Study designs

On this page
📊 The Research Design Architecture: Your Evidence Blueprint
Every clinical decision you make rests on evidence, but not all evidence is created equal-the design of a study determines whether its conclusions are trustworthy or misleading. You'll learn to distinguish experimental from observational approaches, recognize the biases that threaten validity, master strategies to control confounding, and evaluate how evidence is synthesized across studies. By understanding the architecture of research design, you'll transform from a passive consumer of medical literature into a critical appraiser who can separate signal from noise and apply the right evidence to the right patient.
Study Design Classification Framework
Study designs organize into distinct categories based on researcher control and temporal relationships:
-
Experimental Studies (High Control)
- Randomized Controlled Trials (95% confidence in causality)
- Quasi-experimental designs (75-85% reliability)
- Clinical trials with Phase I-IV progression
- Phase I: Safety testing (20-100 participants)
- Phase II: Efficacy assessment (100-300 participants)
- Phase III: Large-scale comparison (1,000-3,000 participants)
- Phase IV: Post-marketing surveillance (10,000+ participants)
-
Observational Studies (Natural Observation)
- Cohort studies: Forward-looking investigation
- Case-control studies: Backward-looking analysis
- Cross-sectional studies: Snapshot assessment
- Prevalence accuracy: ±3-5% margin of error
- Sample size requirements: 384 minimum for population studies
📌 Remember: ECHO for study hierarchy - Experimental (strongest), Cohort (prospective), Historical cohort (retrospective), Observational cross-sectional (weakest for causation)
| Study Type | Control Level | Causality Evidence | Time Investment | Cost Factor | Bias Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCT | Maximum | 95% confidence | 2-5 years | $1-10M | Minimal |
| Cohort | Moderate | 70-80% | 5-20 years | $500K-2M | Low-Moderate |
| Case-Control | Limited | 50-70% | 6 months-2 years | $50-200K | Moderate |
| Cross-Sectional | Minimal | <30% | 3-12 months | $10-50K | High |
| Case Series | None | <10% | 1-6 months | $5-20K | Very High |
Connect study design mastery through methodological rigor to understand how research quality determines clinical application strength.
📊 The Research Design Architecture: Your Evidence Blueprint
🔬 Experimental Design Mastery: The Controlled Investigation
Randomized Controlled Trial Architecture
RCTs achieve methodological excellence through systematic control mechanisms:
-
Randomization Strategies
- Simple randomization: 50% allocation probability
- Block randomization: Balanced groups every 4-8 participants
- Stratified randomization: Subgroup balance for key variables
- Age stratification: ±2 years mean difference maximum
- Gender balance: 45-55% distribution acceptable
- Disease severity: Matched baseline characteristics
-
Control Group Selection
- Placebo controls: Gold standard for blinding
- Active controls: Head-to-head comparisons
- Historical controls: Acceptable when ethics prohibit placebo
- Placebo response rates: 20-40% in pain studies
- 60-80% in depression trials
- 10-15% in oncology research
📌 Remember: CONSORT guidelines for RCT reporting - Consolidated Standards Of Reporting Trials ensure methodological transparency and reproducibility
Blinding Implementation Framework
-
Single-Blind Studies
- Participants unaware of allocation (Observer bias reduction)
- Investigator knowledge maintained for safety monitoring
- Effectiveness: 40-60% bias reduction compared to open-label
-
Double-Blind Studies
- Participants AND investigators blinded (Gold standard)
- 90% reduction in performance and detection bias
- Emergency unblinding protocols: <5% of participants typically
-
Triple-Blind Studies
- Participants, investigators, AND data analysts blinded
- Maximum bias protection for subjective outcomes
- Implementation complexity: 3-5x higher cost
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Allocation concealment prevents selection bias and is distinct from blinding - 85% of studies with inadequate concealment show inflated treatment effects by 30-40%.
💡 Master This: RCT validity depends on intention-to-treat analysis - analyzing participants in originally assigned groups regardless of compliance maintains randomization benefits and provides real-world effectiveness estimates.
Connect experimental design principles through observational methodology to understand how different approaches address specific research questions.
🔬 Experimental Design Mastery: The Controlled Investigation
🔍 Observational Study Strategies: The Natural Laboratory
Cohort Study Architecture
Cohort studies follow groups over time, providing the strongest observational evidence for causality:
-
Prospective Cohorts (Forward-Looking)
- Real-time exposure and outcome assessment
- Minimal recall bias risk
- Timeline: 5-30 years typical follow-up
- Cardiovascular outcomes: 10-20 years minimum
- Cancer development: 15-25 years optimal
- Infectious disease: 6 months-5 years sufficient
-
Retrospective Cohorts (Historical Analysis)
- Existing records provide exposure data
- Faster completion: 1-3 years vs decades
- Cost-effective: 10-20% of prospective study costs
- Medical record availability: 80-95% in electronic systems
- Data quality concerns: 15-25% missing critical variables
📌 Remember: STROBE guidelines for cohort reporting - STRengthening the Reporting of OBservational studies in Epidemiology ensures methodological transparency
Case-Control Study Framework
Case-control studies work backward from outcomes to exposures, providing efficient investigation of rare diseases:
-
Case Selection Criteria
- Incident cases: Newly diagnosed within 6-12 months
- Prevalent cases: Existing diagnoses (survival bias risk)
- Diagnostic certainty: ≥95% confirmation required
- Pathological confirmation: Gold standard for cancer studies
- Clinical criteria: Validated scales for psychiatric conditions
- Laboratory confirmation: Specific biomarkers when available
-
Control Selection Strategies
- Population controls: Random community sampling
- Hospital controls: Same institution, different conditions
- Matched controls: 1:1 to 1:4 case-control ratios
- Age matching: ±5 years typically acceptable
- Gender matching: Exact for hormone-related conditions
- Geographic matching: Same region for environmental exposures
| Study Design | Temporal Direction | Efficiency | Rare Disease Suitability | Causality Evidence |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Prospective Cohort | Forward | Low | Poor | Strong |
| Retrospective Cohort | Forward (Historical) | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate-Strong |
| Case-Control | Backward | High | Excellent | Moderate |
| Cross-Sectional | None (Snapshot) | Highest | Poor | Weak |
| Ecological | Population-Level | High | Variable | Very Weak |
💡 Master This: Odds ratios from case-control studies approximate relative risks when disease prevalence is <10% in the population - this rare disease assumption validates case-control methodology for most clinical conditions.
Connect observational study principles through bias recognition to understand how methodological flaws compromise research validity.
🔍 Observational Study Strategies: The Natural Laboratory
⚠️ Bias Recognition Mastery: The Validity Threats
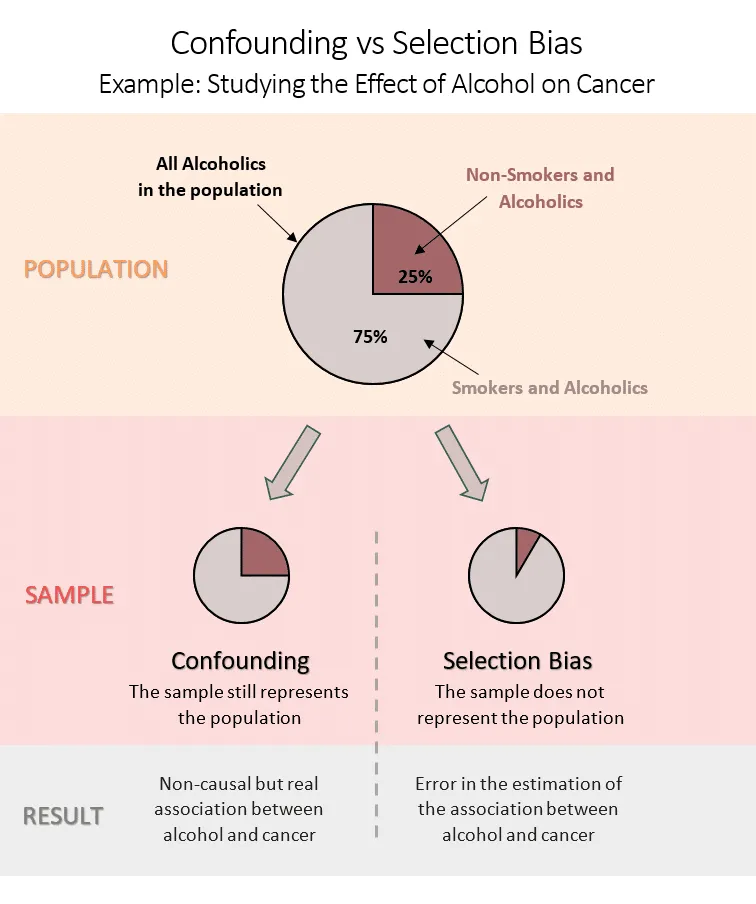
Selection Bias Framework
Selection bias occurs when study participants differ systematically from the target population:
-
Sampling Bias Categories
- Volunteer bias: Self-selected participants differ from general population
- Health-conscious volunteers: 20-30% lower disease rates
- Higher education levels: 40-60% above population average
- Better medication compliance: 80-90% vs 50-60% general population
- Survival bias: Excluding participants who died or were lost
- Cancer studies: 15-25% mortality before enrollment
- Chronic disease research: 30-40% loss to follow-up
- Berkson's bias: Hospital-based controls over-represent comorbid conditions
- Hospital control disease rates: 2-3x population prevalence
- Volunteer bias: Self-selected participants differ from general population
-
Response Bias Patterns
- Healthy worker effect: Employed populations healthier than general
- 10-50% lower mortality rates in occupational studies
- Reduced cardiovascular and respiratory disease
- Loss to follow-up: >20% attrition threatens validity
- Differential loss: Cases vs controls differ in >5% loss rates
- Outcome-related loss: Sicker participants more likely to withdraw
- Healthy worker effect: Employed populations healthier than general
📌 Remember: BIAS framework - Berkson's (hospital controls), Information (measurement error), Attrition (loss to follow-up), Selection (sampling problems)
Information Bias Architecture
Information bias results from systematic measurement errors:
-
Recall Bias Mechanisms
- Differential recall: Cases remember exposures better than controls
- 2-5x higher exposure reporting in cases
- Telescoping effect: Recent events seem more distant
- Maternal recall: 80-90% accuracy for major pregnancy events
- Social desirability bias: Under-reporting stigmatized behaviors
- Alcohol consumption: 20-40% under-reporting
- Sexual behavior: 30-50% under-reporting
- Drug use: 50-70% under-reporting
- Differential recall: Cases remember exposures better than controls
-
Observer Bias Prevention
- Blinding effectiveness: 90% bias reduction when successful
- Standardized protocols: Detailed measurement procedures
- Inter-rater reliability: κ ≥0.8 considered excellent
- Clinical assessments: κ=0.6-0.8 typically achievable
- Radiological readings: κ=0.7-0.9 with training
- Pathological diagnosis: κ=0.8-0.95 for experienced pathologists
| Bias Type | Impact Magnitude | Prevention Strategy | Detection Method | Correction Possibility |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Selection Bias | 20-200% effect distortion | Random sampling | Compare participants vs population | Limited |
| Recall Bias | 50-300% exposure misclassification | Objective measures | Validate subset | Moderate |
| Observer Bias | 30-150% outcome misclassification | Blinding | Inter-rater agreement | Good |
| Confounding | Variable | Randomization/matching | Stratified analysis | Excellent |
| Publication Bias | 10-50% effect inflation | Trial registration | Funnel plots | Moderate |
💡 Master This: Hawthorne effect occurs when participants modify behavior due to observation - 10-25% improvement in measured outcomes simply from study participation, independent of intervention effects.
Connect bias recognition through confounding control to understand how researchers isolate true causal relationships from spurious associations.
⚠️ Bias Recognition Mastery: The Validity Threats
🎯 Confounding Control Strategies: Isolating Truth
Confounding Identification Framework
Confounders must satisfy three criteria simultaneously:
- Confounder Criteria Assessment
- Associated with exposure: Statistical relationship exists
- p<0.05 or clinically meaningful difference
- ≥10% prevalence difference between exposure groups
- Risk factor for outcome: Independent causal pathway
- Biological plausibility supported by evidence
- Temporal precedence: Confounder precedes outcome
- Not intermediate step: Not part of causal pathway
- Mediator vs confounder: Mediators explain mechanism
- Collider bias: Conditioning on common effects creates spurious associations
- Associated with exposure: Statistical relationship exists
Control Strategy Implementation
-
Design-Phase Control
- Randomization: Gold standard for unknown confounders
- Large samples: n>200 per group for balance
- Stratified randomization: Balance key confounders
- Block randomization: Maintain balance throughout recruitment
- Matching: Individual or frequency matching
- 1:1 matching: Exact or ±range criteria
- Caliper matching: Propensity score within 0.1-0.2 standard deviations
- Over-matching risk: Matching on intermediate variables
- Randomization: Gold standard for unknown confounders
-
Analysis-Phase Control
- Stratification: Analyze within confounder levels
- Mantel-Haenszel: Combine stratum-specific estimates
- ≥5 events per stratum for stable estimates
- Test for interaction: p<0.1 suggests effect modification
- Multivariable modeling: Simultaneous adjustment
- 10 events per variable rule for logistic regression
- Collinearity assessment: VIF <5 acceptable
- Model selection: Backward elimination or purposeful selection
- Stratification: Analyze within confounder levels
📌 Remember: MATCH for confounding control - Matching (design), Adjustment (analysis), Time (temporal sequence), Causality (biological plausibility), Homogeneity (effect modification testing)
Advanced Confounding Concepts
- Effect Modification Recognition
- Interaction assessment: Effect varies across subgroups
- Statistical interaction: p<0.1 for interaction term
- Biological interaction: Mechanistic rationale
- Stratified reporting: Present subgroup-specific results
- Precision medicine implications: Personalized treatment effects
- Pharmacogenomics: CYP450 polymorphisms modify drug effects
- Biomarker stratification: HER2 status in breast cancer
- Age interactions: Pediatric vs adult dosing requirements
- Interaction assessment: Effect varies across subgroups
| Control Method | Timing | Effectiveness | Limitations | Cost Impact |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Randomization | Design | Excellent | Ethical constraints | High |
| Matching | Design | Good | Over-matching risk | Moderate |
| Restriction | Design | Good | Generalizability loss | Low |
| Stratification | Analysis | Moderate | Small strata | Low |
| Multivariable | Analysis | Good | Model assumptions | Low |
💡 Master This: Propensity score methods balance observed confounders between treatment groups, creating quasi-randomized comparisons from observational data with 70-90% of RCT validity when well-implemented.
Connect confounding control through evidence synthesis to understand how systematic reviews and meta-analyses combine multiple studies for stronger conclusions.
🎯 Confounding Control Strategies: Isolating Truth
📚 Evidence Synthesis Architecture: The Knowledge Aggregator
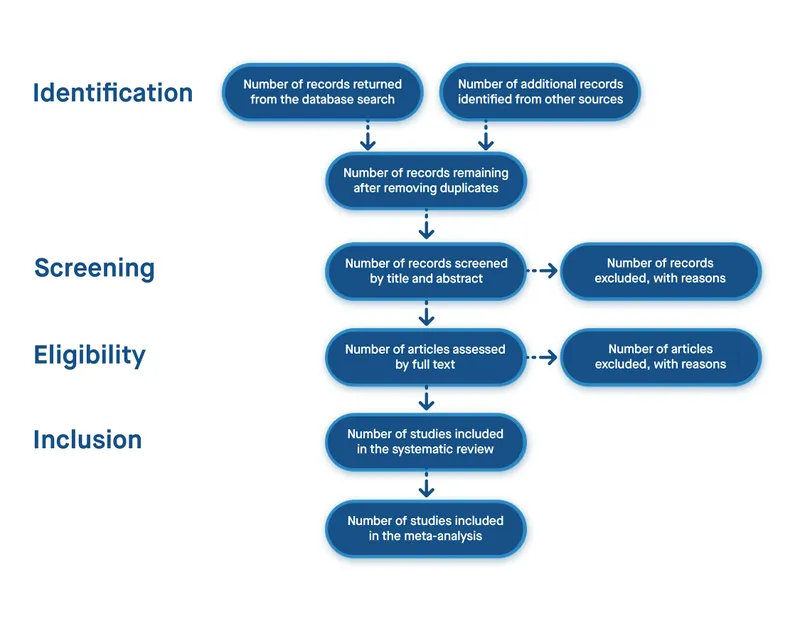
Systematic Review Methodology
Systematic reviews follow predetermined protocols to minimize bias and ensure reproducibility:
- Protocol Development Framework
- PROSPERO registration: Pre-specified methods prevent bias
- Research question: PICO format (Population, Intervention, Comparison, Outcome)
- Search strategy: Comprehensive database coverage
- Selection criteria: Explicit inclusion/exclusion rules
- Search comprehensiveness: Multiple database coverage
- MEDLINE: Primary biomedical database
- EMBASE: European focus, drug literature
- Cochrane Library: High-quality trial registry
- Grey literature: Conference abstracts, dissertations, reports
- PROSPERO registration: Pre-specified methods prevent bias
- Study Selection Process
- Dual screening: Two reviewers independently assess eligibility
- Inter-rater agreement: κ ≥0.6 acceptable
- Disagreement resolution: Third reviewer or consensus
- Selection bias prevention: Blinded study selection when possible
- Author blinding: Remove identifying information
- Journal blinding: Mask publication details
- Results blinding: Hide outcome data during selection
- Dual screening: Two reviewers independently assess eligibility
Meta-Analysis Statistical Framework
Meta-analysis provides quantitative synthesis when studies are sufficiently homogeneous:
-
Heterogeneity Assessment
- I² statistic: Percentage of variation due to heterogeneity
- I² <25%: Low heterogeneity
- I² 25-75%: Moderate heterogeneity
- I² >75%: High heterogeneity (meta-analysis questionable)
- Chi-square test: p<0.1 suggests significant heterogeneity
- Tau-squared: Absolute measure of between-study variance
- I² statistic: Percentage of variation due to heterogeneity
-
Statistical Model Selection
- Fixed-effects model: Assumes single true effect
- Appropriate when I² <25%
- Narrower confidence intervals
- Higher statistical power
- Random-effects model: Allows effect variation
- Preferred when I² ≥25%
- Wider confidence intervals
- More conservative estimates
- Fixed-effects model: Assumes single true effect
| Review Type | Time Investment | Study Number | Statistical Power | Evidence Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Narrative Review | 1-3 months | 20-50 studies | Not applicable | Low |
| Systematic Review | 6-18 months | 50-200 studies | Moderate | High |
| Meta-Analysis | 12-24 months | 10-100 studies | High | Highest |
| Network Meta-Analysis | 18-36 months | 20-150 studies | Very High | Highest |
| Individual Patient Data | 24-60 months | 5-50 studies | Maximum | Highest |
Publication Bias Detection
Publication bias threatens meta-analysis validity when negative studies remain unpublished:
- Detection Methods
- Funnel plot asymmetry: Visual assessment of small-study effects
- Symmetric distribution: No bias suggested
- Asymmetric pattern: Missing studies in lower-left quadrant
- Egger's test: Statistical assessment of funnel plot asymmetry
- p<0.1: Suggests significant publication bias
- Fail-safe N: Number of null studies needed to change conclusions
- >5k+2k: Robust finding (k = number of studies)
- Funnel plot asymmetry: Visual assessment of small-study effects
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Small-study effects affect 30-50% of meta-analyses, with overestimation of treatment effects by 12-32% when publication bias is present.
💡 Master This: Network meta-analysis enables indirect comparisons between treatments never directly compared, providing comprehensive treatment rankings for clinical decision-making with 80-95% concordance with head-to-head trials.
Connect evidence synthesis mastery through rapid reference tools to understand how research design knowledge transforms into clinical practice excellence.
📚 Evidence Synthesis Architecture: The Knowledge Aggregator
🎯 Clinical Research Mastery: Your Evidence Toolkit
Rapid Study Evaluation Framework
- 30-Second Study Assessment Protocol
- Study design identification: RCT > Cohort > Case-control > Cross-sectional
- Sample size adequacy: Power calculation reported
- Follow-up duration: Appropriate for outcome development
- Loss to follow-up: <20% acceptable threshold
- Bias risk evaluation: Selection, information, confounding assessment
- Randomization method: Computer-generated preferred
- Blinding implementation: Double-blind gold standard
- Baseline characteristics: Balanced between groups
- Clinical applicability: External validity for your patient population
- Inclusion criteria: Representative of clinical practice
- Exclusion criteria: Not overly restrictive
- Setting similarity: Comparable healthcare environment
- Study design identification: RCT > Cohort > Case-control > Cross-sectional
📌 Remember: RAPID evaluation - Randomization quality, Applicability to practice, Power adequacy, Intention-to-treat analysis, Dropout rates acceptable
Evidence Integration Arsenal
- Clinical Decision Hierarchy
- Level 1: Systematic reviews of RCTs (Highest confidence)
- Level 2: Individual RCTs with adequate power
- Level 3: Cohort studies with long-term follow-up
- Level 4: Case-control studies for rare outcomes
- Level 5: Case series and expert opinion (Lowest confidence)
| Evidence Source | Confidence Level | Clinical Application | Time to Practice Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cochrane Review | 95% | Immediate implementation | 6-12 months |
| High-Quality RCT | 85% | Consider adoption | 12-24 months |
| Prospective Cohort | 70% | Supportive evidence | 24-36 months |
| Case-Control | 50% | Hypothesis generation | 36+ months |
| Expert Opinion | 30% | Last resort guidance | Variable |
💡 Master This: GRADE evidence profiles integrate study design, risk of bias, inconsistency, indirectness, and imprecision to generate high, moderate, low, or very low quality ratings for clinical recommendations.
Research Design Quick Reference
- Study Selection Decision Tree
- Intervention evaluation: RCT preferred, cohort if ethics prohibit randomization
- Risk factor identification: Cohort for common outcomes, case-control for rare diseases
- Prevalence estimation: Cross-sectional surveys with representative sampling
- Prognosis determination: Cohort studies with adequate follow-up
- Diagnostic accuracy: Cross-sectional with reference standard comparison
📌 Remember: PICO framework drives study design selection - Population characteristics, Intervention feasibility, Comparison group availability, Outcome measurement timeline determine optimal methodology
Master these research design principles, and you possess the analytical framework for evaluating any medical evidence. Every clinical guideline, treatment protocol, and diagnostic recommendation becomes transparent through methodological understanding. This knowledge transforms you from passive evidence consumer to active evidence evaluator, ensuring optimal patient care through rigorous scientific reasoning.
🎯 Clinical Research Mastery: Your Evidence Toolkit
Practice Questions: Study designs
Test your understanding with these related questions
A researcher is studying whether a new knee implant is better than existing alternatives in terms of pain after knee replacement. She designs the study so that it includes all the surgeries performed at a certain hospital. Interestingly, she notices that patients who underwent surgeries on Mondays and Thursdays reported much better pain outcomes on a survey compared with those who underwent the same surgeries from the same surgeons on Tuesdays and Fridays. Upon performing further analysis, she discovers that one of the staff members who works on Mondays and Thursdays is aware of the study and tells all the patients about how wonderful the new implant is. Which of the following forms of bias does this most likely represent?












