Bias identification and mitigation US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Bias identification and mitigation. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Bias identification and mitigation US Medical PG Question 1: A study is funded by the tobacco industry to examine the association between smoking and lung cancer. They design a study with a prospective cohort of 1,000 smokers between the ages of 20-30. The length of the study is five years. After the study period ends, they conclude that there is no relationship between smoking and lung cancer. Which of the following study features is the most likely reason for the failure of the study to note an association between tobacco use and cancer?
- A. Late-look bias
- B. Latency period (Correct Answer)
- C. Confounding
- D. Effect modification
- E. Pygmalion effect
Bias identification and mitigation Explanation: ***Latency period***
- **Lung cancer** typically has a **long latency period**, often **20-30+ years**, between initial exposure to tobacco carcinogens and the development of clinically detectable disease.
- A **five-year study duration** in young smokers (ages 20-30) is **far too short** to observe the development of lung cancer, which explains the false negative finding.
- This represents a **fundamental flaw in study design** rather than a bias—the biological timeline of disease development was not adequately considered.
*Late-look bias*
- **Late-look bias** occurs when a study enrolls participants who have already survived the early high-risk period of a disease, leading to **underestimation of true mortality or incidence**.
- Also called **survival bias**, it involves studying a population that has already been "selected" by survival.
- This is not applicable here, as the study simply ended before sufficient time elapsed for disease to develop.
*Confounding*
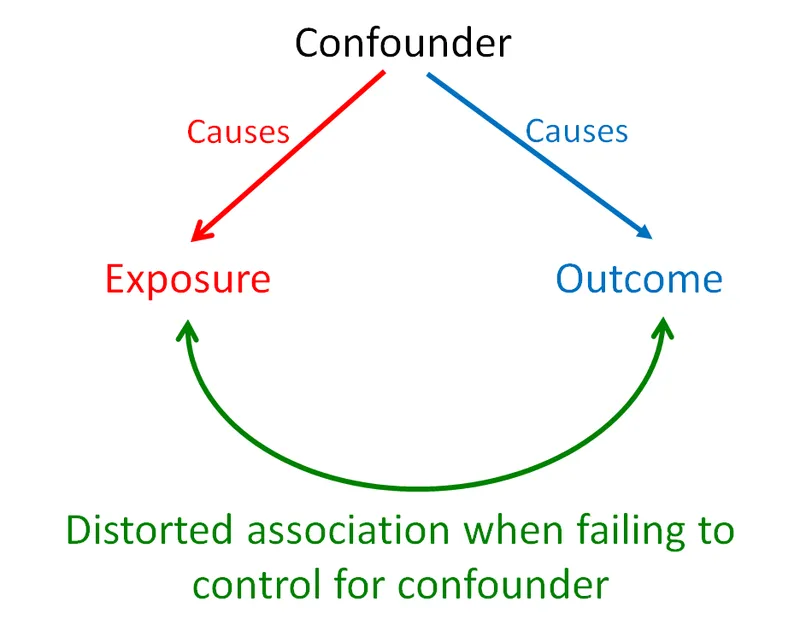
- **Confounding** occurs when a third variable is associated with both the exposure and outcome, distorting the apparent relationship between them.
- While confounding can affect study results, it would not completely eliminate the detection of a strong, well-established association like smoking and lung cancer in a properly conducted prospective cohort study.
- The issue here is temporal (insufficient follow-up time), not the presence of an unmeasured confounder.
*Effect modification*
- **Effect modification** (also called interaction) occurs when the magnitude of an association between exposure and outcome differs across levels of a third variable.
- This represents a **true biological phenomenon**, not a study design flaw or bias.
- It would not explain the complete failure to detect any association.
*Pygmalion effect*
- The **Pygmalion effect** (observer-expectancy effect) refers to a psychological phenomenon where higher expectations lead to improved performance in the observed subjects.
- This concept is relevant to **behavioral and educational research**, not to objective epidemiological studies of disease incidence.
- It has no relevance to the biological relationship between carcinogen exposure and cancer development.
Bias identification and mitigation US Medical PG Question 2: A researcher is studying whether a new knee implant is better than existing alternatives in terms of pain after knee replacement. She designs the study so that it includes all the surgeries performed at a certain hospital. Interestingly, she notices that patients who underwent surgeries on Mondays and Thursdays reported much better pain outcomes on a survey compared with those who underwent the same surgeries from the same surgeons on Tuesdays and Fridays. Upon performing further analysis, she discovers that one of the staff members who works on Mondays and Thursdays is aware of the study and tells all the patients about how wonderful the new implant is. Which of the following forms of bias does this most likely represent?
- A. Hawthorne effect
- B. Pygmalion effect (Correct Answer)
- C. Attrition bias
- D. Golem effect
Bias identification and mitigation Explanation: ***Pygmalion effect***
- This bias occurs when higher expectations lead to an increase in performance. In this scenario, the staff member's positive reinforcement about the new implant likely instilled **higher patient expectations**, leading to better reported pain outcomes.
- The patients' belief in the implant's superiority, influenced by the staff member, acted as a **self-fulfilling prophecy**, improving their subjective pain experience.
*Hawthorne effect*
- This effect describes how individuals modify an aspect of their behavior in response to their awareness of being observed. While patients were part of a study, their improved outcomes were specifically linked to a staff member's verbal influence, not solely the act of observation.
- The improved pain outcomes stem from the **expectations created by the staff member's praise**, rather than a general awareness of being studied.
*Attrition bias*
- Attrition bias refers to systematic differences between groups in the loss of participants from a study.
- This scenario describes differences in patient outcomes based on staff influence during the study, not due to **patients dropping out differentially** between groups.
*Golem effect*
- The Golem effect is the opposite of the Pygmalion effect, where lower expectations placed upon individuals lead to poorer performance from them.
- In this case, the staff member's influence created **high expectations and positive outcomes**, not negative expectations leading to worse outcomes.
Bias identification and mitigation US Medical PG Question 3: A researcher is conducting a study to compare fracture risk in male patients above the age of 65 who received annual DEXA screening to peers who did not receive screening. He conducts a randomized controlled trial in 900 patients, with half of participants assigned to each experimental group. The researcher ultimately finds similar rates of fractures in the two groups. He then notices that he had forgotten to include 400 patients in his analysis. Including the additional participants in his analysis would most likely affect the study's results in which of the following ways?
- A. Wider confidence intervals of results
- B. Increased probability of committing a type II error
- C. Decreased significance level of results
- D. Increased external validity of results
- E. Increased probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is truly false (Correct Answer)
Bias identification and mitigation Explanation: ***Increased probability of rejecting the null hypothesis when it is truly false***
- Including more participants increases the **statistical power** of the study, making it more likely to detect a true effect if one exists.
- A higher sample size provides a more precise estimate of the population parameters, leading to a greater ability to **reject a false null hypothesis**.
*Wider confidence intervals of results*
- A larger sample size generally leads to **narrower confidence intervals**, as it reduces the standard error of the estimate.
- Narrower confidence intervals indicate **greater precision** in the estimation of the true population parameter.
*Increased probability of committing a type II error*
- A **Type II error** (false negative) occurs when a study fails to reject a false null hypothesis.
- Increasing the sample size typically **reduces the probability of a Type II error** because it increases statistical power.
*Decreased significance level of results*
- The **significance level (alpha)** is a pre-determined threshold set by the researcher before the study begins, typically 0.05.
- It is independent of sample size and represents the **acceptable probability of committing a Type I error** (false positive).
*Increased external validity of results*
- **External validity** refers to the generalizability of findings to other populations, settings, or times.
- While a larger sample size can enhance the representativeness of the study population, external validity is primarily determined by the **sampling method** and the study's design context, not just sample size alone.
Bias identification and mitigation US Medical PG Question 4: The success of a new treatment designed to deter people from smoking was evaluated by a team of researchers. However, the heaviest and most committed smokers in the study group were less interested in quitting and subsequently dropped out of the study. Nonetheless, the researchers continued with their research (disregarding those who dropped out), which resulted in a false conclusion that the treatment was more successful than the results would have shown under ideal study conditions. The smokers who were confirmed as quitters were actually the ones who were more interested in giving up smoking, which is why they remained in the study. Which of the following is the bias that invalidates the researchers’ conclusion in this example?
- A. Attrition bias (Correct Answer)
- B. Detection bias
- C. Ascertainment bias
- D. Exclusion bias
- E. Non-response bias
Bias identification and mitigation Explanation: ***Attrition bias***
- **Attrition bias** occurs when participants drop out of a study in a non-random way, leading to differential loss between study groups. In this case, the more committed smokers, less likely to quit, disproportionately dropped out, making the treatment appear more successful than it was.
- This selective dropout distorts the **study results** because the remaining participants are not representative of the original study population, and the positive outcomes observed are largely due to the loss of those less likely to succeed.
*Detection bias*
- **Detection bias** arises when the outcome of interest is detected unequally between study groups, typically due to different monitoring or diagnostic procedures.
- This bias would involve differences in how smoking cessation was measured or observed, rather than who remained in the study.
*Ascertainment bias*
- **Ascertainment bias** (also known as observer bias or recall bias) occurs when information is collected or interpreted differently due to the observer's expectations or the participant's recall.
- This bias is not concerned with participants dropping out but rather with systematic errors in how data about the outcome is gathered or recalled.
*Exclusion bias*
- **Exclusion bias** can occur when researchers exclude specific individuals or groups from analysis after randomization, often for reasons related to their outcomes or adherence, thereby distorting the results.
- While related to exclusion, **attrition bias** specifically refers to participants *dropping out themselves* in a way that confounds results, rather than being excluded by researchers post-randomization.
*Non-response bias*
- **Non-response bias** typically occurs in surveys or questionnaires when certain types of individuals are less likely to respond, making the sample unrepresentative of the population.
- This bias applies more to initial participation rates in a survey rather than participants dropping out of an intervention study after enrollment.
Bias identification and mitigation US Medical PG Question 5: A group of gastroenterologists is concerned about low colonoscopy screening rates. They decide to implement a free patient navigation program to assist local residents and encourage them to obtain colonoscopies in accordance with U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) guidelines. Local residents were recruited at community centers. Participants attended monthly meetings with patient navigators and were regularly reminded that their adherence to screening guidelines was being evaluated. Colonoscopy screening rates were assessed via chart review, which showed that 90% of participants adhered to screening guidelines. Data collected via chart review for local residents recruited at community centers who did not participate in the free patient navigation system found that 34% of that population adhered to USPSTF guidelines. Which of the following has most likely contributed to the observed disparity in colonoscopy screening rates?
- A. Recall bias
- B. Confirmation bias
- C. Reporting bias
- D. Hawthorne effect (Correct Answer)
- E. Sampling bias
Bias identification and mitigation Explanation: ***Hawthorne effect***
- The **Hawthorne effect** is a type of reactivity in which individuals modify an aspect of their behavior in response to their awareness of being observed.
- In this study, participants were aware that their adherence to screening guidelines was being evaluated, likely leading to increased compliance simply due to this awareness rather than the efficacy of the patient navigation program alone.
*Recall bias*
- **Recall bias** occurs when participants disproportionately remember or inaccurately recall past events, often due to their current health status or beliefs.
- This bias is less likely here as colonoscopy screening rates were assessed via **chart review**, an objective measure, rather than participant self-report.
*Confirmation bias*
- **Confirmation bias** is the tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms one's preexisting beliefs or hypotheses.
- This bias typically affects the researchers or observers, not the participants' behavior in the observed manner, as the question focuses on the participants' increased screening rates.
*Reporting bias*
- **Reporting bias** refers to selective revealing or suppression of information during the reporting of research findings, and can occur when study participants selectively report symptoms or behaviors.
- While participants might selectively report, the data here was gathered through **chart review**, which is a more objective measure of actual behavior, making reporting bias less likely to explain the disparity in screening rates.
*Sampling bias*
- **Sampling bias** occurs when a sample is not representative of the population from which it is drawn, leading to skewed results.
- While there might be some sampling bias in who chose to participate in the free program, the observed disparity is specifically about behavior change in those *being observed*, pointing more strongly to the Hawthorne effect.
Bias identification and mitigation US Medical PG Question 6: A research group wants to assess the safety and toxicity profile of a new drug. A clinical trial is conducted with 20 volunteers to estimate the maximum tolerated dose and monitor the apparent toxicity of the drug. The study design is best described as which of the following phases of a clinical trial?
- A. Phase 0
- B. Phase III
- C. Phase V
- D. Phase II
- E. Phase I (Correct Answer)
Bias identification and mitigation Explanation: ***Phase I***
- **Phase I clinical trials** involve a small group of healthy volunteers (typically 20-100) to primarily assess **drug safety**, determine a safe dosage range, and identify side effects.
- The main goal is to establish the **maximum tolerated dose (MTD)** and evaluate the drug's pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic profiles.
*Phase 0*
- **Phase 0 trials** are exploratory studies conducted in a very small number of subjects (10-15) to gather preliminary data on a drug's **pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics** in humans.
- They involve microdoses, not intended to have therapeutic effects, and thus cannot determine toxicity or MTD.
*Phase III*
- **Phase III trials** are large-scale studies involving hundreds to thousands of patients to confirm the drug's **efficacy**, monitor side effects, compare it to standard treatments, and collect information that will allow the drug to be used safely.
- These trials are conducted after safety and initial efficacy have been established in earlier phases.
*Phase V*
- "Phase V" is not a standard, recognized phase in the traditional clinical trial classification (Phase 0, I, II, III, IV).
- This term might be used in some non-standard research contexts or for post-marketing studies that go beyond Phase IV surveillance, but it is not a formal phase for initial drug development.
*Phase II*
- **Phase II trials** involve several hundred patients with the condition the drug is intended to treat, focusing on **drug efficacy** and further evaluating safety.
- While safety is still monitored, the primary objective shifts to determining if the drug works for its intended purpose and at what dose.
Bias identification and mitigation US Medical PG Question 7: Study X examined the relationship between coffee consumption and lung cancer. The authors of Study X retrospectively reviewed patients' reported coffee consumption and found that drinking greater than 6 cups of coffee per day was associated with an increased risk of developing lung cancer. However, Study X was criticized by the authors of Study Y. Study Y showed that increased coffee consumption was associated with smoking. What type of bias affected Study X, and what study design is geared to reduce the chance of that bias?
- A. Observer bias; double blind analysis
- B. Selection bias; randomization
- C. Lead time bias; placebo
- D. Measurement bias; blinding
- E. Confounding; randomization (Correct Answer)
Bias identification and mitigation Explanation: ***Confounding; randomization***
- Study Y suggests that **smoking** is a **confounding variable** because it is associated with both increased coffee consumption (exposure) and increased risk of lung cancer (outcome), distorting the apparent relationship between coffee and lung cancer.
- **Randomization** in experimental studies (such as randomized controlled trials) helps reduce confounding by ensuring that known and unknown confounding factors are evenly distributed among study groups.
- In observational studies where randomization is not possible, confounding can be addressed through **stratification**, **matching**, or **multivariable adjustment** during analysis.
*Observer bias; double blind analysis*
- **Observer bias** occurs when researchers' beliefs or expectations influence the study outcome, which is not the primary issue described here regarding the relationship between coffee, smoking, and lung cancer.
- **Double-blind analysis** is a method to mitigate observer bias by ensuring neither participants nor researchers know who is in the control or experimental groups.
*Selection bias; randomization*
- **Selection bias** happens when the study population is not representative of the target population, leading to inaccurate results, which is not directly indicated by the interaction between coffee and smoking.
- While **randomization** is used to reduce selection bias by creating comparable groups, the core problem identified in Study X is confounding, not flawed participant selection.
*Lead time bias; placebo*
- **Lead time bias** occurs in screening programs when early detection without improved outcomes makes survival appear longer, an issue unrelated to the described association between coffee, smoking, and lung cancer.
- A **placebo** is an inactive treatment used in clinical trials to control for psychological effects, and its relevance here is limited to treatment intervention studies.
*Measurement bias; blinding*
- **Measurement bias** arises from systematic errors in data collection, such as inaccurate patient reporting of coffee consumption, but the main criticism from Study Y points to a third variable (smoking) affecting the association, not just flawed measurement.
- **Blinding** helps reduce measurement bias by preventing participants or researchers from knowing group assignments, thus minimizing conscious or unconscious influences on data collection.
Bias identification and mitigation US Medical PG Question 8: A resident in the department of obstetrics and gynecology is reading about a randomized clinical trial from the late 1990s that was conducted to compare breast cancer mortality risk, disease localization, and tumor size in women who were randomized to groups receiving either annual mammograms starting at age 40 or annual mammograms starting at age 50. One of the tables in the study compares the two experimental groups with regard to socioeconomic demographics (e.g., age, income), medical conditions at the time of recruitment, and family history of breast cancer. The purpose of this table is most likely to evaluate which of the following?
- A. Observer bias
- B. Statistical power
- C. Confounding
- D. Randomization (Correct Answer)
- E. Effect modification
Bias identification and mitigation Explanation: ***Randomization***
- In a randomized clinical trial, the purpose of comparing baseline characteristics between experimental groups is to assess if **randomization successfully distributed potential confounders** evenly.
- An even distribution of baseline characteristics suggests that any observed differences in outcomes are more likely due to the intervention rather than **pre-existing differences** between the groups.
*Observer bias*
- **Observer bias** occurs when researchers' expectations influence their observations or interpretation of results, which is not evaluated by comparing baseline demographics.
- This type of bias is typically mitigated through **blinding** of researchers or participants, rather than checking baseline characteristics.
*Statistical power*
- **Statistical power** refers to the probability of correctly rejecting a false null hypothesis and detecting a true effect.
- It is determined by factors like sample size and effect size, not by the **balance of baseline characteristics** between groups.
*Effect modification*
- **Effect modification** occurs when the effect of an exposure on an outcome varies across different levels of a third variable.
- This is an **analytical consideration** explored in later stages of data analysis, not a concern addressed by comparing baseline characteristics.
*Confounding*
- **Confounding** occurs when an extraneous variable is associated with both the exposure and the outcome, distorting the true relationship.
- While the baseline table helps verify that potential confounders are evenly distributed, the primary purpose is to evaluate whether **randomization was successful**, not to directly assess confounding as an analysis concern.
Bias identification and mitigation US Medical PG Question 9: A survey was conducted in a US midwestern town in an effort to assess maternal mortality over the past year. The data from the survey are given in the table below:
Women of childbearing age 250,000
Maternal deaths 2,500
Number of live births 100, 000
Number of deaths of women of childbearing age 7,500
Maternal death is defined as the death of a woman while pregnant or within 42 days of termination of pregnancy from any cause related to or aggravated by, the pregnancy. Which of the following is the maternal mortality rate in this midwestern town?
- A. 1,000 per 100,000 live births
- B. 33 per 100,000 live births
- C. 3,000 per 100,000 live births
- D. 33,300 per 100,000 live births
- E. 2,500 per 100,000 live births (Correct Answer)
Bias identification and mitigation Explanation: ***2,500 per 100,000 live births***
- The maternal mortality rate is calculated as the number of **maternal deaths** per 100,000 **live births**. The given data directly provide these values.
- Calculation: (2,500 maternal deaths / 100,000 live births) × 100,000 = **2,500 per 100,000 live births**.
*1,000 per 100,000 live births*
- This value is incorrect as it does not align with the provided numbers for maternal deaths and live births in the calculation.
- It might result from a miscalculation or using incorrect numerator/denominator values from the dataset.
*33 per 100,000 live births*
- This value is significantly lower than the correct rate and suggests a substantial error in calculation or an incorrect understanding of how the maternal mortality rate is derived.
- It could potentially result from dividing the number of live births by maternal deaths, which is the inverse of the correct formula.
*3,000 per 100,000 live births*
- This option is close to the correct answer but slightly higher, indicating a possible calculation error, for instance, including non-maternal deaths or other causes of deaths in the numerator.
- The definition of maternal death is specific to pregnancy-related or aggravated causes, so extraneous deaths would inflate the rate.
*33,300 per 100,000 live births*
- This figure results from incorrectly calculating the proportion of maternal deaths among all deaths of women of childbearing age: (2,500 / 7,500) × 100,000 = 33,333.
- This is a conceptual error as the maternal mortality rate should use live births as the denominator, not total deaths of women of childbearing age.
Bias identification and mitigation US Medical PG Question 10: A 65-year-old man is admitted to the hospital because of a 1-month history of fatigue, intermittent fever, and weakness. Results from a peripheral blood smear taken during his evaluation are indicative of possible acute myeloid leukemia. Bone marrow aspiration and subsequent cytogenetic studies confirm the diagnosis. The physician sets aside an appointed time-slot and arranges a meeting in a quiet office to inform him about the diagnosis and discuss his options. He has been encouraged to bring someone along to the appointment if he wanted. He comes to your office at the appointed time with his daughter. He appears relaxed, with a full range of affect. Which of the following is the most appropriate opening statement in this situation?
- A. Your lab reports show that you have an acute myeloid leukemia
- B. What is your understanding of the reasons we did bone marrow aspiration and cytogenetic studies? (Correct Answer)
- C. You must be curious and maybe even anxious about the results of your tests.
- D. I may need to refer you to a blood cancer specialist because of your diagnosis. You may need chemotherapy or radiotherapy, which we are not equipped for.
- E. Would you like to know all the details of your diagnosis, or would you prefer I just explain to you what our options are?
Bias identification and mitigation Explanation: ***"What is your understanding of the reasons we did bone marrow aspiration and cytogenetic studies?"***
- This **open-ended question** allows the patient to express their current knowledge and perceptions, which helps the physician tailor the discussion.
- It establishes a **patient-centered approach**, respecting the patient's existing understanding and preparing them for further information.
*"You must be curious and maybe even anxious about the results of your tests."*
- While empathic, this statement makes an **assumption about the patient's feelings** rather than inviting them to share their own.
- It is often better to ask directly or use more open-ended questions that allow the patient to express their true emotions, especially given their **relaxed demeanor**.
*"I may need to refer you to a blood cancer specialist because of your diagnosis. You may need chemotherapy or radiotherapy, which we are not equipped for.”"*
- This statement immediately introduces **overwhelming and potentially alarming information** (referral, chemotherapy, radiotherapy) without first establishing the diagnosis or assessing the patient's readiness to receive it.
- It prematurely jumps to treatment and logistics, potentially causing **unnecessary distress** before the patient has processed the core diagnosis.
*"Would you like to know all the details of your diagnosis, or would you prefer I just explain to you what our options are?""*
- While it attempts to assess the patient's preference for information, this question is a **closed-ended "either/or" choice** that might limit the patient's ability to express nuanced needs.
- It also prematurely introduces the idea of "options" without first explaining the diagnosis in an understandable context.
*"Your lab reports show that you have an acute myeloid leukemia"*
- This is a **direct and blunt delivery of a serious diagnosis** without any preparatory context or assessment of the patient's existing knowledge or emotional state.
- Delivering such news abruptly can be shocking and overwhelming, potentially **hindering effective communication** and rapport building.
More Bias identification and mitigation US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.