Amino acid metabolism and disorders

On this page
🧬 The Amino Acid Universe: Metabolic Highways and Clinical Crossroads
Amino acids are far more than protein building blocks-they're metabolic hubs where energy production, neurotransmitter synthesis, and detoxification pathways converge, and when these pathways fail, the clinical consequences range from subtle developmental delays to life-threatening metabolic crises. You'll master how cells orchestrate nitrogen trafficking through transamination and deamination, recognize the distinctive clinical signatures of inherited disorders like phenylketonuria and maple syrup urine disease, and deploy evidence-based therapeutic protocols that can prevent irreversible neurological damage when minutes matter.
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Amino acid disorders affect 1 in 500 newborns, with 85% being treatable if diagnosed within the first 48 hours of life
The metabolic fate of amino acids follows four major pathways: protein synthesis (40% of dietary intake), gluconeogenesis (25%), ketogenesis (20%), and direct oxidation (15%). Each pathway requires specific cofactors, and deficiencies create predictable clinical patterns.
📌 Remember: PEST - Protein synthesis, Energy production, Specialized molecules (neurotransmitters), Transamination reactions define the four fates of amino acids
-
Protein Synthesis Pathway
- Requires all 20 amino acids simultaneously
- Rate-limited by essential amino acid availability
- mTOR pathway activation requires leucine >2.5 mM
- Muscle protein synthesis peaks at leucine 10-15g daily
- Timing: 30-minute window post-exercise optimal
-
Energy Production Routes
- Glucogenic amino acids → glucose via gluconeogenesis
- Ketogenic amino acids → acetyl-CoA and ketones
- Alanine-glucose cycle provides 10-15% of hepatic glucose
- Alanine 0.3-0.6 mM normal plasma concentration
- Increases 3-fold during prolonged fasting
💡 Master This: Every amino acid disorder creates a substrate accumulation pattern above the blocked enzyme and product deficiency below - this principle predicts 90% of clinical presentations
The clinical significance becomes apparent when considering that amino acid disorders can mimic psychiatric conditions, neurological diseases, or metabolic crises. Maple syrup urine disease presents with the sweet odor of sotolone at concentrations >50 μg/L, while phenylketonuria causes intellectual disability if phenylalanine exceeds 20 mg/dL (1200 μM) during brain development.
| Amino Acid Class | Primary Fate | Clinical Marker | Normal Range | Pathological Threshold | Key Enzyme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Branched-chain (Leu, Ile, Val) | Muscle energy | Plasma BCAA | 300-600 μM | >2000 μM | BCKDH |
| Aromatic (Phe, Tyr, Trp) | Neurotransmitters | Phenylalanine | 30-120 μM | >1200 μM | PAH |
| Sulfur (Met, Cys) | Methylation | Homocysteine | 5-15 μM | >100 μM | CBS |
| Basic (Arg, Lys, His) | Urea cycle | Ammonia | 10-35 μM | >150 μM | Multiple |
| Acidic (Asp, Glu) | Neurotransmission | Glutamate | 20-120 μM | >500 μM | GAD |
🧬 The Amino Acid Universe: Metabolic Highways and Clinical Crossroads
⚡ Metabolic Command Centers: Essential vs Non-Essential Architecture
📌 Remember: PVT TIM HALL - Phenylalanine, Valine, Threonine, Tryptophan, Isoleucine, Methionine, Histidine, Arginine, Leucine, Lysine (essential amino acids)
- Essential Amino Acids (9 total)
- Branched-chain: Leucine, Isoleucine, Valine
- Leucine 14mg/kg/day minimum requirement
- BCAA ratio 2:1:1 (Leu:Ile:Val) optimal for protein synthesis
- Aromatic: Phenylalanine, Tryptophan
- Phenylalanine 14mg/kg/day (includes tyrosine conversion)
- Tryptophan 4mg/kg/day (rate-limiting for serotonin)
- Sulfur-containing: Methionine
- Methionine 13mg/kg/day (includes cysteine synthesis)
- SAM regeneration requires folate and B12 cofactors
- Branched-chain: Leucine, Isoleucine, Valine
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Kwashiorkor develops when essential amino acid intake falls below 70% of requirements, even with adequate calories - explains the protein-energy malnutrition paradox
The conditionally essential amino acids become dietary requirements during stress, growth, or disease. Arginine becomes essential during wound healing, requiring 6-20g daily for optimal immune function. Glutamine becomes essential during critical illness, with plasma levels dropping 50% within 24 hours of major surgery.
- Non-Essential Amino Acid Synthesis
- From glucose: Alanine, Serine, Glycine
- Serine synthesis requires 3-phosphoglycerate from glycolysis
- Glycine cleavage provides one-carbon units for folate metabolism
- From TCA intermediates: Aspartate, Asparagine, Glutamate, Glutamine
- Glutamine synthetase consumes 1 ATP per molecule
- Glutamine 500-750 μM normal plasma concentration
- From other amino acids: Tyrosine (from Phe), Cysteine (from Met)
- Tyrosine hydroxylase rate-limits catecholamine synthesis
- Cysteine synthesis requires serine and homocysteine
- From glucose: Alanine, Serine, Glycine
💡 Master This: Essential amino acid deficiency creates a negative nitrogen balance within 3-5 days, while non-essential deficiency can be compensated for weeks through endogenous synthesis
| Amino Acid | Classification | Daily Requirement | Synthesis Pathway | Clinical Deficiency | Plasma Normal Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leucine | Essential | 39 mg/kg | None | Muscle wasting | 120-200 μM |
| Arginine | Conditional | 6-20 g | From citrulline | Poor wound healing | 50-200 μM |
| Glutamine | Conditional | 5-15 g | From glutamate | Immune dysfunction | 500-750 μM |
| Alanine | Non-essential | Variable | From pyruvate | Rare | 300-600 μM |
| Tyrosine | Conditional | 14 mg/kg | From phenylalanine | Catecholamine deficiency | 45-125 μM |
⚡ Metabolic Command Centers: Essential vs Non-Essential Architecture
🔄 The Nitrogen Recycling Plant: Transamination and Deamination Mastery

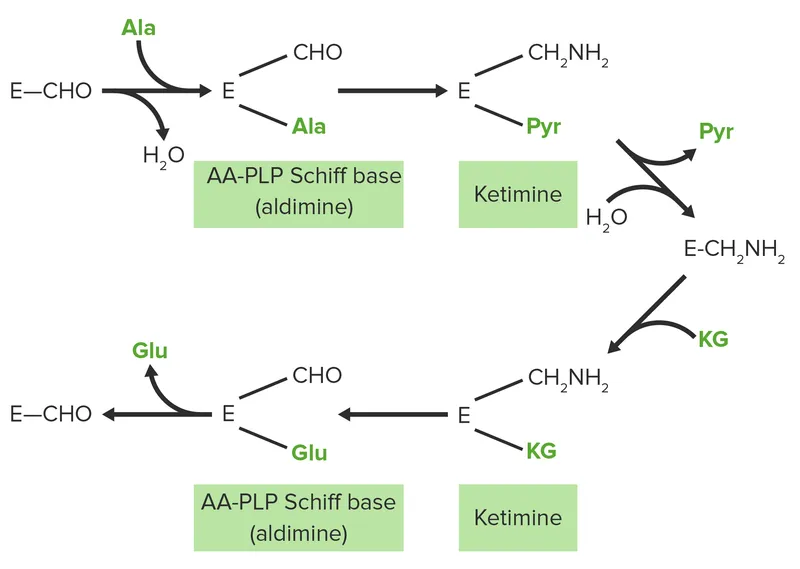
Transamination represents the body's most elegant recycling system, allowing interconversion of amino acids without losing nitrogen. Alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) serve as the primary nitrogen shuttles, with pyridoxal phosphate (PLP) as the essential cofactor.
📌 Remember: ALPHA - Alanine + α-ketoglutarate ↔ Pyruvate + Glutamate (ALT reaction), ASAP - ASpartate + α-ketoglutarate ↔ Oxaloacetate + Glutamate (AST reaction)
- Transamination Mechanism
- PLP-dependent Schiff base formation
- Vitamin B6 deficiency blocks all transamination
- PLP 5-50 μM required for optimal enzyme activity
- Reversible reactions maintain amino acid pools
- Glutamate serves as universal amino donor
- α-ketoglutarate accepts 85% of amino nitrogen
- Tissue-specific patterns
- ALT predominant in liver (hepatocyte marker)
- AST present in heart, liver, muscle, brain
- PLP-dependent Schiff base formation
⭐ Clinical Pearl: ALT:AST ratio >2 suggests hepatocellular injury, while AST:ALT ratio >2 indicates alcoholic liver disease or muscle damage - reflects tissue enzyme distribution patterns
The glucose-alanine cycle demonstrates transamination's physiological importance. Muscle protein breakdown generates alanine carrying nitrogen to liver, where transamination produces glutamate for urea synthesis and pyruvate for gluconeogenesis. This cycle provides 10-15% of hepatic glucose production during fasting.
- Deamination Pathways
- Oxidative deamination (glutamate dehydrogenase)
- Glutamate + NAD+ → α-ketoglutarate + NH4+ + NADH
- Allosteric regulation by ADP (activator) and GTP (inhibitor)
- Mitochondrial enzyme links amino acid and energy metabolism
- Non-oxidative deamination (amino acid oxidases)
- D-amino acid oxidase handles dietary D-amino acids
- Monoamine oxidase degrades neurotransmitter amino acids
- Histidase specifically deaminates histidine
- Oxidative deamination (glutamate dehydrogenase)
💡 Master This: Glutamate dehydrogenase serves as the metabolic switch - when energy is needed (high ADP), it promotes amino acid oxidation; when energy is abundant (high GTP), it favors amino acid synthesis
The clinical significance becomes apparent in liver disease, where impaired transamination leads to altered amino acid profiles. Branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) decrease while aromatic amino acids increase, creating the Fischer ratio (BCAA/AAA) that drops from normal 3.0-3.5 to <1.0 in hepatic encephalopathy.
| Enzyme | Tissue Distribution | Normal Range | Clinical Significance | Cofactor | Km Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ALT | Liver >> Heart, Muscle | 7-35 U/L | Hepatocellular injury | PLP | 15 mM (alanine) |
| AST | Heart, Liver, Muscle | 8-40 U/L | Tissue damage | PLP | 9 mM (aspartate) |
| GDH | Liver, Kidney, Brain | Not routinely measured | Hyperinsulinism | NAD+/NADP+ | 2 mM (glutamate) |
| BCAT | Muscle, Brain | Not routinely measured | BCAA metabolism | PLP | 5 mM (leucine) |
| Histidase | Liver, Skin | Not routinely measured | Histidinemia | None | 8 mM (histidine) |
🔄 The Nitrogen Recycling Plant: Transamination and Deamination Mastery
🎯 Pattern Recognition Arsenal: Clinical Amino Acid Signatures
📌 Remember: SCENT - Smell, Cognitive changes, Elevated substrates, Neurological signs, Timing of onset - the five-point framework for amino acid disorder recognition
- Aromatic Amino Acid Disorders
- Phenylketonuria (PKU)
- Phenylalanine >20 mg/dL (>1200 μM) diagnostic
- Musty odor from phenylacetic acid accumulation
- Intellectual disability if untreated by 6 months
- Hypopigmentation from tyrosine deficiency
- Alkaptonuria
- Homogentisic acid in urine turns black on standing
- Ochronosis - dark cartilage pigmentation
- Arthritis develops by age 30-40
- Phenylketonuria (PKU)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: PKU screening must occur after 24 hours of protein feeding - earlier testing yields 15% false negatives due to insufficient phenylalanine accumulation
- Branched-Chain Amino Acid Disorders
- Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)
- Sweet maple syrup odor from sotolone accumulation
- BCAA elevation: Leucine >1000 μM (normal 120-200 μM)
- Ketoacidosis and cerebral edema in severe forms
- Feeding difficulties and lethargy in neonates
- Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD)
- Sulfur Amino Acid Disorders
- Classical Homocystinuria
- Homocysteine >100 μM (normal 5-15 μM)
- Marfanoid habitus with lens dislocation
- Thromboembolism risk increased 50-fold
- Intellectual disability in 50% if untreated
- Cystinuria
- Cystine stones - hexagonal crystals in urine
- COLA amino acids elevated: Cystine, Ornithine, Lysine, Arginine
- Recurrent nephrolithiasis starting in childhood
- Classical Homocystinuria
💡 Master This: The "4 H's" of homocystinuria - Heart (thrombosis), Habitus (Marfanoid), Head (intellectual disability), High homocysteine - predict 90% of clinical presentations
The timing of presentation provides crucial diagnostic clues. Neonatal onset suggests severe enzyme deficiency, while later onset indicates partial enzyme activity or cofactor-responsive variants. MSUD presents within days of birth, PKU becomes apparent by months, and alkaptonuria may not manifest until adulthood.
| Disorder | Key Metabolite | Diagnostic Threshold | Clinical Triad | Age of Onset | Treatment Response |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PKU | Phenylalanine | >20 mg/dL | ID, seizures, eczema | 3-6 months | Diet 95% effective |
| MSUD | Leucine | >1000 μM | Odor, ketosis, encephalopathy | 4-7 days | Diet + thiamine |
| Homocystinuria | Homocysteine | >100 μM | Lens, thrombosis, ID | 6 months-years | B6 50% responsive |
| Alkaptonuria | HGA | Qualitative positive | Ochronosis, arthritis, stones | 20-40 years | Supportive only |
| Cystinuria | Cystine | >250 mg/g creatinine | Stones, crystals, pain | Childhood | Hydration + alkalinization |
🎯 Pattern Recognition Arsenal: Clinical Amino Acid Signatures
⚖️ Therapeutic Command Protocols: Evidence-Based Management Algorithms
📌 Remember: DIRECT - Dietary restriction, Increase cofactors, Reduce substrates, Emergency protocols, Cofactor trials, Transplant options - the six-pillar approach to amino acid disorder management
- Dietary Management Strategies
- Phenylalanine restriction (PKU)
- Target phenylalanine 2-6 mg/dL (120-360 μM)
- Medical foods provide other amino acids
- Sapropterin (synthetic BH4) reduces dietary restriction in 30%
- BCAA restriction (MSUD)
- Leucine target 2-5 mg/dL (150-380 μM)
- Isoleucine and valine must be supplemented
- Thiamine 10-20 mg/kg/day improves enzyme activity
- Phenylalanine restriction (PKU)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Protein tolerance in amino acid disorders correlates with residual enzyme activity - patients with >5% enzyme function typically tolerate 2-3x more dietary protein than those with <2% activity
- Cofactor Supplementation Protocols
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) for homocystinuria
- Trial dose: 100-500 mg/day for 4-6 weeks
- Response rate: 50% in classical homocystinuria
- Monitor homocysteine - target <50 μM
- Thiamine for MSUD
- Dose: 10-20 mg/kg/day (up to 500 mg/day)
- Response rate: 20% show significant improvement
- BCAA levels decrease 30-50% in responders
- Biotin for multiple carboxylase deficiency
- Dose: 10-40 mg/day
- Response: 100% in biotinidase deficiency
- Prevents seizures and developmental delay
- Vitamin B6 (Pyridoxine) for homocystinuria
💡 Master This: Cofactor responsiveness indicates missense mutations with residual enzyme activity - these patients have better prognosis and greater dietary flexibility than those with null mutations
- Emergency Management Protocols
- Acute decompensation (MSUD, methylmalonic acidemia)
- Stop protein intake immediately
- IV glucose 10-15 mg/kg/min to prevent catabolism
- Hemodialysis if leucine >1000 μM or ammonia >150 μM
- Insulin + glucose promotes anabolism
- Metabolic stroke prevention
- Homocysteine >100 μM requires immediate anticoagulation
- Aspirin 81 mg daily for thrombosis prevention
- Folate 5-15 mg/day supports remethylation
- Acute decompensation (MSUD, methylmalonic acidemia)
| Disorder | First-line Treatment | Cofactor Trial | Emergency Threshold | Long-term Monitoring | Outcome with Treatment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PKU | Phe-restricted diet | Sapropterin 20 mg/kg | Phe >20 mg/dL | Monthly Phe levels | Normal development 95% |
| MSUD | BCAA-restricted diet | Thiamine 20 mg/kg | Leucine >1000 μM | Weekly BCAA levels | Normal development 80% |
| Homocystinuria | Methionine restriction | B6 500 mg/day | Homocysteine >100 μM | Quarterly homocysteine | Prevents complications 90% |
| Methylmalonic acidemia | Protein restriction | B12 1 mg IM daily | MMA >1000 μM | Monthly MMA levels | Variable response 60% |
| Tyrosinemia I | Tyrosine restriction | NTBC 1-2 mg/kg | Succinylacetone positive | Monthly liver function | Prevents liver failure 95% |
⚖️ Therapeutic Command Protocols: Evidence-Based Management Algorithms
🔗 Systems Integration Matrix: Multi-Pathway Metabolic Networks
📌 Remember: NETWORK - Neurotransmitters, Energy pathways, Transamination, Waste elimination, One-carbon metabolism, Redox balance, Ketogenesis - the seven interconnected systems affected by amino acid disorders
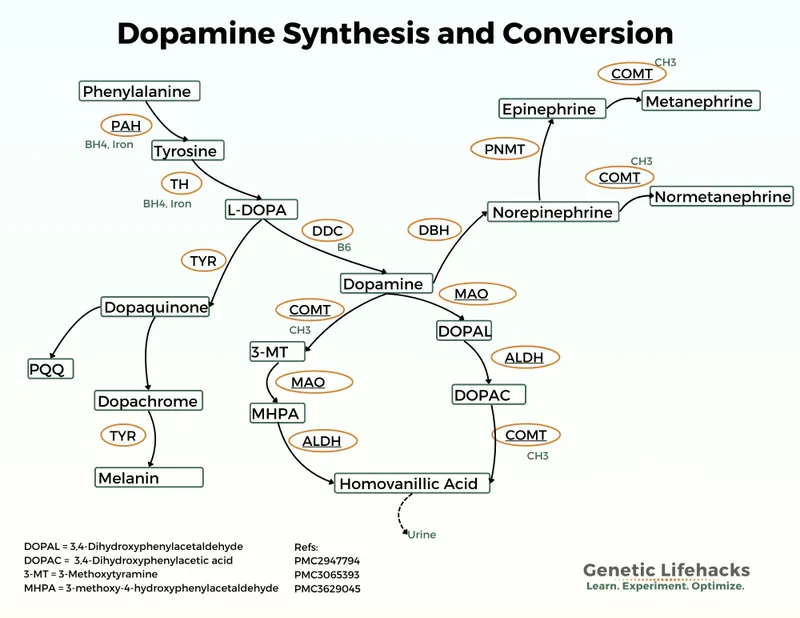
- Neurotransmitter Synthesis Integration
- Tyrosine → Dopamine → Norepinephrine → Epinephrine
- Tyrosine hydroxylase rate-limiting step
- PKU reduces tyrosine availability by 60-80%
- Dopamine deficiency explains movement disorders in untreated PKU
- Tryptophan → Serotonin → Melatonin
- Tryptophan 2,3-dioxygenase competes with serotonin synthesis
- Hartnup disease reduces tryptophan absorption by 90%
- Depression and sleep disorders common in tryptophan deficiency
- Histidine → Histamine
- Histidine decarboxylase requires PLP cofactor
- B6 deficiency impairs allergic responses and gastric acid production
- Tyrosine → Dopamine → Norepinephrine → Epinephrine
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Large neutral amino acid transporter (LAT1) competition explains why high phenylalanine blocks tyrosine and tryptophan brain uptake - phenylalanine >1200 μM reduces brain tyrosine by 70%
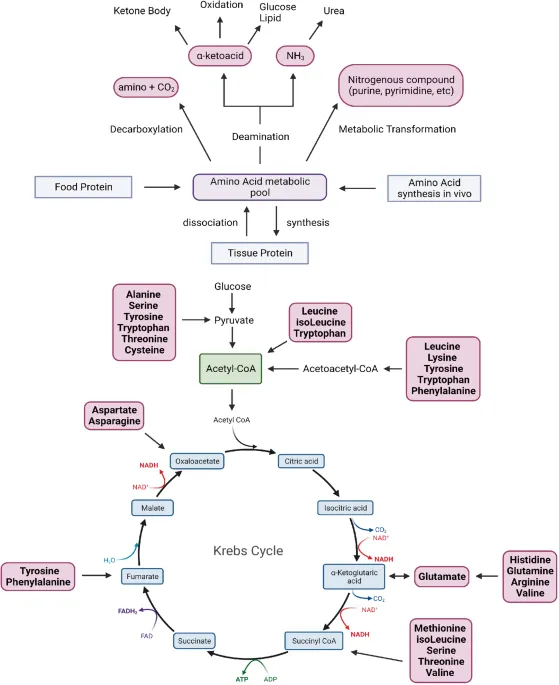
- Energy Metabolism Connections
- Glucogenic amino acids (18 of 20)
- Alanine provides 10-15% of hepatic glucose
- Glutamine serves as renal gluconeogenesis substrate
- Glycine and serine contribute 5-10% during fasting
- Ketogenic amino acids (leucine, lysine)
- Leucine stimulates mTOR and insulin secretion
- Ketogenic flux increases 3-fold during BCAA catabolism
- MSUD creates ketoacidosis from leucine accumulation
- TCA cycle integration
- Aspartate and glutamate link to oxaloacetate and α-ketoglutarate
- Amino acid oxidation provides 15-20% of ATP during fasting
- Branched-chain amino acids bypass liver metabolism - direct muscle oxidation
- Glucogenic amino acids (18 of 20)
💡 Master This: Amino acid disorders create secondary deficiencies in downstream pathways - PKU causes tyrosine deficiency, MSUD causes alanine excess, homocystinuria causes cysteine deficiency
- One-Carbon Metabolism Integration
- Methionine cycle connections
- Methionine → SAM → homocysteine → methionine (remethylation)
- Folate and B12 required for homocysteine remethylation
- Betaine provides alternative remethylation pathway
- Glycine cleavage system
- Glycine → CO2 + NH3 + one-carbon unit
- Nonketotic hyperglycinemia from glycine cleavage defects
- Seizures from glycine acting as NMDA agonist
- Serine synthesis pathway
- 3-phosphoglycerate → serine → glycine + one-carbon
- Serine deficiency causes microcephaly and seizures
- Folate deficiency mimics serine synthesis defects
- Methionine cycle connections
| Integration System | Key Amino Acids | Clinical Manifestation | Biochemical Marker | Treatment Approach | Success Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neurotransmitter | Phe, Tyr, Trp | Movement disorders, depression | Neurotransmitter metabolites | Precursor supplementation | 70-80% |
| Energy metabolism | BCAA, Ala, Gln | Hypoglycemia, ketosis | Glucose, ketones | Glucose support | 90-95% |
| One-carbon | Met, Gly, Ser | Neural tube defects, seizures | Homocysteine, folate | Folate, B12, betaine | 80-90% |
| Urea cycle | Arg, Orn, Cit | Hyperammonemia | Ammonia, orotic acid | Nitrogen scavengers | 85-90% |
| Antioxidant | Cys, Met, Gly | Oxidative stress | Glutathione | Antioxidant support | 60-70% |
🔗 Systems Integration Matrix: Multi-Pathway Metabolic Networks
🎯 Clinical Mastery Toolkit: Rapid Assessment and Decision Frameworks
📌 Remember: RAPID-AA - Recognize patterns, Assess severity, Prevent complications, Initiate treatment, Determine cofactor response, Arrange long-term care - the six-step emergency approach to amino acid disorders
- Emergency Recognition Framework
- "SCENT" Assessment (30-second evaluation)
- Smell: Maple syrup (MSUD), musty (PKU), sweaty feet (isovaleric acidemia)
- Cognitive: Lethargy, seizures, developmental delay
- Elevated substrates: Specific amino acids >10x normal
- Neurological: Hypotonia, movement disorders, encephalopathy
- Timing: Neonatal vs. later onset patterns
- Critical Thresholds (immediate action required)
- Phenylalanine >30 mg/dL (>1800 μM)
- Leucine >1000 μM with ketosis
- Ammonia >150 μM with amino acid elevation
- Homocysteine >100 μM with thrombotic risk
- "SCENT" Assessment (30-second evaluation)
⭐ Clinical Pearl: "Rule of 10s" - amino acid disorders typically show >10x elevation of specific substrates, <10% normal enzyme activity, and >10-fold increased risk of complications if untreated
- Rapid Diagnostic Arsenal
- Bedside Tests (results in minutes)
- Urine odor assessment - sotolone (maple syrup), phenylacetic acid (musty)
- Ketone strips - positive in MSUD, methylmalonic acidemia
- Ferric chloride test - green color with PKU
- Laboratory Priorities (results in hours)
- Quantitative amino acids - plasma and urine
- Acylcarnitine profile - identifies organic acidemias
- Urine organic acids - confirms specific disorders
- Confirmatory Studies (results in days-weeks)
- Enzyme activity assays in fibroblasts
- Molecular genetic testing
- Cofactor responsiveness trials
- Bedside Tests (results in minutes)
💡 Master This: Time-sensitive interventions - MSUD requires treatment within 24 hours, PKU within weeks, homocystinuria within months - the window for preventing irreversible damage varies 1000-fold between disorders
| Clinical Scenario | Key Features | Immediate Action | Diagnostic Test | Treatment Priority | Time Window |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neonatal encephalopathy + odor | MSUD | Stop protein, IV glucose | Plasma leucine | Hemodialysis if >1000 μM | 24-48 hours |
| Developmental delay + seizures | PKU | Dietary restriction | Plasma phenylalanine | Phe-restricted diet | 2-6 months |
| Lens dislocation + thrombosis | Homocystinuria | Anticoagulation | Plasma homocysteine | B6 trial + diet | 6-12 months |
| Recurrent kidney stones | Cystinuria | Hydration + alkalinization | Urine amino acids | High fluid intake | Ongoing |
| Dark urine + arthritis | Alkaptonuria | Supportive care | Urine HGA | Symptom management | Lifelong |
- Severity Assessment (guides intervention intensity)
- Mild: Substrate 2-5x normal, normal development
- Moderate: Substrate 5-10x normal, mild symptoms
- Severe: Substrate >10x normal, acute decompensation
- Cofactor Responsiveness (determines dietary flexibility)
- Responsive: >50% reduction in substrate with cofactor
- Partial: 25-50% reduction - combination therapy
- Non-responsive: <25% reduction - strict dietary control
- Long-term Monitoring (prevents complications)
- Monthly monitoring during first year
- Quarterly monitoring for stable patients
- Emergency protocols for illness or pregnancy
The mastery toolkit transforms complex biochemical knowledge into actionable clinical protocols, enabling rapid recognition and appropriate management of amino acid disorders across all healthcare settings.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Toolkit: Rapid Assessment and Decision Frameworks
Practice Questions: Amino acid metabolism and disorders
Test your understanding with these related questions
An 8-day-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother because of vomiting and poor feeding. The pregnancy was uncomplicated, and he was born at full term. He appears pale and lethargic. Physical examination shows diffusely increased muscle tone. His urine is noted to have a sweet odor. This patient's symptoms are most likely caused by the accumulation of which of the following?











