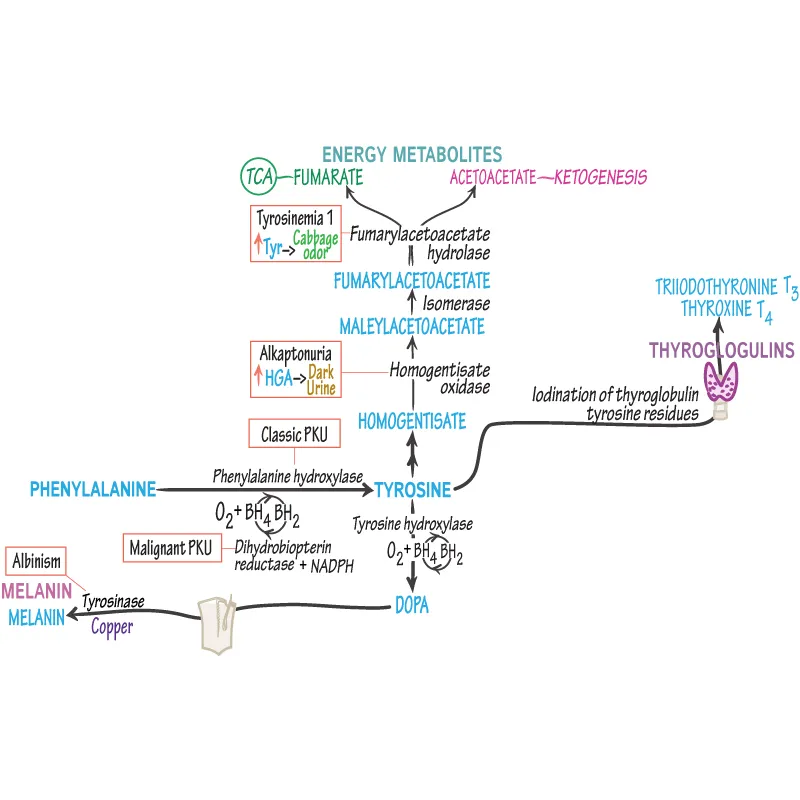
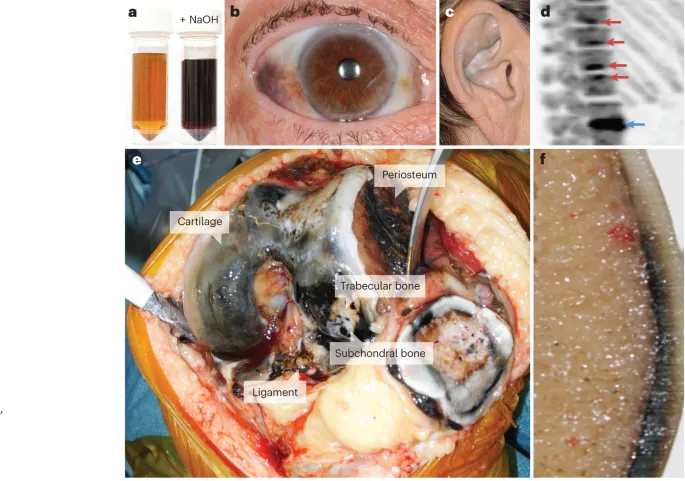
- Deficiency in **homogentisate oxidase** causes **alkaptonuria**, a disorder of tyrosine metabolism.
- This condition is characterized by **dark urine** upon standing, **ochronosis** (bluish-black discoloration of cartilage and connective tissue later in life), and **arthropathy**, not hyperammonemia or acute neonatal crisis.
*Cystathionine synthase*
- A defect in **cystathionine synthase** leads to **homocystinuria**, an inherited disorder of methionine metabolism.
- Symptoms include **ectopia lentis**, **skeletal abnormalities**, **thromboembolic events**, and **developmental delay**, not acute neonatal hyperammonemic encephalopathy.
*Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase*
- Deficiency in **branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase** causes **maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)**, a disorder of branched-chain amino acid metabolism.
- While it can present with vomiting, lethargy, and seizures in neonates, it is characterized by a distinctive **maple syrup odor** in urine and elevated branched-chain amino acids, not hyperammonemia and low BUN.
*Phenylalanine hydroxylase*
- A deficiency in **phenylalanine hydroxylase** causes **phenylketonuria (PKU)**, an amino acid metabolism disorder.
- PKU typically presents with intellectual disability, seizures, and a musty odor if untreated, but generally does not manifest as an acute neonatal crisis with hyperammonemia, as seen in urea cycle defects.
Aromatic amino acid metabolism US Medical PG Question 3: A 30-year-old African American G1P0 mother gives birth to a male infant at 33 weeks' gestation. The mother had no prenatal care and took no prenatal vitamins. The child’s postnatal period was complicated by neonatal sepsis due to group B Streptococcus. He required a two week stay in the neonatal intensive care unit to receive antibiotics, cardiopulmonary support, and intravenous nutrition. He eventually recovered and was discharged. At a normal follow-up visit to the pediatrician’s office one month later, the mother asks about the child’s skin color and hair color. On examination, the child has white hair and diffusely pale skin. The child’s irises appear translucent. Further questioning of the mother reveals that there is a distant family history of blindness. This child most likely has a defect in an enzyme involved in the metabolism of which of the following molecules?
- A. Leucine
- B. Homocysteine
- C. Phenylalanine
- D. Homogentisic acid
- E. DOPA (Correct Answer)
Aromatic amino acid metabolism Explanation: ***DOPA***
- The symptoms of **white hair**, **pale skin**, and **translucent irises**, along with a family history of **blindness**, are classic signs of **oculocutaneous albinism**.
- **Oculocutaneous albinism** results from a defect in **tyrosinase**, an enzyme responsible for converting **DOPA** (3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine) into **melanin**.
*Leucine*
- Defects in **leucine** metabolism are associated with **Maple Syrup Urine Disease**, characterized by sweet-smelling urine and neurological complications, not albinism.
- This condition involves impaired **branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase** complex activity, leading to an accumulation of branched-chain amino acids.
*Homocysteine*
- Problems with **homocysteine** metabolism are seen in conditions like **homocystinuria**, which can cause developmental delay, skeletal abnormalities, and vascular issues, but not hypopigmentation.
- This is often due to deficiencies in **cystathionine beta-synthase** or other enzymes involved in folate and vitamin B12 metabolism.
*Phenylalanine*
- A defect in **phenylalanine** metabolism, specifically **phenylalanine hydroxylase**, leads to **phenylketonuria (PKU)**, which causes intellectual disability, seizures, and a musty odor, but not the specific ocular and cutaneous features described for albinism.
- While PKU can cause milder hypopigmentation due to reduced tyrosine availability, the described translucent irises and severe white hair are more indicative of albinism.
*Homogentisic acid*
- A defect in **homogentisic acid** metabolism causes **alkaptonuria**, characterized by dark urine upon standing, blue-black discoloration of cartilage (ochronosis), and early-onset arthritis, which are not present in this case.
- This condition results from a deficiency of **homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase**.
Aromatic amino acid metabolism US Medical PG Question 4: You are counseling a mother whose newborn has just screened positive for a deficit of phenylalanine hydroxylase enzyme. You inform her that her child will require dietary supplementation of which of the following?
- A. Aspartame
- B. Niacin
- C. Homogentisic Acid
- D. Tyrosine (Correct Answer)
- E. Leucine
Aromatic amino acid metabolism Explanation: ***Tyrosine***
- A deficit of **phenylalanine hydroxylase** prevents the conversion of phenylalanine to tyrosine, making **tyrosine** an essential amino acid that must be supplemented.
- Dietary restriction of **phenylalanine** is also crucial to prevent the accumulation of toxic byproducts that can cause severe neurological damage.
*Aspartame*
- **Aspartame** is an artificial sweetener that contains **phenylalanine**, which would be harmful for a child with phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency.
- Consumption of aspartame would increase the body's phenylalanine load, exacerbating the metabolic disorder.
*Niacin*
- **Niacin** (vitamin B3) is a vitamin and its supplementation is not related to the phenylalanine hydroxylase pathway or its deficiency.
- Deficiency of niacin is associated with **pellagra**, characterized by dermatitis, diarrhea, and dementia.
*Homogentisic Acid*
- **Homogentisic acid** is an intermediate in the metabolism of tyrosine, and its accumulation is characteristic of **alkaptonuria**, a different metabolic disorder.
- It is not a therapeutic supplement for phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency.
*Leucine*
- **Leucine** is a branched-chain amino acid, and its metabolism is unrelated to phenylalanine hydroxylase deficiency.
- Supplemental leucine is not required in this condition and would not address the metabolic defect.
Aromatic amino acid metabolism US Medical PG Question 5: A 2-week-old boy presents to the emergency department because of unusual irritability and lethargy. The patient is admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit and minutes later develops metabolic encephalopathy. This progressed to a coma, followed by death before any laboratory tests are completed. The infant was born at home via vaginal delivery at 39 weeks' of gestation. His mother says that the symptoms started since the infant was 4-days-old, but since he only seemed ‘tired’, she decided not to seek medical attention. Further testing during autopsy shows hyperammonemia, low citrulline, and increased orotic acid. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase
- B. Propionyl-CoA carboxylase
- C. Homogentisic acid dioxygenase
- D. Ornithine transcarbamylase (Correct Answer)
- E. Cystathionine beta-synthase
Aromatic amino acid metabolism Explanation: **Ornithine transcarbamylase**
- **Hyperammonemia**, **low citrulline**, and **increased orotic acid** are classic findings in **Ornithine Transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency**. OTC is an X-linked urea cycle disorder.
- The rapid progression to **metabolic encephalopathy** and death in a neonate with these laboratory findings is highly characteristic of severe OTC deficiency, often presenting in the first few days of life.
*Branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes **Maple Syrup Urine Disease**, characterized by elevated **branched-chain amino acids** and their corresponding ketoacids in blood and urine.
- While it can cause neurological symptoms, it does not typically present with the specific constellation of **hyperammonemia**, low citrulline, and high orotic acid.
*Propionyl-CoA carboxylase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme leads to **Propionic acidemia**, a type of organic acidemia, characterized by **propionic acid accumulation** and often **metabolic acidosis**, ketosis, and hyperammonemia.
- However, it would not typically cause **low citrulline** or isolated **elevated orotic acid** as seen in urea cycle disorders.
*Homogentisic acid dioxygenase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes **Alkaptonuria**, an inborn error of metabolism characterized by the accumulation of **homogentisic acid**.
- This condition is usually benign in infancy, with symptoms appearing later in life such as **dark urine** on standing and **ochronosis** (darkening of cartilage). It does not present with acute hyperammonemia or metabolic encephalopathy.
*Cystathionine beta-synthase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes **homocystinuria**, an inborn error of methionine metabolism, leading to elevated **homocysteine** and methionine.
- Clinical features include **ectopia lentis**, skeletal abnormalities, and intellectual disability, but not usually acute neonatal hyperammonemia or the specific findings of low citrulline and high orotic acid.
Aromatic amino acid metabolism US Medical PG Question 6: A 9-month-old female is brought to the emergency department after experiencing a seizure. She was born at home and was normal at birth according to her parents. Since then, they have noticed that she does not appear to be achieving developmental milestones as quickly as her siblings, and often appears lethargic. Physical exam reveals microcephaly, very light pigmentation (as compared to her family), and a "musty" body odor. The varied manifestations of this disease can most likely be attributed to which of the following genetic principles?
- A. Incomplete penetrance
- B. Multiple gene mutations
- C. Pleiotropy (Correct Answer)
- D. Anticipation
- E. Variable expressivity
Aromatic amino acid metabolism Explanation: ***Pleiotropy***
- **Pleiotropy** refers to a single gene affecting multiple seemingly unrelated phenotypic traits, which is evident in this case of **phenylketonuria (PKU)** where a single enzyme deficiency (phenylalanine hydroxylase) leads to **seizures**, developmental delay, **microcephaly**, hypopigmentation, and a **"musty" odor**.
- The diverse clinical manifestations arise from the accumulation of phenylalanine and its metabolites, which are toxic to various organ systems, primarily the brain and also interfering with melanin synthesis.
*Incomplete penetrance*
- **Incomplete penetrance** describes a situation where individuals with a specific genotype do not always express the associated phenotype, meaning some might carry the gene but show no symptoms.
- This principle usually describes "all or nothing" manifestation of the disease, not varied manifestations of one disease.
*Multiple gene mutations*
- This principle applies when a disease is caused by defects in **several different genes** working together or independently, leading to a complex inheritance pattern.
- While many complex diseases involve multiple genes, the constellation of symptoms described (seizures, developmental delay, hypopigmentation, odor) in PKU points to a single primary defect with widespread effects.
*Anticipation*
- **Anticipation** describes a genetic phenomenon where the severity of disease increases and/or age of onset decreases in successive generations, typically seen in diseases like Huntington's or myotonic dystrophy due to unstable trinucleotide repeats.
- The clinical presentation in this child does not suggest a pattern of worsening symptoms across generations within the family.
*Variable expressivity*
- **Variable expressivity** describes how individuals with the same genotype can exhibit different clinical features or varying degrees of disease severity.
- While PKU can have variable expressivity (depending on dietary control or residual enzyme activity), the core concept explaining *why* so many *different types* of symptoms exist from a single gene defect is pleiotropy, not just variability in one type of symptom.
Aromatic amino acid metabolism US Medical PG Question 7: A 5 year old child was brought to the physician with a history of black urine. There is no history of fever or any other complaints. There is no growth retardation and all the developmental milestones are normal. The child is suspected to have an enzyme defect for metabolism of an aromatic amino acid. What is the enzyme deficient
- A. Homogentisate dehydrogenase
- B. Homogentistae oxidase (Correct Answer)
- C. Tyrosine Transaminase
- D. Tryptophan Hydroxylase
- E. Phenylalanine Hydroxylase
Aromatic amino acid metabolism Explanation: ***Homogentistae oxidase***
- The presentation of a child with **black urine** (alkaptonuria) in the absence of other symptoms is characteristic of a deficiency in **homogentisate oxidase**.
- This enzyme is crucial in the catabolism of **tyrosine**, and its deficiency leads to the accumulation of **homogentisic acid**, which oxidizes upon exposure to air, turning urine black.
*Homogentisate dehydrogenase*
- This enzyme is not a recognized component of the **tyrosine degradation pathway** in humans.
- The correct enzyme involved in the breakdown of **homogentisate** is an oxidase, not a dehydrogenase, in this context.
*Tyrosine Transaminase*
- A deficiency in **tyrosine transaminase** (tyrosinemia type II) would lead to elevated tyrosine levels and typically presents with symptoms affecting the eyes, skin, and intellectual disability, not primarily black urine.
- This condition is characterized by **ocular findings** (corneal ulcers), **skin lesions**, and **neurological symptoms**.
*Tryptophan Hydroxylase*
- This enzyme is involved in the synthesis of **serotonin** and **melatonin** from tryptophan, a different amino acid pathway.
- A deficiency or abnormality in **tryptophan hydroxylase** would not cause black urine but could lead to neurological or mood disorders.
*Phenylalanine Hydroxylase*
- A deficiency in **phenylalanine hydroxylase** causes **phenylketonuria (PKU)**, which affects phenylalanine metabolism, not tyrosine metabolism directly.
- PKU typically presents with **intellectual disability**, **musty odor**, **fair skin**, and **seizures** if untreated, not black urine.
Aromatic amino acid metabolism US Medical PG Question 8: A 9-month-old infant presents to your office for a check-up. Exam reveals developmental delay, microcephaly, and a mousy odor to his breath. You should be concerned that the infant may have which of the following?
- A. Excess tetrahydrobiopterin cofactor
- B. Deficit of porphobilinogen deaminase activity
- C. Deficit of tyrosine hydroxylase activity
- D. Excess phenylalanine hydroxylase activity
- E. Deficit of phenylalanine hydroxylase activity (Correct Answer)
Aromatic amino acid metabolism Explanation: ***Deficit of phenylalanine hydroxylase activity***
- The combination of **developmental delay**, **microcephaly**, and a **mousy odor** is characteristic of **phenylketonuria (PKU)**.
- PKU is caused by a deficient **phenylalanine hydroxylase** enzyme, leading to a buildup of phenylalanine and its metabolites, which are toxic to the developing brain.
*Excess tetrahydrobiopterin cofactor*
- This condition (**BH4 excess**) is rare and does not typically present with the classic signs of PKU; rather, it often involves neurological symptoms due to other metabolic imbalances.
- An excess of the BH4 cofactor would theoretically enhance rather than inhibit phenylalanine hydroxylase activity, if the enzyme itself were functional.
*Deficit of porphobilinogen deaminase activity*
- A deficit in **porphobilinogen deaminase** is associated with **Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP)**, which presents with acute neurovisceral attacks.
- Symptoms of AIP include severe abdominal pain, psychiatric disturbances, and neurological deficits, but not developmental delay or a mousy odor.
*Deficit of tyrosine hydroxylase activity*
- A deficiency in **tyrosine hydroxylase** affects the synthesis of **dopamine** and other catecholamines, leading to neurological disorders, including **dystonia** and **Parkinsonian symptoms**.
- While it can cause developmental delay, it does not typically present with a mousy odor or microcephaly, and its primary symptoms relate to motor control.
*Excess phenylalanine hydroxylase activity*
- An **excess** of phenylalanine hydroxylase activity would lead to increased breakdown of phenylalanine, preventing its buildup.
- This would not cause the symptoms described; instead, it would likely result in lower-than-normal phenylalanine levels, which is generally not problematic.
Aromatic amino acid metabolism US Medical PG Question 9: An 8-day-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother because of vomiting and poor feeding. The pregnancy was uncomplicated, and he was born at full term. He appears pale and lethargic. Physical examination shows diffusely increased muscle tone. His urine is noted to have a sweet odor. This patient's symptoms are most likely caused by the accumulation of which of the following?
- A. Phenylalanine
- B. Homogentisic acid
- C. Isoleucine (Correct Answer)
- D. Homocysteine
- E. Phytanic acid
Aromatic amino acid metabolism Explanation: ***Isoleucine***
- The combination of **vomiting**, poor feeding, lethargy, **increased muscle tone**, and a **sweet-smelling urine** (often described as maple syrup odor) in a neonate strongly points to **Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)**.
- MSUD is caused by a defect in the **branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex**, leading to the accumulation of branched-chain amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, and valine) and their corresponding alpha-keto acids.
*Phenylalanine*
- Accumulation of **phenylalanine** is characteristic of **Phenylketonuria (PKU)**, which typically presents with intellectual disability, seizures, and an eczematous rash if untreated, but not a maple syrup odor in urine or acute neonatal crisis.
- The urine odor in PKU is often described as **mousy** or musty, distinctly different from a sweet or maple syrup odor.
*Homogentisic acid*
- Accumulation of **homogentisic acid** is seen in **Alkaptonuria**, an inborn error of metabolism that primarily causes dark urine upon standing (due to oxidation of homogentisic acid), ochronosis (blue-black pigmentation of cartilage and connective tissue later in life), and arthritis.
- It does not present with acute neonatal symptoms such as vomiting, lethargy, or a sweet urine odor.
*Homocysteine*
- Elevated levels of **homocysteine** are found in **Homocystinuria**, which can lead to intellectual disability, developmental delay, dislocation of the ocular lens (ectopia lentis), Marfanoid habitus, and thromboembolic events.
- It does not typically present in the neonatal period with a sweet urine odor or acute neurological symptoms like increased muscle tone.
*Phytanic acid*
- Accumulation of **phytanic acid** is characteristic of **Refsum disease**, a rare peroxisomal disorder that causes progressive neurological symptoms such as retinitis pigmentosa, peripheral neuropathy, ataxia, and deafness in childhood or adulthood.
- It does not present in the neonatal period with the described acute symptoms or unique urine odor.
Aromatic amino acid metabolism US Medical PG Question 10: An investigator is studying the activity level of several different enzymes in human subjects from various demographic groups. An elevated level of activity of phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate synthetase is found in one of the study subjects. This patient is most likely to have which of the following conditions?
- A. Phenylketonuria
- B. Homocystinuria
- C. Gout (Correct Answer)
- D. Alkaptonuria
- E. Maple syrup urine disease
Aromatic amino acid metabolism Explanation: ***Gout***
- **Elevated phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) synthetase activity** leads to increased production of PRPP, a precursor for **purine biosynthesis**.
- Increased purine synthesis results in overproduction of **uric acid**, which can precipitate as monosodium urate crystals in joints, causing **gout**.
*Phenylketonuria*
- Caused by a deficiency in **phenylalanine hydroxylase**, leading to an accumulation of **phenylalanine**.
- Not directly related to increased PRPP synthetase activity or purine metabolism.
*Homocystinuria*
- Primarily due to a deficiency in **cystathionine beta-synthase**, leading to elevated levels of **homocysteine**.
- This condition involves methionine metabolism, not purine metabolism or PRPP synthetase.
*Alkaptonuria*
- Results from a deficiency in **homogentisate 1,2-dioxygenase**, causing the accumulation of **homogentisic acid**.
- It is an inborn error of tyrosine metabolism and is unrelated to PRPP synthetase activity.
*Maple syrup urine disease*
- Caused by a deficiency in the **branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex**, leading to accumulation of **leucine, isoleucine, and valine**.
- This condition affects branched-chain amino acid metabolism, not purine metabolism.
More Aromatic amino acid metabolism US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.