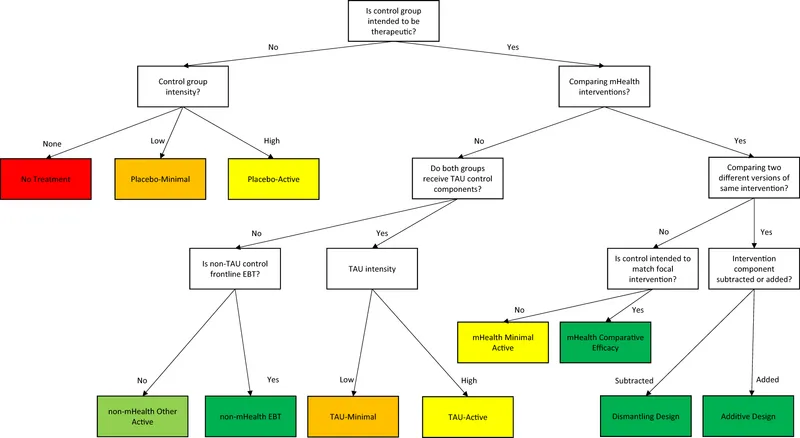
Blinding and controls US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Blinding and controls. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Blinding and controls US Medical PG Question 1: A research team develops a new monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitor for advanced melanoma that has shown promise in animal studies as well as high efficacy and low toxicity in early phase human clinical trials. The research team would now like to compare this drug to existing standard of care immunotherapy for advanced melanoma. The research team decides to conduct a non-randomized study where the novel drug will be offered to patients who are deemed to be at risk for toxicity with the current standard of care immunotherapy, while patients without such risk factors will receive the standard treatment. Which of the following best describes the level of evidence that this study can offer?
- A. Level 1
- B. Level 3 (Correct Answer)
- C. Level 5
- D. Level 4
- E. Level 2
Blinding and controls Explanation: ***Level 3***
- A **non-randomized controlled trial** like the one described, where patient assignment to treatment groups is based on specific characteristics (risk of toxicity), falls into Level 3 evidence.
- This level typically includes **non-randomized controlled trials** and **well-designed cohort studies** with comparison groups, which are prone to selection bias and confounding.
- The study compares two treatments but lacks randomization, making it Level 3 evidence.
*Level 1*
- Level 1 evidence is the **highest level of evidence**, derived from **systematic reviews and meta-analyses** of multiple well-designed randomized controlled trials or large, high-quality randomized controlled trials.
- The described study is explicitly stated as non-randomized, ruling out Level 1.
*Level 2*
- Level 2 evidence involves at least one **well-designed randomized controlled trial** (RCT) or **systematic reviews** of randomized trials.
- The current study is *non-randomized*, which means it cannot be classified as Level 2 evidence, as randomization is a key criterion for this level.
*Level 4*
- Level 4 evidence includes **case series**, **case-control studies**, and **poorly designed cohort or case-control studies**.
- While the study is non-randomized, it is a controlled comparative trial rather than a case series or retrospective case-control study, placing it at Level 3.
*Level 5*
- Level 5 evidence is the **lowest level of evidence**, typically consisting of **expert opinion** without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research, or animal studies.
- While the drug was initially tested in animal studies, the current human comparative study offers a higher level of evidence than expert opinion or preclinical data.
Blinding and controls US Medical PG Question 2: A researcher is conducting a study to compare fracture risk in male patients above the age of 65 who received annual DEXA screening to peers who did not receive screening. He conducts a randomized controlled trial in 900 patients, with half of participants assigned to each experimental group. The researcher ultimately finds similar rates of fractures in the two groups. He then notices that he had forgotten to include 400 patients in his analysis. Including the additional participants in his analysis would most likely affect the study's results in which of the following ways?
- A. Wider confidence intervals of results
- B. Increased probability of committing a type II error
- C. Decreased significance level of results
- D. Increased external validity of results
- E. Increased probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is truly false (Correct Answer)
Blinding and controls Explanation: ***Increased probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is truly false***
- Including more participants increases the **statistical power** of the study, making it more likely to detect a true effect if one exists.
- A higher sample size provides a more precise estimate of the population parameters, leading to a greater ability to **reject a false null hypothesis**.
*Wider confidence intervals of results*
- A larger sample size generally leads to **narrower confidence intervals**, as it reduces the standard error of the estimate.
- Narrower confidence intervals indicate **greater precision** in the estimation of the true population parameter.
*Increased probability of committing a type II error*
- A **Type II error** (false negative) occurs when a study fails to reject a false null hypothesis.
- Increasing the sample size typically **reduces the probability of a Type II error** because it increases statistical power.
*Decreased significance level of results*
- The **significance level (alpha)** is a pre-determined threshold set by the researcher before the study begins, typically 0.05.
- It is independent of sample size and represents the **acceptable probability of committing a Type I error** (false positive).
*Increased external validity of results*
- **External validity** refers to the generalizability of findings to other populations, settings, or times.
- While a larger sample size can enhance the representativeness of the study population, external validity is primarily determined by the **sampling method** and the study's design context, not just sample size alone.
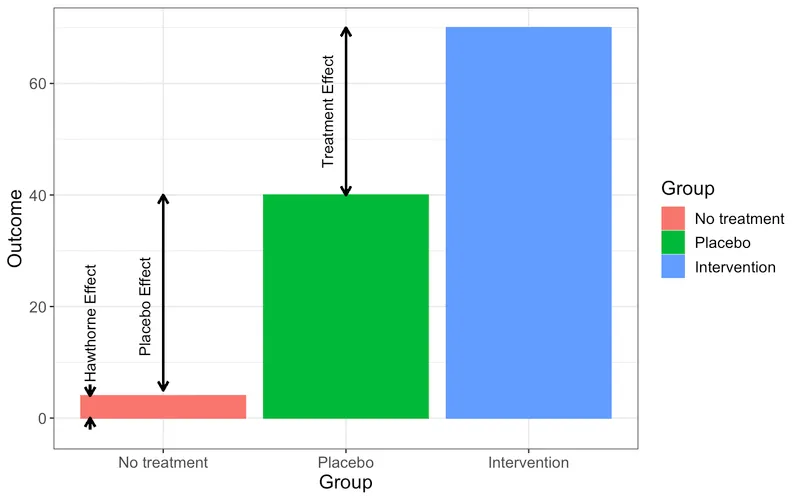
Blinding and controls US Medical PG Question 3: A study is performed to determine whether cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) increases compliance to dietary regimens. In order to test this hypothesis, a random group of volunteers who want to lose weight are selected from the community and subsequently randomized to no intervention and CBT groups. They are asked to record what they ate every day in a food journal and these recordings are correlated with objective serum and urine biomarkers for food intake. Surprisingly, it was found that even the group with no intervention had much higher rates of compliance to dietary regimens than the general population. Multivariate analysis showed no significant demographic or medical differences between the two groups. Which of the following most likely explains this finding from the study?
- A. Confounding effect
- B. Hawthorne effect (Correct Answer)
- C. Recall bias
- D. Pygmalion effect
- E. Procedure bias
Blinding and controls Explanation: ***Correct: Hawthorne effect***
- The **Hawthorne effect** describes the phenomenon where individuals modify their behavior in response to being observed or knowing they are part of a study. In this case, both groups knew they were being studied for dietary compliance, leading to increased adherence even in the control group.
- The act of **recording daily food intake** and the knowledge of participation in a study can itself serve as a motivator for improved compliance, leading to higher rates in both intervention and control groups compared to the general population.
*Incorrect: Confounding effect*
- A **confounding effect** occurs when an unmeasured or uncontrolled third variable influences both the independent and dependent variables, creating a spurious association. However, the study explicitly stated that "multivariate analysis showed no significant demographic or medical differences" between the groups, making confounding less likely.
- While confounding can occur in research, the specific scenario describing increased compliance due to awareness of observation is an example of the Hawthorne effect, not general confounding.
*Incorrect: Recall bias*
- **Recall bias** is a systematic error that occurs when there are differences in the accuracy or completeness of memories of past events between study participants. This typically happens in retrospective studies where participants are asked to remember past exposures or outcomes.
- While the study involved recording food intake, the problem describes an unexpected improvement in compliance across both groups due to participation, rather than a systematic distortion of reported past events. The recordings were real-time, reducing recall issues.
*Incorrect: Pygmalion effect*
- The **Pygmalion effect**, or Rosenthal effect, describes the phenomenon where higher expectations lead to an increase in performance. It usually refers to an effect on the participant's performance influenced by the experimenter's expectations.
- While expectations can influence behavior, the observation here is tied to the act of being studied and observed, rather than specific high expectations imposed by the researchers on the participants themselves.
*Incorrect: Procedure bias*
- **Procedure bias**, or selection bias, occurs when the procedures used to select participants or assign them to groups lead to systematic differences between the groups. This can affect the generalizability or internal validity of the study.
- The study explicitly states that participants were "randomly selected" and "randomized to no intervention and CBT groups," which aims to minimize procedure or selection bias. The observed effect applies to both groups, suggesting it's not due to a flaw in allocation.
Blinding and controls US Medical PG Question 4: An office team is being observed by an outside agency at the request of management to make sure they are completing all their tasks appropriately. Several of the employees are nervous that they are being watched and take care to perform their jobs with extra care, more so than they would have done during a normal workday. What best describes this behavior?
- A. Pygmalion effect
- B. Novelty effect
- C. Hawthorne effect (Correct Answer)
- D. Observer bias
- E. Ringelmann effect
Blinding and controls Explanation: ***Hawthorne effect***
- The **Hawthorne effect** describes changes in behavior that occur among individuals who are aware that they are being observed.
- In this scenario, the employees' increased diligence due to being watched by an outside agency aligns perfectly with this psychological phenomenon.
*Pygmalion effect*
- The **Pygmalion effect** refers to the phenomenon where higher expectations lead to improved performance in a given area.
- It focuses on how an observer's expectations can influence the subject's behavior, rather than the subject's awareness of observation itself.
*Novelty effect*
- The **novelty effect** occurs when the initial interest or enthusiasm for a new item or intervention temporarily improves performance, which then wanes over time.
- This effect is related to the newness of a situation, not the act of being observed.
*Observer bias*
- **Observer bias** (also known as ascertainment bias) happens when the observer's expectations, beliefs, or preconceptions influence how they perceive or record data.
- It refers to a bias in the *observer*, not a change in the *observed subject's behavior* due to being watched.
*Ringelmann effect*
- The **Ringelmann effect** (or social loafing) describes the tendency for individual members of a group to become less productive as the size of their group increases.
- This is a phenomenon of reduced individual effort in a group setting, not an alteration in behavior due to being observed.
Blinding and controls US Medical PG Question 5: Study X examined the relationship between coffee consumption and lung cancer. The authors of Study X retrospectively reviewed patients' reported coffee consumption and found that drinking greater than 6 cups of coffee per day was associated with an increased risk of developing lung cancer. However, Study X was criticized by the authors of Study Y. Study Y showed that increased coffee consumption was associated with smoking. What type of bias affected Study X, and what study design is geared to reduce the chance of that bias?
- A. Observer bias; double blind analysis
- B. Selection bias; randomization
- C. Lead time bias; placebo
- D. Measurement bias; blinding
- E. Confounding; randomization (Correct Answer)
Blinding and controls Explanation: ***Confounding; randomization***
- Study Y suggests that **smoking** is a **confounding variable** because it is associated with both increased coffee consumption (exposure) and increased risk of lung cancer (outcome), distorting the apparent relationship between coffee and lung cancer.
- **Randomization** in experimental studies (such as randomized controlled trials) helps reduce confounding by ensuring that known and unknown confounding factors are evenly distributed among study groups.
- In observational studies where randomization is not possible, confounding can be addressed through **stratification**, **matching**, or **multivariable adjustment** during analysis.
*Observer bias; double blind analysis*
- **Observer bias** occurs when researchers' beliefs or expectations influence the study outcome, which is not the primary issue described here regarding the relationship between coffee, smoking, and lung cancer.
- **Double-blind analysis** is a method to mitigate observer bias by ensuring neither participants nor researchers know who is in the control or experimental groups.
*Selection bias; randomization*
- **Selection bias** happens when the study population is not representative of the target population, leading to inaccurate results, which is not directly indicated by the interaction between coffee and smoking.
- While **randomization** is used to reduce selection bias by creating comparable groups, the core problem identified in Study X is confounding, not flawed participant selection.
*Lead time bias; placebo*
- **Lead time bias** occurs in screening programs when early detection without improved outcomes makes survival appear longer, an issue unrelated to the described association between coffee, smoking, and lung cancer.
- A **placebo** is an inactive treatment used in clinical trials to control for psychological effects, and its relevance here is limited to treatment intervention studies.
*Measurement bias; blinding*
- **Measurement bias** arises from systematic errors in data collection, such as inaccurate patient reporting of coffee consumption, but the main criticism from Study Y points to a third variable (smoking) affecting the association, not just flawed measurement.
- **Blinding** helps reduce measurement bias by preventing participants or researchers from knowing group assignments, thus minimizing conscious or unconscious influences on data collection.
Blinding and controls US Medical PG Question 6: A scientist is designing a study to determine whether eating a new diet is able to lower blood pressure in a group of patients. In particular, he believes that starting the diet may help decrease peak blood pressures throughout the day. Therefore, he will equip study participants with blood pressure monitors and follow pressure trends over a 24-hour period. He decides that after recruiting subjects, he will start them on either the new diet or a control diet and follow them for 1 month. After this time, he will switch patients onto the other diet and follow them for an additional month. He will analyze the results from the first month against the results from the second month for each patient. This type of study design is best at controlling for which of the following problems with studies?
- A. Hawthorne effect
- B. Recall bias
- C. Confounding (Correct Answer)
- D. Selection bias
- E. Pygmalion effect
Blinding and controls Explanation: ***Confounding***
- This **crossover design** (switching patients to the other diet) effectively controls for **confounding variables** by making each patient their own control, ensuring that inherent patient characteristics do not bias the comparison between diets.
- By comparing the effects of both diets within the same individual, individual variability in factors such as genetics, lifestyle, and other co-morbidities are accounted for, reducing their potential as confounders.
*Hawthorne effect*
- The **Hawthorne effect** refers to subjects modifying their behavior in response to being observed, which this study design does not specifically address or eliminate.
- While patients are being monitored, the design aims to compare the diets' effects, not to prevent behavioral changes due to observation itself.
*Recall bias*
- **Recall bias** occurs when participants' memories of past events are inaccurate, often influenced by their current health status or beliefs.
- This study measures **real-time blood pressure** data, not relying on recollection of past exposures or outcomes, thereby mitigating recall bias.
*Selection bias*
- **Selection bias** arises from non-random selection of participants into study groups, leading to systematic differences between groups.
- While patient recruitment could introduce selection bias into the overall study population, the **crossover design** itself helps control for differences between treatment arms because all participants eventually receive both treatments.
*Pygmalion effect*
- The **Pygmalion effect** (or observer-expectancy effect) describes phenomena where higher expectations lead to increased performance, usually from a researcher influencing a subject.
- This effect is not directly addressed by the crossover design; the design focuses on controlling for patient-specific confounders rather than investigator bias in expectations.
Blinding and controls US Medical PG Question 7: A clinical trial is conducted to determine the efficacy of ginkgo biloba in the treatment of Parkinson disease. A sample of patients with Parkinson disease is divided into two groups. Participants in the first group are treated with ginkgo biloba, and participants in the other group receive a placebo. A change in the Movement Disorder Society-Unified Parkinson Disease Rating Scale (MDS-UPDRS) score is used as the primary endpoint for the study. The investigators, participants, and data analysts were meant to be blinded throughout the trial. However, while the trial is being conducted, the patients' demographics and their allocated treatment groups are mistakenly disclosed to the investigators, but not to the participants or the data analysts, because of a technical flaw. The study concludes that there is a significant decrease in MDS-UPDRS scores in patients treated with ginkgo biloba. Which of the following is most likely to have affected the validity of this study?
- A. Effect modification
- B. Recall bias
- C. Pygmalion effect (Correct Answer)
- D. Hawthorne effect
- E. Procedure bias
Blinding and controls Explanation: ***Pygmalion effect***
- The **Pygmalion effect**, also known as **observer-expectancy bias** or experimenter bias, occurs when an investigator's expectations about the outcome of a study unintentionally influence the results.
- In this case, the **investigators becoming unblinded** to treatment assignments could lead them to unconsciously influence patient assessments or interactions based on their knowledge of who received ginkgo biloba, potentially leading to inflated positive outcomes for the treatment group.
*Effect modification*
- **Effect modification** describes a phenomenon where the effect of an exposure on an outcome is different across various strata of a third variable.
- This is a true biological interaction and does not represent a bias or flaw in the study design due to unblinding.
*Recall bias*
- **Recall bias** occurs when participants' memories of past exposures or events differ based on their current health status or knowledge of their condition.
- This bias primarily affects studies that rely on **retrospective reporting** of past events and is not relevant to the unblinding of investigators in a prospective clinical trial.
*Hawthorne effect*
- The **Hawthorne effect** describes a phenomenon where participants in a study change their behavior simply because they are aware of being observed, regardless of the intervention they receive.
- While participant blinding is important to prevent this, the scenario describes investigators being unblinded, not the participants.
*Procedure bias*
- **Procedure bias** (also known as interviewer bias or performance bias) arises from systematic differences in the way data is collected or procedures are performed for different study groups.
- While investigator unblinding can lead to elements of procedure bias, the more specific and encompassing term for an investigator's expectations influencing results is the **Pygmalion effect** (observer-expectancy bias).
Blinding and controls US Medical PG Question 8: A 16-year-old girl comes to the physician because she is worried about gaining weight. She reports that at least twice a week, she eats excessive amounts of food but feels ashamed about losing control soon after. She is very active in her high school's tennis team and goes running daily to lose weight. She has a history of cutting her forearms with the metal tab from a soda can. Her last menstrual period was 3 weeks ago. She is 165 cm (5 ft 5 in) tall and weighs 57 kg (125 lb); BMI is 21 kg/m2. Physical examination shows enlarged, firm parotid glands bilaterally. There are erosions of the enamel on the lingual surfaces of the teeth. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Borderline personality disorder
- B. Bulimia nervosa (Correct Answer)
- C. Body dysmorphic disorder
- D. Anorexia nervosa
- E. Obsessive-compulsive disorder
Blinding and controls Explanation: ***Bulimia nervosa***
- This patient exhibits characteristic features of bulimia nervosa, including recurrent episodes of **binge eating** (at least twice weekly) followed by inappropriate **compensatory behaviors**.
- The **bilateral parotid gland enlargement** and **lingual enamel erosion** are **pathognomonic physical signs of chronic self-induced vomiting** (purging behavior), combined with excessive exercise as additional compensation.
- Her normal BMI of 21 kg/m² is highly consistent with bulimia nervosa, as individuals with this condition typically maintain a **normal weight or are overweight**, unlike those with anorexia nervosa.
- The sense of **loss of control** and **shame** about eating episodes are core features of this disorder.
*Borderline personality disorder*
- While **self-harm** (cutting) can be associated with borderline personality disorder, the primary concern in this patient is the prominent eating disorder symptoms with pathognomonic physical findings.
- Borderline personality disorder is characterized by a pervasive pattern of **instability in interpersonal relationships**, self-image, affects, and marked impulsivity; these are not the main presenting complaints here.
- Self-harm behavior can occur in multiple psychiatric conditions and does not alone establish this diagnosis.
*Body dysmorphic disorder*
- This disorder involves a **preoccupation with perceived flaws in physical appearance** that are minimal or unobservable to others, leading to significant distress or impairment.
- While the patient is concerned about gaining weight, her primary symptoms revolve around **binge-purge cycles** with physical evidence of purging behavior, rather than a sole preoccupation with a specific body defect.
*Anorexia nervosa*
- Anorexia nervosa is characterized by **restriction of energy intake** leading to a significantly low body weight (BMI usually <17.5 kg/m²) and intense fear of gaining weight despite being underweight.
- This patient has a **normal BMI (21 kg/m²)** and engages in binge-eating followed by compensatory behaviors (purging and exercise), which represents bulimia nervosa rather than anorexia nervosa.
- Additionally, she has **regular menses** (last period 3 weeks ago), whereas amenorrhea is common in anorexia nervosa due to low body weight.
*Obsessive-compulsive disorder*
- OCD involves recurrent, persistent, **intrusive thoughts (obsessions)** and/or repetitive behaviors or mental acts that an individual feels driven to perform **(compulsions)** to reduce anxiety.
- While some of the patient's behaviors might seem ritualistic, the core symptoms are clearly related to **eating disorder pathology with binge-purge cycles**, not typical OCD themes like contamination, symmetry, or checking behaviors.
- The physical signs of chronic purging behavior definitively point to an eating disorder diagnosis.
Blinding and controls US Medical PG Question 9: A 45-year-old man presents for his annual checkup. The patient has a past medical history of diabetes mellitus (DM) type 2 that is well-controlled with diet. In addition, he was admitted to this hospital 1-year ago for a myocardial infarction (MI). The patient reports a 40-pack-year smoking history. However, after his MI, his doctors informed him about how detrimental smoking was to his heart condition. Since then, he has made efforts to cut down and now, for the past seven months, has stopped smoking. He says he used to use smoking as a means of dealing with his work and family stresses. He now attends wellness sessions at work and meditates early every morning before the family wakes up. Which of the following stages of the transtheoretical model is this patient most likely in?
- A. Preparation
- B. Contemplation
- C. Action
- D. Precontemplation
- E. Maintenance (Correct Answer)
Blinding and controls Explanation: ***Maintenance***
- The patient has **successfully stopped smoking for seven months**, indicating sustained behavior change.
- He has also adopted **new coping mechanisms** like wellness sessions and meditation, which are crucial for preventing relapse and falls under this stage.
*Preparation*
- This stage involves **intending to take action** in the immediate future (e.g., within the next month) and involves some steps towards change, such as making a plan.
- The patient has already acted and sustained the behavior change, moving past mere preparation.
*Contemplation*
- Individuals in this stage are **aware a problem exists** and are seriously thinking about overcoming it but have not yet committed to taking action.
- The patient has clearly moved past just thinking about quitting and has actively stopped smoking.
*Action*
- This stage involves **modifying behavior, experiences, or environment** in order to overcome problems.
- While the patient was in the action stage when he initially quit, he has now maintained this change for an extended period (seven months), progressing beyond the initial action phase.
*Precontemplation*
- In this stage, individuals are **not intending to take action** in the foreseeable future (e.g., within 6 months) and are often unaware or underaware of their problems.
- This patient actively quit smoking and maintained cessation, showing he was not in precontemplation.
Blinding and controls US Medical PG Question 10: A 7-year-old girl presents for a follow-up visit after recent discharge from the hospital. She was admitted about 4 months ago for symptoms of seizures, altered mental status, and fever. She was diagnosed during that admission with herpes encephalitis and recovered well after being treated with acyclovir. However, at this visit, her parents complain of some “strange behaviors” that have developed over the past several weeks. For example, she seems to be snacking uncontrollably and eats significantly more than she did before. Her teacher has also sent home notes stating that she has been chewing on art supplies such as crayons and glue and that she has been sent to the principal twice for rubbing her genitals inappropriately during class. The pediatric neurologist decides to get a follow-up MRI. Which of the following parts of the brain is most likely to have abnormal findings?
- A. Amygdala (Correct Answer)
- B. Hippocampus
- C. Brainstem
- D. Lateral geniculate nucleus
- E. Substantia nigra
Blinding and controls Explanation: ***Amygdala***
- Herpes encephalitis commonly affects the **temporal lobes**, which house the amygdala, leading to **Klüver-Bucy syndrome** symptoms like hyperorality, hypersexuality, and hyperphagia.
- The described "strange behaviors" (uncontrolled snacking, chewing non-food items, inappropriate genital rubbing) are classic manifestations of **Klüver-Bucy syndrome**, which results from bilateral damage to the amygdala.
*Hippocampus*
- While the hippocampus is also located in the temporal lobe and can be affected by herpes encephalitis, damage primarily leads to **memory deficits** (anterograde amnesia).
- It is not directly responsible for the behavioral changes seen in Klüver-Bucy syndrome.
*Brainstem*
- The brainstem controls **vital functions** (e.g., breathing, heart rate) and consciousness.
- Damage to the brainstem would present with more severe and acute symptoms, such as **coma**, respiratory failure, or cranial nerve palsies, not the specific behavioral disturbances observed.
*Lateral geniculate nucleus*
- The lateral geniculate nucleus is a relay center for **visual information** in the thalamus.
- Damage would primarily result in **visual field defects** or problems with visual processing, not the behavioral changes described.
*Substantia nigra*
- Located in the midbrain, the substantia nigra is crucial for **motor control** due to its role in dopamine production.
- Damage is classically associated with **Parkinsonian symptoms** (e.g., tremor, rigidity, bradykinesia), which are not present in this patient.
More Blinding and controls US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.