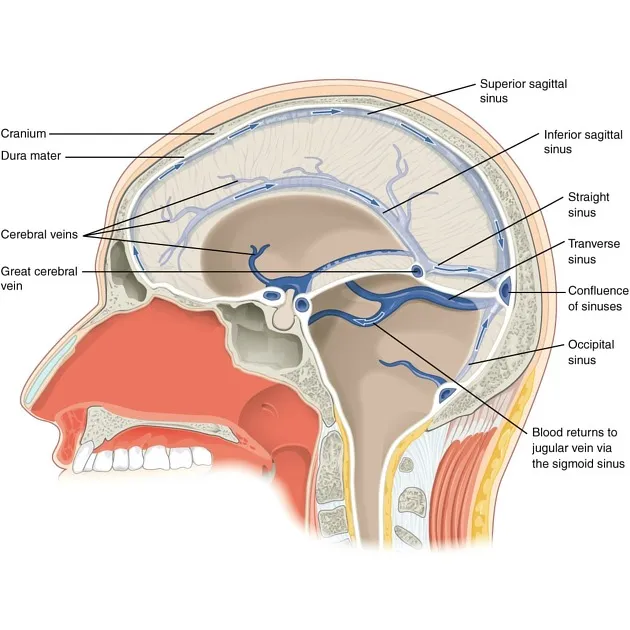
Venous drainage of brain US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Venous drainage of brain. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Venous drainage of brain US Medical PG Question 1: A 52-year-old man presents to the emergency department because of pain and swelling in his left leg over the past few hours. He traveled from Sydney to Los Angeles 2 days ago. He has had type 2 diabetes mellitus for 10 years and takes metformin for it. He has smoked a pack of cigarettes daily for 25 years. His temperature is 36.9°C (98.4°F), the blood pressure is 140/90 mm Hg, and the pulse is 90/min. On examination, the left calf is 5 cm greater in circumference than the right. The left leg appears more erythematous than the right with dilated superficial veins. Venous duplex ultrasound shows non-compressibility. Which of the following best represents the mechanism of this patient’s illness?
- A. Impaired venous blood flow (Correct Answer)
- B. Subcutaneous soft-tissue infection that may extend to the deep fascia
- C. Infection of the dermis and subcutaneous tissues
- D. Impaired arterial blood flow
- E. Impaired lymphatic flow
Venous drainage of brain Explanation: ***Impaired venous blood flow***
- The patient's symptoms (unilateral leg pain and swelling, erythema, dilated superficial veins, recent long-haul travel) and the **venous duplex ultrasound** finding of **non-compressibility** are highly indicative of **deep vein thrombosis (DVT)**, which results from impaired venous outflow.
- Risk factors such as **long-haul travel** (venous stasis), **smoking** (endothelial damage), and potentially **diabetes** contribute to a hypercoagulable state.
*Impaired lymphatic flow*
- This typically presents as **lymphedema**, characterized by chronic, often pitting edema, and skin changes like thickening (peau d'orange), but usually without acute erythema or dilated superficial veins in this context.
- **Venous duplex ultrasound** would not show non-compressibility in cases of impaired lymphatic flow, as veins themselves would be clear.
*Subcutaneous soft-tissue infection that may extend to the deep fascia*
- This describes **necrotizing fasciitis**, a severe infection often characterized by rapid progression, severe pain disproportionate to examination findings, blistering, and systemic toxicity, which are not clearly evident here.
- While there is erythema, the key diagnostic finding is the **non-compressible vein**, not signs of crepitus or rapidly spreading infection.
*Infection of the dermis and subcutaneous tissues*
- This describes **cellulitis**, which presents with localized redness, warmth, swelling, and tenderness, often with an entry point.
- While some symptoms overlap (erythema, swelling), the **venous duplex ultrasound finding of non-compressibility** definitively points away from a simple skin infection and towards a vascular obstruction.
*Impaired arterial blood flow*
- This presents as **acute limb ischemia**, characterized by the "6 Ps": pain, pallor, pulselessness, paresthesias, poikilothermia (coldness), and paralysis.
- The patient's leg is swollen and erythematous, not pale and cold, and the ultrasound directly implicates venous rather than arterial occlusion.
Venous drainage of brain US Medical PG Question 2: A 48-year-old man presents to the ER with a sudden-onset, severe headache. He is vomiting and appears confused. His wife, who accompanied him, says that he has not had any trauma, and that the patient has no relevant family history. He undergoes a non-contrast head CT that shows blood between the arachnoid and pia mater. What is the most likely complication from this condition?
- A. Hemorrhagic shock
- B. Arterial Vasospasm (Correct Answer)
- C. Renal failure
- D. Bacterial Meningitis
- E. Blindness
Venous drainage of brain Explanation: **Arterial Vasospasm**
- **Arterial vasospasm** is a major delayed complication of **subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)**, typically occurring 3-14 days after the initial bleed.
- The presence of blood products in the subarachnoid space can irritate cerebral arteries, leading to their narrowing and subsequent **delayed cerebral ischemia** or infarction.
*Hemorrhagic shock*
- **Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)** typically involves bleeding within the confines of the skull, which is usually not extensive enough to cause systemic **hypovolemia** or **hemorrhagic shock**.
- **Hemorrhagic shock** would require significant external blood loss or internal bleeding into a large body cavity, which is not characteristic of an isolated SAH.
*Renal failure*
- **Renal failure** is not a direct or common complication of **subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)**.
- While systemic complications can sometimes arise in critically ill patients, there is no direct pathophysiological link between SAH and primary kidney injury.
*Bacterial Meningitis*
- The presence of blood in the **subarachnoid space** can cause a **chemical meningitis** due to irritation, mimicking some symptoms of bacterial meningitis.
- However, it does not typically predispose to **bacterial infection** unless there's an iatrogenic cause (e.g., lumbar puncture contamination).
*Blindness*
- While damage to the **optic nerves** or visual pathways can occur with severe neurological events or increased intracranial pressure, **blindness** is not a common or direct complication specifically arising from the bleed itself or its immediate sequelae in SAH.
- Visual disturbances are possible due to elevated **intracranial pressure** or specific anatomical lesion, but not primary blindness.
Venous drainage of brain US Medical PG Question 3: A previously healthy 36-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of a progressively worsening headache for 5 days. She vomited twice after waking up this morning. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. She is sexually active with one male partner and uses an oral contraceptive. Her temperature is 37.5°C (99.5°F), pulse is 105/min, and blood pressure is 125/80 mm Hg. Examination shows tearing of the right eye. The pupils are equal and reactive to light; right lateral gaze is limited. Fundoscopic examination shows bilateral optic disc swelling. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. An MR venography of the head shows a heterogeneous intensity in the left lateral sinus. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Administer dalteparin (Correct Answer)
- B. Analyze cerebrospinal fluid
- C. Administer intravenous antibiotics
- D. Perform endovascular thrombolysis
- E. Measure D-dimer levels
Venous drainage of brain Explanation: **Administer dalteparin**
- The patient presents with classic signs and symptoms of **cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (CVST)**: worsening headache, vomiting, papilledema (optic disc swelling), and a risk factor (oral contraceptive use). The MR venography confirms a heterogeneous intensity in the left lateral sinus, consistent with a thrombus. **Anticoagulation with unfractionated or low molecular weight heparin (such as dalteparin)** is the first-line treatment to prevent clot propagation and recanalize the occluded sinus.
- **Dalteparin** is a **low molecular weight heparin (LMWH)**, which is preferred over unfractionated heparin in many situations due to its predictable anticoagulant response and lower risk of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Prompt anticoagulation is crucial in preventing further neurological deficits and reducing morbidity.
*Analyze cerebrospinal fluid*
- While a **lumbar puncture** might show elevated opening pressure in CVST, it is **contraindicated prior to imaging** to exclude mass effect or obtundation, and in this case, imaging has already confirmed a thrombus.
- CSF analysis is generally not the initial diagnostic or management priority in suspected CVST, especially when imaging has identified the thrombus.
*Administer intravenous antibiotics*
- The patient's symptoms are not suggestive of an **infectious etiology** like meningitis or encephalitis; despite a low-grade fever, there are no other clear signs of infection.
- Administering antibiotics without a strong indication for infection would be inappropriate and delay the necessary treatment for the confirmed **thrombosis**.
*Perform endovascular thrombolysis*
- **Endovascular thrombolysis** is a more invasive procedure generally reserved for patients who **fail to improve with anticoagulation** or have severe neurological deficits that are rapidly progressing despite adequate medical management.
- It carries higher risks compared to systemic anticoagulation and is not the first-line treatment for CVST.
*Measure D-dimer levels*
- While **elevated D-dimer levels** can indicate an active thrombotic process, they are **non-specific** and can be elevated in various conditions.
- D-dimer testing would not provide additional diagnostic information beyond what the MR venography has already confirmed and would not guide immediate management.
Venous drainage of brain US Medical PG Question 4: A 45-year-old man is rushed to the emergency department by his wife after complaining of sudden onset excruciating headache that started about an hour ago. On further questioning, the patient's wife gives a prior history of flank pain, hematuria, and hypertension in the patient, and she recalls that similar symptoms were present in his uncle. On examination, his GCS is 12/15. When his hip and knee are flexed, he resists subsequent extension of the knee. When the neck is passively flexed, there is severe neck stiffness and the patient's hips and knees flex involuntarily. During the examination, he lapses into unconsciousness. Which of the following mechanisms best explains what led to this patient's presentation?
- A. Uremic encephalopathy from chronic renal disease
- B. Meningeal irritation from a space occupying lesion
- C. Increased wall tension within an aneurysm (Correct Answer)
- D. Embolic occlusion of a cerebral vessel
- E. Intracerebral hemorrhage due to vascular malformations
Venous drainage of brain Explanation: ***Increased wall tension within an aneurysm***
- The sudden onset of an **excruciating headache** ("thunderclap headache") followed by rapid deterioration of consciousness (lapsing into unconsciousness) is highly suggestive of a **subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH)**.
- The patient's history of **flank pain, hematuria, hypertension**, and a **family history** of similar symptoms (uncle) point towards **autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD)**, which is strongly associated with an increased risk of **cerebral aneurysms** and SAH. The neurological signs (**GCS 12/15**, resistance to knee extension with hip flexion (positive Kernig's sign: resistance to knee extension when hip is flexed), and flexion of hips and knees with neck flexion (positive Brudzinski's sign: active flexion of the neck causes involuntary flexion of hips and knees)) indicate **meningeal irritation** due to blood in the subarachnoid space and further support the diagnosis of SAH, likely from a ruptured aneurysm.
*Uremic encephalopathy from chronic renal disease*
- While the patient has signs suggestive of ADPKD, which can lead to chronic renal disease and uremic encephalopathy, the acute presentation of a **thunderclap headache** and rapid neurological decline is not typical of uremic encephalopathy, which usually has a more protracted and fluctuating course.
- Uremic encephalopathy primarily results from the accumulation of **uremic toxins**, leading to altered mental status, asterixis, and seizures, but typically without the dramatic acute onset and meningeal signs seen here.
*Meningeal irritation from a space occupying lesion*
- Meningeal irritation can be caused by a space-occupying lesion if it bleeds or causes significant mass effect and inflammation, but the **sudden, excruciating headache** (thunderclap headache) followed by rapid neurological deterioration is not the primary presentation for most space-occupying lesions.
- A space-occupying lesion would typically cause focal neurological deficits, seizures, or a more gradual onset of headache, rather than the abrupt, severe global headache and signs of meningeal irritation observed.
*Embolic occlusion of a cerebral vessel*
- **Embolic occlusion** typically causes an **ischemic stroke**, presenting with sudden focal neurological deficits such as hemiparesis, aphasia, or visual field loss, usually without severe headache as the primary symptom.
- While a severe headache can occur in some ischemic strokes, it is not typically described as an "excruciating thunderclap" headache, and meningeal signs like Kernig's and Brudzinski's are absent unless there is hemorrhagic transformation.
*Intracerebral hemorrhage due to vascular malformations*
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) can cause a sudden severe headache and neurological deterioration, but it typically presents with **focal neurological deficits** corresponding to the area of hemorrhage.
- While there may be some degree of meningeal irritation if the hemorrhage extends to the ventricles or subarachnoid space, the strong association with **ADPKD** and cerebral aneurysms makes SAH leading to meningeal irritation a more likely and specific explanation for this presentation.
Venous drainage of brain US Medical PG Question 5: Which change in CSF production most directly affects intracranial pressure?
- A. Decreased arachnoid granulation function
- B. Increased choroid plexus blood flow
- C. Decreased carbonic anhydrase activity (Correct Answer)
- D. Increased osmotic gradient
Venous drainage of brain Explanation: ***Decreased carbonic anhydrase activity***
- The **choroid plexus** produces CSF primarily through an active secretion process involving carbonic anhydrase.
- Decreased activity of this enzyme directly reduces the formation of **bicarbonate ions** and **protons (H+)**, which are crucial for the active transport of Na+ and Cl- into the CSF, thereby lowering CSF production and subsequently **intracranial pressure**.
*Decreased arachnoid granulation function*
- This change would lead to a **decreased reabsorption** of CSF, which would *increase* intracranial pressure, not directly affect production to lower it.
- Arachnoid granulations are responsible for the **resorption of CSF** into the venous system.
*Increased choroid plexus blood flow*
- While increased blood flow could potentially increase the delivery of substrates for CSF production, it is **not the most direct or primary determinant** of CSF production rate.
- CSF production is predominantly an **active secretory process**, not a passive filtration process dependent solely on blood flow.
*Increased osmotic gradient*
- An increased osmotic gradient, if referring to a higher osmolality in the CSF compared to plasma, would tend to **draw water into the CSF**, potentially *increasing* CSF volume and intracranial pressure.
- If referring to a gradient drawing water *out* of the CSF, it would *decrease* intracranial pressure but is not a primary mechanism of CSF production regulation.
Venous drainage of brain US Medical PG Question 6: Where does the only cranial nerve without a thalamic relay nucleus enter the skull?
- A. Superior orbital fissure
- B. Internal auditory meatus
- C. Foramen rotundum
- D. Jugular foramen
- E. Cribriform plate (Correct Answer)
Venous drainage of brain Explanation: ***Cribriform plate***
- The **olfactory nerve (CN I)** is the only cranial nerve that does not have a thalamic relay nucleus before reaching the cerebral cortex.
- It passes through the **cribriform plate** of the ethmoid bone to reach the olfactory bulbs.
*Superior orbital fissure*
- This opening transmits the **oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), ophthalmic division of trigeminal (CN V1)**, and **abducens (CN VI)** nerves.
- These nerves all have sensory or motor components that relay through the thalamus, directly or indirectly.
*Internal auditory meatus*
- This canal transmits the **facial (CN VII)** and **vestibulocochlear (CN VIII)** nerves.
- The vestibulocochlear nerve's auditory pathway involves a thalamic relay in the **medial geniculate nucleus**.
*Foramen rotundum*
- The **maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V2)** passes through the foramen rotundum.
- Sensory information carried by CN V2 relays through the **thalamus**.
*Jugular foramen*
- This opening transmits the **glossopharyngeal (CN IX), vagus (CN X)**, and **accessory (CN XI)** nerves.
- Sensory components of these nerves, particularly taste and visceral sensation, involve thalamic nuclei.
Venous drainage of brain US Medical PG Question 7: A 29-year-old man presents to his primary care provider complaining of testicular pain. He reports a four-day history of dull chronic pain in his left testicle that is worse with standing. His past medical history is notable for asthma and major depressive disorder. He takes inhaled albuterol as needed and sertraline. He is sexually active with a single female partner and always uses barrier protection. His temperature is 99.2°F (37.3°C), blood pressure is 125/75 mmHg, pulse is 85/min, and respirations are 17/min. Physical examination reveals a non-tender twisted mass along the left spermatic cord that disappears when the patient lies supine. This patient’s condition most likely stems from decreased laminar flow at which of the following vascular junctions?
- A. Descending aorta – Left testicular artery
- B. Left testicular vein – Left suprarenal vein
- C. Left testicular vein – Inferior vena cava
- D. Left testicular vein – Left renal vein (Correct Answer)
- E. Left testicular vein – Left internal iliac vein
Venous drainage of brain Explanation: ***Left testicular vein – Left renal vein***
- This clinical presentation of a **nontender, twisted mass along the spermatic cord** that disappears when supine is classic for a **varicocele**. Varicoceles are more common on the left side due to the **anatomic drainage of the left testicular vein** into the left renal vein at a **perpendicular angle**.
- This perpendicular angle, along with the **increased length of the left testicular vein** and its drainage into the higher-pressure left renal vein, creates conditions for **increased hydrostatic pressure** and **decreased laminar flow**, leading to venous engorgement and varicocele formation.
*Descending aorta – Left testicular artery*
- This junction involves an **artery**, not a vein. Varicoceles are caused by **venous insufficiency and dilatation**, not arterial issues.
- The left testicular artery branches directly from the aorta and supplies blood to the testicle; problems with this junction would typically manifest as **ischemia or arterial insufficiency**, not venous congestion.
*Left testicular vein – Left suprarenal vein*
- While the left suprarenal vein also drains into the left renal vein, the **left testicular vein does not directly connect to the left suprarenal vein**.
- This junction is not anatomically relevant to the direct drainage pathway causing a varicocele.
*Left testicular vein – Inferior vena cava*
- The **right testicular vein drains directly into the inferior vena cava**, explaining why varicoceles are less common on the right side.
- The left testicular vein typically drains into the left renal vein, not directly into the inferior vena cava.
*Left testicular vein – Left internal iliac vein*
- The **left internal iliac vein primarily drains pelvic structures** and has no direct anatomical connection or primary drainage role for the left testicular vein.
- The testicular veins follow a retroperitoneal course and do not typically involve the internal iliac venous system in their main drainage.
Venous drainage of brain US Medical PG Question 8: A 68-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after he was found to be altered at home. Specifically, his wife says that he fell and was unable to get back up while walking to bed. When she approached him, she found that he was unable to move his left leg. His past medical history is significant for hypertension, atrial fibrillation, and diabetes. In addition, he has a 20-pack-year smoking history. On presentation, he is found to still have difficulty moving his left leg though motor function in his left arm is completely intact. The cause of this patient's symptoms most likely occurred in an artery supplying which of the following brain regions?
- A. Motor cortex (ACA) (Correct Answer)
- B. Cerebellum (PICA/SCA)
- C. Occipital cortex (PCA)
- D. Brainstem (Vertebrobasilar)
- E. Motor cortex (MCA)
Venous drainage of brain Explanation: ***Motor cortex (ACA)***
- The patient's inability to move his **left leg** while his **left arm** remains intact points to an injury in the **right cerebral hemisphere** affecting the leg area of the motor cortex.
- The leg area of the **primary motor cortex** is primarily supplied by the **anterior cerebral artery (ACA)**, making an ACA stroke the most likely cause.
*Motor cortex (MCA)*
- The **middle cerebral artery (MCA)** primarily supplies the motor cortex areas responsible for the **face and arm**, not typically isolated leg weakness.
- If the MCA were affected, you would expect to see involvement of the face and/or arm on the contralateral side in addition to leg weakness.
*Brainstem (Vertebrobasilar)*
- A **brainstem stroke** would likely present with more widespread neurological deficits, including **cranial nerve palsies**, ataxia, or altered consciousness.
- Isolated contralateral leg weakness without arm involvement is not characteristic of a brainstem lesion.
*Cerebellum (PICA/SCA)*
- The **cerebellum** is primarily involved in **coordination and balance**, not direct motor strength.
- A cerebellar stroke would present with symptoms like **ataxia**, dysarthria, or nystagmus, not isolated paralysis.
*Occipital cortex (PCA)*
- The **occipital cortex** is primarily responsible for **vision**.
- A posterior cerebral artery (PCA) stroke would typically cause **visual field defects** (e.g., contralateral homonymous hemianopia) rather than motor weakness.
Venous drainage of brain US Medical PG Question 9: A 71-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with a headache for the past 30 minutes. She says that this is the worst headache of her life and that it came on suddenly after she hit her head. She says that she has also been experiencing visual problems with double vision when she looks to the left or the right. Visual examination reveals that her right eye cannot move right past the midline and her left eye cannot move left past the midline. Which of the following is most likely responsible for this patient's visual defects?
- A. Bilateral uncal herniation
- B. Unilateral uncal herniation
- C. Central herniation (Correct Answer)
- D. Subfalcine herniation
- E. Tonsillar herniation
Venous drainage of brain Explanation: ***Central herniation***
- The sudden onset of severe headache after head trauma with **bilateral lateral rectus palsies** (right eye cannot move right, left eye cannot move left) indicates **bilateral abducens nerve (CN VI) dysfunction**.
- Central herniation involves **downward displacement of the diencephalon and midbrain** through the tentorial notch, which causes **increased intracranial pressure** and **stretching of CN VI bilaterally** as it has the longest intracranial course.
- CN VI is particularly vulnerable to **stretching over the petrous ridge** with increased ICP, and bilateral involvement is characteristic of **diffuse increased pressure** or **rostrocaudal deterioration** seen in central herniation.
- While central herniation can progress to pupillary changes and posturing, **early bilateral CN VI palsies** are a recognized finding with increased ICP.
*Bilateral uncal herniation*
- This is an extremely rare occurrence that would primarily affect **CN III (oculomotor nerve) bilaterally**, causing bilateral pupil dilation and "down and out" eye positioning.
- **Uncal herniation does NOT typically cause CN VI palsy**; it compresses CN III as the uncus herniates over the tentorial edge.
- The described findings (bilateral lateral rectus weakness) are not consistent with uncal herniation.
*Unilateral uncal herniation*
- Causes **ipsilateral CN III palsy** with a dilated pupil and "down and out" eye on one side.
- Would not explain the **bilateral abducens nerve deficits** described in this case.
- This is the classic herniation syndrome from temporal lobe mass effect.
*Subfalcine herniation*
- Involves the **cingulate gyrus** passing beneath the **falx cerebri**.
- Typically affects the **anterior cerebral artery**, leading to leg weakness, but **spares cranial nerves entirely**.
- Would not cause any extraocular movement abnormalities.
*Tonsillar herniation*
- Occurs when **cerebellar tonsils** descend through the **foramen magnum**.
- Presents with **respiratory depression, bradycardia, and cardiovascular instability** due to medullary compression.
- Does not typically affect CN VI or cause isolated extraocular movement deficits.
Venous drainage of brain US Medical PG Question 10: An 8-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his mother because of a 3-week history of irritability and frequent bed wetting. She also reports that he has been unable to look upward without tilting his head back for the past 2 months. He is at the 50th percentile for height and weight. His vital signs are within normal limits. Ophthalmological examination shows dilated pupils that are not reactive to light and bilateral optic disc swelling. Pubic hair development is Tanner stage 2. The most likely cause of this patient's condition is a tumor in which of the following locations?
- A. Fourth ventricle
- B. Sella turcica
- C. Cerebellar vermis
- D. Cerebral falx
- E. Dorsal midbrain (Correct Answer)
Venous drainage of brain Explanation: ***Dorsal midbrain***
- The inability to look upward (**Parinaud's syndrome**), dilated pupils with poor light reflex, and **optic disc swelling** (indicating increased intracranial pressure) are classic signs of a mass lesion compressing the **dorsal midbrain**, specifically the **tectal plate**.
- **Irritability and bedwetting** are nonspecific symptoms, but in this context, they could be related to **hydrocephalus** due to **aqueductal compression** by the tumor.
*Fourth ventricle*
- Tumors of the fourth ventricle typically present with symptoms related to **hydrocephalus** (headache, nausea, vomiting, papilledema) and **ataxia** due to cerebellar involvement, but not specifically with **Parinaud's syndrome**.
- **Truncal ataxia** and **gait instability** are common with posterior fossa tumors affecting the cerebellum.
*Sella turcica*
- Tumors in the sella turcica primarily affect the **pituitary gland** and **optic chiasm**, leading to **endocrine dysfunction** (e.g., growth retardation, precocious puberty, hypogonadism) and **bitemporal hemianopsia**.
- **Parinaud's syndrome** and **dilated, unreactive pupils** are not typical presentations for sellar tumors.
*Cerebral falx*
- Tumors associated with the cerebral falx (e.g., meningiomas) are often located **supratentorially** and can cause focal neurological deficits like **seizures** or **hemiparesis**, depending on their location and size.
- They do not typically cause the specific eye movement disorders or pupillary abnormalities seen in this patient.
*Cerebellar vermis*
- Cerebellar vermis tumors often lead to **truncal ataxia**, **gait disturbance**, and **hydrocephalus** due to compression of the aqueduct or fourth ventricle outflow.
- While they can cause increased intracranial pressure, they do not directly cause **Parinaud's syndrome** or isolated deficits of upward gaze.
More Venous drainage of brain US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.