Clinical correlations of upper limb US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Clinical correlations of upper limb. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Clinical correlations of upper limb US Medical PG Question 1: A 61-year-old woman presents to the emergency room with right hand pain and numbness. She was jogging around her neighborhood when she tripped and fell on her outstretched hand 3 hours prior to presentation. She reports severe wrist pain and numbness along the medial aspect of her hand. Her past medical history is notable for osteoporosis and gastroesophageal reflux disease. She takes omeprazole. She has a 10-pack-year smoking history. She has severe tenderness to palpation diffusely around her right wrist. She has decreased sensation to light touch along the palmar medial 2 digits. Sensation to light touch is normal throughout the palm and in the lateral 3 digits. When she is asked to extend all of her fingers, her 4th and 5th fingers are hyperextended at the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints and flexed at the interphalangeal (IP) joints. Which of the following nerves is most likely affected in this patient?
- A. Posterior interosseous nerve
- B. Proximal ulnar nerve
- C. Distal median nerve
- D. Recurrent branch of the median nerve
- E. Distal ulnar nerve (Correct Answer)
Clinical correlations of upper limb Explanation: ***Distal ulnar nerve***
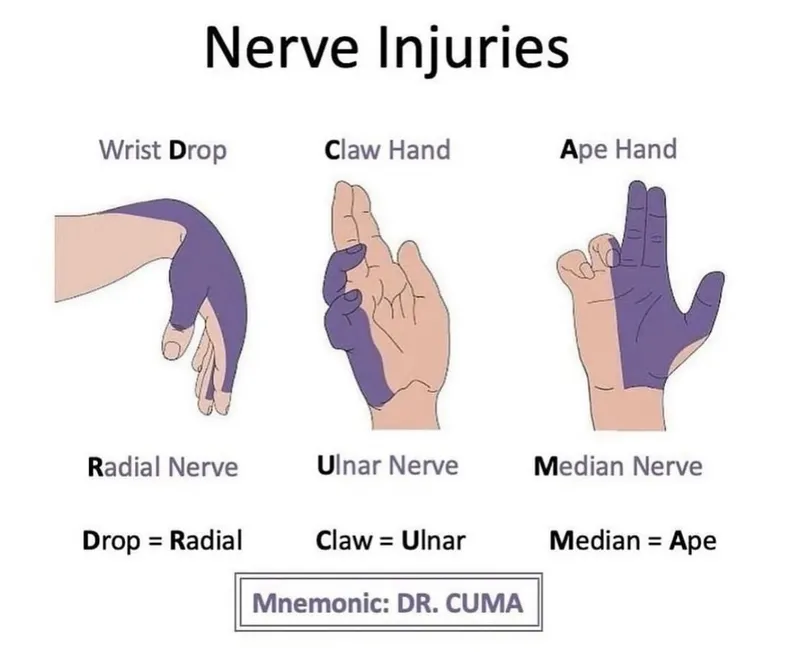
- The patient's symptoms, including numbness along the **medial aspect of the hand** (specifically the 4th and 5th digits), and the characteristic **flexion of the 4th and 5th fingers at the interphalangeal (IP) joints** with hyperextension at the metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints (known as **ulnar claw**), are highly indicative of distal ulnar nerve injury.
- Distal ulnar nerve injury, often seen with trauma to the wrist like a **fall on an outstretched hand**, impacts the intrinsic hand muscles it innervates, leading to this specific **deformity**.
*Posterior interosseous nerve*
- Injury to the **posterior interosseous nerve** would primarily affect extensor function in the forearm and hand, leading to a **wrist drop** or inability to extend fingers and thumb.
- It does not cause sensory deficits in the hand, as it is a **purely motor nerve**.
*Proximal ulnar nerve*
- A **proximal ulnar nerve** injury (e.g., at the elbow) would cause a more widespread motor deficit, affecting the **flexor carpi ulnaris** and **medial half of the flexor digitorum profundus**, in addition to the intrinsic hand muscles.
- Sensory loss would extend to the **dorsal medial hand**, which is not entirely consistent with this patient's presentation.
*Distal median nerve*
- Injury to the **distal median nerve** (e.g., carpal tunnel syndrome) typically causes sensory loss in the **first three and a half digits** and weakness of **thenar muscles** (e.g., opposition of the thumb).
- It would not cause the described ulnar claw deformity of the 4th and 5th fingers.
*Recurrent branch of the median nerve*
- The **recurrent branch of the median nerve** is a **purely motor nerve** that innervates the **thenar muscles** (abductor pollicis brevis, opponens pollicis, superficial head of flexor pollicis brevis).
- Damage to this nerve causes **thenar atrophy** and weakness in thumb opposition, without sensory deficits or effects on the 4th and 5th digits.
Clinical correlations of upper limb US Medical PG Question 2: A 53-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of intermittent severe left neck, shoulder, and arm pain and paresthesias of the left hand. The pain radiates to the radial aspect of her left forearm, thumb, and index finger. She first noticed her symptoms after helping a friend set up a canopy tent. There is no family history of serious illness. She appears healthy. Vital signs are within normal limits. When the patient extends and rotates her head to the left and downward pressure is applied, she reports paresthesias along the radial aspect of her left forearm and thumb. There is weakness when extending the left wrist against resistance. The brachioradialis reflex is 1+ on the left and 2+ on the right. The radial pulse is palpable bilaterally. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Carpal tunnel syndrome
- B. Syringomyelia
- C. Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- D. C5-C6 disc herniation (Correct Answer)
- E. Thoracic outlet syndrome
Clinical correlations of upper limb Explanation: ***C5-C6 disc herniation***
- The patient's symptoms of neck, shoulder, and arm pain, along with paresthesias radiating to the **radial aspect of the forearm, thumb, and index finger**, are consistent with **C6 dermatomal distribution**.
- The positive **Spurling's maneuver** (extension, rotation, and downward pressure causing paresthesias) and decreased **brachioradialis reflex** (C5-C6 reflex) strongly suggest **cervical radiculopathy**, most likely due to a disc herniation affecting the C6 nerve root.
*Carpal tunnel syndrome*
- Characterized by **median nerve compression** at the wrist, causing paresthesias and pain primarily in the **thumb, index, middle, and radial half of the ring finger**, typically worsening at night.
- Would not explain the neck, shoulder, or upper arm pain, or the positive Spurling's maneuver, which indicates a more proximal nerve root compression.
*Syringomyelia*
- A rare chronic progressive disorder where a **syrinx (fluid-filled cyst)** forms within the spinal cord, often presenting with a **cape-like distribution of sensory loss** (loss of pain and temperature sensation) over the shoulders and upper extremities.
- Motor weakness can occur but the pain and paresthesia pattern, along with the positive Spurling's maneuver, are not typical for syringomyelia.
*Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis*
- A progressive neurodegenerative disease affecting **upper and lower motor neurons**, leading to widespread muscle weakness, atrophy, fasciculations, and spasticity.
- It does not typically present with acute, radicular pain and paresthesias restricted to a specific dermatome, and sensory involvement is absent.
*Thoracic outlet syndrome*
- Involves compression of the **brachial plexus** and/or subclavian vessels in the thoracic outlet, causing neurogenic symptoms (pain, paresthesias) primarily in the **ulnar nerve distribution** and vascular symptoms (edema, discoloration).
- The pain and paresthesias in the radial aspect of the hand and forearm, along with the specific reflex changes and positive neck maneuver, are not characteristic of thoracic outlet syndrome.
Clinical correlations of upper limb US Medical PG Question 3: A 33-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with shoulder pain. He states that he can't remember a specific instance when the injury occurred. He is a weight lifter and competes in martial arts. The patient has no past medical history and is currently taking a multivitamin. Physical exam demonstrates pain with abduction of the patient's right shoulder and with external rotation of the right arm. There is subacromial tenderness with palpation. His left arm demonstrates 10/10 strength with abduction as compared to 4/10 strength with abduction of the right arm. Which of the following best confirms the underlying diagnosis?
- A. Ultrasound
- B. Radiography
- C. MRI (Correct Answer)
- D. CT
- E. Physical exam and history
Clinical correlations of upper limb Explanation: ***MRI***
- An **MRI is the gold standard** for diagnosing soft tissue injuries of the shoulder, including **rotator cuff pathology**, which is highly suspected given the patient's symptoms (pain with abduction and external rotation, subacromial tenderness, and weakness).
- It provides detailed imaging of tendons, ligaments, and cartilage, allowing for precise identification of **tears, inflammation, or impingement**.
*Ultrasound*
- While ultrasound can assess **rotator cuff integrity** and identify fluid collections, it is highly operator-dependent and may not provide the same level of detail as MRI for complex tears or associated pathologies.
- It can be a good initial screening tool but might **underestimate the extent** of an injury compared to MRI.
*Radiography*
- **Radiography (X-rays)** primarily visualizes bone structures and would be useful for detecting fractures, dislocations, or significant degenerative joint disease.
- It would **not directly visualize** the soft tissue injuries of the rotator cuff or other tendons that are likely causing this patient's symptoms.
*CT*
- **CT scans** provide excellent detail of bone structures and can identify subtle fractures, erosions, or bony impingement.
- However, like X-rays, they are **less effective for visualizing soft tissues** like tendons and ligaments compared to MRI.
*Physical exam and history*
- The **physical exam and history** are crucial for narrowing down the differential diagnosis and guiding further imaging.
- While strongly suggestive of a rotator cuff injury, they alone **cannot definitively confirm the extent or nature** of the underlying soft tissue pathology.
Clinical correlations of upper limb US Medical PG Question 4: A 65-year-old woman presents to her primary care provider for shoulder pain. She reports that she initially thought the pain was due to "sleeping funny" on the arm, but that the pain has now lasted for 4 weeks. She denies trauma to the joint and says that the pain is worse when reaching overhead to retrieve things from her kitchen cabinets. On physical exam, the patient's shoulders are symmetric, and the right lateral shoulder is tender to palpation. The shoulder has full passive and active range of motion, although pain is reproduced on active abduction of the right arm above 90 degrees. Pain is also reproduced on passively internally rotating and then lifting the shoulder. The patient is able to resist elbow flexion without pain, and she otherwise has 5/5 strength. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Biceps tendinopathy
- B. Rotator cuff tendinopathy (Correct Answer)
- C. Adhesive capsulitis
- D. Glenohumeral osteoarthritis
- E. Rotator cuff tear
Clinical correlations of upper limb Explanation: ***Rotator cuff tendinopathy***
- The patient's presentation of gradual onset shoulder pain, worse with overhead activities, tenderness of the **lateral shoulder** to palpation, and pain with active abduction beyond 90 degrees and passive internal rotation and lifting
is highly characteristic of **rotator cuff tendinopathy**.
- **Full active range of motion** despite pain indicates that the tendon is intact, but inflamed, making tendinopathy more likely than a tear.
*Biceps tendinopathy*
- This condition typically causes pain in the anterior shoulder, especially with **lifting** or **carrying heavy objects**, and tenderness in the **bicipital groove**.
- The patient's pain is primarily located in the lateral shoulder and is reproduced with abduction and internal rotation, which are less typical for biceps tendinopathy.
*Adhesive capsulitis*
- Characterized by significant **restriction of both active and passive range of motion** in multiple planes, often described as a "frozen shoulder."
- This patient maintains full passive and active range of motion, which rules out adhesive capsulitis.
*Glenohumeral osteoarthritis*
- While it can cause pain and stiffness, osteoarthritis typically presents with **crepitus**, **limited range of motion** (both active and passive) with an insidious onset, and pain that often worsens with activity but does not specifically point to subacromial involvement.
- The patient's full passive range of motion makes severe osteoarthritis unlikely.
*Rotator cuff tear*
- A rotator cuff tear usually presents with **weakness** in specific movements (e.g., abduction, external rotation) and often **limited active range of motion**, even if passive range of motion is preserved.
- The patient's ability to maintain full active range of motion and 5/5 strength makes a complete tear less likely, although a partial tear could be considered if tendinopathy doesn't improve with conservative management.
Clinical correlations of upper limb US Medical PG Question 5: A 12-year-old boy presents to the emergency department after falling from his bike. He is holding his right arm tenderly and complains of pain in his right wrist. When asked, he says that he fell after his front tire hit a rock and landed hard on his right hand. Upon physical examination he is found to have tenderness on the dorsal aspect of his wrist in between the extensor pollicis longus and the extensor pollicis brevis. Given this presentation, which of the following is the most likely bone to have been fractured?
- A. Pisiform
- B. Scaphoid (Correct Answer)
- C. Lunate
- D. Capitate
- E. Trapezoid
Clinical correlations of upper limb Explanation: ***Scaphoid***
- The mechanism of injury (**fall on an outstretched hand**) and the location of tenderness (**dorsal aspect of the wrist between the extensor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis**, which corresponds to the **anatomical snuffbox**) are classic signs of a scaphoid fracture.
- The **scaphoid** is the most commonly fractured carpal bone and its fracture can lead to **avascular necrosis** due to its retrograde blood supply if not properly managed.
*Pisiform*
- Fractures of the **pisiform** are rare and typically result from direct trauma to the hypothenar eminence, not from a fall on an outstretched hand.
- Pain would be localized to the **ulnar side of the wrist**, distinct from the anatomical snuffbox.
*Lunate*
- A **lunate fracture** is rare and usually associated with high-energy trauma, often leading to **Kienbock's disease** (avascular necrosis of the lunate).
- Tenderness would be more centrally located on the dorsal aspect of the wrist, not specifically within the anatomical snuffbox.
*Capitate*
- **Capitate fractures** are uncommon and often occur in conjunction with other carpal injuries due to its central and protected position.
- Pain and tenderness would be more diffuse in the midcarpal region rather than localized to the anatomical snuffbox.
*Trapezoid*
- **Trapezoid fractures** are very rare and typically result from axial loading force through the second metacarpal.
- Tenderness would be located more distally, at the base of the **second metacarpal**, not within the anatomical snuffbox.
Clinical correlations of upper limb US Medical PG Question 6: A 40-year-old male presents to the physician's office complaining of an inability to push doors open. He has had this problem since he was playing football with his children and was tackled underneath his right arm on his lateral chest. On examination, he has a winged scapula on the right side. Which of the following nerves is most likely the cause of this presentation?
- A. Phrenic nerve
- B. Spinal accessory nerve
- C. Long thoracic nerve (Correct Answer)
- D. Greater auricular nerve
- E. Musculocutaneous nerve
Clinical correlations of upper limb Explanation: ***Long thoracic nerve***
- The **long thoracic nerve** innervates the **serratus anterior muscle**, which is responsible for scapular protraction and upward rotation.
- Damage to this nerve, often from trauma to the lateral chest wall (tackled underneath the arm), leads to paralysis of the serratus anterior and a characteristic **winged scapula** with lateral and inferior prominence.
- Patients have difficulty with **pushing movements** (protraction) and overhead activities.
*Phrenic nerve*
- The **phrenic nerve** primarily innervates the **diaphragm** and is crucial for respiration.
- Damage to the phrenic nerve would cause respiratory compromise, not a winged scapula or difficulty pushing doors.
*Spinal accessory nerve*
- The **spinal accessory nerve (cranial nerve XI)** innervates the **sternocleidomastoid** and **trapezius muscles**.
- Injury to this nerve can cause scapular winging due to **trapezius paralysis**, but the winging is typically **medial** with the inferior angle moving medially, unlike the lateral winging from serratus anterior paralysis.
- The mechanism of injury (lateral chest trauma during tackling) and inability to push are classic for **long thoracic nerve** injury, not spinal accessory nerve.
*Greater auricular nerve*
- The **greater auricular nerve** is a cutaneous nerve that provides sensation to the skin over the parotid gland, mastoid process, and auricle.
- Damage to this nerve would result in sensory loss in these areas and is unrelated to muscle weakness or a winged scapula.
*Musculocutaneous nerve*
- The **musculocutaneous nerve** innervates the **biceps brachii**, **brachialis**, and **coracobrachialis muscles**, responsible for elbow flexion and forearm supination.
- Damage to this nerve would primarily affect these movements and sensation in the lateral forearm, not leading to a winged scapula.
Clinical correlations of upper limb US Medical PG Question 7: A 7-year-old child is brought to the emergency room by his parents in severe pain. They state that he fell on his outstretched right arm while playing with his friends. He is unable to move his right arm which is being supported by his left. On exam, his vitals are normal. His right extremity reveals normal pulses without swelling in any compartments, but there is crepitus above the elbow upon movement. The child is able to flex and extend his wrist, but this is limited by pain. The child has decreased sensation along his thumb and is unable to make the "OK" sign with his thumb and index finger. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Scaphoid fracture
- B. Distal ulnar fracture
- C. Supracondylar humerus fracture (Correct Answer)
- D. Distal radius fracture
- E. Midhumerus fracture
Clinical correlations of upper limb Explanation: ***Supracondylar humerus fracture***
- The classic presentation of a **fall on an outstretched arm** with **crepitus above the elbow** is highly indicative of a supracondylar humerus fracture.
- **Decreased sensation along the thumb** and inability to make an **"OK" sign** points to **anterior interosseous nerve (AIN)** palsy, a common complication of this fracture type due to compression or injury.
*Scaphoid fracture*
- This fracture typically presents with **pain in the anatomical snuffbox** and occurs at the wrist, not above the elbow.
- While it can result from a fall on an outstretched hand, it does not explain the crepitus above the elbow or the specific nerve palsy described.
*Distal ulnar fracture*
- This injury would cause pain and swelling at the **distal forearm/wrist**, not crepitus above the elbow.
- Nerve involvement, if present, would typically affect the **ulnar nerve**, not the anterior interosseous nerve.
*Distal radius fracture*
- Also known as a **Colles fracture** when dorsal displacement is present, this injury occurs at the wrist and presents with pain and deformity there.
- It does not account for the crepitus above the elbow or the specific AIN palsy symptoms.
*Midhumerus fracture*
- While a midhumerus fracture can occur from a fall on an outstretched arm and cause crepitus, it would be located in the **middle third of the upper arm**, not specifically above the elbow joint.
- The specific AIN palsy is less commonly associated with mid-shaft humeral fractures, which are more likely to involve the **radial nerve**.
Clinical correlations of upper limb US Medical PG Question 8: An 18-year-old man comes to the clinic with his mom for “pins and needles” of both of his arms. He denies any past medical history besides a recent anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) tear that was repaired 1 week ago. The patient reports that the paresthesias are mostly located along the posterior forearms, left more than the right. What physical examination finding would you expect from this patient?
- A. Loss of finger abduction
- B. Loss of forearm flexion and supination
- C. Loss of arm abduction
- D. Loss of thumb opposition
- E. Loss of wrist extension (Correct Answer)
Clinical correlations of upper limb Explanation: ***Loss of wrist extension***
- The patient describes "pins and needles" predominantly along the **posterior forearms**, indicating **radial nerve involvement**.
- The **radial nerve** provides sensory innervation to the posterior forearm via the **posterior cutaneous nerve of the forearm**.
- Motor function: The radial nerve innervates the **extensor carpi radialis longus and brevis** and **extensor carpi ulnaris**, which are responsible for **wrist extension**.
- The recent **ACL repair surgery** suggests a **positional compression injury** to the radial nerves from prolonged arm positioning during the procedure.
- Expected finding: **Wrist drop** (inability to extend the wrist against gravity).
*Loss of finger abduction*
- **Finger abduction** is controlled by the **interossei muscles**, which are innervated by the **ulnar nerve**.
- The ulnar nerve provides sensory innervation to the **medial forearm** (via medial cutaneous nerve of forearm) and **medial 1.5 digits**, NOT the posterior forearm.
- Posterior forearm paresthesias do not indicate ulnar nerve involvement.
*Loss of forearm flexion and supination*
- **Forearm flexion** is primarily controlled by the **musculocutaneous nerve** (supplying the **biceps brachii** and **brachialis**).
- The musculocutaneous nerve becomes the **lateral cutaneous nerve of the forearm**, supplying the **lateral forearm**, not the posterior forearm.
- Supination involves the biceps (musculocutaneous) and supinator (radial nerve, posterior interosseous branch).
*Loss of arm abduction*
- **Arm abduction** is primarily controlled by the **deltoid** muscle (innervated by the **axillary nerve**) and **supraspinatus** (suprascapular nerve).
- Axillary nerve injury causes sensory loss over the **lateral shoulder** (regimental badge area), not the forearm.
*Loss of thumb opposition*
- **Thumb opposition** is a function of the **opponens pollicis** and **flexor pollicis brevis** (superficial head), primarily innervated by the **median nerve**.
- Median nerve compression typically causes paresthesias in the **lateral 3.5 digits** and **thenar eminence**, not the posterior forearm.
Clinical correlations of upper limb US Medical PG Question 9: A 61-year-old man is brought to the emergency department because of increasing weakness of his right arm and leg that began when he woke up that morning. He did not notice any weakness when he went to bed the night before. He has hypertension and hypercholesterolemia. Current medications include hydrochlorothiazide and atorvastatin. He is alert and oriented to person, time, place. His temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 91/min, and blood pressure is 132/84 mm Hg. Examination shows drooping of the right side of the face. Muscle strength is decreased in the right upper and lower extremities. Deep tendon reflexes are 4+ on the right side. Sensation is intact. His speech is normal in rate and rhythm. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. An infarction of which of the following sites is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Base of the left pons
- B. Left cerebellar vermis
- C. Left posterolateral thalamus
- D. Posterior limb of the left internal capsule (Correct Answer)
- E. Left lateral medulla
Clinical correlations of upper limb Explanation: ***Posterior limb of the left internal capsule***
- The patient presents with sudden onset of **right-sided weakness**, including the face, arm, and leg (hemiparesis), consistent with a **pure motor stroke**.
- The **posterior limb of the internal capsule** contains UMN fibers of the **corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts**, which project to the contralateral side of the body, thus lesions here cause contralateral pure motor deficits.
*Base of the left pons*
- A lesion here would typically cause **contralateral hemiparesis or hemiplegia** (right side in this case).
- However, pontine lesions also often include **cranial nerve palsies** (e.g., abducens or facial nerve) or **ataxia**, which are not described.
*Left cerebellar vermis*
- Damage to the cerebellar vermis primarily results in **truncal ataxia** and disorders of gait and balance.
- It would not cause contralateral hemiparesis or facial droop, as seen in this patient.
*Left posterolateral thalamus*
- An infarct in this area would primarily cause **contralateral sensory deficits**, such as hemianesthesia or dysesthesia.
- While motor deficits can occur, they are typically less prominent than sensory issues and would not be the isolated pure motor syndrome described.
*Left lateral medulla*
- A lesion in the lateral medulla (e.g., Wallenberg syndrome) typically presents with **contralateral pain and temperature loss**, ipsilateral Horner's syndrome, ataxia, and dysphagia.
- It would not manifest as an isolated pure motor hemiparesis.
Clinical correlations of upper limb US Medical PG Question 10: A 28-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of pain in his left shoulder. He is physically active and plays baseball twice a week. The pain is reproduced when the shoulder is externally rotated against resistance. Injury of which of the following tendons is most likely in this patient?
- A. Infraspinatus (Correct Answer)
- B. Subscapularis
- C. Pectoralis major
- D. Supraspinatus
- E. Teres major
Clinical correlations of upper limb Explanation: ***Infraspinatus***
- Pain during **external rotation against resistance** is a classic sign of infraspinatus tendon injury, as it is a primary muscle for this action.
- The patient's history of playing baseball and experiencing pain, especially with resistive external rotation, points to an injury of this **rotator cuff muscle**.
*Subscapularis*
- The subscapularis primarily causes **internal rotation** of the shoulder; injury would typically present with pain during resisted internal rotation, not external.
- While it is a rotator cuff muscle, its function does not align with the specific maneuver causing pain described in the patient.
*Pectoralis major*
- The pectoralis major is a large chest muscle involved primarily in **adduction**, **internal rotation**, and **flexion of the humerus**, not external rotation.
- Injury to this muscle would present with pain during these specific movements, not resisted external rotation.
*Supraspinatus*
- The supraspinatus is primarily involved in **initiation of abduction** and helps stabilize the shoulder joint, and pain would usually be elicited during these movements.
- While a common site of rotator cuff injury, its function does not directly cause pain with resisted external rotation as described.
*Teres major*
- The teres major acts as an **adductor** and **internal rotator** of the humerus, similar to the latissimus dorsi.
- Pain from a teres major injury would be associated with these actions, not with resisted external rotation.
More Clinical correlations of upper limb US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.