Hypothesis testing US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Hypothesis testing. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Hypothesis testing US Medical PG Question 1: A research team develops a new monoclonal antibody checkpoint inhibitor for advanced melanoma that has shown promise in animal studies as well as high efficacy and low toxicity in early phase human clinical trials. The research team would now like to compare this drug to existing standard of care immunotherapy for advanced melanoma. The research team decides to conduct a non-randomized study where the novel drug will be offered to patients who are deemed to be at risk for toxicity with the current standard of care immunotherapy, while patients without such risk factors will receive the standard treatment. Which of the following best describes the level of evidence that this study can offer?
- A. Level 1
- B. Level 3 (Correct Answer)
- C. Level 5
- D. Level 4
- E. Level 2
Hypothesis testing Explanation: ***Level 3***
- A **non-randomized controlled trial** like the one described, where patient assignment to treatment groups is based on specific characteristics (risk of toxicity), falls into Level 3 evidence.
- This level typically includes **non-randomized controlled trials** and **well-designed cohort studies** with comparison groups, which are prone to selection bias and confounding.
- The study compares two treatments but lacks randomization, making it Level 3 evidence.
*Level 1*
- Level 1 evidence is the **highest level of evidence**, derived from **systematic reviews and meta-analyses** of multiple well-designed randomized controlled trials or large, high-quality randomized controlled trials.
- The described study is explicitly stated as non-randomized, ruling out Level 1.
*Level 2*
- Level 2 evidence involves at least one **well-designed randomized controlled trial** (RCT) or **systematic reviews** of randomized trials.
- The current study is *non-randomized*, which means it cannot be classified as Level 2 evidence, as randomization is a key criterion for this level.
*Level 4*
- Level 4 evidence includes **case series**, **case-control studies**, and **poorly designed cohort or case-control studies**.
- While the study is non-randomized, it is a controlled comparative trial rather than a case series or retrospective case-control study, placing it at Level 3.
*Level 5*
- Level 5 evidence is the **lowest level of evidence**, typically consisting of **expert opinion** without explicit critical appraisal, or based on physiology, bench research, or animal studies.
- While the drug was initially tested in animal studies, the current human comparative study offers a higher level of evidence than expert opinion or preclinical data.
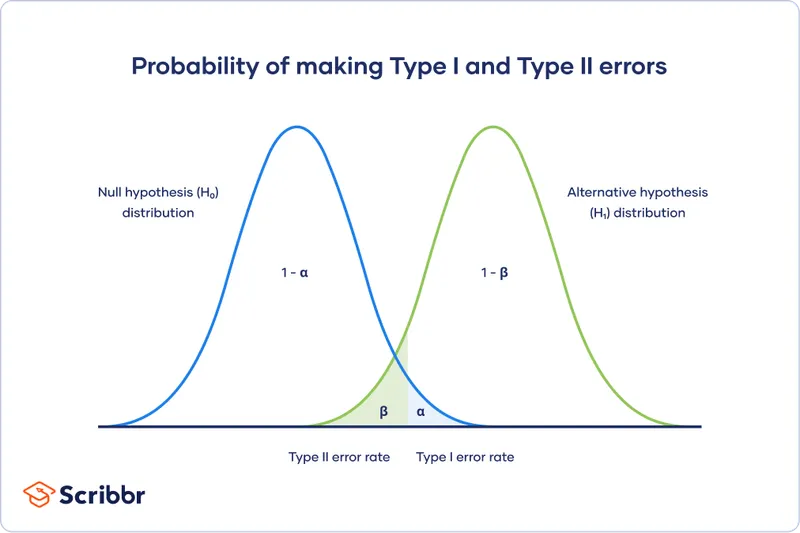
Hypothesis testing US Medical PG Question 2: A randomized control double-blind study is conducted on the efficacy of 2 sulfonylureas. The study concluded that medication 1 was more efficacious in lowering fasting blood glucose than medication 2 (p ≤ 0.05; 95% CI: 14 [10-21]). Which of the following is true regarding a 95% confidence interval (CI)?
- A. If the same study were repeated multiple times, approximately 95% of the calculated confidence intervals would contain the true population parameter. (Correct Answer)
- B. The 95% confidence interval is the probability chosen by the researcher to be the threshold of statistical significance.
- C. When a 95% CI for the estimated difference between groups contains the value ‘0’, the results are significant.
- D. It represents the probability that chance would not produce the difference shown, 95% of the time.
- E. The study is adequately powered at the 95% confidence interval.
Hypothesis testing Explanation: ***If the same study were repeated multiple times, approximately 95% of the calculated confidence intervals would contain the true population parameter.***
- This statement accurately defines the **frequentist interpretation** of a confidence interval (CI). It reflects the long-run behavior of the CI over hypothetical repetitions of the study.
- A 95% CI means that if you were to repeat the experiment many times, 95% of the CIs calculated from those experiments would capture the **true underlying population parameter**.
*The 95% confidence interval is the probability chosen by the researcher to be the threshold of statistical significance.*
- The **alpha level (α)**, typically set at 0.05 (or 5%), is the threshold for statistical significance (p ≤ 0.05), representing the probability of a Type I error.
- The 95% confidence level (1-α) is related to statistical significance, but it is not the *threshold* itself; rather, it indicates the **reliability** of the interval estimate.
*When a 95% CI for the estimated difference between groups contains the value ‘0’, the results are significant.*
- If a 95% CI for the difference between groups **contains 0**, it implies that there is **no statistically significant difference** between the groups at the 0.05 alpha level.
- A statistically significant difference (p ≤ 0.05) would be indicated if the 95% CI **does NOT contain 0**, suggesting that the intervention had a real effect.
*It represents the probability that chance would not produce the difference shown, 95% of the time.*
- This statement misinterprets the meaning of a CI and probability. The chance of not producing the observed difference is typically addressed by the **p-value**, not directly by the CI in this manner.
- A CI provides a **range of plausible values** for the population parameter, not a probability about the role of chance in producing the observed difference.
*The study is adequately powered at the 95% confidence interval.*
- **Statistical power** is the probability of correctly rejecting a false null hypothesis, typically set at 80% or 90%. It is primarily determined by sample size, effect size, and alpha level.
- A 95% CI is a measure of the **precision** of an estimate, while power refers to the **ability of a study to detect an effect** if one exists. They are related but distinct concepts.
Hypothesis testing US Medical PG Question 3: A researcher is trying to determine whether a newly discovered substance X can be useful in promoting wound healing after surgery. She conducts this study by enrolling the next 100 patients that will be undergoing this surgery and separating them into 2 groups. She decides which patient will be in which group by using a random number generator. Subsequently, she prepares 1 set of syringes with the novel substance X and 1 set of syringes with a saline control. Both of these sets of syringes are unlabeled and the substances inside cannot be distinguished. She gives the surgeon performing the surgery 1 of the syringes and does not inform him nor the patient which syringe was used. After the study is complete, she analyzes all the data that was collected and performs statistical analysis. This study most likely provides which level of evidence for use of substance X?
- A. Level 3
- B. Level 1 (Correct Answer)
- C. Level 4
- D. Level 5
- E. Level 2
Hypothesis testing Explanation: ***Level 1***
- The study design described is a **randomized controlled trial (RCT)**, which is considered the **highest level of evidence (Level 1)** in the hierarchy of medical evidence.
- Key features like **randomization**, **control group**, and **blinding (double-blind)** help minimize bias and strengthen the validity of the findings.
*Level 2*
- Level 2 evidence typically comprises **well-designed controlled trials without randomization** (non-randomized controlled trials) or **high-quality cohort studies**.
- While strong, they do not possess the same level of internal validity as randomized controlled trials.
*Level 3*
- Level 3 evidence typically includes **case-control studies** or **cohort studies**, which are observational designs and carry a higher risk of bias compared to RCTs.
- These studies generally do not involve randomization or intervention assignment by the researchers.
*Level 4*
- Level 4 evidence is usually derived from **case series** or **poor quality cohort and case-control studies**.
- These studies provide descriptive information or investigate associations without strong control for confounding factors.
*Level 5*
- Level 5 evidence is the **lowest level of evidence**, consisting of **expert opinion** or **animal research/bench research**.
- This level lacks human clinical data or systematic investigative rigor needed for higher evidence levels.
Hypothesis testing US Medical PG Question 4: A medical research study is beginning to evaluate the positive predictive value of a novel blood test for non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. The diagnostic arm contains 700 patients with NHL, of which 400 tested positive for the novel blood test. In the control arm, 700 age-matched control patients are enrolled and 0 are found positive for the novel test. What is the PPV of this test?
- A. 400 / (400 + 0) (Correct Answer)
- B. 700 / (700 + 300)
- C. 400 / (400 + 300)
- D. 700 / (700 + 0)
- E. 700 / (400 + 400)
Hypothesis testing Explanation: ***400 / (400 + 0) = 1.0 or 100%***
- The **positive predictive value (PPV)** is calculated as **True Positives / (True Positives + False Positives)**.
- In this scenario, **True Positives (TP)** are the 400 patients with NHL who tested positive, and **False Positives (FP)** are 0, as no control patients tested positive.
- This gives a PPV of 400/400 = **1.0 or 100%**, indicating that all patients who tested positive actually had the disease.
*700 / (700 + 300)*
- This calculation does not align with the formula for PPV based on the given data.
- The denominator `(700+300)` suggests an incorrect combination of various patient groups.
*400 / (400 + 300)*
- The denominator `(400+300)` incorrectly includes 300, which is the number of **False Negatives** (patients with NHL who tested negative), not False Positives.
- PPV focuses on the proportion of true positives among all positive tests, not all diseased individuals.
*700 / (700 + 0)*
- This calculation incorrectly uses the total number of patients with NHL (700) as the numerator, rather than the number of positive test results in that group.
- The numerator should be the **True Positives** (400), not the total number of diseased individuals.
*700 / (400 + 400)*
- This calculation uses incorrect values for both the numerator and denominator, not corresponding to the PPV formula.
- The numerator 700 represents the total number of patients with the disease, not those who tested positive, and the denominator incorrectly sums up values that don't represent the proper PPV calculation.
Hypothesis testing US Medical PG Question 5: An academic medical center in the United States is approached by a pharmaceutical company to run a small clinical trial to test the effectiveness of its new drug, compound X. The company wants to know if the measured hemoglobin a1c (Hba1c) of patients with type 2 diabetes receiving metformin and compound X would be lower than that of control subjects receiving only metformin. After a year of study and data analysis, researchers conclude that the control and treatment groups did not differ significantly in their Hba1c levels.
However, parallel clinical trials in several other countries found that compound X led to a significant decrease in Hba1c. Interested in the discrepancy between these findings, the company funded a larger study in the United States, which confirmed that compound X decreased Hba1c levels. After compound X was approved by the FDA, and after several years of use in the general population, outcomes data confirmed that it effectively lowered Hba1c levels and increased overall survival. What term best describes the discrepant findings in the initial clinical trial run by institution A?
- A. Type I error
- B. Hawthorne effect
- C. Type II error (Correct Answer)
- D. Publication bias
- E. Confirmation bias
Hypothesis testing Explanation: ***Type II error***
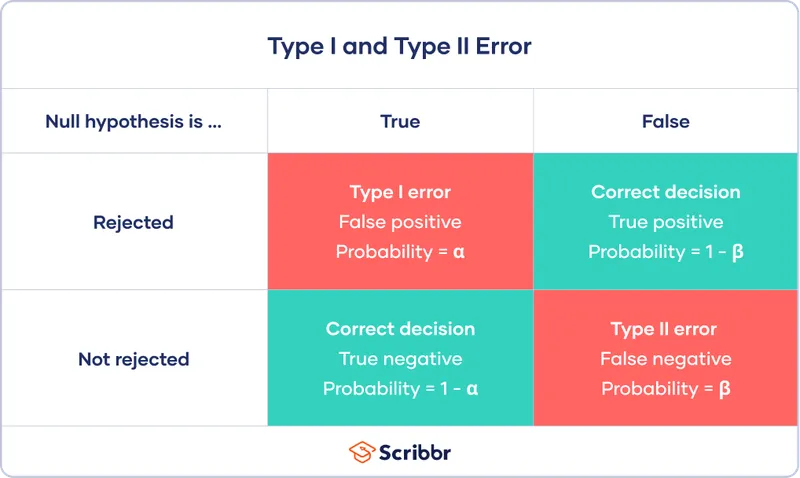
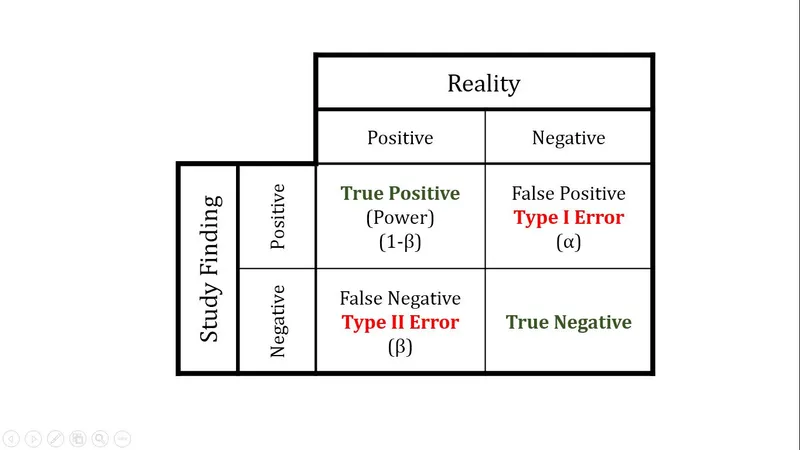
- A **Type II error** occurs when a study fails to **reject a false null hypothesis**, meaning it concludes there is no significant difference or effect when one actually exists.
- In this case, the initial US trial incorrectly concluded that Compound X had no significant effect on HbA1c, while subsequent larger studies and real-world data proved it did.
*Type I error*
- A **Type I error** (alpha error) occurs when a study incorrectly **rejects a true null hypothesis**, concluding there is a significant difference or effect when there isn't.
- This scenario describes the opposite: the initial study failed to find an effect that genuinely existed, indicating a Type II error, not a Type I error.
*Hawthorne effect*
- The **Hawthorne effect** is a type of reactivity in which individuals modify an aspect of their behavior in response to their awareness of being observed.
- This effect does not explain the initial trial's failure to detect a real drug effect; rather, it relates to participants changing behavior due to study participation itself.
*Publication bias*
- **Publication bias** occurs when studies with positive or statistically significant results are more likely to be published than those with negative or non-significant results.
- While relevant to the literature as a whole, it doesn't explain the discrepancy in findings within a single drug's development where a real effect was initially missed.
*Confirmation bias*
- **Confirmation bias** is the tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms one's preexisting beliefs or hypotheses.
- This bias would likely lead researchers to *find* an effect if they expected one, or to disregard data that contradicts their beliefs, which is not what happened in the initial trial.
Hypothesis testing US Medical PG Question 6: You submit a paper to a prestigious journal about the effects of coffee consumption on mesothelioma risk. The first reviewer lauds your clinical and scientific acumen, but expresses concern that your study does not have adequate statistical power. Statistical power refers to which of the following?
- A. The probability of detecting an association when no association exists.
- B. The probability of not detecting an association when an association does exist.
- C. The probability of detecting an association when an association does exist. (Correct Answer)
- D. The first derivative of work.
- E. The square root of the variance.
Hypothesis testing Explanation: ***The probability of detecting an association when an association does exist.***
- **Statistical power** is defined as the probability that a study will correctly reject a false null hypothesis, meaning it will detect a true effect or association if one exists.
- A study with **adequate statistical power** is less likely to miss a real effect.
*The probability of detecting an association when no association exists.*
- This describes a **Type I error** or **false positive**, often represented by **alpha (α)**.
- It is the probability of incorrectly concluding an effect or association exists when, in reality, there is none.
*The probability of not detecting an association when an association does exist.*
- This refers to a **Type II error** or **false negative**, represented by **beta (β)**.
- **Statistical power** is calculated as **1 - β**, so this option describes the complement of power.
*The first derivative of work.*
- The first derivative of work with respect to time represents **power** in physics, which is the rate at which work is done.
- This option is a **distractor** from physics and is unrelated to statistical power in research.
*The square root of the variance.*
- The **square root of the variance** is the **standard deviation**, a measure of the dispersion or spread of data.
- This is a statistical concept but is not the definition of statistical power.
Hypothesis testing US Medical PG Question 7: A child is learning the steps of hand hygiene. Which domain of learning is primarily involved?
- A. Cognitive
- B. Affective
- C. Psychomotor (Correct Answer)
- D. Affective & cognitive
- E. Cognitive & Psychomotor
Hypothesis testing Explanation: ***Psychomotor***
- The **psychomotor domain** involves the acquisition of skills that require coordination of mental and physical activities, such as performing a physical task like hand hygiene.
- This domain focuses on the ability to carry out **physical movements** with precision and coordination.
*Cognitive*
- The **cognitive domain** primarily deals with intellectual understanding, knowledge, and problem-solving, which would involve understanding *why* hand hygiene is important, not the physical act itself.
- While essential for appreciating the *rationale* behind the steps, it does not encompass the *execution* of the skill.
*Affective*
- The **affective domain** relates to emotions, attitudes, values, and appreciation for the task, such as a child's **willingness to perform hand hygiene**.
- It involves feelings and motivations rather than the physical or intellectual mastery of a skill.
*Affective & cognitive*
- While both affective (motivation, willingness) and cognitive (understanding the importance) domains play a supportive role, neither directly addresses the **physical execution** of the learned steps.
- The primary domain for *learning the steps* (i.e., actually performing the actions) is psychomotor.
*Cognitive & Psychomotor*
- While both cognitive (understanding) and psychomotor (physical execution) domains are involved in the overall learning process, the question specifically asks about **learning the steps**, which primarily emphasizes the **psychomotor** aspect.
- The cognitive component is foundational but secondary to the actual motor skill acquisition being described.
Hypothesis testing US Medical PG Question 8: A 46-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up evaluation one week after being discharged from the hospital for acute pancreatitis and alcohol withdrawal. He drinks 8 to 10 beers daily. When the physician asks him about his alcohol use, the patient says, “This is the second time in a year that I have experienced such severe belly pain because of my pancreas. I realize that it really could be happening because of the amount of alcohol I am drinking. However, I don't think I have the willpower to cut down.” This patient is most likely in which of the following stages of behavioral change?
- A. Action
- B. Precontemplation
- C. Preparation
- D. Maintenance
- E. Contemplation (Correct Answer)
Hypothesis testing Explanation: ***Contemplation***
- The patient **acknowledges** the problem ("realize that it really could be happening because of the amount of alcohol I am drinking") and considers the link between his behavior and health issues.
- He expresses an intent to change but also feelings of **ambivalence** or a lack of willpower ("I don't think I have the willpower to cut down"), which are hallmarks of this stage.
*Action*
- This stage involves **actively modifying behavior**, environment, or experiences to overcome the problem.
- The patient has not yet taken concrete steps to cut down on alcohol, indicating he is not in this stage.
*Precontemplation*
- In this stage, individuals are **unaware or unwilling to acknowledge** that a problem exists.
- The patient clearly recognizes the problem and its consequences, ruling out precontemplation.
*Preparation*
- This stage involves **planning for change** and making small, tentative steps towards the desired behavior.
- While he expresses a desire to change, he hasn't articulated a concrete plan or taken any preparatory actions.
*Maintenance*
- This stage focuses on **sustaining the new behavior** and preventing relapse.
- The patient has not yet initiated the change, so he cannot be in the maintenance stage.
Hypothesis testing US Medical PG Question 9: A 37-year-old man comes to the emergency department with his wife because of a 3-day history of severe pain in his right arm. He also reports that he cannot move his right arm. The symptoms began after the patient woke up one morning, having slept on his side. He is otherwise healthy. He works as a waiter and says that he feels exhausted from working several night shifts per week. He adds that he “can barely keep his eyes open” when looking after their daughter the next day. Since the onset of the pain, he has been unable to work and is fully dependent on his wife, who took an extra shift to make enough money to pay their monthly bills. The patient appears relaxed but only allows himself to be examined after his wife convinces him. His vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows 1/5 muscle strength in the right arm. Reflexes are normal. He has no sensation to light touch over the entire right arm and forearm. When a pin prick test is conducted, the patient rapidly withdraws the right arm. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Malingering (Correct Answer)
- B. Factitious disorder
- C. Radial nerve palsy
- D. Illness anxiety disorder
- E. Brachial neuritis
Hypothesis testing Explanation: ***Malingering***
- The patient's presentation with **selective symptoms** (no sensation but rapid withdrawal from pinprick) and the **secondary gain** (avoiding work, dependence on wife for bills) are classic signs of malingering.
- The patient appears *relaxed* despite "severe pain" and only allows examination after persuasion, suggesting a **conscious fabrication of symptoms** for an external incentive.
*Factitious disorder*
- Involves the **deceptive production of symptoms** in oneself or others, but the primary motivation is to assume the **sick role**, without obvious external rewards.
- The patient in this scenario clearly benefits from avoiding work, which points away from factitious disorder.
*Radial nerve palsy*
- Would present with a specific **motor and sensory deficit pattern** corresponding to the radial nerve distribution, typically **wrist drop** and sensory loss over the dorsum of the hand.
- The patient's reported "entire right arm and forearm" sensory loss and paradoxical withdrawal to pinprick are inconsistent with a true neurological lesion.
*Illness anxiety disorder*
- Involves **preoccupations with having or acquiring a serious illness** despite minimal or no somatic symptoms, and is characterized by high levels of anxiety about health.
- This patient's presentation is more about symptom production for an external gain rather than anxiety about disease or actual illness.
*Brachial neuritis*
- Typically causes **severe pain** followed by **weakness and muscle atrophy** in the muscles innervated by the brachial plexus, but the sensory loss typically follows a dermatomal or nerve distribution.
- The reported global sensory loss in the entire arm and forearm, with preserved reflexes and paradoxical withdrawal to pinprick, is inconsistent with a specific nerve inflammation or damage.
Hypothesis testing US Medical PG Question 10: A 40-year-old man is physically and verbally abusive towards his wife and two children. When he was a child, he and his mother were similarly abused by his father. Which of the following psychological defense mechanisms is this man demonstrating?
- A. Splitting
- B. Regression
- C. Identification (Correct Answer)
- D. Projection
- E. Distortion
Hypothesis testing Explanation: ***Identification***
- This man is unconsciously adopting the behaviors and characteristics of his abusive father, demonstrating **identification with the aggressor**—a specific form of identification where a victim copes with trauma by adopting the characteristics of their abuser.
- Identification is a defense mechanism where an individual **incorporates the characteristics** of another person, often a significant figure, into their own personality.
- This pattern of **intergenerational transmission of abuse** is commonly seen in domestic violence cases.
*Splitting*
- Splitting is the failure to integrate the positive and negative qualities of oneself or others into a **cohesive whole**, typically seen in **borderline personality disorder**.
- It involves viewing people or situations in **all-good or all-bad terms**, cycling between idealization and devaluation.
*Regression*
- Regression involves retreating to an **earlier, less mature stage of development** in response to stress or anxiety.
- This typically manifests as more childish behaviors, such as **throwing tantrums** or increased dependence, which are not described here.
*Projection*
- Projection is attributing one's own **unacceptable thoughts or feelings** to another person.
- The man would be accusing his wife or children of being abusive, instead of enacting the abuse himself.
*Distortion*
- Distortion involves significantly **reshaping external reality** to suit internal needs, beliefs, or desires.
- This might involves gross misrepresentations of reality, such as **denial of obvious facts** or strong delusional convictions, none of which are indicated in the scenario.
More Hypothesis testing US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.