Amino acid transport disorders US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Amino acid transport disorders. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Amino acid transport disorders US Medical PG Question 1: An 8-day-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother because of vomiting and poor feeding. The pregnancy was uncomplicated, and he was born at full term. He appears pale and lethargic. Physical examination shows diffusely increased muscle tone. His urine is noted to have a sweet odor. This patient's symptoms are most likely caused by the accumulation of which of the following?
- A. Phenylalanine
- B. Homogentisic acid
- C. Isoleucine (Correct Answer)
- D. Homocysteine
- E. Phytanic acid
Amino acid transport disorders Explanation: ***Isoleucine***
- The combination of **vomiting**, poor feeding, lethargy, **increased muscle tone**, and a **sweet-smelling urine** (often described as maple syrup odor) in a neonate strongly points to **Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)**.
- MSUD is caused by a defect in the **branched-chain alpha-keto acid dehydrogenase complex**, leading to the accumulation of branched-chain amino acids (leucine, isoleucine, and valine) and their corresponding alpha-keto acids.
*Phenylalanine*
- Accumulation of **phenylalanine** is characteristic of **Phenylketonuria (PKU)**, which typically presents with intellectual disability, seizures, and an eczematous rash if untreated, but not a maple syrup odor in urine or acute neonatal crisis.
- The urine odor in PKU is often described as **mousy** or musty, distinctly different from a sweet or maple syrup odor.
*Homogentisic acid*
- Accumulation of **homogentisic acid** is seen in **Alkaptonuria**, an inborn error of metabolism that primarily causes dark urine upon standing (due to oxidation of homogentisic acid), ochronosis (blue-black pigmentation of cartilage and connective tissue later in life), and arthritis.
- It does not present with acute neonatal symptoms such as vomiting, lethargy, or a sweet urine odor.
*Homocysteine*
- Elevated levels of **homocysteine** are found in **Homocystinuria**, which can lead to intellectual disability, developmental delay, dislocation of the ocular lens (ectopia lentis), Marfanoid habitus, and thromboembolic events.
- It does not typically present in the neonatal period with a sweet urine odor or acute neurological symptoms like increased muscle tone.
*Phytanic acid*
- Accumulation of **phytanic acid** is characteristic of **Refsum disease**, a rare peroxisomal disorder that causes progressive neurological symptoms such as retinitis pigmentosa, peripheral neuropathy, ataxia, and deafness in childhood or adulthood.
- It does not present in the neonatal period with the described acute symptoms or unique urine odor.
Amino acid transport disorders US Medical PG Question 2: You are examining a 3-day-old newborn who was delivered vaginally without any complications. The newborn presents with vomiting, hyperventilation, lethargy, and seizures. Blood work demonstrates hyperammonemia, elevated glutamine levels, and decreased blood urea nitrogen. A CT scan demonstrates cerebral edema. Defects in which of the following enzymes would result in a clinical presentation similar to this infant?
- A. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (Correct Answer)
- B. Homogentisate oxidase
- C. Cystathionine synthase
- D. Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase
- E. Phenylalanine hydroxylase
Amino acid transport disorders Explanation: **Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I**
- **Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase I (CPSI)** deficiency is a severe **urea cycle disorder** that typically presents in the neonatal period with **hyperammonemia**, **vomiting**, **lethargy**, **seizures**, and **hyperventilation**.
- The enzyme CPSI catalyzes the first step of the urea cycle, which is crucial for detoxifying ammonia, leading to **elevated glutamine** and **decreased blood urea nitrogen** when defective.
*Homogentisate oxidase*
- Deficiency in **homogentisate oxidase** causes **alkaptonuria**, a disorder of tyrosine metabolism.
- This condition is characterized by **dark urine** upon standing, **ochronosis** (bluish-black discoloration of cartilage and connective tissue later in life), and **arthropathy**, not hyperammonemia or acute neonatal crisis.
*Cystathionine synthase*
- A defect in **cystathionine synthase** leads to **homocystinuria**, an inherited disorder of methionine metabolism.
- Symptoms include **ectopia lentis**, **skeletal abnormalities**, **thromboembolic events**, and **developmental delay**, not acute neonatal hyperammonemic encephalopathy.
*Branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase*
- Deficiency in **branched-chain ketoacid dehydrogenase** causes **maple syrup urine disease (MSUD)**, a disorder of branched-chain amino acid metabolism.
- While it can present with vomiting, lethargy, and seizures in neonates, it is characterized by a distinctive **maple syrup odor** in urine and elevated branched-chain amino acids, not hyperammonemia and low BUN.
*Phenylalanine hydroxylase*
- A deficiency in **phenylalanine hydroxylase** causes **phenylketonuria (PKU)**, an amino acid metabolism disorder.
- PKU typically presents with intellectual disability, seizures, and a musty odor if untreated, but generally does not manifest as an acute neonatal crisis with hyperammonemia, as seen in urea cycle defects.
Amino acid transport disorders US Medical PG Question 3: An investigator studying epigenetic mechanisms isolates histone proteins, the structural motifs involved in DNA binding and regulation of transcription. The peptide bonds of histone proteins are hydrolyzed and one type of amino acid is isolated. At normal body pH, this amino acid has a net charge of +1 . The investigator performs titration of this amino acid and obtains the graph shown. The isolated amino acid is most likely which of the following?
- A. Proline
- B. Lysine (Correct Answer)
- C. Aspartate
- D. Serine
- E. Histidine
Amino acid transport disorders Explanation: ***Lysine***
- Histones are **positively charged** proteins rich in **basic amino acids** like lysine and arginine, which allows them to bind tightly to the negatively charged DNA.
- The titration curve shown with three distinct pKa values and a net charge of +1 at normal body pH (around 7.4) is characteristic of **lysine**, which has both an alpha-amino group (pKa ~9-10) and a basic side chain (pKa ~10.5).
*Proline*
- **Proline is a nonpolar** amino acid that does not contribute significantly to the positive charge of histones required for DNA binding.
- Furthermore, its unique cyclic structure incorporates its amino group into the ring, impacting its pKa relative to other primary amino acids but not making it a primary basic residue in the histone context.
*Aspartate*
- **Aspartate is an acidic amino acid** with a negatively charged side chain at physiological pH, which would repel DNA rather than bind to it.
- Its titration curve would show a net negative charge at normal body pH, not a positive one.
*Serine*
- **Serine is a polar, uncharged** amino acid and would not contribute the necessary positive charge for histone-DNA interaction.
- Its side chain lacks an ionizable group within the physiological pH range, so its titration curve would only show two pKa values (for the carboxyl and amino groups) and a net charge of 0 at neutral pH.
*Histidine*
- While **histidine is a basic amino acid**, its side chain pKa is around 6.0, meaning it is only partially protonated and positively charged at physiological pH.
- A protein rich in **histidine** would not consistently carry a strong positive charge across the typical physiological pH range as effectively as one rich in lysine or arginine.
Amino acid transport disorders US Medical PG Question 4: A 32-year-old man with hypertension and gout comes to the physician with left flank pain and bloody urine for two days. He does not smoke cigarettes but drinks two beers daily. Home medications include hydrochlorothiazide and ibuprofen as needed for pain. Physical examination shows left costovertebral angle tenderness. Urine dipstick is strongly positive for blood. Microscopic analysis of a stone found in the urine reveals a composition of magnesium ammonium phosphate. Which of the following is the strongest predisposing factor for this patient's condition?
- A. Uric acid precipitation
- B. Hereditary deficiency in amino acid reabsorption
- C. Use of vitamin C supplements
- D. Urinary tract infection (Correct Answer)
- E. Ethylene glycol ingestion
Amino acid transport disorders Explanation: ***Urinary tract infection***
- The presence of a **magnesium ammonium phosphate stone**, also known as a **struvite stone**, is highly indicative of a urinary tract infection (UTI). These stones are formed in the presence of **urease-producing bacteria** (e.g., *Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae*) that metabolize urea into ammonia, increasing localized pH and promoting crystal formation.
- While the patient has multiple predisposing factors for other types of kidney stones (e.g., gout and hydrochlorothiazide for calcium and uric acid stones), the specific composition of the stone points directly to an underlying infection as the primary predisposing factor.
*Uric acid precipitation*
- This typically leads to **uric acid stones**, which are common in patients with **gout** and **hyperuricemia**. The stone described is magnesium ammonium phosphate, not uric acid.
- Uric acid stones are usually radiolucent and are not directly associated with infection, unlike struvite stones.
*Hereditary deficiency in amino acid reabsorption*
- This condition, such as **cystinuria**, leads to the formation of **cystine stones**. These stones are hexagonal in shape and are caused by impaired tubular reabsorption of certain amino acids.
- The described stone composition is magnesium ammonium phosphate, not cystine.
*Use of vitamin C supplements*
- Excessive vitamin C (ascorbic acid) intake can be metabolized to **oxalate**, potentially contributing to **calcium oxalate stone** formation, especially in susceptible individuals.
- This patient's stone is a struvite stone, not a calcium oxalate stone.
*Ethylene glycol ingestion*
- Ethylene glycol poisoning is associated with the formation of **calcium oxalate monohydrate crystals** in the urine, which can lead to acute kidney injury and flank pain.
- The stone composition here is magnesium ammonium phosphate, indicating a different etiology.
Amino acid transport disorders US Medical PG Question 5: A 53-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of severe right-sided flank pain for 3 hours. The pain is colicky, radiates towards his right groin, and he describes it as 8/10 in intensity. He has vomited once. He has no history of similar episodes in the past. Last year, he was treated with naproxen for swelling and pain of his right toe. He has a history of hypertension. He drinks one to two beers on the weekends. Current medications include amlodipine. He appears uncomfortable. His temperature is 37.1°C (99.3°F), pulse is 101/min, and blood pressure is 130/90 mm Hg. Examination shows a soft, nontender abdomen and right costovertebral angle tenderness. An upright x-ray of the abdomen shows no abnormalities. A CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis shows a 7-mm stone in the proximal ureter and grade I hydronephrosis on the right. Which of the following is most likely to be seen on urinalysis?
- A. Urinary pH: 4.7 (Correct Answer)
- B. Positive nitrites test
- C. Hexagon shaped crystals
- D. Urinary pH: 7.3
- E. Largely positive urinary protein
Amino acid transport disorders Explanation: ***Urinary pH: 4.7***
- The patient's history of right toe pain and swelling treated with naproxen, despite no confirmed gout diagnosis, suggests a predisposition to **hyperuricemia** and uric acid stone formation.
- **Uric acid stones** are the only common kidney stone type that is radiolucent (explaining the normal X-ray) and characteristically form in acidic urine (pH < 5.5).
*Positive nitrites test*
- A positive nitrites test indicates the presence of **nitrate-reducing bacteria**, suggesting a **urinary tract infection (UTI)**.
- While UTIs can complicate kidney stones, the patient's presentation with acute, severe pain and no fever makes a primary UTI with positive nitrites less likely as the most prominent finding.
*Hexagon shaped crystals*
- **Hexagonal crystals** in urine are pathognomonic for **cystine stones**.
- Cystine stones are rare, inherited metabolic disorders, and there is nothing in this patient's history to suggest cystinuria.
*Urinary pH: 7.3*
- An alkaline urinary pH (e.g., 7.3) is typically associated with **struvite stones** (magnesium ammonium phosphate), which form in the presence of urease-producing bacteria (often causing UTIs), or sometimes with calcium phosphate stones.
- This is inconsistent with the patient's likely uric acid stone, which forms in acidic urine.
*Largely positive urinary protein*
- Significant proteinuria (largely positive urinary protein) usually indicates **glomerular or severe renal parenchymal disease**.
- While microscopic hematuria is common with kidney stones, gross proteinuria is not a typical finding in simple nephrolithiasis and implies a different underlying renal pathology.
Amino acid transport disorders US Medical PG Question 6: A 10-year-old boy is brought into your clinic by his mother for sunburns that have not been healing. The mother states that he easily gets sunburned. The mother admits she gave birth to him at home and has never taken him to see a doctor. The patient walks with a wide stance gait and appears unstable on his feet. He has an extensive erythematous, scaling, hyperkeratotic rash on his face, neck, arms and legs. After extensive workup, the patient is found to have a genetic disorder that results in defective absorption of an important vitamin. Which of the following is likely to be low if measured?
- A. Vitamin K
- B. Niacin (Correct Answer)
- C. Folate
- D. Vitamin A
- E. Vitamin B12
Amino acid transport disorders Explanation: ***Niacin***
- The constellation of **sunburns that don't heal**, a **wide-stanced unstable gait**, and an **erythematous, scaling, hyperkeratotic rash** (consistent with dermatitis) strongly suggests **pellagra**.
- Pellagra is caused by a deficiency of **niacin (Vitamin B3)**, which is characterized by the "3 Ds": **dermatitis**, **diarrhea**, and **dementia (or neurological symptoms like ataxia)**.
*Vitamin K*
- Deficiency typically leads to **bleeding disorders** due to impaired coagulation, which is not indicated by the patient's symptoms.
- While newborns often receive a **vitamin K shot**, his current symptoms are unrelated to its deficiency.
*Folate*
- Folate deficiency primarily causes **megaloblastic anemia** and can lead to **neural tube defects** in developing fetuses.
- It does not explain the characteristic dermatological and neurological symptoms described.
*Vitamin A*
- Vitamin A deficiency is known to cause **night blindness** and **xerophthalmia** (dry eyes), and impaired immune function.
- While it plays a role in skin health, the specific rash and gait abnormalities point away from primary vitamin A deficiency.
*Vitamin B12*
- Deficiency leads to **megaloblastic anemia** with **neurological symptoms** such as peripheral neuropathy, but the dermatological manifestations (scaling, hyperkeratotic rash) and unhealing sunburn are not typical.
- The gait could be linked to neurological symptoms, but the overall presentation is better explained by niacin deficiency.
Amino acid transport disorders US Medical PG Question 7: A 2-week-old boy presents to the emergency department because of unusual irritability and lethargy. The patient is admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit and minutes later develops metabolic encephalopathy. This progressed to a coma, followed by death before any laboratory tests are completed. The infant was born at home via vaginal delivery at 39 weeks' of gestation. His mother says that the symptoms started since the infant was 4-days-old, but since he only seemed ‘tired’, she decided not to seek medical attention. Further testing during autopsy shows hyperammonemia, low citrulline, and increased orotic acid. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase
- B. Propionyl-CoA carboxylase
- C. Homogentisic acid dioxygenase
- D. Ornithine transcarbamylase (Correct Answer)
- E. Cystathionine beta-synthase
Amino acid transport disorders Explanation: **Ornithine transcarbamylase**
- **Hyperammonemia**, **low citrulline**, and **increased orotic acid** are classic findings in **Ornithine Transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency**. OTC is an X-linked urea cycle disorder.
- The rapid progression to **metabolic encephalopathy** and death in a neonate with these laboratory findings is highly characteristic of severe OTC deficiency, often presenting in the first few days of life.
*Branched-chain alpha-ketoacid dehydrogenase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes **Maple Syrup Urine Disease**, characterized by elevated **branched-chain amino acids** and their corresponding ketoacids in blood and urine.
- While it can cause neurological symptoms, it does not typically present with the specific constellation of **hyperammonemia**, low citrulline, and high orotic acid.
*Propionyl-CoA carboxylase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme leads to **Propionic acidemia**, a type of organic acidemia, characterized by **propionic acid accumulation** and often **metabolic acidosis**, ketosis, and hyperammonemia.
- However, it would not typically cause **low citrulline** or isolated **elevated orotic acid** as seen in urea cycle disorders.
*Homogentisic acid dioxygenase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes **Alkaptonuria**, an inborn error of metabolism characterized by the accumulation of **homogentisic acid**.
- This condition is usually benign in infancy, with symptoms appearing later in life such as **dark urine** on standing and **ochronosis** (darkening of cartilage). It does not present with acute hyperammonemia or metabolic encephalopathy.
*Cystathionine beta-synthase*
- Deficiency of this enzyme causes **homocystinuria**, an inborn error of methionine metabolism, leading to elevated **homocysteine** and methionine.
- Clinical features include **ectopia lentis**, skeletal abnormalities, and intellectual disability, but not usually acute neonatal hyperammonemia or the specific findings of low citrulline and high orotic acid.
Amino acid transport disorders US Medical PG Question 8: A 55-year-old man with a history of repeated hospitalization for chronic pancreatitis comes to the physician because of difficulty walking and standing steadily. Neurological examination shows an unsteady, broad-based gait, distal muscle weakness, decreased deep tendon reflexes, and an abnormal Romberg test. His hemoglobin concentration is 11.9 g/dL, mean corpuscular volume is 89/μm3, and serum lactate dehydrogenase is 105 U/L. His serum haptoglobin is slightly decreased. A deficiency of which of the following substances is the most likely cause of this patient's findings?
- A. Niacin
- B. Folate
- C. Phytomenadione
- D. Tocopherol (Correct Answer)
- E. Pyridoxine
Amino acid transport disorders Explanation: ***Tocopherol***
- **Tocopherol (Vitamin E)** deficiency can cause neurological symptoms such as **ataxia**, **distal muscle weakness**, decreased deep tendon reflexes, and an **abnormal Romberg test** due to its role in nerve function and antioxidant properties.
- **Chronic pancreatitis** often leads to **fat malabsorption** as pancreatic enzymes are crucial for fat digestion, which impairs the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like Vitamin E.
*Niacin*
- **Niacin (Vitamin B3)** deficiency causes **pellagra**, characterized by the "3 Ds": **dermatitis**, **diarrhea**, and **dementia**, none of which are the primary presenting symptoms here.
- While neurological symptoms can occur in severe cases, the specific presentation of ataxia and peripheral neuropathy points away from pellagra.
*Folate*
- **Folate (Vitamin B9)** deficiency primarily causes **megaloblastic anemia** with an elevated **mean corpuscular volume (MCV)**, which is normal in this patient (MCV 89/μm3).
- While neurological symptoms can be present, they are less specific to folate deficiency compared to the classic presentation seen here.
*Phytomenadione*
- **Phytomenadione (Vitamin K)** deficiency leads to **coagulopathy** due to impaired synthesis of clotting factors, resulting in bleeding tendencies.
- It does not typically cause neurological symptoms like ataxia or peripheral neuropathy.
*Pyridoxine*
- **Pyridoxine (Vitamin B6)** deficiency can cause **peripheral neuropathy** and **ataxia**, but it's often associated with **sideroblastic anemia** or seizures.
- While some symptoms overlap, the strong history of chronic pancreatitis and fat malabsorption makes a fat-soluble vitamin deficiency more likely.
Amino acid transport disorders US Medical PG Question 9: A 23-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 2-month history of diarrhea, flatulence, and fatigue. She reports having 3–5 episodes of loose stools daily that have an oily appearance. The symptoms are worse after eating. She also complains of an itchy rash on her elbows and knees. A photograph of the rash is shown. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Elevated exhaled hydrogen concentration
- B. Microcytic, hypochromic red blood cells
- C. Elevated urine tryptophan levels
- D. PAS-positive intestinal macrophages
- E. HLA-DQ2 serotype (Correct Answer)
Amino acid transport disorders Explanation: ***HLA-DQ2 serotype***
- The patient's symptoms of **diarrhea, flatulence, fatigue, and oily stools** (steatorrhea) are highly suggestive of **malabsorption**. The itchy rash on the elbows and knees, known as **dermatitis herpetiformis**, is pathognomonic for **celiac disease**.
- **Celiac disease** is strongly associated with the **HLA-DQ2** (and less commonly HLA-DQ8) serotypes. Testing for these HLA alleles can help confirm genetic susceptibility to the condition.
*Elevated exhaled hydrogen concentration*
- An **elevated exhaled hydrogen concentration** is indicative of **small intestinal bacterial overgrowth (SIBO)** or **lactose intolerance**.
- While these can cause symptoms similar to malabsorption (diarrhea, flatulence), they do not typically present with **dermatitis herpetiformis**.
*Microcytic, hypochromic red blood cells*
- **Microcytic, hypochromic red blood cells** are characteristic of **iron deficiency anemia**, which commonly occurs in **celiac disease** due to malabsorption in the proximal small intestine (duodenum and jejunum).
- While iron deficiency can be seen in celiac disease, it is not specific to this condition and does not explain the pathognomonic **dermatitis herpetiformis** rash.
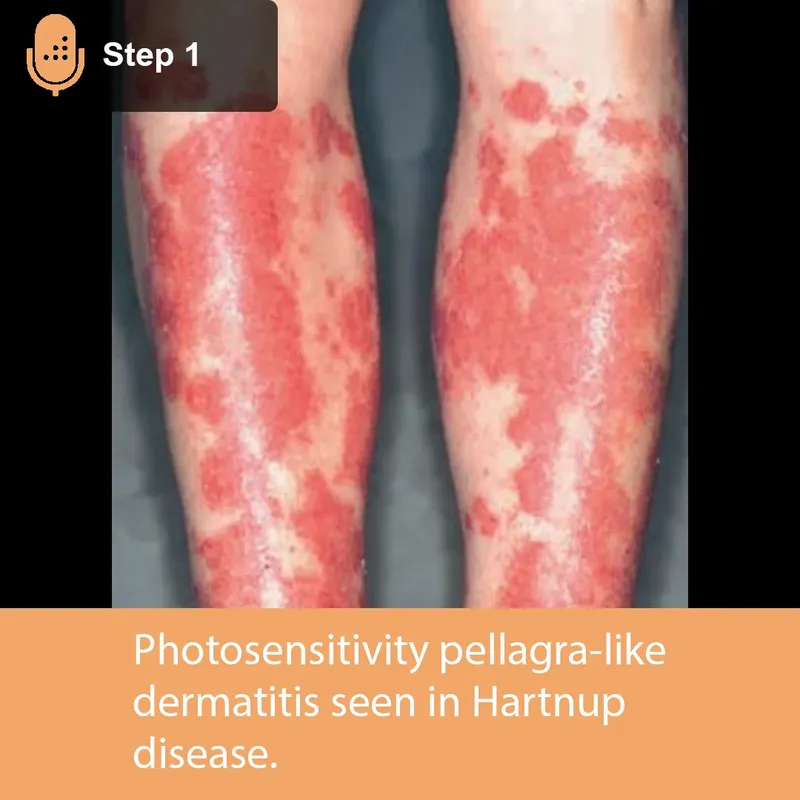
*Elevated urine tryptophan levels*
- **Elevated urine tryptophan levels** are associated with **Hartnup disease**, a rare inherited disorder affecting neutral amino acid transport.
- This finding is not directly related to the common manifestations of malabsorption or dermatitis herpetiformis seen in celiac disease.
*PAS-positive intestinal macrophages*
- **PAS-positive intestinal macrophages** are a characteristic histological finding in **Whipple's disease**, caused by the bacterium *Tropheryma whipplei*.
- While Whipple's disease can cause malabsorption, it is a much rarer condition and does not typically present with **dermatitis herpetiformis**.
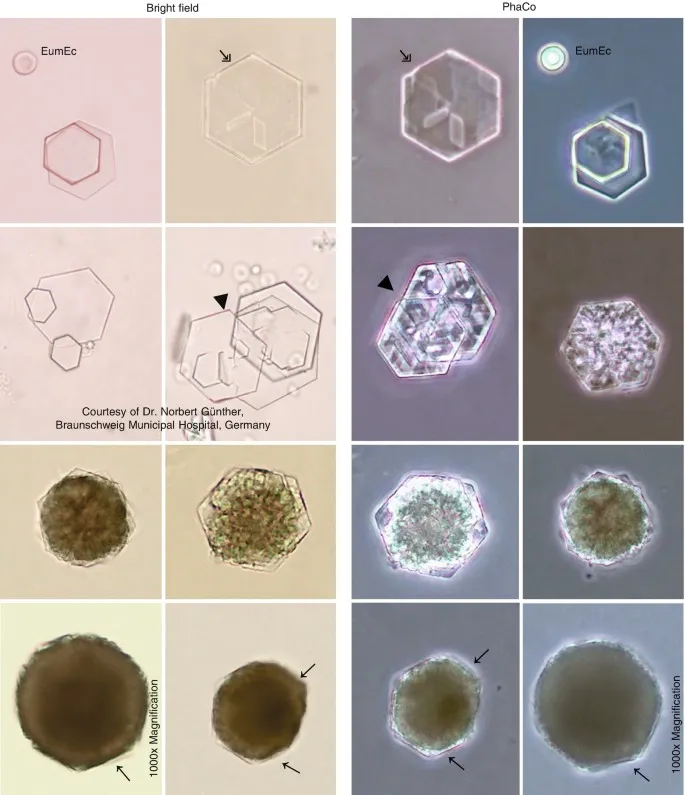
Amino acid transport disorders US Medical PG Question 10: A 21-year-old man presents to the emergency department with acute back pain. The pain began a few hours prior to presentation and is located on the left lower back. The pain is described to be “shock-like,” 9/10 in pain severity, and radiates to the left groin. His temperature is 98.6°F (37°C), blood pressure is 120/75 mmHg, pulse is 101/min, and respirations are 18/min. The patient appears uncomfortable and is mildly diaphoretic. There is costovertebral angle tenderness and genitourinary exam is unremarkable. A non-contrast computerized tomography (CT) scan of the abdomen and pelvis demonstrates an opaque lesion affecting the left ureter with mild hydronephrosis. Straining of the urine with urine crystal analysis is demonstrated. Which of the following amino acids is most likely poorly reabsorbed by this patient’s kidney?
- A. Isoleucine
- B. Aspartic acid
- C. Phenylalanine
- D. Lysine (Correct Answer)
- E. Histidine
Amino acid transport disorders Explanation:
***Lysine***
- The patient's symptoms (acute, severe, radiating back pain, CVA tenderness, hydronephrosis, and opaque lesion on CT) are highly characteristic of a **kidney stone**.
- Given the patient's young age and the nature of the amino acid question, thinking of **cystinuria** is appropriate, where the basic amino acids **COLA** (cystine, ornithine, lysine, arginine) are poorly reabsorbed.
*Isoleucine*
- **Isoleucine** is a branched-chain amino acid, not one of the basic amino acids impacted by cystinuria.
- Its malabsorption is not associated with the formation of kidney stones.
*Aspartic acid*
- **Aspartic acid** is an acidic amino acid and is not involved in the transport defects seen in cystinuria.
- There is no direct link between aspartic acid malabsorption and kidney stone formation.
*Phenylalanine*
- **Phenylalanine** is an aromatic amino acid and its metabolism is associated with disorders like phenylketonuria, not kidney stones.
- It is not one of the amino acids whose renal reabsorption is impaired in cystinuria.
*Histidine*
- **Histidine** is an essential amino acid, but it is not one of the basic amino acids (COLA) whose transport is affected in cystinuria.
- Poor reabsorption of histidine is not typically associated with kidney stone formation.
More Amino acid transport disorders US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.