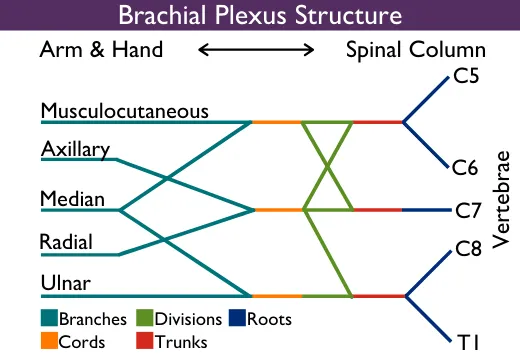
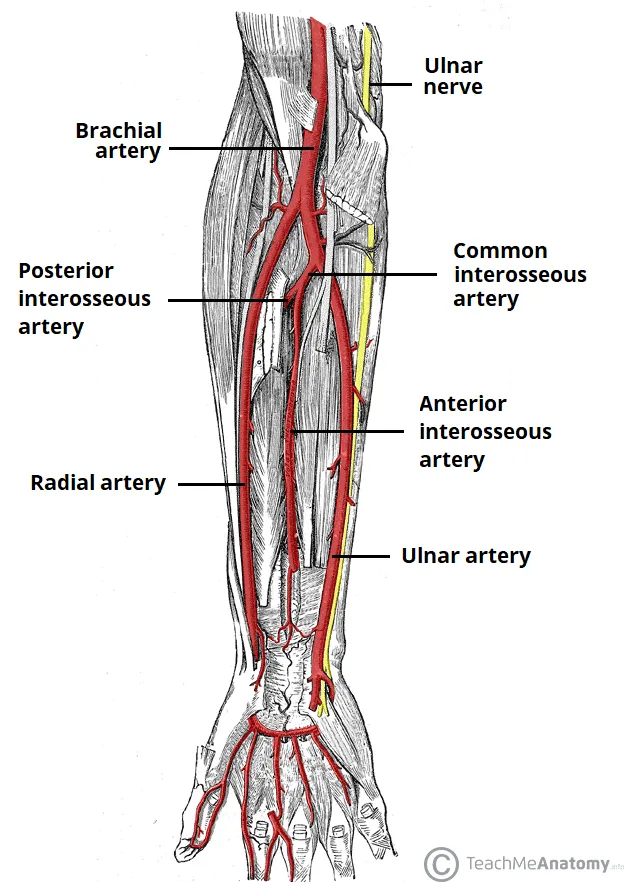
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Nerves and blood supply of upper limb. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb US Medical PG Question 1: A patient presents with difficulty extending their wrist following trauma to the posterior forearm. Which of the following muscles would be most affected by injury to the posterior interosseous nerve?
- A. Extensor carpi ulnaris
- B. Extensor carpi radialis brevis
- C. Extensor pollicis longus
- D. Extensor digitorum (Correct Answer)
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb Explanation: ***Extensor digitorum***
- The **posterior interosseous nerve (PIN)** innervates most muscles of the **posterior compartment of the forearm**, including the extensor digitorum. [1]
- Loss of function in the **extensor digitorum** would directly impair **extension of the fingers** and contribute significantly to difficulty extending the wrist. [1]
*Extensor carpi ulnaris*
- This muscle is also innervated by the **posterior interosseous nerve (PIN)** and contributes to **wrist extension** and **ulnar deviation**.
- While its innervation by the PIN is correct, injury to the PIN would affect this muscle, but the *extensor digitorum* is more broadly responsible for the stated primary symptom (difficulty extending the wrist), as its primary action is finger and thus wrist extension.
*Extensor carpi radialis brevis*
- While it is a **wrist extensor**, it is innervated by the **deep branch of the radial nerve** *before* it becomes the posterior interosseous nerve.
- Therefore, an isolated injury to the **posterior interosseous nerve** proper would typically spare the extensor carpi radialis brevis.
*Extensor pollicis longus*
- This muscle is indeed innervated by the **posterior interosseous nerve (PIN)** and acts to extend the **thumb**. [1]
- While it would be affected, the primary problem described is difficulty extending the *wrist*, for which the extensor digitorum plays a more significant and general role than the extensor pollicis longus.
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb US Medical PG Question 2: A 53-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of intermittent severe left neck, shoulder, and arm pain and paresthesias of the left hand. The pain radiates to the radial aspect of her left forearm, thumb, and index finger. She first noticed her symptoms after helping a friend set up a canopy tent. There is no family history of serious illness. She appears healthy. Vital signs are within normal limits. When the patient extends and rotates her head to the left and downward pressure is applied, she reports paresthesias along the radial aspect of her left forearm and thumb. There is weakness when extending the left wrist against resistance. The brachioradialis reflex is 1+ on the left and 2+ on the right. The radial pulse is palpable bilaterally. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Carpal tunnel syndrome
- B. Syringomyelia
- C. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- D. C5-C6 disc herniation (Correct Answer)
- E. Thoracic outlet syndrome
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb Explanation: ***C5-C6 disc herniation***
- The patient's symptoms of neck, shoulder, and arm pain, along with paresthesias radiating to the **radial aspect of the forearm, thumb, and index finger**, are consistent with **C6 dermatomal distribution**.
- The positive **Spurling's maneuver** (extension, rotation, and downward pressure causing paresthesias) and decreased **brachioradialis reflex** (C5-C6 reflex) strongly suggest **cervical radiculopathy**, most likely due to a disc herniation affecting the C6 nerve root.
*Carpal tunnel syndrome*
- Characterized by **median nerve compression** at the wrist, causing paresthesias and pain primarily in the **thumb, index, middle, and radial half of the ring finger**, typically worsening at night.
- Would not explain the neck, shoulder, or upper arm pain, or the positive Spurling's maneuver, which indicates a more proximal nerve root compression.
*Syringomyelia*
- A rare chronic progressive disorder where a **syrinx (fluid-filled cyst)** forms within the spinal cord, often presenting with a **cape-like distribution of sensory loss** (loss of pain and temperature sensation) over the shoulders and upper extremities.
- Motor weakness can occur but the pain and paresthesia pattern, along with the positive Spurling's maneuver, are not typical for syringomyelia.
*Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis*
- A progressive neurodegenerative disease affecting **upper and lower motor neurons**, leading to widespread muscle weakness, atrophy, fasciculations, and spasticity.
- It does not typically present with acute, radicular pain and paresthesias restricted to a specific dermatome, and sensory involvement is absent.
*Thoracic outlet syndrome*
- Involves compression of the **brachial plexus** and/or subclavian vessels in the thoracic outlet, causing neurogenic symptoms (pain, paresthesias) primarily in the **ulnar nerve distribution** and vascular symptoms (edema, discoloration).
- The pain and paresthesias in the radial aspect of the hand and forearm, along with the specific reflex changes and positive neck maneuver, are not characteristic of thoracic outlet syndrome.
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb US Medical PG Question 3: A 30-year-old man presents with weakness in his right hand. He says he has been an avid cyclist since the age of 20. He denies any recent trauma. Physical examination reveals decreased sensations over the 4th and 5th digits with difficulty extending the 4th and 5th digits. Strength is 4 out of 5 in the extensor muscles of the right hand and wrist. When the patient is asked to extend his fingers, the result is shown in the image. Which of the following nerves is most likely damaged in this patient?
- A. Median nerve
- B. Musculocutaneous nerve
- C. Axillary nerve
- D. Ulnar nerve (Correct Answer)
- E. Radial nerve
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb Explanation: ***Ulnar nerve***
- The symptoms, including weakness in the **right hand**, decreased sensation over the **4th and 5th digits**, and difficulty extending the 4th and 5th digits (which suggests **ulnar claw**), are characteristic of **ulnar nerve damage**.
- **Avid cycling** can lead to compression of the ulnar nerve in the **Guyon's canal** (handlebar palsy) or at the **cubital tunnel** in the elbow, causing these specific signs.
*Median nerve*
- Damage to the median nerve typically affects the **thumb**, **index**, **middle finger**, and radial half of the ring finger, causing **ape hand deformity** or **carpal tunnel syndrome**.
- It controls movements like **thumb opposition** and **flexion of the first three digits**, which are not primarily described as impaired here.
*Musculocutaneous nerve*
- This nerve primarily innervates the **biceps brachii**, **brachialis**, and **coracobrachialis muscles**, affecting **elbow flexion** and **forearm supination**.
- It provides sensory innervation to the **lateral forearm**, symptoms not consistent with this patient's presentation.
*Axillary nerve*
- Damage to the axillary nerve results in weakness of the **deltoid** and **teres minor muscles**, leading to impaired **shoulder abduction** and external rotation.
- Sensory loss would be over the **lateral aspect of the shoulder**, which is unrelated to the described hand symptoms.
*Radial nerve*
- Radial nerve damage typically results in **wrist drop** and impaired **extension of the fingers and thumb** due to innervation of the extensors.
- While there is difficulty extending the 4th and 5th digits, the sensory loss pattern (4th and 5th digits) and specific **ulnar claw** appearance are more indicative of ulnar nerve involvement.
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb US Medical PG Question 4: A 40-year-old male presents to the physician's office complaining of an inability to push doors open. He has had this problem since he was playing football with his children and was tackled underneath his right arm on his lateral chest. On examination, he has a winged scapula on the right side. Which of the following nerves is most likely the cause of this presentation?
- A. Phrenic nerve
- B. Spinal accessory nerve
- C. Long thoracic nerve (Correct Answer)
- D. Greater auricular nerve
- E. Musculocutaneous nerve
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb Explanation: ***Long thoracic nerve***
- The **long thoracic nerve** innervates the **serratus anterior muscle**, which is responsible for scapular protraction and upward rotation.
- Damage to this nerve, often from trauma to the lateral chest wall (tackled underneath the arm), leads to paralysis of the serratus anterior and a characteristic **winged scapula** with lateral and inferior prominence.
- Patients have difficulty with **pushing movements** (protraction) and overhead activities.
*Phrenic nerve*
- The **phrenic nerve** primarily innervates the **diaphragm** and is crucial for respiration.
- Damage to the phrenic nerve would cause respiratory compromise, not a winged scapula or difficulty pushing doors.
*Spinal accessory nerve*
- The **spinal accessory nerve (cranial nerve XI)** innervates the **sternocleidomastoid** and **trapezius muscles**.
- Injury to this nerve can cause scapular winging due to **trapezius paralysis**, but the winging is typically **medial** with the inferior angle moving medially, unlike the lateral winging from serratus anterior paralysis.
- The mechanism of injury (lateral chest trauma during tackling) and inability to push are classic for **long thoracic nerve** injury, not spinal accessory nerve.
*Greater auricular nerve*
- The **greater auricular nerve** is a cutaneous nerve that provides sensation to the skin over the parotid gland, mastoid process, and auricle.
- Damage to this nerve would result in sensory loss in these areas and is unrelated to muscle weakness or a winged scapula.
*Musculocutaneous nerve*
- The **musculocutaneous nerve** innervates the **biceps brachii**, **brachialis**, and **coracobrachialis muscles**, responsible for elbow flexion and forearm supination.
- Damage to this nerve would primarily affect these movements and sensation in the lateral forearm, not leading to a winged scapula.
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb US Medical PG Question 5: A 23-year-old college student was playing basketball when he fell directly onto his left elbow. He had sudden, intense pain and was unable to move his elbow. He was taken immediately to the emergency room by his teammates. He has no prior history of trauma or any chronic medical conditions. His blood pressure is 128/84 mm Hg, the heart rate is 92/min, and the respiratory rate is 14/min. He is in moderate distress and is holding onto his left elbow. On physical examination, pinprick sensation is absent in the left 5th digit and the medial aspect of the left 4th digit. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this patient’s condition?
- A. Axillary neuropathy
- B. Median neuropathy
- C. Radial neuropathy
- D. Musculocutaneous neuropathy
- E. Ulnar neuropathy (Correct Answer)
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb Explanation: ***Ulnar neuropathy***
- Direct trauma to the elbow, combined with **pinprick sensation loss** in the **5th digit** and the **medial aspect of the 4th digit**, is highly indicative of **ulnar nerve injury**.
- The ulnar nerve passes through the **cubital tunnel** at the elbow, making it vulnerable to compression or trauma from direct falls.
*Axillary neuropathy*
- An **axillary nerve injury** typically presents with weakness in **shoulder abduction** (deltoid muscle) and sensory loss over the **lateral aspect of the shoulder**.
- This clinical picture does not match the patient's sensory deficits in the fingers.
*Median neuropathy*
- **Median nerve injury** at the elbow would typically cause sensory loss in the **first three fingers and the lateral half of the fourth finger**, along with **weakness in thumb opposition** and **flexion of the index and middle fingers**.
- The sensory loss described in the patient does not align with median nerve distribution.
*Radial neuropathy*
- **Radial nerve injury** at the elbow level would primarily result in **wrist drop** and sensory loss over the **dorsal aspect of the hand**, particularly the **first three and a half digits**.
- These are not the clinical findings presented by the patient.
*Musculocutaneous neuropathy*
- **Musculocutaneous nerve injury** would cause weakness in **elbow flexion** (biceps and brachialis muscles) and sensory loss over the **lateral forearm**.
- The patient's reported sensory loss is in a different distribution and no specific motor deficits of elbow flexion are mentioned.
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb US Medical PG Question 6: A 50-year-old man undergoes parathyroidectomy for treatment-resistant hyperparathyroidism. The procedure is complicated by brisk bleeding from the superior thyroid artery near the external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve. To stop the bleeding, the artery is ligated at its origin. Which of the following is most likely the origin of the artery that was injured in this patient?
- A. Thyrocervical trunk
- B. Ascending pharyngeal artery
- C. Internal carotid artery
- D. Subclavian artery
- E. External carotid artery (Correct Answer)
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb Explanation: ***External carotid artery***
- The **superior thyroid artery** is the first branch to arise from the **external carotid artery** in the neck.
- Ligation of this artery at its origin is a common surgical maneuver to control bleeding during thyroid or parathyroid surgery.
*Thyrocervical trunk*
- The **thyrocervical trunk** is a branch of the **subclavian artery** and gives rise to the inferior thyroid artery, not the superior thyroid artery.
- Injury to the superior thyroid artery would not necessitate ligation of a vessel originating from the thyrocervical trunk.
*Ascending pharyngeal artery*
- The **ascending pharyngeal artery** is a small artery that branches from the **external carotid artery** but supplies the pharynx, not the thyroid gland.
- It is not typically implicated in bleeding during parathyroidectomy or in relation to the superior laryngeal nerve.
*Internal carotid artery*
- The **internal carotid artery** primarily supplies the brain and does not have branches in the neck that supply the thyroid or parathyroid glands.
- It arises from the common carotid artery but does not give off the superior thyroid artery.
*Subclavian artery*
- The **subclavian artery** gives rise to the **thyrocervical trunk**, which then supplies the inferior thyroid artery, but not directly the superior thyroid artery.
- The superior thyroid artery originates higher up from the external carotid artery.
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb US Medical PG Question 7: A 32-year-old woman presents with new left-arm pain. She was previously well but for 2 months has had episodes of low-grade fever, night sweats, and dizziness. She works as a stock assistant and has noticed left arm pain when she stocks shelves. She is taking a multivitamin but no other medications. On physical examination, her blood pressure is 126/72 in her right arm, but it cannot be measured in her left arm. The left radial pulse is not detectable. There is a bruit over the left subclavian area. Femoral and pedal pulses are normal and no abdominal bruits are heard. The left hand is cool but has no other evidence of ischemia. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of this patient’s condition?
- A. Raynaud’s phenomenon
- B. Fibromuscular dysplasia
- C. Subclavian steal syndrome
- D. Aortic coarctation
- E. Takayasu arteritis (Correct Answer)
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb Explanation: ***Takayasu arteritis***
- This **large-vessel vasculitis** predominantly affects **young women** (typically <40 years old) and involves the aorta and its major branches, including the subclavian arteries.
- The patient's **constitutional symptoms** (low-grade fever, night sweats) reflect the systemic inflammatory nature of the disease.
- The **absent left radial pulse**, **unmeasurable left arm blood pressure**, and **subclavian bruit** indicate significant stenosis or occlusion of the left subclavian artery, a hallmark of Takayasu arteritis.
- This arterial stenosis can lead to **subclavian steal syndrome** (a manifestation, not the etiology) and **arm claudication** with exertion (pain when stocking shelves).
- The **normal femoral and pedal pulses** help localize the pathology to the upper extremity vessels.
*Subclavian steal syndrome*
- This is a **hemodynamic phenomenon** (manifestation), not an underlying etiology.
- It occurs when subclavian artery stenosis causes retrograde flow from the vertebral artery to supply the affected arm, which can cause dizziness due to vertebrobasilar insufficiency.
- The underlying **cause** in this young woman with systemic symptoms is most likely Takayasu arteritis.
*Raynaud's phenomenon*
- Characterized by **episodic vasospasm** of digital arteries in response to cold or stress, causing color changes (white-blue-red).
- Does not cause **absent pulses**, **unequal blood pressures between arms**, **bruits**, or **constitutional symptoms**.
*Aortic coarctation*
- A **congenital narrowing of the aorta**, typically just distal to the left subclavian artery origin.
- Would cause **hypertension in both upper extremities** with **diminished lower extremity pulses and blood pressures** (upper-lower discrepancy, not left-right arm discrepancy).
- Does not explain the constitutional symptoms or isolated left arm findings.
*Fibromuscular dysplasia*
- A **noninflammatory arteriopathy** causing abnormal cellular proliferation in arterial walls, most commonly affecting **renal and carotid arteries**.
- Typically occurs in **middle-aged women** without systemic symptoms.
- While it can rarely affect subclavian arteries, the **constitutional symptoms** and pattern of large-vessel involvement strongly favor an inflammatory vasculitis like Takayasu arteritis.
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb US Medical PG Question 8: An 80-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department for left hip pain 30 minutes after she fell while walking around in her room. Examination shows left groin tenderness. The range of motion of the left hip is limited because of pain. An x-ray of the hip shows a linear fracture of the left femoral neck with slight posterior displacement of the femur. Which of the following arteries was most likely damaged in the patient's fall?
- A. Superior gluteal artery
- B. Deep circumflex iliac
- C. Deep femoral artery
- D. Obturator
- E. Medial circumflex femoral (Correct Answer)
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb Explanation: ***Medial circumflex femoral***
- This artery is the **primary blood supply** to the femoral head and neck, making it highly vulnerable to injury in cases of femoral neck fractures.
- Damage to the medial circumflex femoral artery significantly increases the risk of **avascular necrosis** of the femoral head.
*Superior gluteal artery*
- The superior gluteal artery primarily supplies the **gluteus medius** and **minimus muscles**.
- It is **not directly involved** in the primary blood supply to the femoral head and neck.
*Deep circumflex iliac*
- This artery mainly supplies the **iliac fossa** and the **abdominal wall muscles**.
- It does not contribute significantly to the blood supply of the femoral neck.
*Deep femoral artery*
- The deep femoral artery, also known as the **profunda femoris artery**, is the main supply to the **thigh muscles**.
- While it gives rise to the circumflex arteries, it is not the artery directly compromised in a femoral neck fracture.
*Obturator*
- The obturator artery primarily supplies the **adductor muscles** of the thigh and contributes a small branch to the femoral head via the **ligamentum teres**.
- This contribution is **insufficient** to maintain viability of the femoral head, especially in trauma to the femoral neck.
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb US Medical PG Question 9: A 39-year-old male who recently presented with acetaminophen overdose was admitted to the MICU, where several attempts were made at obtaining intravenous access without success. The decision was made to place a right axillary arterial line, which became infected and was removed by the medical student while the patient was still intubated. It was later noticed that he had substantial swelling and bruising of the upper extremity. Given his sedation, a proper neuro exam was not performed at that time. Several days later, after the patient's liver function improved, he was successfully extubated. On exam, he complained of lack of sensation over the palmar and dorsal surface of the small finger and half of the ring finger, as well as weak digit abduction, weak thumb adduction, and weak thumb-index finger pinch of the affected extremity. What is the most likely cause and corresponding location of the injury?
- A. Compression of ulnar nerve secondary to coagulopathy (Correct Answer)
- B. Compression of median nerve secondary to coagulopathy
- C. Stretch injury to ulnar nerve secondary to frequent repositioning
- D. Needle injury to ulnar nerve secondary to blind line placement
- E. Needle injury to median nerve secondary to blind line placement
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb Explanation: ***Compression of ulnar nerve secondary to coagulopathy***
- The described sensory deficits (palmar and dorsal surface of the small finger and half of the ring finger) and motor deficits (weak digit abduction, weak thumb adduction, and weak thumb-index finger pinch) are classic signs of **ulnar nerve injury**.
- The patient's history of an infected axillary arterial line, substantial upper extremity swelling/bruising, and likely **coagulopathy** (given acetaminophen overdose and liver dysfunction) predispose to hemorrhage and compression of the ulnar nerve in the axillary region or more distally.
*Compression of median nerve secondary to coagulopathy*
- **Median nerve injury** would typically present with sensory loss over the thumb, index, middle finger, and radial half of the ring finger, as well as weakness in thumb abduction and opposition. These findings are inconsistent with the patient's symptoms.
- While coagulopathy could cause nerve compression, the specific neurological deficits point away from the median nerve.
*Stretch injury to ulnar nerve secondary to frequent repositioning*
- While repositioning can cause stretch injuries, the context of an infected arterial line insertion, swelling, and bruising strongly suggests a **compressive etiology** rather than just a stretch injury.
- The degree of injury and the associated swelling make compression a more probable cause than simple stretch.
*Needle injury to ulnar nerve secondary to blind line placement*
- While blind line placement can cause needle injury, the delayed onset of symptoms after line removal, combined with the presence of **substantial swelling and bruising**, suggests a developing hematoma or compressive process rather than direct acute needle trauma.
- Direct needle injury would typically manifest immediately or very soon after the attempted placement.
*Needle injury to median nerve secondary to blind line placement*
- As with other median nerve options, the sensory and motor symptoms provided in the clinical vignette do not align with a **median nerve injury**.
- Furthermore, the clinical picture points to a compressive injury developing over time due to bleeding rather than a direct needle strike onto a nerve, especially given the axillary location where the median nerve is well protected within the neurovascular bundle.
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb US Medical PG Question 10: A 32-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-month history of intermittent tingling of his hand. He is an avid cyclist and has recently started training for a cycle marathon. Physical examination shows decreased grip strength in the right hand and wasting of the hypothenar eminence. On asking the patient to grasp a piece of paper between his right thumb and right index finger in the first web space, there is hyperflexion of the right thumb interphalangeal joint. Which of the following additional findings is most likely in this patient?
- A. Loss of sensation over the dorsum of the medial half of the hand
- B. Inability to extend the ring finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint
- C. Inability to flex the index finger at the interphalangeal joints
- D. Loss of sensation over the palmar aspect of the middle finger
- E. Inability to extend the little finger at the proximal interphalangeal joints (Correct Answer)
Nerves and blood supply of upper limb Explanation: ***Inability to extend the little finger at the proximal interphalangeal joints***
- The patient's symptoms (tingling, decreased grip strength, hypothenar eminence wasting, and **Froment's sign**) indicate **ulnar nerve compression at Guyon's canal** (handlebar palsy) from cycling.
- The ulnar nerve innervates the **3rd and 4th lumbricals** (medial two), which extend the PIP and DIP joints of the ring and little fingers.
- The ulnar nerve also innervates the **interossei muscles**, which assist in MCP flexion and IP extension.
- Loss of these intrinsic muscles results in **claw hand deformity** affecting the 4th and 5th digits, with hyperextension at MCP joints and flexion (inability to extend) at PIP and DIP joints.
- This is a classic finding in ulnar nerve palsy.
*Inability to extend the ring finger at the metacarpophalangeal joint*
- Extension at the MCP joint is primarily performed by the **extensor digitorum** (innervated by the **radial nerve**).
- The patient's findings indicate ulnar nerve compression, not radial nerve injury.
- In ulnar nerve palsy, the unopposed extensor digitorum actually causes MCP **hyperextension**, not inability to extend.
*Inability to flex the index finger at the interphalangeal joints*
- Flexion of the index finger IP joints is controlled by **flexor digitorum superficialis** (FDS) and **flexor digitorum profundus** (FDP).
- Both muscles to the index finger are innervated by the **median nerve**, not the ulnar nerve.
- This finding would indicate median nerve injury (e.g., carpal tunnel syndrome or anterior interosseous syndrome).
*Loss of sensation over the palmar aspect of the middle finger*
- Palmar sensation of the middle finger is supplied by the **median nerve**.
- The ulnar nerve supplies sensation to the medial 1.5 digits (little finger and medial half of ring finger).
- This finding would indicate median nerve pathology, not ulnar nerve compression.
*Loss of sensation over the dorsum of the medial half of the hand*
- The **dorsal cutaneous branch of the ulnar nerve** branches approximately 5-8 cm proximal to the wrist and passes **superficially**, NOT through Guyon's canal.
- In **Guyon's canal compression** (handlebar palsy), the dorsal cutaneous branch is **SPARED**, so dorsal sensation remains intact.
- The patient would have palmar sensory loss over the medial 1.5 digits but **preserved dorsal sensation**.
- Loss of dorsal sensation would suggest a more proximal ulnar nerve lesion (at the elbow or forearm), not at the wrist.
More Nerves and blood supply of upper limb US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.