Negative predictive value US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Negative predictive value. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Negative predictive value US Medical PG Question 1: A scientist in Chicago is studying a new blood test to detect Ab to EBV with increased sensitivity and specificity. So far, her best attempt at creating such an exam reached 82% sensitivity and 88% specificity. She is hoping to increase these numbers by at least 2 percent for each value. After several years of work, she believes that she has actually managed to reach a sensitivity and specificity much greater than what she had originally hoped for. She travels to China to begin testing her newest blood test. She finds 2,000 patients who are willing to participate in her study. Of the 2,000 patients, 1,200 of them are known to be infected with EBV. The scientist tests these 1,200 patients' blood and finds that only 120 of them tested negative with her new exam. Of the patients who are known to be EBV-free, only 20 of them tested positive. Given these results, which of the following correlates with the exam's specificity?
- A. 82%
- B. 90%
- C. 84%
- D. 86%
- E. 98% (Correct Answer)
Negative predictive value Explanation: ***98%***
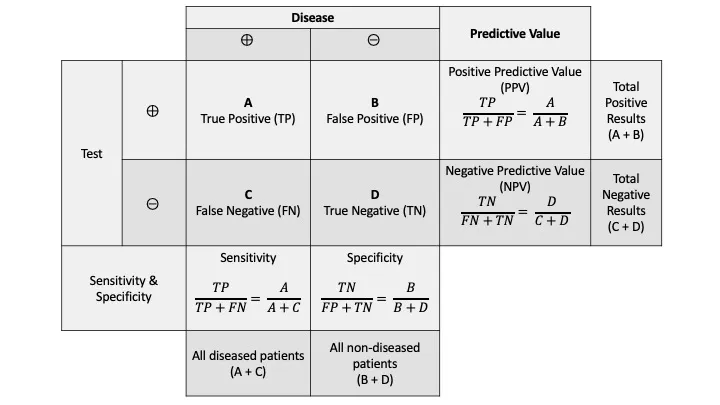
- **Specificity** measures the proportion of **true negatives** among all actual negatives.
- In this case, 800 patients are known to be EBV-free (actual negatives), and 20 of them tested positive (false positives). This means 800 - 20 = 780 tested negative (true negatives). Specificity = (780 / 800) * 100% = **98%**.
*82%*
- This value represents the *original sensitivity* before the scientist’s new attempts to improve the test.
- It does not reflect the *newly calculated specificity* based on the provided data.
*90%*
- This value represents the *newly calculated sensitivity* of the test, not the specificity.
- Out of 1200 EBV-infected patients, 120 tested negative (false negatives), meaning 1080 tested positive (true positives). Sensitivity = (1080 / 1200) * 100% = 90%.
*84%*
- This percentage is not directly derived from the information given for either sensitivity or specificity after the new test results.
- It does not correspond to any of the calculated values for the new test's performance.
*86%*
- This percentage is not directly derived from the information given for either sensitivity or specificity after the new test results.
- It does not correspond to any of the calculated values for the new test's performance.
Negative predictive value US Medical PG Question 2: A new assay for Lyme disease has been developed. While the assay has been tested extensively in Maine, a group of inventors are planning to test it in Southern California. In comparison to the assay's performance in Maine, testing the assay in Southern California would affect the performance of the assay in which of the following ways?
- A. Greater likelihood that an individual with a positive test will truly have Lyme disease
- B. Decreased positive likelihood ratio of the Lyme disease assay
- C. Decrease negative likelihood ratio of the Lyme disease assay
- D. Lower likelihood that a patient without Lyme disease truly has a negative test
- E. Greater likelihood that an individual with a negative test will truly not have Lyme disease (Correct Answer)
Negative predictive value Explanation: ***Greater likelihood that an individual with a negative test will truly not have Lyme disease***
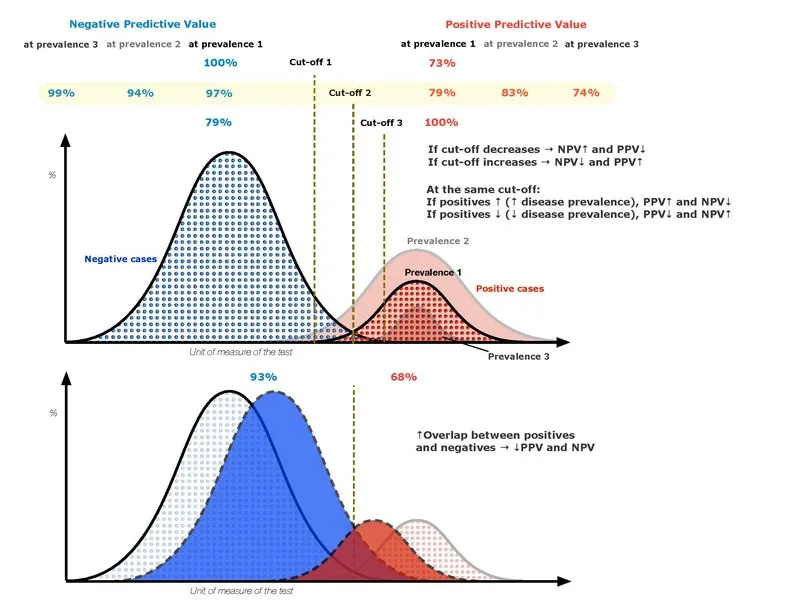
- This scenario describes an increase in the **negative predictive value (NPV)** of the assay. In an area with lower disease prevalence (Southern California compared to Maine for Lyme disease), the NPV increases because there are fewer true cases to miss, making a negative result more reliable in ruling out the disease.
- The intrinsic properties of the test (sensitivity and specificity) remain the same, but the interpretation of its results is influenced by the **pre-test probability** (prevalence).
*Greater likelihood that an individual with a positive test will truly have Lyme disease*
- This describes an increase in the **positive predictive value (PPV)**. This would occur if the test were moved to an area with higher **prevalence**, not lower prevalence like Southern California for Lyme disease.
- In an area with lower prevalence, the PPV would actually **decrease**, meaning a positive test is less likely to represent a true positive.
*Decreased positive likelihood ratio of the Lyme disease assay*
- The **likelihood ratio (LR)** of a diagnostic test is an intrinsic property that depends on its **sensitivity** and **specificity**, and it is generally independent of disease prevalence.
- Therefore, moving the test to an area with different prevalence should not change its positive likelihood ratio.
*Decrease negative likelihood ratio of the Lyme disease assay*
- Similar to the positive LR, the **negative likelihood ratio** is an intrinsic characteristic of the test (calculated from sensitivity and specificity).
- It remains constant regardless of the **disease prevalence** in the population being tested.
*Lower likelihood that a patient without Lyme disease truly has a negative test*
- This statement describes a decrease in **specificity** (a decrease in the true negative rate) or an increase in the **false negative rate**.
- The intrinsic **specificity** of the assay does not change with population prevalence, only the interpretation of the results through metrics like predictive values.
Negative predictive value US Medical PG Question 3: A 20-year-old man presents to the emergency department with complaints of severe malaise, fevers, and sore throat for the past 7 days. He also has had episodes of nausea and vomiting during this period. He does not smoke or drink alcohol. There is no family history of liver disease. His blood pressure is 130/80 mm Hg, temperature is 38.3℃ (100.9℉), pulse is 102/min, and respiratory rate is 20/min. On physical examination, he appears ill with bilateral cervical lymphadenopathy. His tonsils are erythematous and enlarged. There is no jaundice and he is mildly dehydrated. Abdominal examination demonstrates splenomegaly. The laboratory findings are shown below:
Hemoglobin 15 g/dL
Platelet count 95,000/mm³
Leukocytes 13,500/mm³
Neutrophils 50%
Atypical lymphocytes 34%
AST 232 U/L
ALT 312 U/L
ALP 120 U/L
GGT 35 U/L
Total bilirubin 1.2 mg/dL
Direct bilirubin 0.2 mg/dL
PT 12 seconds
The serologic test for hepatitis A, B, and C, CMV, and leptospirosis are negative. Serology for both serum IgM and IgG antibodies for EBV capsid antigen are positive, but the heterophile antibody test is negative. What is the most likely reason for the negative heterophile test?
- A. Concurrent viral hepatitis A infection
- B. CMV infection
- C. Low specificity
- D. Age of the patient
- E. False negative (Correct Answer)
Negative predictive value Explanation: ***False negative***
- The **heterophile antibody test (Monospot test)** has a sensitivity of only **70-92%** for infectious mononucleosis, meaning false negatives occur in **10-25% of cases**.
- Heterophile antibodies typically appear **1-2 weeks after symptom onset**, and this patient has been symptomatic for only **7 days**, making it likely the heterophile antibodies have not yet developed to detectable levels.
- The positive **EBV IgM and IgG for capsid antigen** confirm acute EBV infection, so the negative heterophile test is a **false negative** result.
- False negatives are especially common **early in the course of illness**.
*Age of the patient*
- Age 20 years is actually within the **peak sensitivity range** for heterophile antibody testing (adolescents and young adults 15-25 years have 85-90% sensitivity).
- The heterophile test is **less sensitive in young children (<12 years)**, with sensitivity as low as 30-50% in children under 4 years.
- This patient's age would not explain the negative result.
*Concurrent viral hepatitis A infection*
- Serologic testing for **hepatitis A is negative**, ruling out co-infection.
- Hepatitis A co-infection would not cause a false negative heterophile test.
*CMV infection*
- Serologic testing for **CMV is negative**, and the patient has **positive EBV-specific serology**.
- While CMV can cause heterophile-negative mononucleosis syndrome, the confirmed EBV infection makes this irrelevant.
*Low specificity*
- The heterophile antibody test has **high specificity (95-100%)** for infectious mononucleosis, meaning false positives are rare.
- The limitation of the test is its **low sensitivity**, not low specificity, which explains false negatives but doesn't directly answer why this specific test is negative.
Negative predictive value US Medical PG Question 4: You are developing a new diagnostic test to identify patients with disease X. Of 100 patients tested with the gold standard test, 10% tested positive. Of those that tested positive, the experimental test was positive for 90% of those patients. The specificity of the experimental test is 20%. What is the positive predictive value of this new test?
- A. 10%
- B. 90%
- C. 95%
- D. 11% (Correct Answer)
- E. 20%
Negative predictive value Explanation: ***11%***
- The positive predictive value (PPV) is calculated as **true positives / (true positives + false positives)**.
- From 100 patients, 10 have disease (prevalence 10%). With 90% sensitivity, the test correctly identifies **9 true positives** (90% of 10).
- Of 90 patients without disease, specificity of 20% means 20% are correctly identified as negative (18 true negatives), so **72 false positives** = 90 × (1 - 0.20).
- Therefore, PPV = 9 / (9 + 72) = 9/81 = **11.1% ≈ 11%**.
*10%*
- This value represents the **prevalence** of the disease in the population, not the positive predictive value of the test.
- Prevalence is the proportion of individuals who have the disease (10 out of 100 patients).
*90%*
- This figure represents the **sensitivity** of the test, which is the percentage of true positives correctly identified by the experimental test.
- Sensitivity = true positives / (true positives + false negatives) = 9/10 = 90%.
*95%*
- This value is not directly derivable from the given data and does not represent any standard test characteristic in this context.
- It would imply a much higher PPV than what can be calculated given the low specificity of 20%.
*20%*
- This is the stated **specificity** of the test, which measures the proportion of true negatives correctly identified.
- Specificity = true negatives / (true negatives + false positives) = 18/90 = 20%.
Negative predictive value US Medical PG Question 5: A 6-month-old male presents for a routine visit to his pediatrician. Two months ago, the patient was seen for tachypnea and wheezing, and diagnosed with severe respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) bronchiolitis. After admission to the hospital and supportive care, the patient recovered and currently is not experiencing any trouble breathing. Regarding the possibility of future reactive airway disease, which of the following statements is most accurate?
- A. “There is no clear relationship between RSV and the development of asthma.”
- B. “Your child has a greater than 20% chance of developing asthma” (Correct Answer)
- C. “Your child’s risk of asthma is less than the general population.”
- D. “Your child has a less than 5% chance of developing asthma”
- E. “Your child’s risk of asthma is the same as the general population.”
Negative predictive value Explanation: ***“Your child has a greater than 20% chance of developing asthma”***
- Severe **RSV bronchiolitis** in infancy is a significant risk factor for the development of **recurrent wheezing** and **childhood asthma**.
- Studies estimate that a substantial proportion, often greater than 20%, of infants with severe RSV bronchiolitis will go on to develop **asthma** later in childhood.
*“There is no clear relationship between RSV and the development of asthma.”*
- This statement is incorrect as there is a **well-established link** between severe RSV infection in early life and an increased risk of developing **asthma**.
- Numerous epidemiological and longitudinal studies have documented this association.
*“Your child’s risk of asthma is less than the general population.”*
- This is incorrect, as severe RSV infection **increases** the risk of asthma, not decreases it.
- Children with a history of severe RSV have a **higher incidence** of asthma compared to the general pediatric population.
*“Your child has a less than 5% chance of developing asthma”*
- This percentage is **too low** given the known association between severe RSV bronchiolitis and subsequent asthma.
- The actual risk is considerably higher, typically falling into the range of 20-50% for those with severe RSV.
*“Your child’s risk of asthma is the same as the general population.”*
- This statement is inaccurate because severe RSV infection in infancy is a recognized independent **risk factor** for **asthma development**.
- Therefore, the child's risk is elevated above that of the general population.
Negative predictive value US Medical PG Question 6: You are reading through a recent article that reports significant decreases in all-cause mortality for patients with malignant melanoma following treatment with a novel biological infusion. Which of the following choices refers to the probability that a study will find a statistically significant difference when one truly does exist?
- A. Type II error
- B. Type I error
- C. Confidence interval
- D. p-value
- E. Power (Correct Answer)
Negative predictive value Explanation: ***Power***
- **Power** is the probability that a study will correctly reject the null hypothesis when it is, in fact, false (i.e., will find a statistically significant difference when one truly exists).
- A study with high power minimizes the risk of a **Type II error** (failing to detect a real effect).
*Type II error*
- A **Type II error** (or **beta error**) occurs when a study fails to reject a false null hypothesis, meaning it concludes there is no significant difference when one actually exists.
- This is the **opposite** of what the question describes, which asks for the probability of *finding* a difference.
*Type I error*
- A **Type I error** (or **alpha error**) occurs when a study incorrectly rejects a true null hypothesis, concluding there is a significant difference when one does not actually exist.
- This relates to the **p-value** and the level of statistical significance (e.g., p < 0.05).
*Confidence interval*
- A **confidence interval** provides a range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to lie with a certain degree of confidence (e.g., 95%).
- It does not directly represent the probability of finding a statistically significant difference when one truly exists.
*p-value*
- The **p-value** is the probability of observing data as extreme as, or more extreme than, that obtained in the study, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
- It is used to determine statistical significance, but it is not the probability of detecting a true effect.
Negative predictive value US Medical PG Question 7: Four days after undergoing an elective total hip replacement, a 65-year-old woman develops a DVT that embolizes to the lung. Along with tachypnea, tachycardia, and cough, the patient would most likely present with a PaO2 of what?
- A. 120 mmHg
- B. 100 mmHg
- C. 85 mmHg (Correct Answer)
- D. 110 mmHg
- E. 60 mmHg
Negative predictive value Explanation: ***85 mmHg***
- A pulmonary embolism (PE) causes a **ventilation-perfusion (V/Q) mismatch**, leading to **hypoxemia** and a reduced PaO2.
- While exact values vary, a PaO2 of 85 mmHg indicates **mild to moderate hypoxemia**, which is common in PE, especially with accompanying symptoms like tachypnea and tachycardia.
*120 mmHg*
- This value is significantly **higher than normal (75-100 mmHg)** and would indicate **hyperoxia**, which is inconsistent with acute pulmonary embolism causing respiratory distress.
- A patient with PE would typically have **reduced oxygenation**, not supernormal levels, unless receiving high-flow supplemental oxygen.
*100 mmHg*
- A PaO2 of 100 mmHg is at the **upper end of the normal range** (75-100 mmHg) and would imply **no significant hypoxemia**.
- Given the patient's symptoms of tachypnea, tachycardia, and cough following a DVT with embolization, a normal or high-normal PaO2 is unlikely without aggressive oxygen therapy (which is not stated).
*110 mmHg*
- This value is **above the normal range** and suggests **hyperoxia**, which is contrary to the pathophysiology of a pulmonary embolism.
- A PE impairs gas exchange, leading to a decrease in PaO2, not an increase.
*60 mmHg*
- A PaO2 of 60 mmHg indicates **significant hypoxemia**, which might occur in a severe, large pulmonary embolism or in a patient with underlying lung disease.
- While possible, 85 mmHg represents a more common, moderate hypoxemia seen in PE, especially given the prompt presentation of symptoms.
Negative predictive value US Medical PG Question 8: A pharmaceutical company develops a sequential testing protocol for a rare genetic disorder (prevalence 0.01%). Initial screening test has sensitivity 95% and specificity 90%. Positive results undergo confirmatory testing with sensitivity 99% and specificity 99.5%. The company claims this approach achieves PPV >80% for the final positive result. Evaluate this claim and the rationale for sequential testing in this context.
- A. The claim is true; sequential testing increases PPV by enriching the population tested in the second step (Correct Answer)
- B. The claim is false; sensitivity decreases with sequential testing, reducing PPV
- C. Sequential testing is unnecessary; the first test alone achieves adequate PPV
- D. The claim is false; sequential testing cannot achieve PPV >80% with such low prevalence
- E. The claim is true; the high specificity of the confirmatory test ensures high PPV regardless of prevalence
Negative predictive value Explanation: ***The claim is true; sequential testing increases PPV by enriching the population tested in the second step***
- Sequential testing works by increasing the **pre-test probability** for the second test, as the cohort being tested has already screened positive once.
- By applying a highly specific confirmatory test to this enriched group, the number of **false positives** is significantly reduced, which drastically improves the **Positive Predictive Value (PPV)**.
*The claim is false; sequential testing cannot achieve PPV >80% with such low prevalence*
- Even with a low **prevalence**, the multiplication of specificities in a sequential process can reduce the **False Positive** rate to a level where the PPV exceeds 80%.
- This line of reasoning ignores that the **denominator** of the PPV calculation (True Positives + False Positives) decreases much faster than the numerator during the second stage.
*The claim is true; the high specificity of the confirmatory test ensures high PPV regardless of prevalence*
- While high **specificity** is crucial, PPV is always dependent on the **prevalence** (pre-test probability) of the condition in the group being tested.
- The claim is true because sequential testing specifically raises that **pre-test probability**, not because prevalence is irrelevant to the calculation.
*The claim is false; sensitivity decreases with sequential testing, reducing PPV*
- It is true that **net sensitivity** decreases in sequential testing, but a decrease in sensitivity actually tends to have a negligible effect on PPV compared to specificity gains.
- **PPV** is primarily driven by the **specificity** and the prevalence in the tested population, both of which are optimized in this two-step protocol.
*Sequential testing is unnecessary; the first test alone achieves adequate PPV*
- Given a prevalence of 0.01% and 90% specificity, the **first test** alone would yield a massive amount of false positives, resulting in a very low PPV (~0.09%).
- A **confirmatory test** is clinically and ethically necessary to avoid wrongly diagnosing thousands of healthy individuals with a **rare genetic disorder**.
Negative predictive value US Medical PG Question 9: A hospital system is implementing a sepsis screening algorithm using clinical criteria with sensitivity of 92% and specificity of 75%. False positives result in unnecessary antibiotics, cultures, and ICU evaluations costing $3,000 per case. Missing true sepsis cases (false negatives) results in average increased mortality and morbidity costs of $50,000 per case. Hospital sepsis prevalence is 8%. Evaluate the optimal threshold adjustment strategy.
- A. Maintain current threshold as it balances sensitivity and specificity equally
- B. Implement risk stratification with different thresholds for different populations
- C. Abandon screening due to unacceptable false positive rate
- D. Increase threshold to improve specificity and reduce costs from false positives
- E. Decrease threshold to improve sensitivity despite more false positives (Correct Answer)
Negative predictive value Explanation: ***Decrease threshold to improve sensitivity despite more false positives***
- In sepsis screening, the **cost of a false negative** ($50,000) is nearly 17 times higher than the **cost of a false positive** ($3,000), necessitating a strategy that prioritizes **sensitivity** to minimize missed cases.
- Lowering the threshold further ensures fewer high-cost **mortality and morbidity** events occur, which is the most economically and clinically sound approach given the significant **weighted cost** of missing a diagnosis.
*Increase threshold to improve specificity and reduce costs from false positives*
- Increasing the threshold would increase the number of **false negatives**, leading to massive financial losses due to the $50,000 cost per missed **sepsis case**.
- While it reduces the $3,000 expense of unnecessary **antibiotics and cultures**, the savings are mathematically dwarfed by the increased costs of untreated sepsis.
*Maintain current threshold as it balances sensitivity and specificity equally*
- A balanced threshold is inappropriate when the **consequences of error types** are highly asymmetrical; the algorithm should favor the side with the more severe outcome.
- Simply balancing **sensitivity and specificity** fails to account for the 8% **prevalence** and the extreme disparity in costs between false positives and false negatives.
*Implement risk stratification with different thresholds for different populations*
- While risk stratification is useful, it does not address the fundamental need to minimize **false negatives** across the entire 8% prevalence population.
- This approach adds **operational complexity** without necessarily solving the primary economic imbalance between **screening costs** and mortality costs.
*Abandon screening due to unacceptable false positive rate*
- Abandoning screening would lead to an even higher rate of **missed sepsis cases**, resulting in catastrophic clinical outcomes and **increased hospital liability**.
- The current 75% **specificity** is acceptable because the clinical priority in sepsis is **early detection** to prevent rapid physiological deterioration.
Negative predictive value US Medical PG Question 10: A 58-year-old man with chronic cough undergoes evaluation for tuberculosis. A tuberculin skin test (TST) is positive (15mm induration). TST has sensitivity of 80% and specificity of 95% in immunocompetent adults. However, he received BCG vaccination as a child in Asia. Local TB prevalence is 0.5%, but his occupational exposure increases his pre-test probability to 10%. Evaluate the most appropriate interpretation and management approach.
- A. Calculate post-test probability and obtain interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA) (Correct Answer)
- B. Repeat TST in 2 weeks to confirm
- C. Treat empirically regardless of test characteristics
- D. Positive test confirms TB; start treatment immediately
- E. False positive due to BCG; no further testing needed
Negative predictive value Explanation: ***Calculate post-test probability and obtain interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA)***
- In individuals previously vaccinated with **BCG**, the **Tuberculin Skin Test (TST)** can yield **false positives** because the test cross-reacts with BCG antigens, whereas **IGRA** is more specific.
- Clinical decision-making requires integrating **pre-test probability** (10% in this case) with test characteristics to determine **post-test probability** before starting long-term therapy.
*Positive test confirms TB; start treatment immediately*
- A positive **TST** in a patient with a **BCG vaccination** history does not automatically confirm infection; it lacks the specificity to distinguish between vaccination and actual **Mycobacterium tuberculosis** infection.
- Starting **antitubercular therapy** immediately without ruling out a false positive or assessing for **active versus latent disease** violates standard diagnostic protocols.
*False positive due to BCG; no further testing needed*
- While **BCG** causes false positives, the patient’s **occupational exposure** and a significant **15mm induration** make infection plausible; dismissing the result is unsafe.
- High-risk individuals require definitive testing, usually via **IGRA**, to ensure **latent tuberculosis infection (LTBI)** is not overlooked.
*Repeat TST in 2 weeks to confirm*
- Repeating a **TST** within a short window can lead to the **booster effect**, where the second test appears positive due to immunological memory rather than new infection.
- Re-testing with the same diagnostic tool does not solve the underlying issue of **BCG cross-reactivity**; a different, more specific test is required.
*Treat empirically regardless of test characteristics*
- Empirical treatment ignores the potential for **medication toxicity** (e.g., hepatotoxicity from Isoniazid) in a patient who might not actually have **LTBI**.
- Evidence-based medicine requires utilizing **sensitivity, specificity, and prevalence** to justify treatment, especially when more specific tests like **IGRA** are available.
More Negative predictive value US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.