Vascular supply (Circle of Willis)

On this page
🔄 Circle of Willis: The Brain's Ultimate Safety Network
The Circle of Willis stands as your brain's most elegant insurance policy-a ring of arteries that can reroute blood flow when vessels fail, yet its anatomical variations determine who survives a stroke intact and who doesn't. You'll master how pressure gradients govern collateral rescue, decode territorial infarct patterns that reveal which artery occluded, and build the clinical reasoning to rapidly assess neurovascular compromise and select evidence-based interventions that save brain tissue and lives.
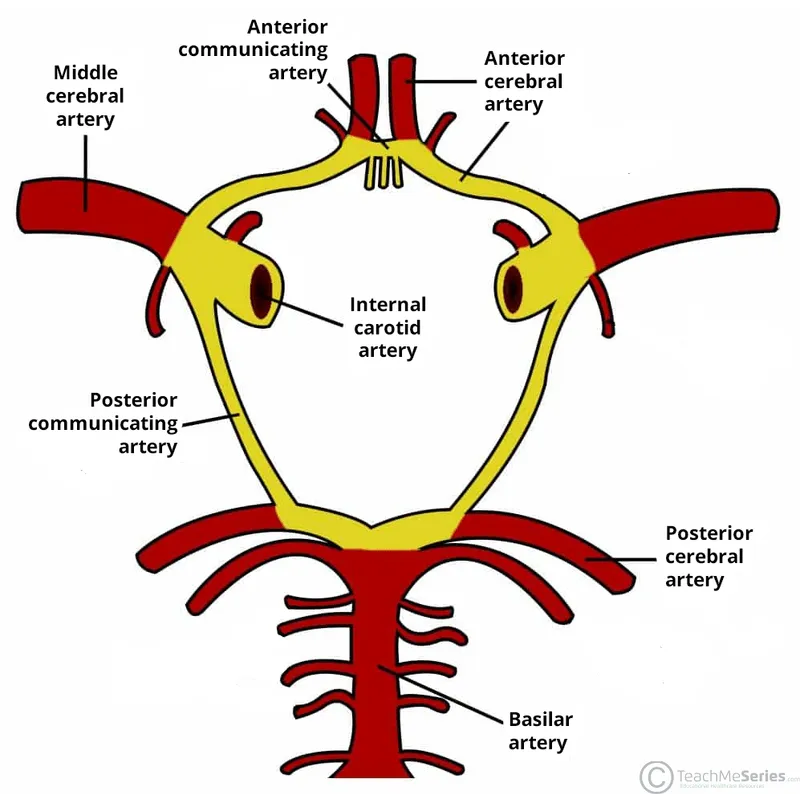
The Circle of Willis represents neurovascular engineering at its finest-a heptagonal arterial ring at the brain's base that connects anterior and posterior circulation systems. This anastomotic network involves 7 key vessels: paired anterior cerebral arteries (A1 segments), paired posterior cerebral arteries (P1 segments), paired posterior communicating arteries, and the single anterior communicating artery.
📌 Remember: PAPA-A - Posterior cerebral (2), Anterior cerebral (2), Posterior communicating (2), Anterior communicating (1) = 7 total vessels forming the complete circle
-
Anterior Circulation Components
- A1 segments of ACAs: 2-3mm diameter, supply medial frontal cortex
- Anterior communicating artery: 1-2mm diameter, shortest vessel in circle
- Connects bilateral A1 segments
- Most common aneurysm site (30-35% of all cerebral aneurysms)
- Critical for cross-flow during unilateral carotid occlusion
-
Posterior Circulation Integration
- P1 segments of PCAs: 2.5-3.5mm diameter, arise from basilar bifurcation
- Posterior communicating arteries: 1.5-2.5mm diameter, most variable vessels
- Connect ICA to PCA systems
- Fetal-type configuration in 15-20% of population
- Second most common aneurysm location (25% of cases)
| Vessel Component | Diameter (mm) | Length (mm) | Aneurysm Risk | Variation Rate | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACA A1 | 2.0-3.0 | 12-15 | Low (5%) | Hypoplasia 10% | Frontal lobe supply |
| ACoA | 1.0-2.0 | 2-4 | Highest (35%) | Duplicate 15% | Cross-circulation |
| PCoA | 1.5-2.5 | 8-12 | High (25%) | Fetal type 20% | Collateral flow |
| PCA P1 | 2.5-3.5 | 6-8 | Moderate (8%) | Hypoplasia 15% | Posterior supply |
| ICA terminus | 4.0-5.0 | 5-7 | High (20%) | Rare | Bifurcation stress |
💡 Master This: The Circle of Willis functions as a pressure-equalizing system-when one vessel occludes, pressure gradients automatically redirect flow through communicating arteries, with cross-flow rates reaching 40-60% of baseline perfusion within seconds
Understanding Circle of Willis anatomy provides the foundation for recognizing stroke patterns, aneurysm distributions, and collateral flow dynamics. Connect this anatomical blueprint through hemodynamic principles to understand how pressure differentials drive compensatory circulation when primary vessels fail.
🔄 Circle of Willis: The Brain's Ultimate Safety Network
⚡ Hemodynamic Command Center: Pressure-Driven Flow Dynamics
📌 Remember: RAPID collateral response - Redirection within 3-5 seconds, Autoregulation maintains 50-150 mmHg, Pressure gradient >20 mmHg triggers flow, Instant compensation up to 60%, Dynamic adjustment continues 24-48 hours
-
Pressure-Flow Relationships
- Autoregulation range: 50-150 mmHg cerebral perfusion pressure
- Critical threshold: <40 mmHg causes ischemic symptoms
- Collateral flow can maintain 40-60% of baseline perfusion
- Symptomatic threshold: <30% of normal flow rate
- Infarction threshold: <20% of normal flow for >6 hours
-
Dynamic Flow Mechanisms
- Communicating artery dilation: 2-3x baseline diameter within minutes
- Pressure-driven recruitment: dormant vessels activate at pressure drops >15 mmHg
- Leptomeningeal collaterals provide 10-20% additional flow
- Ophthalmic artery reversal contributes 5-15% during carotid occlusion
- Circle completion increases collateral capacity by 300-400%
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Fetal-type posterior communicating arteries (diameter >1.5mm) provide superior collateral capacity, reducing stroke risk by 40-50% during anterior circulation occlusion compared to hypoplastic variants (<1mm diameter)
💡 Master This: Circle of Willis hemodynamics follow Poiseuille's Law-flow rate increases with the fourth power of vessel radius, meaning small diameter increases in communicating arteries create exponential improvements in collateral flow capacity
These hemodynamic principles explain why Circle of Willis variations dramatically impact stroke outcomes. Connect this flow understanding through anatomical variants to recognize which patients face highest ischemic risk during vascular compromise.
⚡ Hemodynamic Command Center: Pressure-Driven Flow Dynamics
🎯 Stroke Pattern Recognition: Territorial Mapping Mastery
Circle of Willis stroke patterns follow predictable territorial distributions based on anatomical supply zones and collateral flow capacity. Recognition speed determines treatment windows-mechanical thrombectomy remains effective up to 24 hours for large vessel occlusions with good collaterals.
📌 Remember: FAST-ED stroke recognition - Face (ACA spares), Arms (MCA classic), Speech (dominant MCA), Time critical, Eyes (PCA hallmark), Dizziness (vertebrobasilar)
-
Anterior Circulation Patterns
- ACA territory strokes (5-10% of all strokes)
- Contralateral leg weakness > arm weakness (motor homunculus)
- Abulia and personality changes (frontal lobe involvement)
- Urinary incontinence (paracentral lobule)
- Grasp reflex and primitive reflexes return
- MCA territory strokes (80-85% of anterior circulation)
- Classic triad: contralateral hemiparesis, hemianesthesia, hemianopia
- Dominant hemisphere: aphasia (Broca's or Wernicke's)
- Non-dominant: neglect syndrome and anosognosia
- ACA territory strokes (5-10% of all strokes)
-
Posterior Circulation Patterns
- PCA territory strokes (10-15% of all strokes)
- Homonymous hemianopia (occipital cortex)
- Alexia without agraphia (dominant PCA with splenium)
- Visual agnosia and prosopagnosia (bilateral occipital)
- Memory impairment (hippocampal branches)
- PCA territory strokes (10-15% of all strokes)
| Stroke Territory | Frequency | Key Clinical Signs | Collateral Capacity | Prognosis Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MCA M1 | 40% | Hemiparesis + aphasia | Moderate (60%) | mRS 3-4 |
| ACA A1 | 8% | Leg weakness + abulia | Excellent (85%) | mRS 1-2 |
| PCA P1 | 12% | Hemianopia + memory | Good (70%) | mRS 2-3 |
| Basilar | 5% | Quadriplegia + coma | Poor (20%) | mRS 5-6 |
| Multiple | 15% | Mixed deficits | Variable | mRS 4-5 |
💡 Master This: Collateral flow grading on CT angiography directly correlates with clinical outcomes-good collaterals (>50% filling) predict successful recanalization in 85-90% of cases versus <40% with poor collaterals
Pattern recognition mastery enables rapid triage decisions and treatment selection. Connect these territorial concepts through anatomical variations to understand why Circle of Willis completeness determines individual stroke risk and recovery potential.
🎯 Stroke Pattern Recognition: Territorial Mapping Mastery
🔍 Anatomical Variants: The Imperfect Circle Analysis
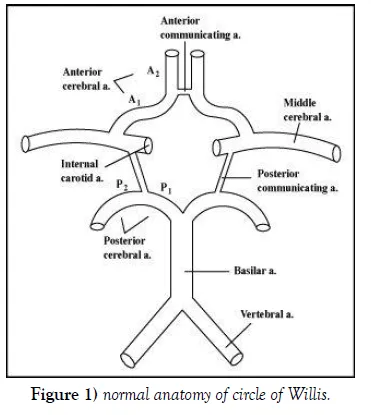
Circle of Willis variations follow predictable patterns with specific clinical implications. Hypoplastic or absent vessels create hemodynamic vulnerabilities, while fetal-type configurations may provide enhanced collateral capacity in certain territories.
📌 Remember: CHAMP variant frequencies - Complete circle 20%, Hypoplastic PCoA 30%, A1 asymmetry 25%, Missing ACoA 10%, P1 hypoplasia 15%
-
Anterior Circulation Variants
- A1 segment asymmetry (present in 25-30%)
- Dominant A1 >1.5mm, hypoplastic A1 <1mm
- Clinical impact: reduced cross-flow during carotid occlusion
- Stroke risk increase: 2-3x higher with severe asymmetry
- Anterior communicating artery variants
- Hypoplastic ACoA (<1mm): 10-15% prevalence
- Duplicate ACoA: 15-20% prevalence, better collateral flow
- Absent ACoA: 5% prevalence, highest stroke risk
- A1 segment asymmetry (present in 25-30%)
-
Posterior Circulation Variants
- Posterior communicating artery configurations
- Hypoplastic PCoA (<1mm): 30-35% prevalence
- Fetal-type PCoA (>1.5mm): 15-20% prevalence
- Bilateral fetal PCoA: 3-5% prevalence, exceptional collaterals
- P1 segment variations
- Hypoplastic P1: 10-15% prevalence
- Absent P1: 2-3% prevalence
- Fetal origin from ICA: 8-12% prevalence
- Posterior communicating artery configurations
| Variant Type | Prevalence | Collateral Impact | Stroke Risk | Aneurysm Risk |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complete Circle | 20% | Excellent | Baseline | Standard |
| Hypoplastic PCoA | 30% | Poor | 2x higher | Reduced |
| Fetal PCoA | 18% | Enhanced | 0.5x lower | Increased |
| A1 Asymmetry | 25% | Moderate | 1.5x higher | Standard |
| Missing ACoA | 8% | Severely impaired | 3x higher | N/A |
💡 Master This: Circle of Willis imaging should be routine in stroke workup-CT angiography identifies clinically significant variants in >90% of cases, directly influencing treatment decisions and prognosis counseling
Anatomical variant recognition enables personalized stroke risk assessment. Connect these structural differences through treatment algorithms to understand how Circle of Willis anatomy guides therapeutic decision-making and intervention timing.
🔍 Anatomical Variants: The Imperfect Circle Analysis
⚖️ Treatment Algorithm: Evidence-Based Intervention Strategies
Modern stroke treatment algorithms incorporate Circle of Willis anatomy and collateral flow assessment as primary decision factors. Mechanical thrombectomy success rates correlate directly with collateral grade-good collaterals achieve TICI 2b-3 recanalization in 85-90% versus <60% with poor collaterals.
📌 Remember: ASPECTS collateral grading - Alberta stroke program, Scores 0-10, Predicts outcomes, Early changes matter, Collaterals >50% = good, Thrombectomy benefit, Success rates correlate
-
Time-Based Treatment Windows
- IV thrombolysis: <4.5 hours from onset
- Contraindications: >80 years + diabetes + prior stroke
- Success rate: 40-45% recanalization for large vessels
- Hemorrhage risk: 6-8% symptomatic ICH
- Mechanical thrombectomy: <24 hours with good collaterals
- TICI 2b-3 rates: 85-90% with complete Circle of Willis
- Functional independence: 45-50% at 90 days (mRS 0-2)
- Number needed to treat: 2.6 for good collateral patients
- IV thrombolysis: <4.5 hours from onset
-
Collateral-Based Decision Making
- Excellent collaterals (>75% filling)
- Thrombectomy benefit: up to 24 hours
- Recanalization rates: 90-95%
- Good outcomes: 60-65% mRS 0-2
- Poor collaterals (<25% filling)
- Limited time window: <6 hours
- Recanalization rates: 60-70%
- Good outcomes: 25-30% mRS 0-2
- Excellent collaterals (>75% filling)
| Treatment Modality | Time Window | Success Rate | mRS 0-2 Rate | NNT | Complications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IV tPA alone | <4.5h | 45% | 35% | 8 | 6% sICH |
| Thrombectomy + tPA | <6h | 90% | 50% | 3 | 4% sICH |
| Thrombectomy alone | 6-24h | 85% | 45% | 4 | 3% sICH |
| Medical only | Any | 15% | 20% | N/A | 2% sICH |
| Bypass surgery | Chronic | 70% | 60% | 6 | 8% stroke |
💡 Master This: Collateral assessment on initial CTA is the strongest predictor of treatment response-good collaterals extend the therapeutic window to 24 hours and increase successful recanalization rates by 25-30% regardless of time from onset
Evidence-based treatment algorithms maximize intervention success through anatomical assessment. Connect these therapeutic principles through system integration to understand how Circle of Willis function influences multi-organ responses during cerebrovascular events.
⚖️ Treatment Algorithm: Evidence-Based Intervention Strategies
🔗 Neurovascular Integration: Multi-System Command Networks
Circle of Willis perfusion directly impacts autonomic control centers in the hypothalamus and brainstem, creating multi-system responses during cerebrovascular events. Posterior circulation supplies cardiovascular control centers, while anterior circulation perfuses neuroendocrine and behavioral regulation areas.
📌 Remember: BRAIN-HEART axis - Brainstem control centers, Regulation of BP/HR, Autonomic responses, Insular cortex integration, Neuroendocrine effects, Hypothalamic control, Emotional processing, Arrhythmia triggers, Respiratory centers, Temperature regulation
-
Cardiovascular Integration Pathways
- Insular cortex perfusion (MCA territory)
- Cardiac autonomic control: heart rate variability regulation
- Stroke impact: cardiac arrhythmias in 60-80% of insular strokes
- Takotsubo cardiomyopathy: 5-10% incidence with right insular involvement
- Hypothalamic connections (ACA/ACoA territory)
- Neuroendocrine control: ADH, cortisol, catecholamine release
- Circadian regulation: sleep-wake cycles, temperature control
- Stress response: HPA axis activation during cerebral ischemia
- Insular cortex perfusion (MCA territory)
-
Brainstem Autonomic Centers (vertebrobasilar territory)
- Medullary cardiovascular centers
- Blood pressure regulation: baroreceptor integration
- Respiratory control: chemoreceptor responses
- Stroke consequences: neurogenic pulmonary edema (20-30% of posterior strokes)
- Pontine arousal systems
- Consciousness regulation: reticular activating system
- Sleep architecture: REM/NREM cycle control
- Cognitive integration: attention and executive function
- Medullary cardiovascular centers
| System Integration | Vascular Territory | Clinical Manifestation | Frequency | Recovery Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cardiac autonomic | Insular cortex | Arrhythmias, HF | 70% | 2-4 weeks |
| BP regulation | Medulla | Hypertensive crisis | 45% | 1-2 weeks |
| Neuroendocrine | Hypothalamus | SIADH, DI | 25% | 4-8 weeks |
| Sleep-wake | Brainstem/hypothalamus | Insomnia, hypersomnia | 60% | 6-12 weeks |
| Temperature | Hypothalamus | Hyperthermia | 15% | 1-3 days |
💡 Master This: Neurovascular coupling explains why Circle of Willis assessment predicts multi-organ dysfunction-good collateral flow maintains autonomic center perfusion, reducing cardiac events by 30-40% and improving overall survival in acute stroke patients
Multi-system integration reveals the Circle of Willis as more than cerebral circulation-it's the command center for physiological homeostasis. Connect this systems understanding through clinical mastery tools to develop rapid assessment and comprehensive management strategies.
🔗 Neurovascular Integration: Multi-System Command Networks
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid Assessment & Decision Tools
Circle of Willis mastery centers on rapid pattern recognition and evidence-based decision algorithms. Expert clinicians identify critical findings within 30 seconds of imaging review, translating anatomical variants into treatment modifications that improve patient outcomes by 20-30%.
📌 Remember: CIRCLE rapid assessment - Collaterals on CTA, Infarct core size, Recanalization potential, Clinical deficit severity, Large vessel occlusion, Eligibility for intervention
-
Essential Clinical Thresholds
- Time windows: <4.5h IV tPA, <6h thrombectomy, <24h with good collaterals
- ASPECTS score: >6 for thrombectomy, <4 poor prognosis
- Collateral grades: >50% filling = good, <25% = poor
- Core infarct: <70ml thrombectomy benefit, >100ml futile
- NIHSS thresholds: >6 for large vessel, >15 severe stroke
-
Rapid Decision Framework
- Complete Circle of Willis (20% of patients)
- Extended time windows: up to 24 hours
- Aggressive intervention: thrombectomy + neuroprotection
- Expected outcomes: 60-70% good recovery
- Incomplete Circle (80% of patients)
- Standard time windows: <6 hours
- Collateral-dependent: CTA assessment critical
- Variable outcomes: 30-50% good recovery
- Complete Circle of Willis (20% of patients)
| Assessment Tool | Time Required | Accuracy | Clinical Impact | Evidence Level |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASPECTS score | 2 min | 85% | Treatment selection | Class I |
| Collateral grade | 1 min | 90% | Outcome prediction | Class I |
| NIHSS | 5 min | 95% | Severity assessment | Class I |
| CTA source images | 3 min | 88% | Core estimation | Class IIa |
| Circle completeness | 30 sec | 92% | Risk stratification | Class IIb |
💡 Master This: The "20-80 Rule" guides Circle of Willis clinical decisions-20% have complete circles with excellent outcomes, 80% have variants requiring individualized assessment based on specific collateral patterns and hemodynamic reserve
Circle of Willis mastery transforms complex neurovascular anatomy into actionable clinical tools. Expert assessment integrates anatomical variants, hemodynamic principles, and evidence-based algorithms to optimize patient outcomes through precision medicine approaches in cerebrovascular care.
🎯 Clinical Mastery Arsenal: Rapid Assessment & Decision Tools
Practice Questions: Vascular supply (Circle of Willis)
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 52-year-man is brought to the physician because of a 2-week history of memory loss. Three weeks ago, he had a cardiac arrest that required cardiopulmonary resuscitation and intravenous epinephrine. On mental status examination, he cannot recall objects shown to him 20 minutes earlier but vividly recalls memories from before the incident. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following structures of the brain is most likely affected?










