Middle cerebral artery territory US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Middle cerebral artery territory. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Middle cerebral artery territory US Medical PG Question 1: A 59-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife for a 1-hour history of sudden behavior changes. They were having lunch together when, at 1:07 PM, he suddenly dropped his sandwich on the floor. Since then, he has been unable to use his right arm. She also reports that he is slurring his speech and dragging his right foot when he walks. Nothing like this has ever happened before. The vital signs include: pulse 95/min, blood pressure 160/90 mm Hg, and respiratory rate 14/min. The physical exam is notable for an irregularly irregular rhythm on cardiac auscultation. On neurological exam, he has a facial droop on the right half of his face but is able to elevate his eyebrows symmetrically. He has 0/5 strength in his right arm, 2/5 strength in his right leg, and reports numbness throughout the right side of his body. Angiography of the brain will most likely show a lesion in which of the following vessels?
- A. Posterior cerebral artery
- B. Internal carotid artery
- C. Middle cerebral artery (Correct Answer)
- D. Basilar artery
- E. Anterior cerebral artery
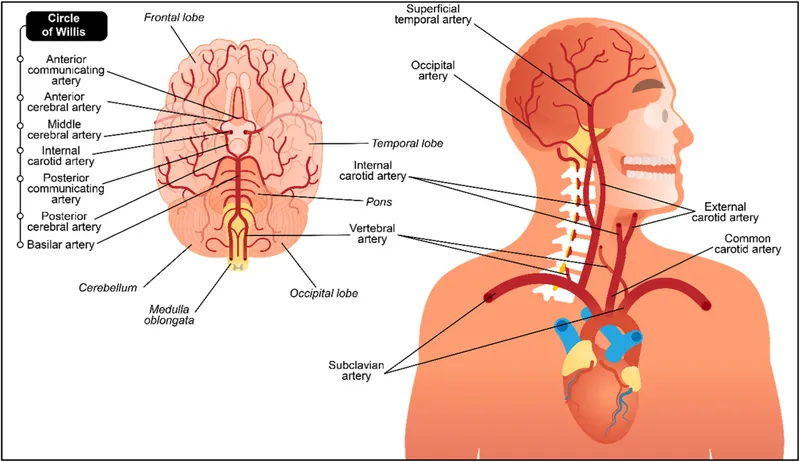
Middle cerebral artery territory Explanation: ***Middle cerebral artery***
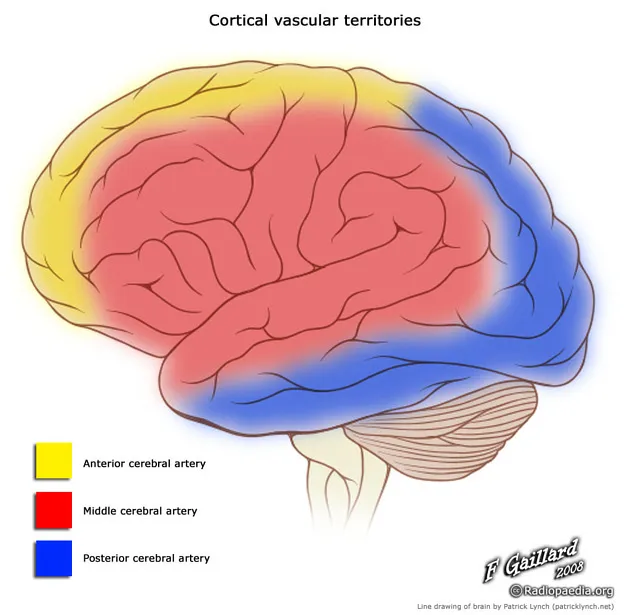
- The patient's symptoms, including **right-sided weakness with arm > leg involvement** (0/5 arm, 2/5 leg), **facial droop** (lower face sparing the forehead), and **slurred speech (dysarthria/aphasia)**, are classic signs of an **MCA stroke**.
- The **arm > leg pattern** is the key distinguishing feature of MCA territory infarction, as the MCA supplies the **lateral motor cortex** (which controls arm and face).
- The finding of an **irregularly irregular rhythm** suggests **atrial fibrillation**, a common cause of **embolic stroke** to the MCA.
*Posterior cerebral artery*
- PCA strokes primarily affect the **occipital lobe** and **medial temporal lobe**, leading to **visual field defects** (e.g., homonymous hemianopsia) or memory deficits.
- While it can cause sensory loss, it typically does not present with the **prominent motor deficits** and **facial droop** seen in this patient.
*Internal carotid artery*
- ICA occlusion can cause symptoms similar to MCA stroke, especially if the **MCA is a direct branch of the ICA**, or it can cause both MCA and ACA symptoms simultaneously.
- However, the specific constellation of symptoms described (predominant motor and sensory deficits, speech issues) points more directly to the **MCA territory downstream**.
*Basilar artery*
- Basilar artery strokes affect the **brainstem** and often present with a combination of **cranial nerve palsies**, **ataxia**, bilateral weakness, **vertigo**, and sometimes **"locked-in" syndrome**.
- The patient's symptoms are more consistent with a **hemispheric lesion**, not a brainstem lesion.
*Anterior cerebral artery*
- ACA strokes typically cause **contralateral leg > arm weakness** (opposite pattern from MCA), as the ACA supplies the **medial motor cortex**.
- ACA strokes may also present with **behavioral changes** (e.g., abulia, apathy) due to involvement of the frontal lobe.
- The patient's prominent **right arm weakness** and **facial droop** are not characteristic of an ACA stroke.
Middle cerebral artery territory US Medical PG Question 2: A 61-year-old man is brought to the emergency room with slurred speech. According to the patient's wife, they were watching a movie together when he developed a minor headache. He soon developed difficulty speaking in complete sentences, at which point she decided to take him to the emergency room. His past medical history is notable for hypertension and hyperlipidemia. He takes aspirin, lisinopril, rosuvastatin. The patient is a retired lawyer. He has a 25-pack-year smoking history and drinks 4-5 beers per day. His father died of a myocardial infarction, and his mother died of breast cancer. His temperature is 98.6°F (37°C), blood pressure is 143/81 mmHg, pulse is 88/min, and respirations are 21/min. On exam, he can understand everything that is being said to him and is able to repeat statements without difficulty. However, when asked to speak freely, he hesitates with every word and takes 30 seconds to finish a short sentence. This patient most likely has an infarct in which of the following vascular distributions?
- A. Proximal middle cerebral artery
- B. Inferior division of the middle cerebral artery
- C. Middle cerebral artery and posterior cerebral artery watershed area
- D. Superior division of the middle cerebral artery (Correct Answer)
- E. Anterior cerebral artery and middle cerebral artery watershed area
Middle cerebral artery territory Explanation: ***Superior division of the middle cerebral artery***
- The patient's inability to speak spontaneously coupled with intact comprehension and repetition is characteristic of **Broca's aphasia**, which results from damage to **Broca's area** in the dominant frontal lobe.
- Broca's area is supplied by the **superior division of the middle cerebral artery (MCA)**.
*Proximal middle cerebral artery*
- An infarct in the proximal MCA, or the main stem, would typically lead to global aphasia if the dominant hemisphere is affected, characterized by **severe deficits in comprehension, repetition, and speech production**.
- This presentation does not align with the patient's ability to understand and repeat statements.
*Inferior division of the middle cerebral artery*
- The inferior division of the MCA supplies Wernicke's area in the dominant hemisphere.
- Damage here causes **Wernicke's aphasia**, characterized by **fluent but nonsensical speech** with **impaired comprehension** and **repetition**, which is contrary to the patient's symptoms.
*Middle cerebral artery and posterior cerebral artery watershed area*
- Watershed infarcts, especially between the MCA and posterior cerebral artery (PCA), can cause **transcortical sensory aphasia** if in the dominant hemisphere.
- This type of aphasia involves impaired comprehension but **intact repetition**, which differs from Broca's aphasia where spontaneous speech is the main deficit.
*Anterior cerebral artery and middle cerebral artery watershed area*
- Infarcts in the watershed area between the anterior cerebral artery (ACA) and MCA can result in **transcortical motor aphasia** if in the dominant hemisphere.
- This condition presents with **non-fluent speech** and **intact repetition**, similar to Broca's aphasia, but Broca's area itself is located specifically within the MCA superior division territory.
Middle cerebral artery territory US Medical PG Question 3: A 76-year-old woman with hypertension and coronary artery disease is brought to the emergency department after the sudden onset of right-sided weakness. Her pulse is 83/min and blood pressure is 156/90 mm Hg. Neurological examination shows right-sided facial drooping and complete paralysis of the right upper and lower extremities. Tongue position is normal and she is able to swallow liquids without difficulty. Knee and ankle deep tendon reflexes are exaggerated on the right. Sensation to vibration, position, and light touch is normal bilaterally. She is oriented to person, place, and time, and is able to speak normally. Occlusion of which of the following vessels is the most likely cause of this patient's current symptoms?
- A. Ipsilateral anterior cerebral artery
- B. Contralateral middle cerebral artery
- C. Anterior spinal artery
- D. Contralateral lenticulostriate artery (Correct Answer)
- E. Ipsilateral posterior inferior cerebellar artery
Middle cerebral artery territory Explanation: ***Contralateral lenticulostriate artery***
- The patient presents with **pure motor hemiparesis** affecting the face, arm, and leg equally on the right side, with **no sensory deficits, aphasia, or cognitive impairment**.
- This clinical pattern is classic for a **lacunar stroke** affecting the **internal capsule**, which is supplied by the **lenticulostriate arteries** (branches of the middle cerebral artery).
- The internal capsule contains tightly packed corticospinal and corticobulbar fibers; a small infarct here causes complete contralateral motor deficits without cortical signs.
- The **absence of cortical findings** (normal speech, cognition, and sensation) distinguishes this from cortical MCA stroke.
*Contralateral middle cerebral artery*
- A **cortical MCA stroke** would typically present with **cortical signs** such as aphasia (if left hemisphere), neglect (if right hemisphere), sensory loss, and visual field defects.
- MCA strokes usually show **arm and face > leg** weakness (the leg area is supplied by ACA).
- This patient's **pure motor syndrome** without cortical signs points to a subcortical lesion, not cortical MCA occlusion.
*Ipsilateral anterior cerebral artery*
- First, the lateralization is incorrect - symptoms are right-sided, indicating left hemisphere pathology, so it would be **contralateral** ACA.
- ACA occlusion causes weakness predominantly in the **contralateral leg > arm**, with relative sparing of the face.
- This patient has equal involvement of face, arm, and leg, which is inconsistent with ACA territory.
*Anterior spinal artery*
- The **anterior spinal artery** supplies the anterior two-thirds of the spinal cord, including the corticospinal tracts and anterior horn cells.
- Occlusion causes **bilateral** motor weakness below the lesion level and bilateral loss of pain/temperature sensation.
- It does not cause **unilateral facial weakness** or the distribution of deficits seen in this patient.
*Ipsilateral posterior inferior cerebellar artery*
- Again, lateralization is incorrect - symptoms would be from **contralateral** PICA for motor findings, but PICA supplies the lateral medulla and inferior cerebellum.
- PICA occlusion causes **lateral medullary syndrome (Wallenberg syndrome)**: ataxia, vertigo, dysphagia, dysarthria, Horner syndrome, and contralateral pain/temperature loss.
- The patient's **pure motor hemiparesis** without cerebellar or brainstem signs is incompatible with PICA occlusion.
Middle cerebral artery territory US Medical PG Question 4: A 78-year-old left-handed woman with hypertension and hyperlipidemia is brought to the emergency room because of sudden-onset right leg weakness and urinary incontinence. Neurologic examination shows decreased sensation over the right thigh. Muscle strength is 2/5 in the right lower extremity and 4/5 in the right upper extremity. Strength and sensation in the face are normal but she has difficulty initiating sentences and she is unable to write her name. The most likely cause of this patient’s condition is an occlusion of which of the following vessels?
- A. Right vertebrobasilar artery
- B. Right middle cerebral artery
- C. Left posterior cerebral artery
- D. Left anterior cerebral artery (Correct Answer)
- E. Right anterior cerebral artery
Middle cerebral artery territory Explanation: ***Left anterior cerebral artery***
- Stroke in the **left anterior cerebral artery (ACA)** territory typically causes **contralateral leg weakness** (right leg in this case) and **urinary incontinence** due to involvement of the paracentral lobule.
- The patient's difficulty writing her name (agraphia) and initiating sentences (transcortical motor aphasia, which can manifest as difficulty initiating speech) is consistent with damage to the supplemental motor area in the dominant (left) hemisphere, provided by the ACA.
*Right vertebrobasilar artery*
- Occlusion of the vertebrobasilar artery typically presents with a wide range of symptoms including **vertigo**, **ataxia**, **dysarthria**, and bilateral or alternating sensory/motor deficits.
- It would not selectively cause isolated right leg weakness, urinary incontinence, and dominant hemisphere language difficulties without other brainstem or cerebellar signs.
*Right middle cerebral artery*
- A stroke in the **right middle cerebral artery (MCA)** would cause **left-sided deficit**, not right-sided.
- Although it can cause motor and sensory deficits, it typically affects the arm and face more than the leg, and would not cause the specific language deficits of the dominant hemisphere seen here.
*Left posterior cerebral artery*
- Occlusion of the **left posterior cerebral artery (PCA)** typically leads to issues like **contralateral homonymous hemianopia**, visual field defects, and potentially memory impairment or alexia without agraphia if the splenium of the corpus callosum is involved.
- It directly affects posterior brain regions, so it would not cause the anterior cerebral artery specific symptoms such as prominent contralateral leg weakness, urinary incontinence, or the described language difficulties.
*Right anterior cerebral artery*
- Occlusion of the **right anterior cerebral artery (ACA)** would cause **left leg weakness** and **left-sided sensory deficits**, not the right-sided deficits observed in this patient.
- While it could cause urinary incontinence, the combination of right-sided weakness and dominant hemisphere language deficits points against a right ACA occlusion.
Middle cerebral artery territory US Medical PG Question 5: An 85-year-old woman otherwise healthy presents with left-sided weakness. Her symptoms started 4 hours ago while she was on the phone with her niece. The patient recalls dropping the phone and not being able to pick it up with her left hand. No significant past medical history. No current medications. Physical examination reveals decreased sensation on the left side, worse in the left face and left upper extremity. There is significant weakness of the left upper extremity and weakness and drooping of the lower half of the left face. Ophthalmic examination reveals conjugate eye deviation to the right. A noncontrast CT of the head is unremarkable. The patient is started on aspirin. A repeat contrast CT of the head a few days later reveals an ischemic stroke involving the lateral convexity of right cerebral hemisphere. Which of the following additional findings would most likely be seen in this patient?
- A. Homonymous hemianopsia (Correct Answer)
- B. Horner's syndrome
- C. Amaurosis fugax
- D. Profound lower limb weakness
- E. Prosopagnosia
Middle cerebral artery territory Explanation: ***Homonymous hemianopsia***
- The patient has an ischemic stroke affecting the **right cerebral hemisphere**, specifically the **lateral convexity**. This suggests involvement of the **middle cerebral artery (MCA)** territory.
- The **optic radiations** carrying visual information from the contralateral visual field pass through the parietal and temporal lobes to the occipital cortex. Damage to these radiations in the right hemisphere would result in a **left homonymous hemianopsia**.
*Horner's syndrome*
- Characterized by **ptosis**, **miosis**, and **anhidrosis** on one side of the face.
- It results from damage to the **sympathetic pathway**, typically in the brainstem, spinal cord above T1, or sympathetic chain, which is not the primary location of this stroke.
*Amaurosis fugax*
- This is a **transient monocular vision loss** ("curtain coming down") due to temporary interruption of blood flow to the retina, usually from an **ipsilateral carotid artery embolus**.
- It is typically a symptom of impending stroke or TIA, not a direct neurological deficit resulting from a cerebral hemisphere stroke.
*Profound lower limb weakness*
- The described stroke involves the **lateral convexity of the right cerebral hemisphere**, fed by the **middle cerebral artery (MCA)**.
- The MCA primarily supplies the upper limb and facial motor/sensory cortices, leading to more pronounced **upper limb and facial weakness** rather than profound lower limb weakness, which is more characteristic of an **anterior cerebral artery (ACA)** stroke.
*Prosopagnosia*
- This is the inability to recognize familiar faces, often due to damage to the **fusiform gyrus** in the temporal and occipital lobes, usually on the **right side**.
- While it can occur with right hemisphere strokes, it is a specific higher-order cognitive deficit and not the *most likely* additional finding in this presentation focused on motor and sensory deficits and conjugate eye deviation.
Middle cerebral artery territory US Medical PG Question 6: A 78-year-old right-handed man with hypertension and hyperlipidemia is brought to the emergency department for sudden onset of nausea and vertigo one hour ago. Physical examination shows 5/5 strength in all extremities. Sensation to light touch and pinprick is decreased in the right arm and leg. A CT scan of the brain shows an acute infarction in the distribution of the left posterior cerebral artery. Further evaluation of this patient is most likely to show which of the following findings?
- A. Right-sided homonymous hemianopia (Correct Answer)
- B. Prosopagnosia
- C. Left-sided gaze deviation
- D. Left-sided hemineglect
- E. Right-sided superior quadrantanopia
Middle cerebral artery territory Explanation: ***Right-sided homonymous hemianopia***
- A **left PCA infarct** typically affects the **occipital lobe**, specifically the visual cortex or optic radiations, leading to a contralateral visual field deficit.
- The **right visual field** from both eyes projects to the left occipital lobe, so infarction here causes a **right homonymous hemianopia**.
*Prosopagnosia*
- **Prosopagnosia**, the inability to recognize faces, is associated with infarction of the **fusiform gyrus**, often a bilateral PCA territory infarction or an infarct affecting the right occipital or temporal lobe.
- This patient has a **left PCA infarct**, so isolated prosopagnosia is less likely.
*Left-sided gaze deviation*
- **Gaze deviation** usually occurs in lesions of the **frontal eye fields** (Brodmann area 8), which are supplied by the middle cerebral artery, causing the eyes to deviate towards the side of the lesion in acute stages.
- A **PCA infarct** typically spares the frontal eye fields and the brainstem gaze centers.
*Left-sided hemineglect*
- **Hemineglect** is most commonly associated with lesions of the **right parietal lobe** or right frontal lobe, primarily in the territory of the right middle cerebral artery.
- With a **left PCA infarct**, left-sided hemineglect is an unexpected finding.
*Right-sided superior quadrantanopia*
- A **superior quadrantanopia** is caused by damage to the **inferior optic radiations** (Meyer's loop), which typically carry information from the superior visual field.
- A complete **homonymous hemianopia** involving the entire right visual field is more characteristic of an occipital lobe lesion due to a PCA infarct, rather than an isolated quadrantanopia.
Middle cerebral artery territory US Medical PG Question 7: A 75-year-old woman presents with sudden loss of vision. She says that she was reading when suddenly she was not able to see the print on half of the page. Her symptoms started 4 hours ago and are accompanied by a severe posterior headache. Vital signs reveal the following: blood pressure 119/76 mm Hg, pulse 89/min, SpO2 98% on room air. The patient was unable to recognize her niece when she arrived to see her. A noncontrast CT of the head shows no evidence of hemorrhagic stroke. What is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Lacunar stroke
- B. Middle cerebral artery stroke
- C. Vertebrobasilar stroke
- D. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- E. Posterior cerebral artery stroke (Correct Answer)
Middle cerebral artery territory Explanation: ***Posterior cerebral artery stroke***
- The sudden severe posterior headache along with **unilateral vision loss** and **prosopagnosia** (inability to recognize familiar faces) are characteristic signs of a **posterior cerebral artery (PCA) stroke**.
- PCA occlusion often affects the **occipital lobe** (vision) and can extend to the **temporal lobe** (facial recognition).
*Lacunar stroke*
- This type of stroke results from the occlusion of small penetrating arteries and typically causes **pure motor** or **pure sensory deficits**, not complex visual or recognition problems.
- While headache can occur, the specific combination of symptoms points away from a lacunar infarct.
*Middle cerebral artery stroke*
- MCA stroke commonly presents with **contralateral hemiparesis**, **aphasia** (if dominant hemisphere), and **hemianopia** but usually not isolated unilateral vision loss or severe posterior headache with prosopagnosia.
- The symptoms are more consistent with involvement of the posterior circulation.
*Vertebrobasilar stroke*
- A vertebrobasilar stroke can cause **visual disturbances**, but it is typically associated with other **brainstem symptoms** like vertigo, ataxia, or cranial nerve deficits, which are not described here.
- The specific presentation of unilateral vision loss and prosopagnosia is less typical for a vertebrobasilar stroke affecting widespread brainstem structures.
*Subarachnoid hemorrhage*
- While a **sudden severe headache (thunderclap headache)** is a hallmark of SAH, it usually presents with meningeal irritation symptoms like **neck stiffness** and often altered mental status, and the visual deficits are usually different (e.g., oculomotor nerve palsy).
- The patient's focal neurological deficits, specifically prosopagnosia and unilateral visual field loss, are more indicative of an ischemic event in a specific vascular territory.
Middle cerebral artery territory US Medical PG Question 8: A 65-year-old man presents with facial weakness. He says he noticed that his face appeared twisted when he looked in the bathroom mirror this morning. He is otherwise well and does not have any other complaints. He denies any facial pain or paresthesia. No significant past medical history. The patient is afebrile and vital signs are within normal limits. Neurological examination reveals difficulty shutting the right eye tight and inability to bring up the right corner of his mouth when asked to smile. Remainder of the exam, including the left side of the face, is unremarkable. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis in this patient?
- A. Idiopathic facial paralysis (Correct Answer)
- B. Right hemisphere stroke
- C. Left middle cerebral artery stroke
- D. Facial nerve schwannoma
- E. Acoustic neuroma
Middle cerebral artery territory Explanation: ***Idiopathic facial paralysis***
- The sudden onset of **unilateral facial weakness** affecting both the upper and lower face (inability to shut eye and inability to smile on the same side) without other neurological symptoms is characteristic of **Bell's palsy**.
- It is a diagnosis of exclusion, and the absence of other symptoms and normal vital signs support this benign, self-limiting condition.
*Right hemisphere stroke*
- A stroke typically causes **upper motor neuron facial weakness**, primarily affecting the **lower half of the contralateral face**, sparing the forehead.
- Would likely present with other neurological deficits such as **hemiparesis** or sensory changes, which are absent here.
*Left middle cerebral artery stroke*
- Similar to a right hemisphere stroke, a left MCA stroke would typically cause **contralateral facial weakness**, predominantly in the **lower face**.
- Would also likely present with additional symptoms such as **aphasia** (if the dominant hemisphere is affected) or right-sided motor/sensory deficits, which are not described.
*Facial nerve schwannoma*
- This condition tends to cause a **slowly progressive facial weakness**, not the acute onset described.
- Often associated with other symptoms such as **persistent facial pain** or paresthesia, which this patient denies.
*Acoustic neuroma*
- Primarily causes **hearing loss** and **tinnitus**, and later, **vestibular symptoms** like dizziness or imbalance.
- While it can eventually compress the facial nerve causing weakness, the onset would be gradual and accompanied by **auditory symptoms**, which are absent here.
Middle cerebral artery territory US Medical PG Question 9: A 47-year-old man presents to you with gradual loss of voice and difficulty swallowing for the past couple of months. The difficulty of swallowing is for both solid and liquid foods. His past medical history is insignificant except for occasional mild headaches. Physical exam also reveals loss of taste sensation on the posterior third of his tongue and palate, weakness in shrugging his shoulders, an absent gag reflex, and deviation of the uvula away from the midline. MRI scanning was suggested which revealed a meningioma that was compressing some cranial nerves leaving the skull. Which of the following openings in the skull transmit the affected cranial nerves?
- A. Jugular foramen (Correct Answer)
- B. Foramen rotundum
- C. Foramen spinosum
- D. Foramen ovale
- E. Foramen lacerum
Middle cerebral artery territory Explanation: ***Jugular foramen***
- The symptoms described—loss of voice, difficulty swallowing, loss of taste on the posterior third of the tongue, absent gag reflex, and uvula deviation—point to impairment of **cranial nerves IX (glossopharyngeal), X (vagus), XI (accessory)**, which all exit the skull via the **jugular foramen**.
- The **vagus nerve** (CN X) is responsible for voice and swallowing (via innervation of the pharynx and larynx), the **glossopharyngeal nerve** (CN IX) for taste from the posterior third of the tongue and the gag reflex, and the **accessory nerve** (CN XI) for shoulder shrugging (trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles).
- Note: Loss of taste on the palate may involve CN VII (facial nerve) fibers, but the dominant clinical picture with absent gag reflex, uvula deviation, dysphagia, and dysphonia clearly indicates jugular foramen pathology.
*Foramen rotundum*
- The **foramen rotundum** transmits the **maxillary nerve (V2)**, a branch of the trigeminal nerve.
- Damage to V2 would primarily cause sensory deficits in the midface and upper teeth, which are not described in this patient.
*Foramen spinosum*
- The **foramen spinosum** transmits the **middle meningeal artery** and the **meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve (V3)**.
- Injury here would not explain the constellation of symptoms related to voice, swallowing, taste, or shoulder movement.
*Foramen ovale*
- The **foramen ovale** transmits the **mandibular nerve (V3)**, the **accessory meningeal artery**, and occasionally the superficial petrosal nerve.
- Damage to V3 would result in sensory loss to the lower face and motor deficits in the muscles of mastication, which are not reported.
*Foramen lacerum*
- The **foramen lacerum** is filled with cartilage in vivo and does not typically transmit major neurovascular structures directly through its aperture.
- The **internal carotid artery** passes superior to it, and some small nerves may traverse its vicinity, but not the specific cranial nerves indicated by the patient's symptoms.
Middle cerebral artery territory US Medical PG Question 10: A 36-year-old woman, gravida 1, para 1, has back pain and numbness in her lower extremities after an emergency cesarean delivery of a healthy 3856-g (8-lb, 8-oz) newborn male. She had a placental abruption and lost approximately 2000 ml of blood. During the procedure, she received two units of packed red blood cells and intravenous fluids. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. She is sexually active with one male partner, and they use condoms inconsistently. She is alert and oriented to person, place, and time. Her temperature is 37.2°C (98.9°F), pulse is 90/min, respirations are 15/min, and blood pressure is 94/58 mm Hg. Examination shows decreased sensation to temperature and pinprick below her waist and 0/5 muscle strength in her lower extremities. She feels the vibrations of a tuning fork placed on both of her great toes. Deep tendon reflexes are absent in the lower extremities and 2+ in the upper extremities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Posterior spinal artery syndrome
- B. Brown-Séquard syndrome
- C. Anterior spinal artery syndrome (Correct Answer)
- D. Guillain-Barré Syndrome
- E. Tabes dorsalis
Middle cerebral artery territory Explanation: ***Anterior spinal artery syndrome***
- This syndrome is characterized by the sudden onset of **bilateral motor paralysis** below the level of the lesion, accompanied by a dissociated sensory loss (**loss of pain and temperature sensation**) while **proprioception and vibratory sensation are preserved**.
- The patient's history of **significant blood loss** and hypotension during delivery makes her susceptible to spinal cord ischemia, particularly in the anterior spinal artery territory, which supplies the anterior two-thirds of the spinal cord.
*Posterior spinal artery syndrome*
- This syndrome primarily affects the **dorsal columns**, leading to a loss of **proprioception and vibratory sensation**, with preservation of motor function and pain/temperature sensation.
- The patient's preserved vibratory sensation and significant motor deficits rule out posterior spinal artery syndrome.
*Brown-Séquard syndrome*
- This syndrome results from **hemitransverse lesion of the spinal cord**, causing **ipsilateral motor paralysis** and loss of proprioception/vibration below the lesion, and **contralateral loss of pain and temperature sensation**.
- The patient's **bilateral motor and sensory deficits** are inconsistent with the unilateral presentation of Brown-Séquard syndrome.
*Guillain-Barré Syndrome*
- GBS typically presents as an **ascending paralysis** with **areflexia**, but sensory loss is usually stocking-glove distribution and often involves proprioception, and it is a **peripheral neuropathy** not a spinal cord infarction.
- The acute, localized nature of the sensory and motor loss below the waist, along with preserved vibratory sensation, differentiates it from the more diffuse presentation of GBS.
*Tabes dorsalis*
- This is a late manifestation of **syphilis** affecting the **dorsal columns** and dorsal roots, characterized by ataxia, lancinating pains, and loss of proprioception and vibration sense.
- The acute onset of symptoms following a hypotensive episode, along with motor paralysis and preserved vibratory sensation, does not fit the chronic, dorsal column pathology of tabes dorsalis.
More Middle cerebral artery territory US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.