Inferential statistics US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Inferential statistics. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Inferential statistics US Medical PG Question 1: You are conducting a study comparing the efficacy of two different statin medications. Two groups are placed on different statin medications, statin A and statin B. Baseline LDL levels are drawn for each group and are subsequently measured every 3 months for 1 year. Average baseline LDL levels for each group were identical. The group receiving statin A exhibited an 11 mg/dL greater reduction in LDL in comparison to the statin B group. Your statistical analysis reports a p-value of 0.052. Which of the following best describes the meaning of this p-value?
- A. There is a 95% chance that the difference in reduction of LDL observed reflects a real difference between the two groups
- B. Though A is more effective than B, there is a 5% chance the difference in reduction of LDL between the two groups is due to chance
- C. If 100 permutations of this experiment were conducted, 5 of them would show similar results to those described above
- D. This is a statistically significant result
- E. There is a 5.2% chance of observing a difference in reduction of LDL of 11 mg/dL or greater even if the two medications have identical effects (Correct Answer)
Inferential statistics Explanation: **There is a 5.2% chance of observing a difference in reduction of LDL of 11 mg/dL or greater even if the two medications have identical effects**
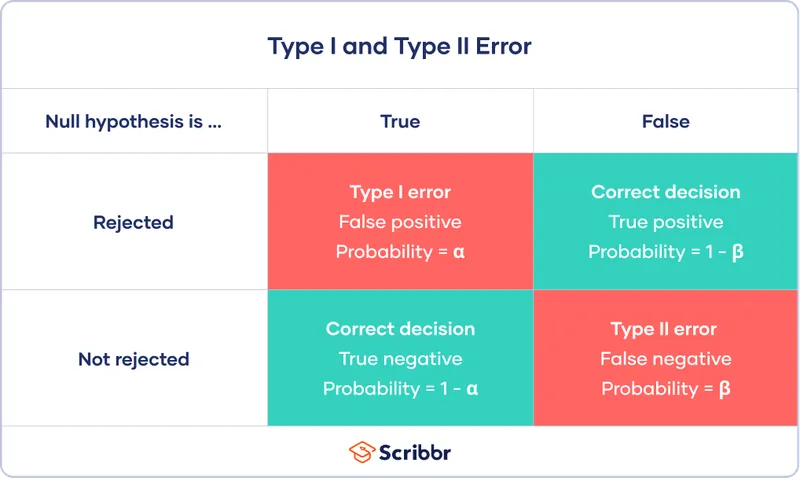
- The **p-value** represents the probability of observing results as extreme as, or more extreme than, the observed data, assuming the **null hypothesis** is true (i.e., there is no true difference between the groups).
- A p-value of 0.052 means there's approximately a **5.2% chance** that the observed 11 mg/dL difference (or a more substantial difference) occurred due to **random variation**, even if both statins were equally effective.
*There is a 95% chance that the difference in reduction of LDL observed reflects a real difference between the two groups*
- This statement is an incorrect interpretation of the p-value; it confuses the p-value with the **probability that the alternative hypothesis is true**.
- A p-value does not directly tell us the probability that the observed difference is "real" or due to the intervention being studied.
*Though A is more effective than B, there is a 5% chance the difference in reduction of LDL between the two groups is due to chance*
- This statement implies that Statin A is more effective, which cannot be concluded with a p-value of 0.052 if the significance level (alpha) was set at 0.05.
- While it's true there's a chance the difference is due to chance, claiming A is "more effective" based on this p-value before statistical significance is usually declared is misleading.
*If 100 permutations of this experiment were conducted, 5 of them would show similar results to those described above*
- This is an incorrect interpretation. The p-value does not predict the outcome of repeated experiments in this manner.
- It refers to the **probability under the null hypothesis in a single experiment**, not the frequency of results across multiple hypothetical repetitions.
*This is a statistically significant result*
- A p-value of 0.052 is generally considered **not statistically significant** if the conventional alpha level (significance level) is set at 0.05 (or 5%).
- For a result to be statistically significant at alpha = 0.05, the p-value must be **less than 0.05**.
Inferential statistics US Medical PG Question 2: A 25-year-old man with a genetic disorder presents for genetic counseling because he is concerned about the risk that any children he has will have the same disease as himself. Specifically, since childhood he has had difficulty breathing requiring bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and chest physiotherapy. He has also had diarrhea and malabsorption requiring enzyme replacement therapy. If his wife comes from a population where 1 in 10,000 people are affected by this same disorder, which of the following best represents the likelihood a child would be affected as well?
- A. 0.01%
- B. 2%
- C. 0.5%
- D. 1% (Correct Answer)
- E. 50%
Inferential statistics Explanation: ***Correct Option: 1%***
- The patient's symptoms (difficulty breathing requiring bronchodilators, inhaled corticosteroids, and chest physiotherapy; diarrhea and malabsorption requiring enzyme replacement therapy) are classic for **cystic fibrosis (CF)**, an **autosomal recessive disorder**.
- For an autosomal recessive disorder with a prevalence of 1 in 10,000 in the general population, **q² = 1/10,000**, so **q = 1/100 = 0.01**. The carrier frequency **(2pq)** is approximately **2q = 2 × (1/100) = 1/50 = 0.02**.
- The affected man is **homozygous recessive (aa)** and will always pass on the recessive allele. His wife has a **1/50 chance of being a carrier (Aa)**. If she is a carrier, she has a **1/2 chance of passing on the recessive allele**.
- Therefore, the probability of an affected child = **(Probability wife is a carrier) × (Probability wife passes recessive allele) = 1/50 × 1/2 = 1/100 = 1%**.
*Incorrect Option: 0.01%*
- This percentage is too low and does not correctly account for the carrier frequency in the population and the probability of transmission from a carrier mother.
*Incorrect Option: 2%*
- This represents approximately the carrier frequency (1/50 ≈ 2%), but does not account for the additional 1/2 probability that a carrier mother would pass on the recessive allele.
*Incorrect Option: 0.5%*
- This value would be correct if the carrier frequency were 1/100 instead of 1/50, which does not match the given population prevalence.
*Incorrect Option: 50%*
- **50%** would be the risk if both parents were carriers of an autosomal recessive disorder (1/4 chance = 25% for affected, but if we know one parent passes the allele, conditional probability changes). More accurately, 50% would apply if the disorder were **autosomal dominant** with one affected parent, which is not the case here.
Inferential statistics US Medical PG Question 3: A group of researchers is looking to study the effect of body weight on blood pressure in the elderly. Previous work measuring body weight and blood pressure at 2-time points in a large group of healthy individuals revealed that a 10% increase in body weight was accompanied by a 7 mm Hg increase in blood pressure. If the researchers want to determine if there is a linear relationship between body weight and blood pressure in a subgroup of elderly individuals in this study, which of the following statistical methods would best be employed to answer this question?
- A. Spearman’s correlation
- B. Pearson’s correlation (Correct Answer)
- C. One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)
- D. Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)
- E. Wilcoxon signed-rank test
Inferential statistics Explanation: ***Pearson’s correlation***
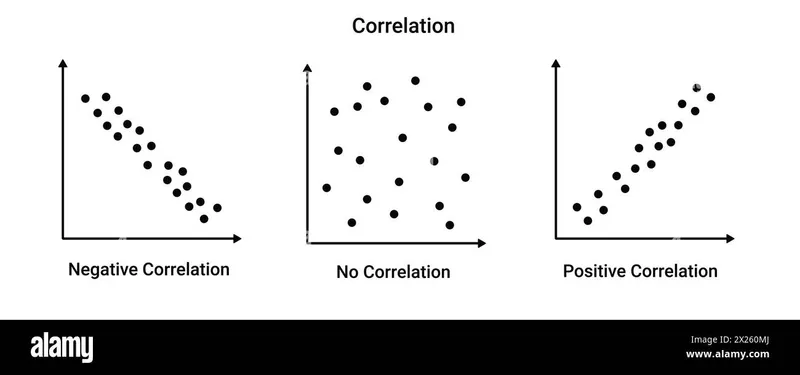
- **Pearson's correlation coefficient** measures the **strength and direction of a linear relationship between two continuous variables**. In this case, both body weight and blood pressure are continuous variables, and the researchers are looking for a *linear relationship*.
- The prior work also suggests a linear relationship ("a 10% increase in body weight was accompanied by a 7 mm Hg increase in blood pressure"), making Pearson's correlation the most appropriate choice to investigate this in a subgroup.
*Spearman’s correlation*
- **Spearman's correlation** measures the **strength and direction of a monotonic relationship (not necessarily linear) between two ranked variables or continuous variables that do not meet the assumptions for Pearson's correlation (e.g., non-normal distribution, outliers).**
- Since the question specifies a "linear relationship" and does not suggest violations of Pearson's assumptions, it is less appropriate than Pearson's.
*One-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)*
- **One-way ANOVA** is used to compare the **means of three or more independent groups** on a single continuous dependent variable.
- This method is not suitable because the researchers are investigating the relationship between two continuous variables (body weight and blood pressure), not comparing means across different discrete groups.
*Two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA)*
- **Two-way ANOVA** is used to examine the **effect of two categorical independent variables on a continuous dependent variable** and to assess any interaction between the two independent variables.
- Similar to one-way ANOVA, this test is inappropriate for determining the linear relationship between two continuous variables.
*Wilcoxon signed-rank test*
- The **Wilcoxon signed-rank test** is a **non-parametric test** used to compare two dependent (paired) samples, or to compare a single sample to a hypothesized median. It assesses whether two related samples differ in their ranks.
- This test is not suitable for investigating the linear relationship between two continuous variables in a single group of individuals.
Inferential statistics US Medical PG Question 4: You are reading through a recent article that reports significant decreases in all-cause mortality for patients with malignant melanoma following treatment with a novel biological infusion. Which of the following choices refers to the probability that a study will find a statistically significant difference when one truly does exist?
- A. Type II error
- B. Type I error
- C. Confidence interval
- D. p-value
- E. Power (Correct Answer)
Inferential statistics Explanation: ***Power***
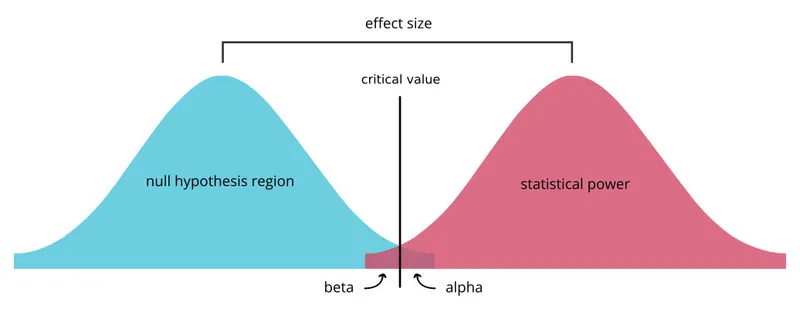
- **Power** is the probability that a study will correctly reject the null hypothesis when it is, in fact, false (i.e., will find a statistically significant difference when one truly exists).
- A study with high power minimizes the risk of a **Type II error** (failing to detect a real effect).
*Type II error*
- A **Type II error** (or **beta error**) occurs when a study fails to reject a false null hypothesis, meaning it concludes there is no significant difference when one actually exists.
- This is the **opposite** of what the question describes, which asks for the probability of *finding* a difference.
*Type I error*
- A **Type I error** (or **alpha error**) occurs when a study incorrectly rejects a true null hypothesis, concluding there is a significant difference when one does not actually exist.
- This relates to the **p-value** and the level of statistical significance (e.g., p < 0.05).
*Confidence interval*
- A **confidence interval** provides a range of values within which the true population parameter is likely to lie with a certain degree of confidence (e.g., 95%).
- It does not directly represent the probability of finding a statistically significant difference when one truly exists.
*p-value*
- The **p-value** is the probability of observing data as extreme as, or more extreme than, that obtained in the study, assuming the null hypothesis is true.
- It is used to determine statistical significance, but it is not the probability of detecting a true effect.
Inferential statistics US Medical PG Question 5: A neuro-oncology investigator has recently conducted a randomized controlled trial in which the addition of a novel alkylating agent to radiotherapy was found to prolong survival in comparison to radiotherapy alone (HR = 0.7, p < 0.01). A number of surviving participants who took the alkylating agent reported that they had experienced significant nausea from the medication. The investigator surveyed all participants in both the treatment and the control group on their nausea symptoms by self-report rated mild, moderate, or severe. The investigator subsequently compared the two treatment groups with regards to nausea level.
| | Mild nausea | Moderate nausea | Severe nausea |
|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment group (%) | 20 | 30 | 50 |
| Control group (%) | 35 | 35 | 30 |
Which of the following statistical methods would be most appropriate to assess the statistical significance of these results?
- A. Chi-square test (Correct Answer)
- B. Pearson correlation coefficient
- C. Multiple logistic regression
- D. Unpaired t-test
- E. Paired t-test
Inferential statistics Explanation: **Chi-square test**
- The **Chi-square test** is appropriate for comparing **categorical data** (mild, moderate, severe) between two or more independent groups (treatment vs. control).
- It assesses whether there is a statistically significant association between the two categorical variables (treatment group and nausea severity).
*Pearson correlation coefficient*
- The **Pearson correlation coefficient** is used to measure the **linear relationship** between two **continuous variables**.
- Nausea severity (mild, moderate, severe) is an **ordinal categorical variable**, not a continuous one.
*Multiple logistic regression*
- **Multiple logistic regression** is used to predict a **binary outcome** (e.g., presence or absence of nausea) based on one or more independent variables, which can be continuous or categorical.
- The outcome here is **ordinal categorical** (mild, moderate, severe nausea), not binary. While logistic regression can be adapted for ordinal outcomes, a simpler Chi-square test is more direct for comparing distributions without prediction.
*Unpaired t-test*
- An **unpaired t-test** is used to compare the **means of two independent continuous variables**.
- Nausea levels are categorical, and we are interested in comparing proportions within categories, not means.
*Paired t-test*
- A **paired t-test** is used to compare the **means of two related (paired) continuous variables**.
- The study involves independent treatment and control groups, and the nausea data is categorical, making the paired t-test unsuitable.
Inferential statistics US Medical PG Question 6: The height of American adults is expected to follow a normal distribution, with a typical male adult having an average height of 69 inches with a standard deviation of 0.1 inches. An investigator has been informed about a community in the American Midwest with a history of heavy air and water pollution in which a lower mean height has been reported. The investigator plans to sample 30 male residents to test the claim that heights in this town differ significantly from the national average based on heights assumed be normally distributed. The significance level is set at 10% and the probability of a type 2 error is assumed to be 15%. Based on this information, which of the following is the power of the proposed study?
- A. 0.10
- B. 0.85 (Correct Answer)
- C. 0.90
- D. 0.15
- E. 0.05
Inferential statistics Explanation: ***0.85***
- **Power** is defined as **1 - β**, where β is the **probability of a Type II error**.
- Given that the probability of a **Type II error (β)** is 15% or 0.15, the power of the study is 1 - 0.15 = **0.85**.
*0.10*
- This value represents the **significance level (α)**, which is the probability of committing a **Type I error** (rejecting a true null hypothesis).
- The significance level is distinct from the **power of the study**, which relates to Type II errors.
*0.90*
- This value would be the power if the **Type II error rate (β)** was 0.10 (1 - 0.10 = 0.90), but the question specifies a β of 0.15.
- It is also the complement of the significance level (1 - α), which is not the definition of power.
*0.15*
- This value is the **probability of a Type II error (β)**, not the power of the study.
- **Power** is the probability of correctly rejecting a false null hypothesis, which is 1 - β.
*0.05*
- While 0.05 is a common significance level (α), it is not given as the significance level in this question (which is 0.10).
- This value also does not represent the power of the study, which would be calculated using the **Type II error rate**.
Inferential statistics US Medical PG Question 7: In 2013 the national mean score on the USMLE Step 1 exam was 227 with a standard deviation of 22. Assuming that the scores for 15,000 people follow a normal distribution, approximately how many students scored above the mean but below 250?
- A. 5,100 (Correct Answer)
- B. 4,500
- C. 6,000
- D. 3,750
- E. 6,750
Inferential statistics Explanation: ***5,100***
- To solve this, first calculate the **z-score** for 250: (250 - 227) / 22 = 1.045.
- Using a **z-table**, the area under the curve from the mean (z=0) to z=1.045 is approximately 0.353. Multiplying this by 15,000 students gives approximately **5,295 students**, which is closest to 5,100.
*4,500*
- This answer would imply a smaller proportion of students between the mean and 250 (around 30%), which is lower than the calculated z-score of 1.045 suggests.
- It does not accurately reflect the area under the **normal distribution curve** for the given range.
*6,000*
- This option would mean that approximately 40% of students scored in this range, which would correspond to a z-score much higher than 1.045 or a different standard deviation.
- This calculation overestimates the number of students within the specified range.
*3,750*
- This value represents 25% of the total students (15,000 * 0.25), indicating that only a quarter of the distribution lies in this range.
- This significantly underestimates the proportion of students scoring between the mean and 250 for the given standard deviation.
*6,750*
- This option reflects approximately 45% of the total student population (15,000 * 0.45), which would correspond to a much larger z-score or a different distribution.
- This value is an overestimation and does not align with the standard normal distribution probabilities for the given parameters.
Inferential statistics US Medical PG Question 8: A child is learning the steps of hand hygiene. Which domain of learning is primarily involved?
- A. Cognitive
- B. Affective
- C. Psychomotor (Correct Answer)
- D. Affective & cognitive
- E. Cognitive & Psychomotor
Inferential statistics Explanation: ***Psychomotor***
- The **psychomotor domain** involves the acquisition of skills that require coordination of mental and physical activities, such as performing a physical task like hand hygiene.
- This domain focuses on the ability to carry out **physical movements** with precision and coordination.
*Cognitive*
- The **cognitive domain** primarily deals with intellectual understanding, knowledge, and problem-solving, which would involve understanding *why* hand hygiene is important, not the physical act itself.
- While essential for appreciating the *rationale* behind the steps, it does not encompass the *execution* of the skill.
*Affective*
- The **affective domain** relates to emotions, attitudes, values, and appreciation for the task, such as a child's **willingness to perform hand hygiene**.
- It involves feelings and motivations rather than the physical or intellectual mastery of a skill.
*Affective & cognitive*
- While both affective (motivation, willingness) and cognitive (understanding the importance) domains play a supportive role, neither directly addresses the **physical execution** of the learned steps.
- The primary domain for *learning the steps* (i.e., actually performing the actions) is psychomotor.
*Cognitive & Psychomotor*
- While both cognitive (understanding) and psychomotor (physical execution) domains are involved in the overall learning process, the question specifically asks about **learning the steps**, which primarily emphasizes the **psychomotor** aspect.
- The cognitive component is foundational but secondary to the actual motor skill acquisition being described.
Inferential statistics US Medical PG Question 9: A 46-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up evaluation one week after being discharged from the hospital for acute pancreatitis and alcohol withdrawal. He drinks 8 to 10 beers daily. When the physician asks him about his alcohol use, the patient says, “This is the second time in a year that I have experienced such severe belly pain because of my pancreas. I realize that it really could be happening because of the amount of alcohol I am drinking. However, I don't think I have the willpower to cut down.” This patient is most likely in which of the following stages of behavioral change?
- A. Action
- B. Precontemplation
- C. Preparation
- D. Maintenance
- E. Contemplation (Correct Answer)
Inferential statistics Explanation: ***Contemplation***
- The patient **acknowledges** the problem ("realize that it really could be happening because of the amount of alcohol I am drinking") and considers the link between his behavior and health issues.
- He expresses an intent to change but also feelings of **ambivalence** or a lack of willpower ("I don't think I have the willpower to cut down"), which are hallmarks of this stage.
*Action*
- This stage involves **actively modifying behavior**, environment, or experiences to overcome the problem.
- The patient has not yet taken concrete steps to cut down on alcohol, indicating he is not in this stage.
*Precontemplation*
- In this stage, individuals are **unaware or unwilling to acknowledge** that a problem exists.
- The patient clearly recognizes the problem and its consequences, ruling out precontemplation.
*Preparation*
- This stage involves **planning for change** and making small, tentative steps towards the desired behavior.
- While he expresses a desire to change, he hasn't articulated a concrete plan or taken any preparatory actions.
*Maintenance*
- This stage focuses on **sustaining the new behavior** and preventing relapse.
- The patient has not yet initiated the change, so he cannot be in the maintenance stage.
Inferential statistics US Medical PG Question 10: A 37-year-old man comes to the emergency department with his wife because of a 3-day history of severe pain in his right arm. He also reports that he cannot move his right arm. The symptoms began after the patient woke up one morning, having slept on his side. He is otherwise healthy. He works as a waiter and says that he feels exhausted from working several night shifts per week. He adds that he “can barely keep his eyes open” when looking after their daughter the next day. Since the onset of the pain, he has been unable to work and is fully dependent on his wife, who took an extra shift to make enough money to pay their monthly bills. The patient appears relaxed but only allows himself to be examined after his wife convinces him. His vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows 1/5 muscle strength in the right arm. Reflexes are normal. He has no sensation to light touch over the entire right arm and forearm. When a pin prick test is conducted, the patient rapidly withdraws the right arm. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Malingering (Correct Answer)
- B. Factitious disorder
- C. Radial nerve palsy
- D. Illness anxiety disorder
- E. Brachial neuritis
Inferential statistics Explanation: ***Malingering***
- The patient's presentation with **selective symptoms** (no sensation but rapid withdrawal from pinprick) and the **secondary gain** (avoiding work, dependence on wife for bills) are classic signs of malingering.
- The patient appears *relaxed* despite "severe pain" and only allows examination after persuasion, suggesting a **conscious fabrication of symptoms** for an external incentive.
*Factitious disorder*
- Involves the **deceptive production of symptoms** in oneself or others, but the primary motivation is to assume the **sick role**, without obvious external rewards.
- The patient in this scenario clearly benefits from avoiding work, which points away from factitious disorder.
*Radial nerve palsy*
- Would present with a specific **motor and sensory deficit pattern** corresponding to the radial nerve distribution, typically **wrist drop** and sensory loss over the dorsum of the hand.
- The patient's reported "entire right arm and forearm" sensory loss and paradoxical withdrawal to pinprick are inconsistent with a true neurological lesion.
*Illness anxiety disorder*
- Involves **preoccupations with having or acquiring a serious illness** despite minimal or no somatic symptoms, and is characterized by high levels of anxiety about health.
- This patient's presentation is more about symptom production for an external gain rather than anxiety about disease or actual illness.
*Brachial neuritis*
- Typically causes **severe pain** followed by **weakness and muscle atrophy** in the muscles innervated by the brachial plexus, but the sensory loss typically follows a dermatomal or nerve distribution.
- The reported global sensory loss in the entire arm and forearm, with preserved reflexes and paradoxical withdrawal to pinprick, is inconsistent with a specific nerve inflammation or damage.
More Inferential statistics US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.