Bayes theorem application US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Bayes theorem application. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Bayes theorem application US Medical PG Question 1: A scientist in Chicago is studying a new blood test to detect Ab to EBV with increased sensitivity and specificity. So far, her best attempt at creating such an exam reached 82% sensitivity and 88% specificity. She is hoping to increase these numbers by at least 2 percent for each value. After several years of work, she believes that she has actually managed to reach a sensitivity and specificity much greater than what she had originally hoped for. She travels to China to begin testing her newest blood test. She finds 2,000 patients who are willing to participate in her study. Of the 2,000 patients, 1,200 of them are known to be infected with EBV. The scientist tests these 1,200 patients' blood and finds that only 120 of them tested negative with her new exam. Of the patients who are known to be EBV-free, only 20 of them tested positive. Given these results, which of the following correlates with the exam's specificity?
- A. 82%
- B. 90%
- C. 84%
- D. 86%
- E. 98% (Correct Answer)
Bayes theorem application Explanation: ***98%***
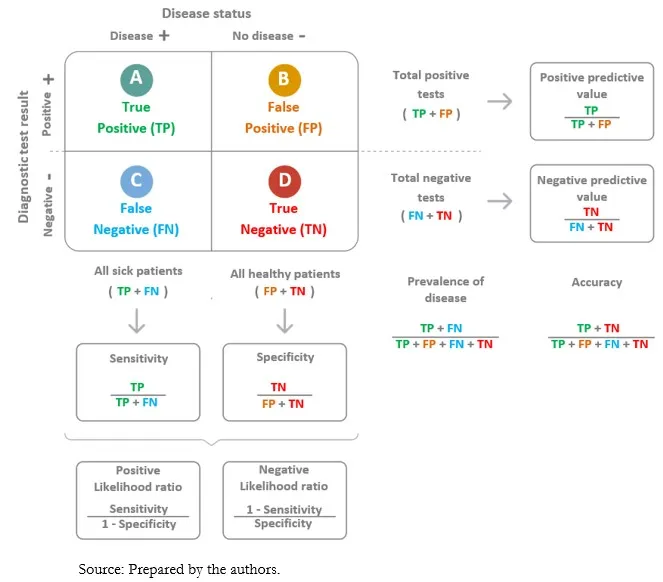
- **Specificity** measures the proportion of **true negatives** among all actual negatives.
- In this case, 800 patients are known to be EBV-free (actual negatives), and 20 of them tested positive (false positives). This means 800 - 20 = 780 tested negative (true negatives). Specificity = (780 / 800) * 100% = **98%**.
*82%*
- This value represents the *original sensitivity* before the scientist’s new attempts to improve the test.
- It does not reflect the *newly calculated specificity* based on the provided data.
*90%*
- This value represents the *newly calculated sensitivity* of the test, not the specificity.
- Out of 1200 EBV-infected patients, 120 tested negative (false negatives), meaning 1080 tested positive (true positives). Sensitivity = (1080 / 1200) * 100% = 90%.
*84%*
- This percentage is not directly derived from the information given for either sensitivity or specificity after the new test results.
- It does not correspond to any of the calculated values for the new test's performance.
*86%*
- This percentage is not directly derived from the information given for either sensitivity or specificity after the new test results.
- It does not correspond to any of the calculated values for the new test's performance.
Bayes theorem application US Medical PG Question 2: A 36-year-old female presents to clinic inquiring about the meaning of a previous negative test result from a new HIV screening test. The efficacy of this new screening test for HIV has been assessed by comparison against existing gold standard detection of HIV RNA via PCR. The study includes 1000 patients, with 850 HIV-negative patients (by PCR) receiving a negative test result, 30 HIV-negative patients receiving a positive test result, 100 HIV positive patients receiving a positive test result, and 20 HIV positive patients receiving a negative test result. Which of the following is most likely to increase the negative predictive value for this test?
- A. Decreased prevalence of HIV in the tested population (Correct Answer)
- B. Increased prevalence of HIV in the tested population
- C. Increased number of false positive test results
- D. Increased number of false negative test results
- E. Decreased number of false positive test results
Bayes theorem application Explanation: ***Decreased prevalence of HIV in the tested population***
- A **lower prevalence** of a disease in the population means there are fewer actual cases, making a **negative test result** more reliable in ruling out the disease.
- This increases the probability that a person with a negative test truly does not have the disease, thus elevating the **negative predictive value (NPV)**.
*Increased prevalence of HIV in the tested population*
- A **higher prevalence** means there are more actual cases of HIV in the population.
- In this scenario, a negative test result is less reassuring, as there's a greater chance of missing a true positive case, leading to a **decreased NPV**.
*Increased number of false positive test results*
- **False positives** are instances where a test indicates disease when it's not present; they do not directly impact the ability of a negative test to predict absence of disease.
- While they affect the **positive predictive value (PPV)**, they do not directly alter the reliability of a negative result to exclude disease, so the NPV is not increased.
*Increased number of false negative test results*
- **False negatives** occur when a test indicates no disease, but the disease is actually present.
- An increase in false negatives directly implies that a negative test result is less trustworthy, leading to a **decrease in the NPV**.
*Decreased number of false positive test results*
- A decrease in false positive results primarily improves the **positive predictive value (PPV)**.
- While it indicates a more accurate test overall, it does not directly affect NPV, which measures the reliability of a negative test result in ruling out disease.
Bayes theorem application US Medical PG Question 3: A 25-year-old man with a genetic disorder presents for genetic counseling because he is concerned about the risk that any children he has will have the same disease as himself. Specifically, since childhood he has had difficulty breathing requiring bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and chest physiotherapy. He has also had diarrhea and malabsorption requiring enzyme replacement therapy. If his wife comes from a population where 1 in 10,000 people are affected by this same disorder, which of the following best represents the likelihood a child would be affected as well?
- A. 0.01%
- B. 2%
- C. 0.5%
- D. 1% (Correct Answer)
- E. 50%
Bayes theorem application Explanation: ***Correct Option: 1%***
- The patient's symptoms (difficulty breathing requiring bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and chest physiotherapy; diarrhea and malabsorption requiring enzyme replacement therapy) are classic for **cystic fibrosis (CF)**, an **autosomal recessive disorder**.
- For an autosomal recessive disorder with a prevalence of 1 in 10,000 in the general population, **q² = 1/10,000**, so **q = 1/100 = 0.01**. The carrier frequency **(2pq)** is approximately **2q = 2 × (1/100) = 1/50 = 0.02**.
- The affected man is **homozygous recessive (aa)** and will always pass on the recessive allele. His wife has a **1/50 chance of being a carrier (Aa)**. If she is a carrier, she has a **1/2 chance of passing on the recessive allele**.
- Therefore, the probability of an affected child = **(Probability wife is a carrier) × (Probability wife passes recessive allele) = 1/50 × 1/2 = 1/100 = 1%**.
*Incorrect Option: 0.01%*
- This percentage is too low and does not correctly account for the carrier frequency in the population and the probability of transmission from a carrier mother.
*Incorrect Option: 2%*
- This represents approximately the carrier frequency (1/50 ≈ 2%), but does not account for the additional 1/2 probability that a carrier mother would pass on the recessive allele.
*Incorrect Option: 0.5%*
- This value would be correct if the carrier frequency were 1/100 instead of 1/50, which does not match the given population prevalence.
*Incorrect Option: 50%*
- **50%** would be the risk if both parents were carriers of an autosomal recessive disorder (1/4 chance = 25% for affected, but if we know one parent passes the allele, conditional probability changes). More accurately, 50% would apply if the disorder were **autosomal dominant** with one affected parent, which is not the case here.
Bayes theorem application US Medical PG Question 4: An infectious disease investigator is evaluating the diagnostic accuracy of a new interferon-gamma-based assay for diagnosing tuberculosis in patients who have previously received a Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) vaccine. Consenting participants with a history of BCG vaccination received an interferon-gamma assay and were subsequently evaluated for tuberculosis by sputum culture. Results of the study are summarized in the table below.
Tuberculosis, confirmed by culture No tuberculosis Total
Positive interferon-gamma assay 90 6 96
Negative interferon-gamma assay 10 194 204
Total 100 200 300
Based on these results, what is the sensitivity of the interferon-gamma-based assay for the diagnosis of tuberculosis in this study?
- A. 90/96
- B. 100/300
- C. 194/200
- D. 90/100 (Correct Answer)
- E. 194/204
Bayes theorem application Explanation: ***90/100***
- **Sensitivity** measures the proportion of **true positive** cases that are correctly identified by the test.
- In this study, there are 90 true positive results (positive interferon-gamma assay in patients with confirmed tuberculosis) out of a total of 100 individuals with confirmed tuberculosis (90 + 10).
*90/96*
- This calculation represents the **positive predictive value** (90 true positives / 96 total positive tests).
- It answers the question: "If the test is positive, what is the likelihood that the patient actually has the disease?"
*100/300*
- This value represents the prevalence of tuberculosis in the study population (100 confirmed cases / 300 total participants).
- It does not reflect a measure of the test's diagnostic accuracy.
*194/200*
- This value represents the **specificity** of the test (194 true negatives / 200 total individuals without tuberculosis).
- Specificity measures the proportion of true negative cases that are correctly identified by the test.
*194/204*
- This calculation represents the **negative predictive value** (194 true negatives / 204 total negative tests).
- It answers the question: "If the test is negative, what is the likelihood that the patient does not have the disease?"
Bayes theorem application US Medical PG Question 5: You are developing a new diagnostic test to identify patients with disease X. Of 100 patients tested with the gold standard test, 10% tested positive. Of those that tested positive, the experimental test was positive for 90% of those patients. The specificity of the experimental test is 20%. What is the positive predictive value of this new test?
- A. 10%
- B. 90%
- C. 95%
- D. 11% (Correct Answer)
- E. 20%
Bayes theorem application Explanation: ***11%***
- The positive predictive value (PPV) is calculated as **true positives / (true positives + false positives)**.
- From 100 patients, 10 have disease (prevalence 10%). With 90% sensitivity, the test correctly identifies **9 true positives** (90% of 10).
- Of 90 patients without disease, specificity of 20% means 20% are correctly identified as negative (18 true negatives), so **72 false positives** = 90 × (1 - 0.20).
- Therefore, PPV = 9 / (9 + 72) = 9/81 = **11.1% ≈ 11%**.
*10%*
- This value represents the **prevalence** of the disease in the population, not the positive predictive value of the test.
- Prevalence is the proportion of individuals who have the disease (10 out of 100 patients).
*90%*
- This figure represents the **sensitivity** of the test, which is the percentage of true positives correctly identified by the experimental test.
- Sensitivity = true positives / (true positives + false negatives) = 9/10 = 90%.
*95%*
- This value is not directly derivable from the given data and does not represent any standard test characteristic in this context.
- It would imply a much higher PPV than what can be calculated given the low specificity of 20%.
*20%*
- This is the stated **specificity** of the test, which measures the proportion of true negatives correctly identified.
- Specificity = true negatives / (true negatives + false positives) = 18/90 = 20%.
Bayes theorem application US Medical PG Question 6: You are reading through a recent article that reports significant decreases in all-cause mortality for patients with malignant melanoma following treatment with a novel biological infusion. Which of the following choices refers to the probability that a study will find a statistically significant difference when one truly does exist?
- A. Type II error
- B. Type I error
- C. Confidence interval
- D. p-value
- E. Power (Correct Answer)
Bayes theorem application Explanation: ***Power***
- **Power** is the probability that a study will correctly reject the null hypothesis when it is, in fact, false (i.e., will find a statistically significant difference when one truly exists).
- A study with high power minimizes the risk of a **Type II error** (failing to detect a real effect).
*Type II error*
- A **Type II error** (or **beta error**) occurs when a study fails to reject a false null hypothesis, meaning it concludes there is no significant difference when one actually exists.
- This is the **opposite** of what the question describes, which asks for the probability of *finding* a difference.
*Type I error*
- A **Type I error** (or **alpha error**) occurs when a study incorrectly rejects a true null hypothesis, concluding there is a significant difference when one does not actually exist.
- This relates to the **p-value** and the level of statistical significance (e.g., p < 0.05).
*Confidence interval*
- A **confidence interval** provides a range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to lie with a certain degree of confidence (e.g., 95%).
- It does not directly represent the probability of finding a statistically significant difference when one truly exists.
*p-value*
- The **p-value** is the probability of observing data as extreme as, or more extreme than, that obtained in the study, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
- It is used to determine statistical significance, but it is not the probability of detecting a true effect.
Bayes theorem application US Medical PG Question 7: A novel PET radiotracer is being evaluated for its ability to aid in the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The study decides to use a sample size of 1,000 patients, and half of the patients enrolled have AD. In the group of patients with AD, 400 are found positive on the novel type of PET imaging examination. In the control group, 50 are found positive. What is the PPV of this novel exam?
- A. 400 / (400+50) (Correct Answer)
- B. 450 / (450 + 100)
- C. 400 / (400+100)
- D. 450 / (450 + 50)
- E. 400 / (400 + 150)
Bayes theorem application Explanation: ***400 / (400+50)***
- The **Positive Predictive Value (PPV)** is the probability that subjects with a positive test result actually have the disease. It's calculated as **True Positives / (True Positives + False Positives)**.
- In this scenario, **True Positives** are 400 (patients with AD who tested positive), and **False Positives** are 50 (control patients without AD who tested positive).
*450 / (450 + 100)*
- This calculation incorrectly includes **False Negatives** (450, total AD patients - true positives) in the numerator or denominator for PPV, and misidentifies other components.
- The formula for PPV specifically focuses on positive test results and the proportion of those that are truly disease-positive.
*400 / (400+100)*
- This option correctly identifies **True Positives** as 400 but incorrectly assumes **False Positives** are 100.
- The problem states that 50 control patients (without AD) tested positive, which are the false positives.
*450 / (450 + 50)*
- This formula incorrectly uses **450** as the number of **True Positives**, which represents the total number of patients with AD testing positive and negative (400 TP + 100 FN).
- PPV only considers those who tested positive in its numerator.
*400 / (400 + 150)*
- While 400 is correctly identified as **True Positives**, the **False Positives** are incorrectly stated as 150.
- The problem explicitly states that 50 control patients were found positive, making 50 the correct number for false positives.
Bayes theorem application US Medical PG Question 8: A 14-month-old boy is brought in by his parents with an 8-month history of diarrhea, abdominal tenderness and concomitant failure to thrive. The pediatric attending physician believes that Crohn’s disease is the best explanation of this patient’s symptoms. Based on the pediatric attending physician’s experience, the pretest probability of this diagnosis is estimated at 40%. According to Fagan nomogram (see image). If the likelihood ratio of a negative test result (LR-) for Crohn’s disease is 0.04, what is the chance that this is the correct diagnosis in this patient with a negative test result?
- A. 40%
- B. 75%
- C. 97.5%
- D. 25%
- E. 2.5% (Correct Answer)
Bayes theorem application Explanation: ***2.5%***
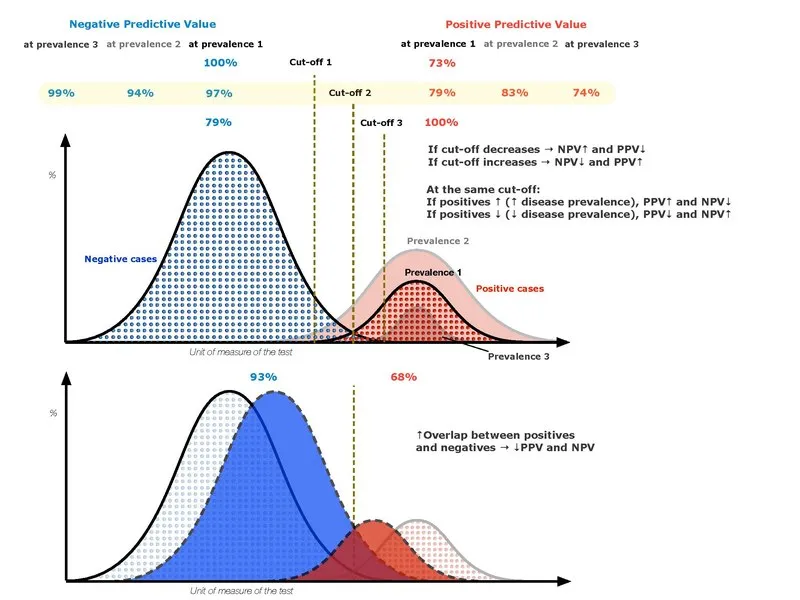
- Begin by locating the **pretest probability of 40%** on the left-hand scale of the **Fagan nomogram**
- Draw a line from this point through the **likelihood ratio negative (LR-) of 0.04** on the middle scale, extending it to the right-hand scale to find the **posttest probability of approximately 2.5%**
- This can be verified mathematically: pretest odds = 0.40/0.60 = 0.667; posttest odds = 0.667 × 0.04 = 0.027; posttest probability = 0.027/1.027 ≈ 2.6% (rounds to 2.5%)
*40%*
- This represents the **initial pretest probability** before incorporating the test result
- It does not account for the impact of the **negative test result** with an LR- of 0.04
- The Fagan nomogram is used to **update this probability** based on the test outcome
*75%*
- This value does not align with a **negative test result** and an **LR- of 0.04**
- A posttest probability higher than the pretest probability would require a positive test with an LR+ greater than 1
- With a negative test and LR- = 0.04, the probability must decrease significantly
*97.5%*
- This extremely high posttest probability would require a **positive test** with a very high **likelihood ratio positive (LR+)**
- It is completely inconsistent with a **negative test result** and a low LR- of 0.04
- An LR- of 0.04 indicates strong evidence against the disease, not for it
*25%*
- While this represents a decrease from the pretest probability of 40%, it underestimates the impact of the test result
- An **LR- of 0.04** means the odds of having the disease are reduced by a factor of 25 (multiplied by 0.04)
- This should yield a much lower posttest probability than 25%
Bayes theorem application US Medical PG Question 9: A 35-year-old woman volunteers for a study on respiratory physiology. Pressure probes A and B are placed as follows:
Probe A: between the parietal and visceral pleura
Probe B: within the cavity of an alveolus
The probes provide a pressure reading relative to atmospheric pressure. To obtain a baseline reading, she is asked to sit comfortably and breathe normally. Which of the following sets of values will most likely be seen at the end of inspiration?
- A. Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg (Correct Answer)
- B. Probe A: 0 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
- C. Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg
- D. Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
- E. Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg
Bayes theorem application Explanation: ***Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg***
- At the **end of inspiration**, the **intrapleural pressure (Probe A)** is at its most negative, typically around -6 to -8 cm H2O (equivalent to -4 to -6 mmHg), reflecting the maximum expansion of the thoracic cavity.
- At the **end of inspiration**, just before exhalation begins, there is **no airflow**, so the **intrapulmonary pressure (Probe B)** equalizes with atmospheric pressure, resulting in a 0 mm Hg reading.
*Probe A: 0 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- An **intrapleural pressure of 0 mm Hg** would indicate a **pneumothorax** since it should always be negative to prevent lung collapse.
- An **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** would indicate that **inspiration is still ongoing**, as air would be flowing into the lungs.
*Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: 0 mm Hg*
- While an **intrapulmonary pressure of 0 mm Hg** is correct at the end of inspiration, an **intrapleural pressure of -4 mm Hg** is typical for the **end of expiration (Functional Residual Capacity)** during quiet breathing, not the end of inspiration.
- The **intrapleural pressure becomes more negative** during inspiration due to increased thoracic volume, so -4 mm Hg would be insufficient.
*Probe A: -4 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- An **intrapleural pressure of -4 mm Hg** is the normal pressure at the **end of expiration**, not the end of inspiration, where it becomes more negative.
- An **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** indicates that **inspiration is still in progress**, not at its end, as air would still be flowing into the lungs.
*Probe A: -6 mm Hg; Probe B: -1 mm Hg*
- While an **intrapleural pressure of -6 mm Hg** is consistent with the end of inspiration, an **intrapulmonary pressure of -1 mm Hg** means that **airflow is still occurring into the lungs**.
- At the **very end of inspiration**, just before the start of exhalation, airflow momentarily ceases, and intrapulmonary pressure becomes zero relative to the atmosphere.
Bayes theorem application US Medical PG Question 10: You are reviewing raw data from a research study performed at your medical center examining the effectiveness of a novel AIDS screening examination. The study enrolled 250 patients with confirmed AIDS, and 240 of these patients demonstrated a positive screening examination. The control arm of the study enrolled 250 patients who do not have AIDS, and only 5 of these patients tested positive on the novel screening examination. What is the NPV of this novel test?
- A. 240 / (240 + 15)
- B. 240 / (240 + 5)
- C. 240 / (240 + 10)
- D. 245 / (245 + 10) (Correct Answer)
- E. 245 / (245 + 5)
Bayes theorem application Explanation: ***245 / (245 + 10)***
- The **negative predictive value (NPV)** is calculated as **true negatives (TN)** divided by the sum of **true negatives (TN)** and **false negatives (FN)**.
- In this study, there are 250 patients with AIDS; 240 tested positive (true positives, TP), meaning 10 tested negative (false negatives, FN = 250 - 240). There are 250 patients without AIDS; 5 tested positive (false positives, FP), meaning 245 tested negative (true negatives, TN = 250 - 5). Therefore, NPV = 245 / (245 + 10).
*240 / (240 + 15)*
- This calculation incorrectly uses the number of **true positives** (240) in the numerator and denominator, which is relevant for **positive predictive value (PPV)**, not NPV.
- The denominator `(240 + 15)` does not correspond to a valid sum for calculating NPV from the given data.
*240 / (240 + 5)*
- This calculation incorrectly uses **true positives** (240) in the numerator, which is not part of the NPV formula.
- The denominator `(240 + 5)` mixes true positives and false positives, which is incorrect for NPV.
*240 / (240 + 10)*
- This incorrectly places **true positives** (240) in the numerator instead of **true negatives**.
- The denominator `(240+10)` represents **true positives + false negatives**, which is related to sensitivity, not NPV.
*245 / (245 + 5)*
- This calculation correctly identifies **true negatives** (245) in the numerator but incorrectly uses **false positives** (5) in the denominator instead of **false negatives**.
- The denominator for NPV should be **true negatives + false negatives**, which is 245 + 10.
More Bayes theorem application US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.