Confounding variables US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Confounding variables. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Confounding variables US Medical PG Question 1: A 25-year-old man with a genetic disorder presents for genetic counseling because he is concerned about the risk that any children he has will have the same disease as himself. Specifically, since childhood he has had difficulty breathing requiring bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and chest physiotherapy. He has also had diarrhea and malabsorption requiring enzyme replacement therapy. If his wife comes from a population where 1 in 10,000 people are affected by this same disorder, which of the following best represents the likelihood a child would be affected as well?
- A. 0.01%
- B. 2%
- C. 0.5%
- D. 1% (Correct Answer)
- E. 50%
Confounding variables Explanation: ***Correct Option: 1%***
- The patient's symptoms (difficulty breathing requiring bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and chest physiotherapy; diarrhea and malabsorption requiring enzyme replacement therapy) are classic for **cystic fibrosis (CF)**, an **autosomal recessive disorder**.
- For an autosomal recessive disorder with a prevalence of 1 in 10,000 in the general population, **q² = 1/10,000**, so **q = 1/100 = 0.01**. The carrier frequency **(2pq)** is approximately **2q = 2 × (1/100) = 1/50 = 0.02**.
- The affected man is **homozygous recessive (aa)** and will always pass on the recessive allele. His wife has a **1/50 chance of being a carrier (Aa)**. If she is a carrier, she has a **1/2 chance of passing on the recessive allele**.
- Therefore, the probability of an affected child = **(Probability wife is a carrier) × (Probability wife passes recessive allele) = 1/50 × 1/2 = 1/100 = 1%**.
*Incorrect Option: 0.01%*
- This percentage is too low and does not correctly account for the carrier frequency in the population and the probability of transmission from a carrier mother.
*Incorrect Option: 2%*
- This represents approximately the carrier frequency (1/50 ≈ 2%), but does not account for the additional 1/2 probability that a carrier mother would pass on the recessive allele.
*Incorrect Option: 0.5%*
- This value would be correct if the carrier frequency were 1/100 instead of 1/50, which does not match the given population prevalence.
*Incorrect Option: 50%*
- **50%** would be the risk if both parents were carriers of an autosomal recessive disorder (1/4 chance = 25% for affected, but if we know one parent passes the allele, conditional probability changes). More accurately, 50% would apply if the disorder were **autosomal dominant** with one affected parent, which is not the case here.
Confounding variables US Medical PG Question 2: A researcher is trying to determine whether a newly discovered substance X can be useful in promoting wound healing after surgery. She conducts this study by enrolling the next 100 patients that will be undergoing this surgery and separating them into 2 groups. She decides which patient will be in which group by using a random number generator. Subsequently, she prepares 1 set of syringes with the novel substance X and 1 set of syringes with a saline control. Both of these sets of syringes are unlabeled and the substances inside cannot be distinguished. She gives the surgeon performing the surgery 1 of the syringes and does not inform him nor the patient which syringe was used. After the study is complete, she analyzes all the data that was collected and performs statistical analysis. This study most likely provides which level of evidence for use of substance X?
- A. Level 3
- B. Level 1 (Correct Answer)
- C. Level 4
- D. Level 5
- E. Level 2
Confounding variables Explanation: ***Level 1***
- The study design described is a **randomized controlled trial (RCT)**, which is considered the **highest level of evidence (Level 1)** in the hierarchy of medical evidence.
- Key features like **randomization**, **control group**, and **blinding (double-blind)** help minimize bias and strengthen the validity of the findings.
*Level 2*
- Level 2 evidence typically comprises **well-designed controlled trials without randomization** (non-randomized controlled trials) or **high-quality cohort studies**.
- While strong, they do not possess the same level of internal validity as randomized controlled trials.
*Level 3*
- Level 3 evidence typically includes **case-control studies** or **cohort studies**, which are observational designs and carry a higher risk of bias compared to RCTs.
- These studies generally do not involve randomization or intervention assignment by the researchers.
*Level 4*
- Level 4 evidence is usually derived from **case series** or **poor quality cohort and case-control studies**.
- These studies provide descriptive information or investigate associations without strong control for confounding factors.
*Level 5*
- Level 5 evidence is the **lowest level of evidence**, consisting of **expert opinion** or **animal research/bench research**.
- This level lacks human clinical data or systematic investigative rigor needed for higher evidence levels.
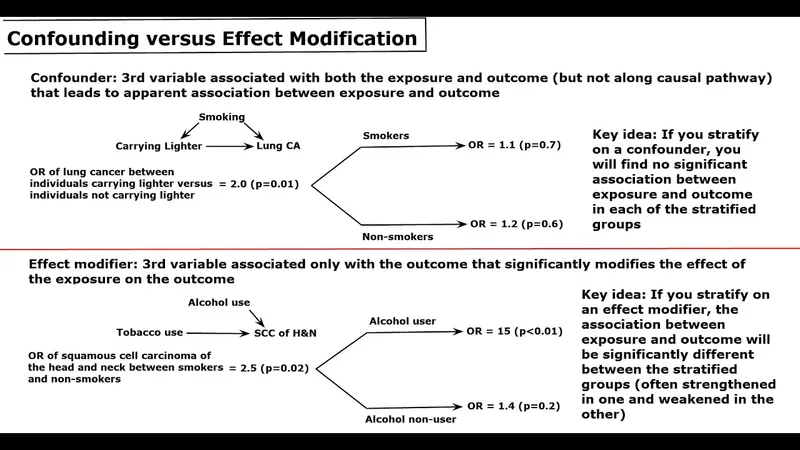
Confounding variables US Medical PG Question 3: A vaccination campaign designed to increase the uptake of HPV vaccine was instituted in chosen counties of a certain state in order to educate parents not only about the disease itself, but also about why children should be vaccinated against this viral sexually transmitted disease. At the end of the campaign, children living in counties in which it was conducted were 3 times more likely to receive the HPV vaccine compared with children living in counties where no campaign was instituted. As well, after evaluating only the counties that were part of the vaccination campaign, the researchers found that families with higher incomes were 2 times more likely to vaccinate their children against HPV compared with families with lower incomes. What conclusion can be drawn from these results?
- A. Family income appears to be an effect modifier. (Correct Answer)
- B. The vaccination campaign appears to have been ineffective.
- C. The vaccination campaign is the study outcome.
- D. The vaccine uptake is the study exposure.
- E. Family income appears to be a confounder.
Confounding variables Explanation: ***Family income appears to be an effect modifier.***
- An **effect modifier** occurs when the relationship between an exposure (vaccination campaign) and an outcome (vaccine uptake) differs across categories of a third variable (family income).
- Here, the campaign's effect on vaccine uptake is *different* depending on family income (higher-income families were still more likely to vaccinate even within campaign counties), indicating **effect modification**.
*The vaccination campaign appears to have been ineffective.*
- The campaign actually led to a **3-fold increase** in HPV vaccine uptake in campaign counties compared to non-campaign counties, demonstrating its effectiveness in increasing overall uptake.
- While income still played a role, the campaign itself achieved its primary goal of increasing vaccination rates where implemented.
*The vaccination campaign is the study outcome.*
- The **vaccination campaign** is the **exposure** or intervention being studied, as its impact on vaccination rates is being assessed.
- The **outcome** is the **HPV vaccine uptake** (i.e., whether children received the vaccine or not).
*The vaccine uptake is the study exposure.*
- **Vaccine uptake** is the **outcome** or the dependent variable that is being measured, to see if it changes in response to the campaign.
- The **exposure** is the **vaccination campaign** itself, or living in a county with a campaign.
*Family income appears to be a confounder.*
- A **confounder** is a variable that is associated with both the exposure and the outcome, and *distorts* the observed association between them.
- While family income is associated with vaccine uptake, its main role here is to show *how* the campaign's effect varied by income, not necessarily to create a spurious association between the campaign and uptake where none existed. If it were a confounder, it would need to be associated with both the campaign (which it isn't, as campaigns were in specific counties regardless of income distribution) and the outcome, and not be on the causal pathway.
Confounding variables US Medical PG Question 4: You are reading through a recent article that reports significant decreases in all-cause mortality for patients with malignant melanoma following treatment with a novel biological infusion. Which of the following choices refers to the probability that a study will find a statistically significant difference when one truly does exist?
- A. Type II error
- B. Type I error
- C. Confidence interval
- D. p-value
- E. Power (Correct Answer)
Confounding variables Explanation: ***Power***
- **Power** is the probability that a study will correctly reject the null hypothesis when it is, in fact, false (i.e., will find a statistically significant difference when one truly exists).
- A study with high power minimizes the risk of a **Type II error** (failing to detect a real effect).
*Type II error*
- A **Type II error** (or **beta error**) occurs when a study fails to reject a false null hypothesis, meaning it concludes there is no significant difference when one actually exists.
- This is the **opposite** of what the question describes, which asks for the probability of *finding* a difference.
*Type I error*
- A **Type I error** (or **alpha error**) occurs when a study incorrectly rejects a true null hypothesis, concluding there is a significant difference when one does not actually exist.
- This relates to the **p-value** and the level of statistical significance (e.g., p < 0.05).
*Confidence interval*
- A **confidence interval** provides a range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to lie with a certain degree of confidence (e.g., 95%).
- It does not directly represent the probability of finding a statistically significant difference when one truly exists.
*p-value*
- The **p-value** is the probability of observing data as extreme as, or more extreme than, that obtained in the study, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
- It is used to determine statistical significance, but it is not the probability of detecting a true effect.
Confounding variables US Medical PG Question 5: Study X examined the relationship between coffee consumption and lung cancer. The authors of Study X retrospectively reviewed patients' reported coffee consumption and found that drinking greater than 6 cups of coffee per day was associated with an increased risk of developing lung cancer. However, Study X was criticized by the authors of Study Y. Study Y showed that increased coffee consumption was associated with smoking. What type of bias affected Study X, and what study design is geared to reduce the chance of that bias?
- A. Observer bias; double blind analysis
- B. Selection bias; randomization
- C. Lead time bias; placebo
- D. Measurement bias; blinding
- E. Confounding; randomization (Correct Answer)
Confounding variables Explanation: ***Confounding; randomization***
- Study Y suggests that **smoking** is a **confounding variable** because it is associated with both increased coffee consumption (exposure) and increased risk of lung cancer (outcome), distorting the apparent relationship between coffee and lung cancer.
- **Randomization** in experimental studies (such as randomized controlled trials) helps reduce confounding by ensuring that known and unknown confounding factors are evenly distributed among study groups.
- In observational studies where randomization is not possible, confounding can be addressed through **stratification**, **matching**, or **multivariable adjustment** during analysis.
*Observer bias; double blind analysis*
- **Observer bias** occurs when researchers' beliefs or expectations influence the study outcome, which is not the primary issue described here regarding the relationship between coffee, smoking, and lung cancer.
- **Double-blind analysis** is a method to mitigate observer bias by ensuring neither participants nor researchers know who is in the control or experimental groups.
*Selection bias; randomization*
- **Selection bias** happens when the study population is not representative of the target population, leading to inaccurate results, which is not directly indicated by the interaction between coffee and smoking.
- While **randomization** is used to reduce selection bias by creating comparable groups, the core problem identified in Study X is confounding, not flawed participant selection.
*Lead time bias; placebo*
- **Lead time bias** occurs in screening programs when early detection without improved outcomes makes survival appear longer, an issue unrelated to the described association between coffee, smoking, and lung cancer.
- A **placebo** is an inactive treatment used in clinical trials to control for psychological effects, and its relevance here is limited to treatment intervention studies.
*Measurement bias; blinding*
- **Measurement bias** arises from systematic errors in data collection, such as inaccurate patient reporting of coffee consumption, but the main criticism from Study Y points to a third variable (smoking) affecting the association, not just flawed measurement.
- **Blinding** helps reduce measurement bias by preventing participants or researchers from knowing group assignments, thus minimizing conscious or unconscious influences on data collection.
Confounding variables US Medical PG Question 6: A physician attempts to study cirrhosis in his state. Using a registry of admitted patients over the last 10 years at the local hospital, he isolates all patients who have been diagnosed with cirrhosis. Subsequently, he contacts this group of patients, asking them to complete a survey assessing their prior exposure to alcohol use, intravenous drug abuse, blood transfusions, personal history of cancer, and other medical comorbidities. An identical survey is given to an equal number of patients in the registry who do not carry a prior diagnosis of cirrhosis. Which of the following is the study design utilized by this physician?
- A. Randomized controlled trial
- B. Case-control study (Correct Answer)
- C. Cross-sectional study
- D. Cohort study
- E. Meta-analysis
Confounding variables Explanation: ***Case-control study***
- This study design **identifies subjects based on their outcome (cases with cirrhosis, controls without cirrhosis)** and then retrospectively investigates their past exposures.
- The physician selected patients with cirrhosis (cases) and patients without cirrhosis (controls), then assessed their prior exposures to risk factors like alcohol use and intravenous drug abuse.
*Randomized controlled trial*
- This design involves randomly assigning participants to an **intervention group** or a **control group** to assess the effect of an intervention.
- There is no intervention being tested or randomization occurring in this study; it is observational.
*Cross-sectional study*
- A cross-sectional study measures the **prevalence of disease and exposure at a single point in time** in a defined population.
- This study collects retrospective exposure data and compares two distinct groups (cases and controls), rather than assessing prevalence at one time point.
*Cohort study*
- A cohort study **follows a group of individuals over time** to see if their exposure to a risk factor is associated with the development of a disease.
- This study starts with the outcome (cirrhosis) and looks backward at exposures, which is the opposite direction of a cohort study.
*Meta-analysis*
- A meta-analysis is a statistical method that **combines the results of multiple independent studies** to produce a single, more powerful estimate of treatment effect or association.
- This is an original research study collecting new data, not a systematic review or synthesis of existing studies.
Confounding variables US Medical PG Question 7: A group of environmental health scientists recently performed a nationwide cross-sectional study that investigated the risk of head and neck cancers in patients with a history of cigar and pipe smoking. In collaboration with three teams of epidemiologists that have each conducted similar cross-sectional studies in their respective countries, they have agreed to contribute their data to an international pooled analysis of the relationship between non-cigarette tobacco consumption and prevalence of head and neck cancers. Which of the following statements regarding the pooled analysis in comparison to the individual studies is true?
- A. The results are less precise.
- B. It overcomes limitations in the quality of individual studies.
- C. It is able to provide evidence of causality.
- D. The level of clinical evidence is lower.
- E. The likelihood of type II errors is decreased. (Correct Answer)
Confounding variables Explanation: ***The likelihood of type II errors is decreased.***
- A pooled analysis or **meta-analysis** combines data from multiple studies, significantly increasing the **overall sample size**.
- A larger sample size enhances the statistical power, making it less likely to miss a real effect and thus reducing the probability of **Type II errors** (false negatives).
*The results are less precise.*
- Combining data from multiple studies in a **pooled analysis** generally leads to **more precise estimates** due to the larger sample size and increased statistical power.
- Increased precision is reflected in narrower confidence intervals, offering a more reliable estimate of the effect.
*It overcomes limitations in the quality of individual studies.*
- A pooled analysis **does not inherently overcome limitations** in the design, methodology, or quality of the individual studies included.
- If the original studies have significant biases or flaws, these limitations can be propagated or even amplified in the pooled results.
*It is able to provide evidence of causality.*
- Pooled analyses of **cross-sectional studies**, like the ones described, can identify **associations** but cannot establish **causality**.
- Cross-sectional studies measure exposure and outcome simultaneously, making it impossible to determine the temporal sequence necessary to infer cause and effect.
*The level of clinical evidence is lower.*
- Combining multiple studies, especially well-conducted ones, in a pooled analysis or **meta-analysis** generally **increases the level of clinical evidence**, placing it higher than individual observational studies.
- This is because a pooled analysis offers a more robust and comprehensive view of the existing evidence.
Confounding variables US Medical PG Question 8: You are currently employed as a clinical researcher working on clinical trials of a new drug to be used for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Currently, you have already determined the safe clinical dose of the drug in a healthy patient. You are in the phase of drug development where the drug is studied in patients with the target disease to determine its efficacy. Which of the following phases is this new drug currently in?
- A. Phase 4
- B. Phase 1
- C. Phase 2 (Correct Answer)
- D. Phase 0
- E. Phase 3
Confounding variables Explanation: ***Phase 2***
- **Phase 2 trials** involve studying the drug in patients with the target disease to assess its **efficacy** and further evaluate safety, typically involving a few hundred patients.
- The question describes a stage after safe dosing in healthy patients (Phase 1) and before large-scale efficacy confirmation (Phase 3), focusing on efficacy in the target population.
*Phase 4*
- **Phase 4 trials** occur **after a drug has been approved** and marketed, monitoring long-term effects, optimal use, and rare side effects in a diverse patient population.
- This phase is conducted post-market approval, whereas the question describes a drug still in development prior to approval.
*Phase 1*
- **Phase 1 trials** primarily focus on determining the **safety and dosage** of a new drug in a **small group of healthy volunteers** (or sometimes patients with advanced disease if the drug is highly toxic).
- The question states that the safe clinical dose in a healthy patient has already been determined, indicating that Phase 1 has been completed.
*Phase 0*
- **Phase 0 trials** are exploratory, very early-stage studies designed to confirm that the drug reaches the target and acts as intended, typically involving a very small number of doses and participants.
- These trials are conducted much earlier in the development process, preceding the determination of safe clinical doses and large-scale efficacy studies.
*Phase 3*
- **Phase 3 trials** are large-scale studies involving hundreds to thousands of patients to confirm **efficacy**, monitor side effects, compare it to commonly used treatments, and collect information that will allow the drug to be used safely.
- While Phase 3 does assess efficacy, it follows Phase 2 and is typically conducted on a much larger scale before submitting for regulatory approval.
Confounding variables US Medical PG Question 9: A scientist is designing a study to determine whether eating a new diet is able to lower blood pressure in a group of patients. In particular, he believes that starting the diet may help decrease peak blood pressures throughout the day. Therefore, he will equip study participants with blood pressure monitors and follow pressure trends over a 24-hour period. He decides that after recruiting subjects, he will start them on either the new diet or a control diet and follow them for 1 month. After this time, he will switch patients onto the other diet and follow them for an additional month. He will analyze the results from the first month against the results from the second month for each patient. This type of study design is best at controlling for which of the following problems with studies?
- A. Hawthorne effect
- B. Recall bias
- C. Confounding (Correct Answer)
- D. Selection bias
- E. Pygmalion effect
Confounding variables Explanation: ***Confounding***
- This **crossover design** (switching patients to the other diet) effectively controls for **confounding variables** by making each patient their own control, ensuring that inherent patient characteristics do not bias the comparison between diets.
- By comparing the effects of both diets within the same individual, individual variability in factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and other co-morbidities are accounted for, reducing their potential as confounders.
*Hawthorne effect*
- The **Hawthorne effect** refers to subjects modifying their behavior in response to being observed, which this study design does not specifically address or eliminate.
- While patients are being monitored, the design aims to compare the diets' effects, not to prevent behavioral changes due to observation itself.
*Recall bias*
- **Recall bias** occurs when participants' memories of past events are inaccurate, often influenced by their current health status or beliefs.
- This study measures **real-time blood pressure** data, not relying on recollection of past exposures or outcomes, thereby mitigating recall bias.
*Selection bias*
- **Selection bias** arises from non-random selection of participants into study groups, leading to systematic differences between groups.
- While patient recruitment could introduce selection bias into the overall study population, the **crossover design** itself helps control for differences between treatment arms because all participants eventually receive both treatments.
*Pygmalion effect*
- The **Pygmalion effect** (or observer-expectancy effect) describes phenomena where higher expectations lead to increased performance, usually from a researcher influencing a subject.
- This effect is not directly addressed by the crossover design; the design focuses on controlling for patient-specific confounders rather than investigator bias in expectations.
Confounding variables US Medical PG Question 10: A 73-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after being found to be non-communicative by his family during dinner. On presentation he appears to be alert, though he is confused and cannot follow instructions. When he tries to speak, he vocalizes a string of fluent but unintelligible syllables. Given this presentation, his physician decides to administer tissue plasminogen activator to this patient. This intervention best represents which of the following principles?
- A. Tertiary prevention
- B. Primary prevention
- C. This does not represent prevention (Correct Answer)
- D. Quaternary prevention
- E. Secondary prevention
Confounding variables Explanation: ***This does not represent prevention***
- The administration of **tissue plasminogen activator (tPA)** during an **acute stroke** is a **therapeutic intervention**, not a form of prevention.
- **Prevention** refers to actions taken to prevent disease occurrence, detect it early, or prevent complications after recovery. Treating an acute, symptomatic event is **acute treatment**, not prevention.
- This is an active medical intervention to treat an ongoing, symptomatic disease process (acute ischemic stroke), which falls under **therapeutic management** rather than any category of prevention.
*Secondary prevention*
- **Secondary prevention** involves **early detection** and treatment of asymptomatic or minimally symptomatic disease to prevent progression (e.g., screening mammography, colonoscopy).
- For stroke specifically, secondary prevention would include interventions **after** the acute event to **prevent recurrence**, such as starting antiplatelet therapy (aspirin, clopidogrel), anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation, statin therapy, or carotid endarterectomy after TIA.
- tPA is given during the acute symptomatic phase, making it treatment rather than secondary prevention.
*Tertiary prevention*
- **Tertiary prevention** focuses on **rehabilitation** and managing established disease to prevent complications and improve quality of life.
- Examples after stroke include physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and managing post-stroke complications like depression or spasticity.
- This occurs in the recovery phase, not during acute treatment.
*Primary prevention*
- **Primary prevention** aims to prevent disease before it occurs in healthy individuals.
- Examples include controlling hypertension, managing diabetes, smoking cessation, exercise, and healthy diet - all interventions that reduce stroke risk **before** any event occurs.
*Quaternary prevention*
- **Quaternary prevention** protects patients from **overmedicalization** and excessive or harmful medical interventions.
- It involves avoiding unnecessary testing or treatment that may cause more harm than benefit.
- Administering tPA for acute stroke (when indicated) is evidence-based treatment, not overtreatment.
More Confounding variables US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.