Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion). These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) US Medical PG Question 1: A 24-year-old woman presents to a medical office for a follow-up evaluation. The medical history is significant for type 1 diabetes, for which she takes insulin. She was recently hospitalized for diabetic ketoacidosis following a respiratory infection. Today she brings in a list of her most recent early morning fasting blood glucose readings for review. Her glucose readings range from 126 mg/dL–134 mg/dL, except for 2 readings of 350 mg/dL and 380 mg/dL, taken at the onset of her recent hospitalization. Given this data set, which measure(s) of central tendency would be most likely affected by these additional extreme values?
- A. Mean (Correct Answer)
- B. Median and mode
- C. Median
- D. Mean and median
- E. Mode
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) Explanation: ***Mean***
* The **mean** is calculated by summing all values and dividing by the total number of values; thus, it is significantly influenced by **extreme values** or outliers.
* The two high blood glucose readings (350 mg/dL and 380 mg/dL) will **disproportionately increase** the mean, pulling it away from the central tendency of the majority of readings.
* *Median and mode*
* The **mode** is the most frequent value, which would likely still be within the 126-134 mg/dL range since most readings fall there, and the **median** (the middle value) is less affected by outliers.
* Even with two extreme values, the median of this dataset, assuming several readings in the 126-134 mg/dL range, would remain close to the central cluster of typical values and not be drastically altered.
* *Median*
* The **median** is resistant to outliers because it is determined by the position of values once ordered, not their magnitude.
* Adding a few extreme values will only shift the median slightly, if at all, especially if the sample size is large enough that the middle position remains within the range of typical values.
* *Mean and median*
* While the **mean** is heavily affected by outliers, the **median** is relatively robust to them.
* Therefore, stating that both would be significantly affected is incorrect because the median would largely retain its representation of the central tendency.
* *Mode*
* The **mode** represents the most frequently occurring value in a dataset and is not influenced by the magnitude of extreme values.
* Unless one of the extreme high readings happens to be the most frequently occurring value, the mode would remain within the range of the more common, lower glucose readings.
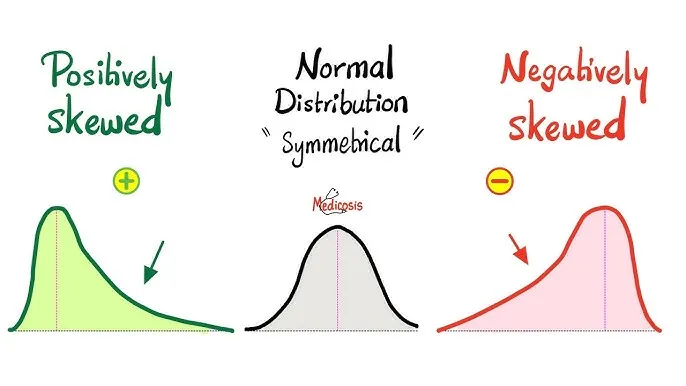
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) US Medical PG Question 2: A biostatistician is processing data for a large clinical trial she is working on. The study is analyzing the use of a novel pharmaceutical compound for the treatment of anorexia after chemotherapy with the outcome of interest being the change in weight while taking the drug. While most participants remained about the same weight or continued to lose weight while on chemotherapy, there were smaller groups of individuals who responded very positively to the orexic agent. As a result, the data had a strong positive skew. The biostatistician wishes to report the measures of central tendency for this project. Just by understanding the skew in the data, which of the following can be expected for this data set?
- A. Mean = median = mode
- B. Mean < median < mode
- C. Mean > median > mode (Correct Answer)
- D. Mean > median = mode
- E. Mean < median = mode
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) Explanation: ***Mean > median > mode***
- In a dataset with a **strong positive skew**, the tail of the distribution is on the right, pulled by a few **unusually large values**.
- These extreme high values disproportionately influence the **mean**, pulling it to the right (higher value), while the **median** (middle value) is less affected, and the **mode** (most frequent value) is often located at the peak of the distribution towards the left.
*Mean = median = mode*
- This relationship between the measures of central tendency is characteristic of a **perfectly symmetrical distribution**, such as a **normal distribution**, where there is no skew.
- In a symmetrical distribution, the mean, median, and mode are all located at the exact center of the data.
*Mean < median < mode*
- This order is typical for a dataset with a **negative skew**, where the tail is on the left due to a few **unusually small values**.
- In a negatively skewed distribution, the mean is pulled to the left (lower value) by the small values, making it less than the median and mode.
*Mean > median = mode*
- This configuration is generally not characteristic of standard skewed distributions and would imply a specific, less common bimodal or complex distribution shape where the mode coincides with the median, but the mean is pulled higher.
- While theoretically possible, it doesn't describe a typical positively skewed distribution where the mode is usually the lowest of the three.
*Mean < median = mode*
- This relationship would suggest a negatively skewed distribution where the median and mode are equal, but the mean is pulled to the left (lower value) by a leftward tail.
- Again, this is a less typical representation of a standard negatively skewed distribution, which often follows the Mean < Median < Mode pattern.
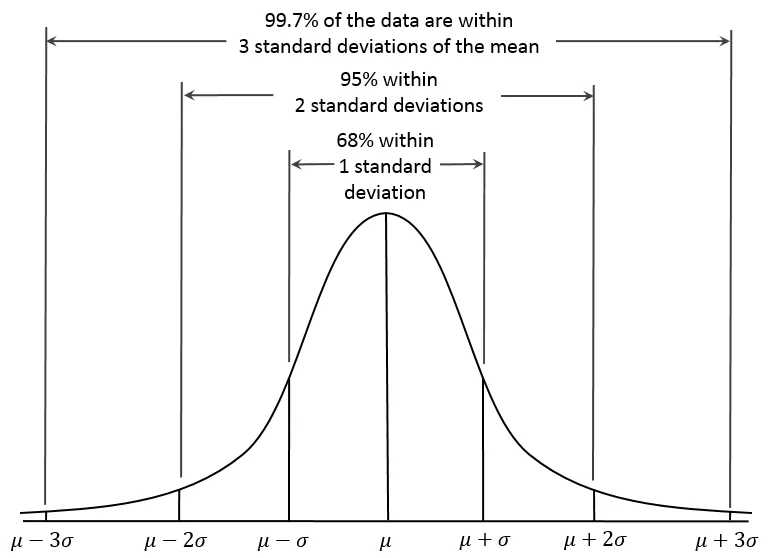
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) US Medical PG Question 3: A study is being conducted on depression using the Patient Health questionnaire (PHQ-9) survey data embedded within a popular social media network with a response size of 500,000 participants. The sample population of this study is approximately normal. The mean PHQ-9 score is 14, and the standard deviation is 4. How many participants have scores greater than 22?
- A. 175,000
- B. 17,500
- C. 160,000
- D. 12,500 (Correct Answer)
- E. 25,000
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) Explanation: ***12,500***
- To find the number of participants with scores greater than 22, first calculate the **z-score** for a score of 22: $Z = \frac{(X - \mu)}{\sigma} = \frac{(22 - 14)}{4} = 2$.
- A z-score of 2 means the score is **2 standard deviations above the mean**. Using the **empirical rule** for a normal distribution, approximately **2.5%** of the data falls beyond 2 standard deviations above the mean (5% total in both tails, so 2.5% in each tail).
- Therefore, $2.5\%$ of the total 500,000 participants is $0.025 \times 500,000 = 12,500$.
*175,000*
- This option would imply a much larger proportion of the population scoring above 22, inconsistent with the **normal distribution's properties** and the calculated z-score.
- It would correspond to a z-score closer to 0, indicating a score closer to the mean, not two standard deviations above it.
*17,500*
- This value represents **3.5%** of the total population ($17,500 / 500,000 = 0.035$).
- A proportion of 3.5% above the mean corresponds to a z-score that is not exactly 2, indicating an incorrect calculation or interpretation of the **normal distribution table**.
*160,000*
- This option represents a very large portion of the participants, roughly **32%** of the total population.
- This percentage would correspond to scores within one standard deviation of the mean, not scores 2 standard deviations above the mean as calculated.
*25,000*
- This value represents **5%** of the total population ($25,000 / 500,000 = 0.05$).
- A z-score greater than 2 corresponds to the far tail of the normal distribution, where only 2.5% of the data lies, not 5%. This would correspond to a z-score of approximately 1.65.
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) US Medical PG Question 4: A young researcher is responsible for graphing laboratory data involving pulmonary blood flow and ventilation pattern obtained from a healthy volunteer who was standing in an upright position. After plotting the following graph, the researcher realizes he forgot to label the curves and the x-axis (which represents the position in the lung). Which of the following is the appropriate label for each point on the graph?
- A. A: Ventilation B: Blood flow C: Base of the lung D: Apex of the lung (Correct Answer)
- B. A: Ventilation B: Blood flow C: Mid-portion of the lung D: Apex of the lung
- C. A: Dead Space B: Shunt C: Base of the lung D: Apex of the lung
- D. A: Blood flow B: Ventilation C: Base of the lung D: Lung hilum
- E. A: Blood flow B: Ventilation C: Apex of the lung D: Lung hilum
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) Explanation: ***A: Ventilation B: Blood flow C: Base of the lung D: Apex of the lung***
- In an upright individual, both **ventilation** and **blood flow** are greater at the **base of the lung** than at the apex due to gravity.
- However, the increase in **perfusion** from apex to base (curve B) is proportionally much greater than the increase in **ventilation** (curve A), leading to a higher V/Q ratio at the apex and a lower V/Q ratio at the base.
*A: Ventilation B: Blood flow C: Mid-portion of the lung D: Apex of the lung*
- This option correctly identifies curves A and B but incorrectly labels C as the **mid-portion of the lung** instead of the base.
- The x-axis represents the lung from base to apex or vice-versa, and the curve indicates the highest values at C.
*A: Dead Space B: Shunt C: Base of the lung D: Apex of the lung*
- This option incorrectly identifies curves A and B; they represent **ventilation** and **blood flow**, not dead space and shunt, which are concepts related to V/Q mismatch.
- **Dead space** refers to ventilated but unperfused areas, while a **shunt** is perfused but unventilated.
*A: Blood flow B: Ventilation C: Base of the lung D: Lung hilum*
- This option incorrectly reverses the labels for curves A and B, as **blood flow** increases more steeply than **ventilation** towards the base.
- The x-axis represents the lung position from base to apex, not the **hilum**, which is a specific anatomical region.
*A: Blood flow B: Ventilation C: Apex of the lung D: Lung hilum*
- This option incorrectly reverses the labels for curves A and B, in addition to mislabeling C as the **apex of the lung**, where values are lowest, not highest.
- The X-axis represents the lung position from base to apex, not focusing on the **hilum**.
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) US Medical PG Question 5: In 2013 the national mean score on the USMLE Step 1 exam was 227 with a standard deviation of 22. Assuming that the scores for 15,000 people follow a normal distribution, approximately how many students scored above the mean but below 250?
- A. 5,100 (Correct Answer)
- B. 4,500
- C. 6,000
- D. 3,750
- E. 6,750
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) Explanation: ***5,100***
- To solve this, first calculate the **z-score** for 250: (250 - 227) / 22 = 1.045.
- Using a **z-table**, the area under the curve from the mean (z=0) to z=1.045 is approximately 0.353. Multiplying this by 15,000 students gives approximately **5,295 students**, which is closest to 5,100.
*4,500*
- This answer would imply a smaller proportion of students between the mean and 250 (around 30%), which is lower than the calculated z-score of 1.045 suggests.
- It does not accurately reflect the area under the **normal distribution curve** for the given range.
*6,000*
- This option would mean that approximately 40% of students scored in this range, which would correspond to a z-score much higher than 1.045 or a different standard deviation.
- This calculation overestimates the number of students within the specified range.
*3,750*
- This value represents 25% of the total students (15,000 * 0.25), indicating that only a quarter of the distribution lies in this range.
- This significantly underestimates the proportion of students scoring between the mean and 250 for the given standard deviation.
*6,750*
- This option reflects approximately 45% of the total student population (15,000 * 0.45), which would correspond to a much larger z-score or a different distribution.
- This value is an overestimation and does not align with the standard normal distribution probabilities for the given parameters.
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) US Medical PG Question 6: A 50-year-old man presents to the office for a routine health check-up. Managing his weight has been his focus to improve his overall health. The doctor discusses his weight loss goals and overall health benefits from weight loss, including better blood pressure management and decreased insulin resistance. The national average weight for males aged 50-59 years old is 90 kg (200 lb) with a standard deviation of 27 kg (60 lb). What would be the most likely expected value if his weight was 2 standard deviations above the mean?
- A. 36 kg (80 lb)
- B. 63 kg (140 lb)
- C. 172 kg (380 lb)
- D. 144 kg (320 lb) (Correct Answer)
- E. 118 kg (260 lb)
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) Explanation: ***144 kg (320 lb)***
- To find a weight 2 standard deviations above the mean, you use the formula: **mean + (2 × standard deviation)**.
- Given a mean of 90 kg and a standard deviation of 27 kg, the calculation is 90 + (2 × 27) = 90 + 54 = **144 kg**. In pounds: 200 lb + (2 × 60 lb) = 200 + 120 = **320 lb**.
*36 kg (80 lb)*
- This value is significantly below the mean and represents a weight **2 standard deviations below the mean**, not above it.
- Calculation: 90 - (2 × 27) = 90 - 54 = 36 kg.
*63 kg (140 lb)*
- This value is **below the mean** and represents a weight approximately **1 standard deviation below the mean**, not above.
- Calculation: 90 - 27 = 63 kg.
*172 kg (380 lb)*
- This value is **too high** for 2 standard deviations above the mean and would represent a weight closer to **3 standard deviations above the mean**.
- Calculation: 90 + (3 × 27) = 90 + 81 = 171 kg (approximately 172 kg).
*118 kg (260 lb)*
- This value represents a weight approximately **1 standard deviation above the mean**, not 2.
- Calculation: 90 + 27 = 117 kg (approximately 118 kg or 260 lb).
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) US Medical PG Question 7: A child is learning the steps of hand hygiene. Which domain of learning is primarily involved?
- A. Cognitive
- B. Affective
- C. Psychomotor (Correct Answer)
- D. Affective & cognitive
- E. Cognitive & Psychomotor
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) Explanation: ***Psychomotor***
- The **psychomotor domain** involves the acquisition of skills that require coordination of mental and physical activities, such as performing a physical task like hand hygiene.
- This domain focuses on the ability to carry out **physical movements** with precision and coordination.
*Cognitive*
- The **cognitive domain** primarily deals with intellectual understanding, knowledge, and problem-solving, which would involve understanding *why* hand hygiene is important, not the physical act itself.
- While essential for appreciating the *rationale* behind the steps, it does not encompass the *execution* of the skill.
*Affective*
- The **affective domain** relates to emotions, attitudes, values, and appreciation for the task, such as a child's **willingness to perform hand hygiene**.
- It involves feelings and motivations rather than the physical or intellectual mastery of a skill.
*Affective & cognitive*
- While both affective (motivation, willingness) and cognitive (understanding the importance) domains play a supportive role, neither directly addresses the **physical execution** of the learned steps.
- The primary domain for *learning the steps* (i.e., actually performing the actions) is psychomotor.
*Cognitive & Psychomotor*
- While both cognitive (understanding) and psychomotor (physical execution) domains are involved in the overall learning process, the question specifically asks about **learning the steps**, which primarily emphasizes the **psychomotor** aspect.
- The cognitive component is foundational but secondary to the actual motor skill acquisition being described.
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) US Medical PG Question 8: A 46-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up evaluation one week after being discharged from the hospital for acute pancreatitis and alcohol withdrawal. He drinks 8 to 10 beers daily. When the physician asks him about his alcohol use, the patient says, “This is the second time in a year that I have experienced such severe belly pain because of my pancreas. I realize that it really could be happening because of the amount of alcohol I am drinking. However, I don't think I have the willpower to cut down.” This patient is most likely in which of the following stages of behavioral change?
- A. Action
- B. Precontemplation
- C. Preparation
- D. Maintenance
- E. Contemplation (Correct Answer)
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) Explanation: ***Contemplation***
- The patient **acknowledges** the problem ("realize that it really could be happening because of the amount of alcohol I am drinking") and considers the link between his behavior and health issues.
- He expresses an intent to change but also feelings of **ambivalence** or a lack of willpower ("I don't think I have the willpower to cut down"), which are hallmarks of this stage.
*Action*
- This stage involves **actively modifying behavior**, environment, or experiences to overcome the problem.
- The patient has not yet taken concrete steps to cut down on alcohol, indicating he is not in this stage.
*Precontemplation*
- In this stage, individuals are **unaware or unwilling to acknowledge** that a problem exists.
- The patient clearly recognizes the problem and its consequences, ruling out precontemplation.
*Preparation*
- This stage involves **planning for change** and making small, tentative steps towards the desired behavior.
- While he expresses a desire to change, he hasn't articulated a concrete plan or taken any preparatory actions.
*Maintenance*
- This stage focuses on **sustaining the new behavior** and preventing relapse.
- The patient has not yet initiated the change, so he cannot be in the maintenance stage.
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) US Medical PG Question 9: A 37-year-old man comes to the emergency department with his wife because of a 3-day history of severe pain in his right arm. He also reports that he cannot move his right arm. The symptoms began after the patient woke up one morning, having slept on his side. He is otherwise healthy. He works as a waiter and says that he feels exhausted from working several night shifts per week. He adds that he “can barely keep his eyes open” when looking after their daughter the next day. Since the onset of the pain, he has been unable to work and is fully dependent on his wife, who took an extra shift to make enough money to pay their monthly bills. The patient appears relaxed but only allows himself to be examined after his wife convinces him. His vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows 1/5 muscle strength in the right arm. Reflexes are normal. He has no sensation to light touch over the entire right arm and forearm. When a pin prick test is conducted, the patient rapidly withdraws the right arm. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Malingering (Correct Answer)
- B. Factitious disorder
- C. Radial nerve palsy
- D. Illness anxiety disorder
- E. Brachial neuritis
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) Explanation: ***Malingering***
- The patient's presentation with **selective symptoms** (no sensation but rapid withdrawal from pinprick) and the **secondary gain** (avoiding work, dependence on wife for bills) are classic signs of malingering.
- The patient appears *relaxed* despite "severe pain" and only allows examination after persuasion, suggesting a **conscious fabrication of symptoms** for an external incentive.
*Factitious disorder*
- Involves the **deceptive production of symptoms** in oneself or others, but the primary motivation is to assume the **sick role**, without obvious external rewards.
- The patient in this scenario clearly benefits from avoiding work, which points away from factitious disorder.
*Radial nerve palsy*
- Would present with a specific **motor and sensory deficit pattern** corresponding to the radial nerve distribution, typically **wrist drop** and sensory loss over the dorsum of the hand.
- The patient's reported "entire right arm and forearm" sensory loss and paradoxical withdrawal to pinprick are inconsistent with a true neurological lesion.
*Illness anxiety disorder*
- Involves **preoccupations with having or acquiring a serious illness** despite minimal or no somatic symptoms, and is characterized by high levels of anxiety about health.
- This patient's presentation is more about symptom production for an external gain rather than anxiety about disease or actual illness.
*Brachial neuritis*
- Typically causes **severe pain** followed by **weakness and muscle atrophy** in the muscles innervated by the brachial plexus, but the sensory loss typically follows a dermatomal or nerve distribution.
- The reported global sensory loss in the entire arm and forearm, with preserved reflexes and paradoxical withdrawal to pinprick, is inconsistent with a specific nerve inflammation or damage.
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) US Medical PG Question 10: A 40-year-old man is physically and verbally abusive towards his wife and two children. When he was a child, he and his mother were similarly abused by his father. Which of the following psychological defense mechanisms is this man demonstrating?
- A. Splitting
- B. Regression
- C. Identification (Correct Answer)
- D. Projection
- E. Distortion
Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) Explanation: ***Identification***
- This man is unconsciously adopting the behaviors and characteristics of his abusive father, demonstrating **identification with the aggressor**—a specific form of identification where a victim copes with trauma by adopting the characteristics of their abuser.
- Identification is a defense mechanism where an individual **incorporates the characteristics** of another person, often a significant figure, into their own personality.
- This pattern of **intergenerational transmission of abuse** is commonly seen in domestic violence cases.
*Splitting*
- Splitting is the failure to integrate the positive and negative qualities of oneself or others into a **cohesive whole**, typically seen in **borderline personality disorder**.
- It involves viewing people or situations in **all-good or all-bad terms**, cycling between idealization and devaluation.
*Regression*
- Regression involves retreating to an **earlier, less mature stage of development** in response to stress or anxiety.
- This typically manifests as more childish behaviors, such as **throwing tantrums** or increased dependence, which are not described here.
*Projection*
- Projection is attributing one's own **unacceptable thoughts or feelings** to another person.
- The man would be accusing his wife or children of being abusive, instead of enacting the abuse himself.
*Distortion*
- Distortion involves significantly **reshaping external reality** to suit internal needs, beliefs, or desires.
- This might involves gross misrepresentations of reality, such as **denial of obvious facts** or strong delusional convictions, none of which are indicated in the scenario.
More Descriptive statistics (central tendency, dispersion) US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.