Muscles and movements of upper limb US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Muscles and movements of upper limb. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Muscles and movements of upper limb US Medical PG Question 1: A 16-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after being tackled at a football game. Per his mom, he is the quarterback of his team and was head-butted in the left shoulder region by the opposing team. Shortly after, the mother noticed that his left arm was hanging by his torso and his hand was “bent backwards and facing the sky.” The patient denies head trauma, loss of consciousness, sensory changes, or gross bleeding. A physical examination demonstrates weakness in abduction, lateral rotation, flexion, and supination of the left arm and tenderness of the left shoulder region with moderate bruising. Radiograph of the left shoulder and arm is unremarkable. Which of the following is most likely damaged in this patient?
- A. C5-C6 nerve roots (Correct Answer)
- B. Ulnar nerve
- C. C8-T1 nerve roots
- D. Long thoracic nerve
Muscles and movements of upper limb Explanation: ***C5-C6 nerve roots***
- The "bent backwards and facing the sky" hand posture indicates **Waiter's tip position**, a classic sign of **Erb-Duchenne palsy**, caused by damage to the upper trunk of the brachial plexus (C5-C6 roots) [1].
- Weakness in **abduction** (deltoid, supraspinatus), **lateral rotation** (infraspinatus, teres minor), **flexion** (biceps, coracobrachialis), and **supination** (biceps, supinator) are all consistent with C5-C6 nerve root involvement.
*Ulnar nerve*
- Ulnar nerve damage would result in a **claw hand deformity** (hyperextension of MCP joints and flexion of DIP/PIP joints of 4th and 5th digits) and weakness in intrinsic hand muscles, not the observed upper arm weakness.
- Sensory loss involves the medial hand and little finger.
*C8-T1 nerve roots*
- Damage to the C8-T1 nerve roots (lower trunk) typically results in **Klumpke's palsy**, characterized by a more severe **claw hand** and paralysis of intrinsic hand muscles [1].
- This presentation does not match the observed functional deficits.
*Long thoracic nerve*
- Injury to the long thoracic nerve causes paralysis of the **serratus anterior muscle**, leading to **scapular winging**, especially when pushing against a wall.
- While possible in shoulder trauma, it does not explain the widespread weakness in abduction, rotation, flexion, and supination of the arm.
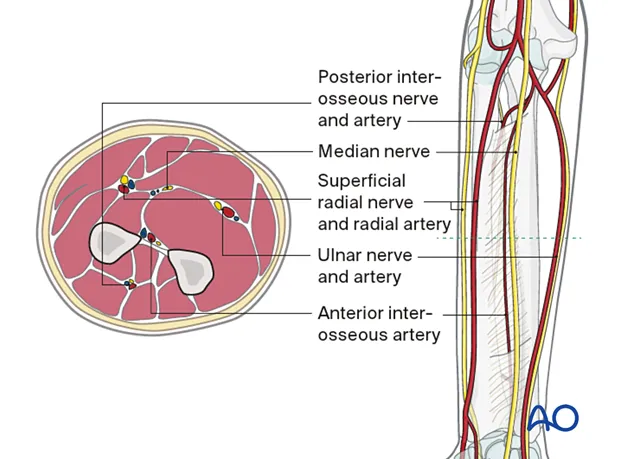
Muscles and movements of upper limb US Medical PG Question 2: A patient presents with difficulty extending their wrist following trauma to the posterior forearm. Which of the following muscles would be most affected by injury to the posterior interosseous nerve?
- A. Extensor carpi ulnaris
- B. Extensor carpi radialis brevis
- C. Extensor pollicis longus
- D. Extensor digitorum (Correct Answer)
Muscles and movements of upper limb Explanation: ***Extensor digitorum***
- The **posterior interosseous nerve (PIN)** innervates most muscles of the **posterior compartment of the forearm**, including the extensor digitorum. [1]
- Loss of function in the **extensor digitorum** would directly impair **extension of the fingers** and contribute significantly to difficulty extending the wrist. [1]
*Extensor carpi ulnaris*
- This muscle is also innervated by the **posterior interosseous nerve (PIN)** and contributes to **wrist extension** and **ulnar deviation**.
- While its innervation by the PIN is correct, injury to the PIN would affect this muscle, but the *extensor digitorum* is more broadly responsible for the stated primary symptom (difficulty extending the wrist), as its primary action is finger and thus wrist extension.
*Extensor carpi radialis brevis*
- While it is a **wrist extensor**, it is innervated by the **deep branch of the radial nerve** *before* it becomes the posterior interosseous nerve.
- Therefore, an isolated injury to the **posterior interosseous nerve** proper would typically spare the extensor carpi radialis brevis.
*Extensor pollicis longus*
- This muscle is indeed innervated by the **posterior interosseous nerve (PIN)** and acts to extend the **thumb**. [1]
- While it would be affected, the primary problem described is difficulty extending the *wrist*, for which the extensor digitorum plays a more significant and general role than the extensor pollicis longus.
Muscles and movements of upper limb US Medical PG Question 3: A 28-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-week history of weakness in the fingers of his right hand. One week ago, he experienced sudden pain in his right forearm during weight training. He has no history of serious illness. Physical examination shows impaired flexion of the proximal interphalangeal joints, while flexion of the distal interphalangeal joints is intact. Which of the following muscles is most likely injured?
- A. Flexor carpi radialis
- B. Flexor digitorum superficialis (Correct Answer)
- C. Palmaris longus
- D. Flexor carpi ulnaris
- E. Flexor digitorum profundus
Muscles and movements of upper limb Explanation: **Flexor digitorum superficialis**
- Injury to the **flexor digitorum superficialis (FDS)** accounts for the impaired flexion of the **proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints** as it is the primary flexor of these joints.
- The **intact flexion of the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints** indicates that the **flexor digitorum profundus (FDP)**, which flexes the DIP joints, is still functional.
*Flexor carpi radialis*
- The **flexor carpi radialis** primarily acts to **flex and abduct the wrist**, not the finger joints.
- An injury would lead to weakness in wrist movements rather than isolated finger joint flexion issues.
*Palmaris longus*
- The **palmaris longus** is a weak flexor of the wrist and tenses the **palmar aponeurosis**.
- It does not contribute to the flexion of the interphalangeal joints of the fingers.
*Flexor carpi ulnaris*
- The **flexor carpi ulnaris** primarily **flexes and adducts the wrist**.
- Injury to this muscle would result in wrist movement deficits, not specific interphalangeal joint flexion dysfunction.
*Flexor digitorum profundus*
- The **flexor digitorum profundus (FDP)** is responsible for **flexion of the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints** as well as assisting with PIP and metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joint flexion.
- Since flexion of the **DIP joints is intact**, the FDP is likely not injured.
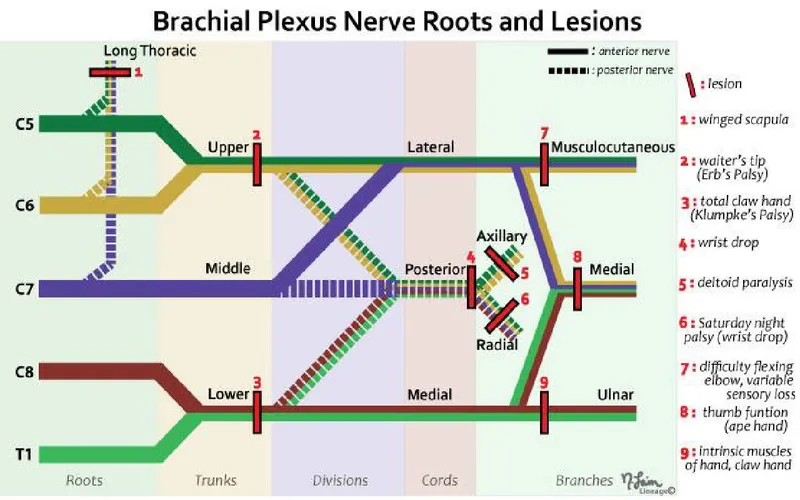
Muscles and movements of upper limb US Medical PG Question 4: A 43-year-old woman comes to the physician because of tingling and weakness in her left arm for the past 2 days. An image of the brachial plexus is shown. Nerve conduction study shows decreased transmission of electrical impulses in the labeled structure. Physical examination is most likely to show impairment of which of the following movements?
- A. Opposition of the thumb
- B. Flexion of the forearm
- C. Abduction of the shoulder above 100 degrees
- D. Extension of the wrist and fingers (Correct Answer)
- E. Flexion of the metacarpophalangeal joints
Muscles and movements of upper limb Explanation: ***Extension of the wrist and fingers***
- The image and description indicate the injury affects the **posterior cord** of the brachial plexus, which gives rise to the **radial nerve**.
- The **radial nerve** innervates the muscles responsible for **extension of the wrist and fingers**, so damage to its parent cord would impair these movements.
*Opposition of the thumb*
- **Opposition of the thumb** is primarily mediated by the **median nerve**, which arises from the lateral and medial cords, not the posterior cord.
- Damage to the posterior cord due to injury would not affect this movement directly.
*Flexion of the forearm*
- **Flexion of the forearm** is primarily controlled by the **musculocutaneous nerve** and a portion by the **median nerve**.
- Both of these nerves originate from the lateral and medial cords, not the posterior cord, making impairment unlikely with posterior cord injury.
*Abduction of the shoulder above 100 degrees*
- **Abduction of the shoulder above 100 degrees** primarily requires **scapular rotation** mediated by the **trapezius muscle** (accessory nerve) and **serratus anterior** (long thoracic nerve).
- While the **axillary nerve** (from the posterior cord) innervates the **deltoid** for initial shoulder abduction, the question stem emphasizes **wrist and finger symptoms**, suggesting the labeled structure is specifically the **radial nerve** branch rather than the axillary nerve branch.
- This makes extension deficits more likely than shoulder abduction impairment.
*Flexion of the metacarpophalangeal joints*
- **Flexion of the metacarpophalangeal joints** is predominantly carried out by the **lumbricals and interossei muscles**, which are primarily innervated by the **ulnar nerve** and partially by the **median nerve**.
- These nerves originate from the medial and lateral cords, not the posterior cord, making impairment unlikely.
Muscles and movements of upper limb US Medical PG Question 5: A 17-year-old boy comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of pain in his right shoulder. He reports that he has stopped playing for his high school football team because of persistent difficulty lifting his right arm. Physical examination shows impaired active abduction of the right arm from 0 to 15 degrees. After passive abduction of the right arm to 15 degrees, the patient is able to raise his arm above his head. The dysfunctional muscle in this patient is most likely to be innervated by which of the following nerves?
- A. Long thoracic nerve
- B. Suprascapular nerve (Correct Answer)
- C. Upper subscapular nerve
- D. Accessory nerve
- E. Axillary nerve
Muscles and movements of upper limb Explanation: ***Suprascapular nerve***
- The patient exhibits impaired active abduction from 0 to 15 degrees but normal abduction after passive assistance, indicating dysfunction of the **supraspinatus muscle**.
- The **supraspinatus muscle** is responsible for **initiating shoulder abduction** from 0 to 15 degrees, after which the deltoid muscle takes over for continued abduction.
- The **suprascapular nerve** innervates both the **supraspinatus** and **infraspinatus muscles**, with the supraspinatus being crucial for the initial phase of abduction.
*Long thoracic nerve*
- This nerve innervates the **serratus anterior muscle**, which is responsible for **scapular protraction** and upward rotation.
- Damage to the long thoracic nerve would typically result in **winged scapula**, not difficulty in initiating abduction.
*Upper subscapular nerve*
- The upper subscapular nerve innervates the **subscapularis muscle**, part of the rotator cuff.
- This muscle is primarily involved in **internal rotation** of the shoulder and contributes to adduction, not abduction.
*Accessory nerve*
- The accessory nerve (cranial nerve XI) innervates the **sternocleidomastoid** and **trapezius muscles**.
- Damage to this nerve would most likely present with weakness in **shrugging the shoulders** or turning the head, not difficulty with shoulder abduction.
*Axillary nerve*
- This nerve innervates the **deltoid muscle** and the **teres minor muscle**, and provides sensory input from the shoulder joint and lateral arm.
- The deltoid is responsible for **shoulder abduction** from 15 to 90 degrees; a deficit here would affect a different range of motion than what is described.
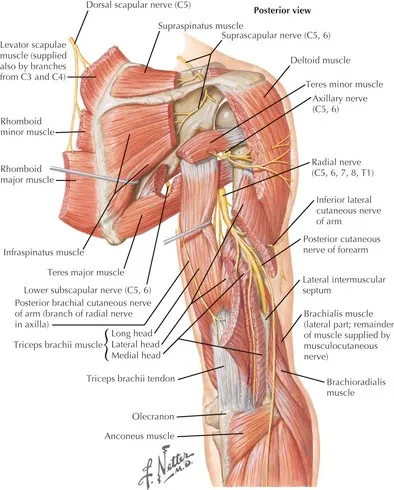
Muscles and movements of upper limb US Medical PG Question 6: A 60-year-old woman is rushed to the emergency room after falling on her right elbow while walking down the stairs. She cannot raise her right arm. Her vital signs are stable, and the physical examination reveals loss of sensation over the upper lateral aspect of the right arm and shoulder. A radiologic evaluation shows a fracture of the surgical neck of the right humerus. Which of the following muscles is supplied by the nerve that is most likely damaged?
- A. Teres minor (Correct Answer)
- B. Teres major
- C. Subscapularis
- D. Infraspinatus
- E. Supraspinatus
Muscles and movements of upper limb Explanation: ***Teres minor***
- A fracture of the **surgical neck of the humerus** often damages the **axillary nerve**, which innervates the **teres minor**.
- The axillary nerve also supplies the **deltoid muscle** and provides cutaneous sensation to the **upper lateral arm**, consistent with the patient's sensory loss.
*Teres major*
- This muscle is innervated by the **lower subscapular nerve**, which is less likely to be damaged in a surgical neck fracture.
- Its primary action is **adduction** and **internal rotation** of the arm.
*Subscapularis*
- The **subscapularis** is innervated by the **upper and lower subscapular nerves**.
- While it contributes to internal rotation, its nerve supply is typically protected in this type of fracture.
*Infraspinatus*
- The **infraspinatus** muscle is innervated by the **suprascapular nerve**.
- This nerve is generally not affected by a fracture of the surgical neck of the humerus.
*Supraspinatus*
- Similar to the infraspinatus, the **supraspinatus** is also innervated by the **suprascapular nerve**.
- Damage to this nerve due to a humeral surgical neck fracture is uncommon.
Muscles and movements of upper limb US Medical PG Question 7: A 78-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department after she fell while gardening and experienced severe pain in her right arm. She has a history of well controlled hypertension and has been found to have osteoporosis. On presentation she is found to have a closed midshaft humerus fracture. No other major findings are discovered on a trauma survey. She is placed in a coaptation splint. The complication that is most associated with this injury has which of the following presentations?
- A. Hand of benediction
- B. Hypothenar atrophy
- C. Flattened deltoid
- D. Elbow flexion deficits
- E. Wrist drop (Correct Answer)
Muscles and movements of upper limb Explanation: ***Wrist drop***
- A **midshaft humerus fracture** is classically associated with injury to the **radial nerve**, which wraps around the humerus at this level.
- **Radial nerve injury** causes paralysis of the extensors of the wrist and fingers, leading to a characteristic **wrist drop** presentation.
*Hand of benediction*
- This presentation, where the **index and middle fingers remain extended** while the ring and little fingers flex, is characteristic of a **proximal median nerve injury**.
- A midshaft humerus fracture is less likely to cause a proximal median nerve injury given the anatomical course of the nerve.
*Hypothenar atrophy*
- **Hypothenar atrophy** is indicative of **ulnar nerve damage**, usually at the cubital tunnel or Guyon's canal.
- While the ulnar nerve courses near the humerus, it is less commonly injured in midshaft fractures compared to the radial nerve.
*Flattened deltoid*
- A **flattened deltoid** is a sign of **axillary nerve injury** or shoulder dislocation, leading to paralysis of the deltoid muscle.
- The axillary nerve is more commonly injured in **proximal humerus fractures** or shoulder trauma, not typically midshaft fractures.
*Elbow flexion deficits*
- **Elbow flexion deficits** are primarily associated with injury to the **musculocutaneous nerve** or the C5/C6 nerve roots.
- While a severe humeral fracture could potentially affect these structures, it is not the most direct or common neurological complication of a midshaft fracture, which targets the radial nerve.
Muscles and movements of upper limb US Medical PG Question 8: A 61-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of increasing weakness of his right arm and leg that began when he woke up that morning. He did not notice any weakness when he went to bed the night before. He has hypertension and hypercholesterolemia. Current medications include hydrochlorothiazide and atorvastatin. He is alert and oriented to person, time, place. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 91/min, and blood pressure is 132/84 mm Hg. Examination shows drooping of the right side of the face. Muscle strength is decreased in the right upper and lower extremities. Deep tendon reflexes are 4+ on the right side. Sensation is intact. His speech is normal in rate and rhythm. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. An infarction of which of the following sites is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Base of the left pons
- B. Left cerebellar vermis
- C. Left posterolateral thalamus
- D. Posterior limb of the left internal capsule (Correct Answer)
- E. Left lateral medulla
Muscles and movements of upper limb Explanation: ***Posterior limb of the left internal capsule***
- The patient presents with sudden onset of **right-sided weakness**, including the face, arm, and leg (hemiparesis), consistent with a **pure motor stroke**.
- The **posterior limb of the internal capsule** contains UMN fibers of the **corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts**, which project to the contralateral side of the body, thus lesions here cause contralateral pure motor deficits.
*Base of the left pons*
- A lesion here would typically cause **contralateral hemiparesis or hemiplegia** (right side in this case).
- However, pontine lesions also often include **cranial nerve palsies** (e.g., abducens or facial nerve) or **ataxia**, which are not described.
*Left cerebellar vermis*
- Damage to the cerebellar vermis primarily results in **truncal ataxia** and disorders of gait and balance.
- It would not cause contralateral hemiparesis or facial droop, as seen in this patient.
*Left posterolateral thalamus*
- An infarct in this area would primarily cause **contralateral sensory deficits**, such as hemianesthesia or dysesthesia.
- While motor deficits can occur, they are typically less prominent than sensory issues and would not be the isolated pure motor syndrome described.
*Left lateral medulla*
- A lesion in the lateral medulla (e.g., Wallenberg syndrome) typically presents with **contralateral pain and temperature loss**, ipsilateral Horner's syndrome, ataxia, and dysphagia.
- It would not manifest as an isolated pure motor hemiparesis.
Muscles and movements of upper limb US Medical PG Question 9: A 31-year-old woman with multiple sclerosis comes to the physician because of a 4-day history of cramps in her left leg. Physical examination shows flexion of the left hip and increased tone in the thigh muscles. A local anesthetic block of which of the following nerves would most likely improve this patient's condition the most?
- A. Inferior gluteal nerve
- B. Superior gluteal nerve
- C. Femoral nerve (Correct Answer)
- D. Sciatic nerve
- E. Obturator nerve
Muscles and movements of upper limb Explanation: ***Femoral nerve***
- The **femoral nerve** innervates the **iliacus** (a primary hip flexor) and the **rectus femoris** (part of the quadriceps that assists in hip flexion), as well as the entire **quadriceps femoris group** (responsible for knee extension and contributing to increased thigh muscle tone).
- In this patient with spasticity, **hip flexion** is caused by hypertonicity of iliopsoas and rectus femoris, while **increased tone in thigh muscles** reflects quadriceps involvement.
- Blocking the femoral nerve would relax these muscles, thereby improving the **cramps, hip flexion, and increased thigh tone**.
*Inferior gluteal nerve*
- The **inferior gluteal nerve** primarily innervates the **gluteus maximus muscle**, which is involved in hip extension and external rotation, not hip flexion.
- Blocking this nerve would not directly address the symptoms of increased thigh muscle tone and hip flexion.
*Superior gluteal nerve*
- The **superior gluteal nerve** mainly innervates the **gluteus medius, gluteus minimus**, and **tensor fasciae latae muscles**, which are involved in hip abduction and internal rotation.
- Its blockade would not relieve hip flexion or thigh muscle cramps.
*Sciatic nerve*
- The **sciatic nerve** innervates the **hamstring muscles** (hip extension, knee flexion) and all muscles below the knee.
- While it affects leg muscles, it does not directly control the muscles causing **hip flexion and increased thigh tone** in this context.
*Obturator nerve*
- The **obturator nerve** primarily innervates the **adductor muscles** of the thigh (adductor longus, brevis, magnus, gracilis), leading to hip adduction.
- Blocking this nerve would not address hip flexion or the increased tone in the quadriceps muscles described.
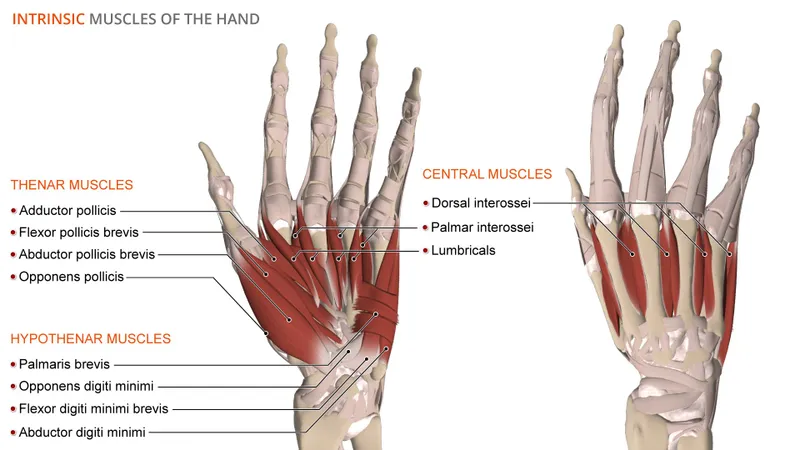
Muscles and movements of upper limb US Medical PG Question 10: A 25-year-old man was referred to a neurologist for right-hand weakness. He was involved in a motor vehicle accident 2 months ago in which his right hand was injured. On examination, his grip is weak, especially in fingers 2, 4, and 5 and he is unable to adduct these fingers. Which of the following groups of muscles is most likely affected?
- A. Flexor digitorum profundus
- B. Palmar interossei muscles (Correct Answer)
- C. Lumbrical muscles
- D. Dorsal interossei muscles
- E. Extensor digitorum
Muscles and movements of upper limb Explanation: ***Palmar interossei muscles***
- The inability to **adduct fingers 2, 4, and 5** (index, ring, and pinky fingers) is the key finding. The **palmar interossei** are responsible for adduction of these fingers towards the middle finger.
- Weak grip in these specific fingers indicates impairment of the muscles controlling their movement and adduction, which are primarily the palmar interossei.
*Flexor digitorum profundus*
- The **flexor digitorum profundus** primarily **flexes the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints** of the fingers, as well as assists in flexing the proximal interphalangeal (PIP) and metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints.
- While it contributes to grip strength, its primary role is flexion, not adduction, and weakness would typically present as difficulty with deep finger flexion rather than specific adduction issues.
*Lumbrical muscles*
- The **lumbrical muscles** **flex the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints** and **extend the interphalangeal (IP) joints**. This action is characteristic of the "lumbrical grip" or "writing position."
- Their primary function does not involve adduction of the fingers, and their weakness would manifest differently.
*Dorsal interossei muscles*
- The **dorsal interossei muscles** are responsible for **abduction of the fingers** (spreading them apart).
- The patient's inability to adduct fingers rules out the dorsal interossei as the primary affected group, as these muscles perform the opposite action.
*Extensor digitorum*
- The **extensor digitorum** primarily **extends the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) and interphalangeal (IP) joints** of the medial four fingers.
- Weakness in this muscle would result in difficulty extending the fingers, leading to a "dropped finger" appearance or inability to straighten the fingers, which is contrary to the described adduction deficit.
More Muscles and movements of upper limb US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.