Bones and joints of upper limb US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Bones and joints of upper limb. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
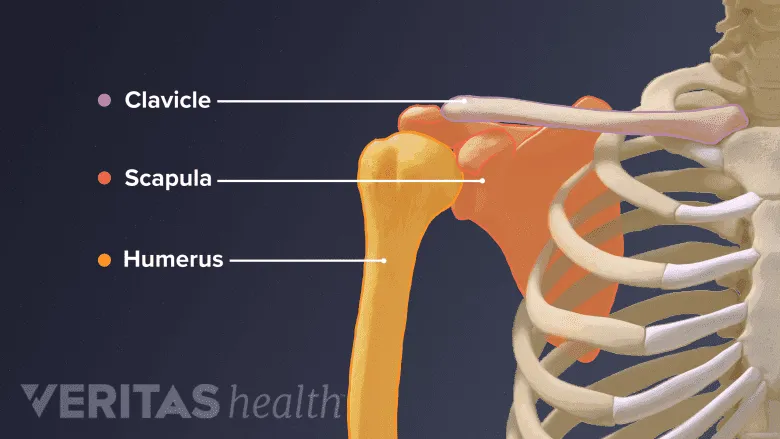
Bones and joints of upper limb US Medical PG Question 1: A 16-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department after being tackled at a football game. Per his mom, he is the quarterback of his team and was head-butted in the left shoulder region by the opposing team. Shortly after, the mother noticed that his left arm was hanging by his torso and his hand was “bent backwards and facing the sky.” The patient denies head trauma, loss of consciousness, sensory changes, or gross bleeding. A physical examination demonstrates weakness in abduction, lateral rotation, flexion, and supination of the left arm and tenderness of the left shoulder region with moderate bruising. Radiograph of the left shoulder and arm is unremarkable. Which of the following is most likely damaged in this patient?
- A. C5-C6 nerve roots (Correct Answer)
- B. Ulnar nerve
- C. C8-T1 nerve roots
- D. Long thoracic nerve
Bones and joints of upper limb Explanation: ***C5-C6 nerve roots***
- The "bent backwards and facing the sky" hand posture indicates **Waiter's tip position**, a classic sign of **Erb-Duchenne palsy**, caused by damage to the upper trunk of the brachial plexus (C5-C6 roots) [1].
- Weakness in **abduction** (deltoid, supraspinatus), **lateral rotation** (infraspinatus, teres minor), **flexion** (biceps, coracobrachialis), and **supination** (biceps, supinator) are all consistent with C5-C6 nerve root involvement.
*Ulnar nerve*
- Ulnar nerve damage would result in a **claw hand deformity** (hyperextension of MCP joints and flexion of DIP/PIP joints of 4th and 5th digits) and weakness in intrinsic hand muscles, not the observed upper arm weakness.
- Sensory loss involves the medial hand and little finger.
*C8-T1 nerve roots*
- Damage to the C8-T1 nerve roots (lower trunk) typically results in **Klumpke's palsy**, characterized by a more severe **claw hand** and paralysis of intrinsic hand muscles [1].
- This presentation does not match the observed functional deficits.
*Long thoracic nerve*
- Injury to the long thoracic nerve causes paralysis of the **serratus anterior muscle**, leading to **scapular winging**, especially when pushing against a wall.
- While possible in shoulder trauma, it does not explain the widespread weakness in abduction, rotation, flexion, and supination of the arm.
Bones and joints of upper limb US Medical PG Question 2: A 16-year-old boy presents to the emergency room with severe right shoulder pain following a painful overhead swing during a competitive volleyball match. On physical examination, the patient has limited active range of motion of the right shoulder and significant pain with passive motion. Suspecting a rotator cuff injury, the physician obtains an MRI, which indicates a minor tear in the tendon of the rotator cuff muscle that is innervated by the axillary nerve. Which of the following muscles was affected?
- A. Teres major
- B. Supraspinatus
- C. Teres minor (Correct Answer)
- D. Infraspinatus
- E. Subscapularis
Bones and joints of upper limb Explanation: ***Correct: Teres minor***
- **Teres minor** is the only rotator cuff muscle innervated by the **axillary nerve** (C5-C6)
- Functions as an **external rotator** of the shoulder and stabilizes the humeral head
- The axillary nerve courses through the **quadrangular space** (bordered by teres minor superiorly, teres major inferiorly, long head of triceps medially, and surgical neck of humerus laterally)
- Injury to this muscle can occur with overhead activities, though less commonly injured than supraspinatus
*Incorrect: Supraspinatus*
- Innervated by the **suprascapular nerve** (C5-C6), not the axillary nerve
- Most commonly injured rotator cuff muscle, particularly with overhead activities
- Functions primarily in **abduction** (initiates first 15° of abduction)
*Incorrect: Infraspinatus*
- Innervated by the **suprascapular nerve** (C5-C6), not the axillary nerve
- Functions as the primary **external rotator** of the shoulder
- Second most commonly injured rotator cuff muscle
*Incorrect: Subscapularis*
- Innervated by the **upper and lower subscapular nerves** (C5-C7), not the axillary nerve
- Only rotator cuff muscle on the **anterior** surface of the scapula
- Functions as an **internal rotator** of the shoulder
*Incorrect: Teres major*
- **NOT part of the rotator cuff** (forms part of the posterior axillary fold)
- Innervated by the **lower subscapular nerve** (C5-C7), not the axillary nerve
- Functions as an **internal rotator, adductor, and extensor** of the shoulder
Bones and joints of upper limb US Medical PG Question 3: A 61-year-old woman comes to the physician for a follow-up examination 1 week after undergoing right-sided radical mastectomy and axillary lymph node dissection for breast cancer. She says that she has been unable to comb her hair with her right hand since the surgery. Physical examination shows shoulder asymmetry. She is unable to abduct her right arm above 90 degrees. When she pushes against a wall, there is protrusion of the medial aspect of the right scapula. Injury to which of the following nerves is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Long thoracic nerve (Correct Answer)
- B. Thoracodorsal nerve
- C. Axillary nerve
- D. Suprascapular nerve
- E. Upper trunk of the brachial plexus
Bones and joints of upper limb Explanation: ***Long thoracic nerve***
- Injury to the **long thoracic nerve** leads to paralysis of the **serratus anterior muscle**, causing **scapular winging** (protrusion of the medial scapula) especially when pushing against a wall.
- The serratus anterior is crucial for **scapular protraction** and stabilizing the scapula during **abduction of the arm above 90 degrees**, explaining her inability to comb her hair.
*Thoracodorsal nerve*
- The **thoracodorsal nerve** innervates the **latissimus dorsi muscle**, which is responsible for **adduction**, extension, and internal rotation of the arm.
- Injury to this nerve would primarily affect these movements, not shoulder abduction above 90 degrees or scapular winging.
*Axillary nerve*
- The **axillary nerve** innervates the **deltoid muscle** and **teres minor**.
- Damage would primarily result in impaired **arm abduction up to 90 degrees** and loss of sensation over the lateral shoulder, but not scapular winging.
*Suprascapular nerve*
- The **suprascapular nerve** supplies the **supraspinatus** and **infraspinatus muscles**, which are involved in the initiation of arm abduction and external rotation, respectively.
- Injury would cause weakness in these movements and shoulder pain, but not scapular winging.
*Upper trunk of the brachial plexus*
- Injury to the **upper trunk of the brachial plexus** (C5-C6) affects several nerves and muscles, leading to conditions like **Erb's palsy**.
- While it can impair shoulder function and abduction, the specific finding of scapular winging points more directly to long thoracic nerve damage rather than a generalized upper trunk injury, as the long thoracic nerve (C5-C7) is often spared in classic Erb's palsy.
Bones and joints of upper limb US Medical PG Question 4: A 52-year-old man comes to the physician because of right shoulder pain that began after he repainted his house 1 week ago. Physical examination shows right subacromial tenderness. The pain is reproduced when the patient is asked to abduct the shoulder against resistance with the arm flexed forward by 30° and the thumb pointing downwards. The tendon of which of the following muscles is most likely to be injured in this patient?
- A. Teres minor
- B. Deltoid
- C. Supraspinatus (Correct Answer)
- D. Subscapularis
- E. Infraspinatus
Bones and joints of upper limb Explanation: ***Supraspinatus***
- The patient's presentation with **right shoulder pain** after painting (an overhead activity), subacromial tenderness, and pain reproduced by the described maneuver (the **"empty can" test**) is highly indicative of a **supraspinatus tendon injury**.
- The supraspinatus is the most commonly injured rotator cuff muscle because its tendon passes through the **subacromial space**, making it vulnerable to impaction and degeneration.
*Teres minor*
- The teres minor is primarily involved in **external rotation** and adduction of the shoulder, not typically tested by the "empty can" maneuver.
- Injury to the teres minor is less common than supraspinatus tears and usually presents with weakness in **external rotation**.
*Deltoid*
- The deltoid is a powerful muscle responsible for **shoulder abduction** (especially beyond the initial 15 degrees) and flexion, but it is less commonly involved in isolated tendonitis or tears from repetitive overhead activity.
- Deltoid pain is usually diffuse and does not localize to the **subacromial space** in the same way as supraspinatus pathology.
*Subscapularis*
- The subscapularis is responsible for **internal rotation** and adduction of the shoulder.
- Injuries typically present with weakness in internal rotation and may be tested with specific maneuvers like the **lift-off test** or **belly-press test**.
*Infraspinatus*
- The infraspinatus is a primary **external rotator** of the shoulder.
- While it can be injured in conjunction with the supraspinatus or in isolation, its primary function is external rotation, and specific tests for it involve assessing resistance to **external rotation**.
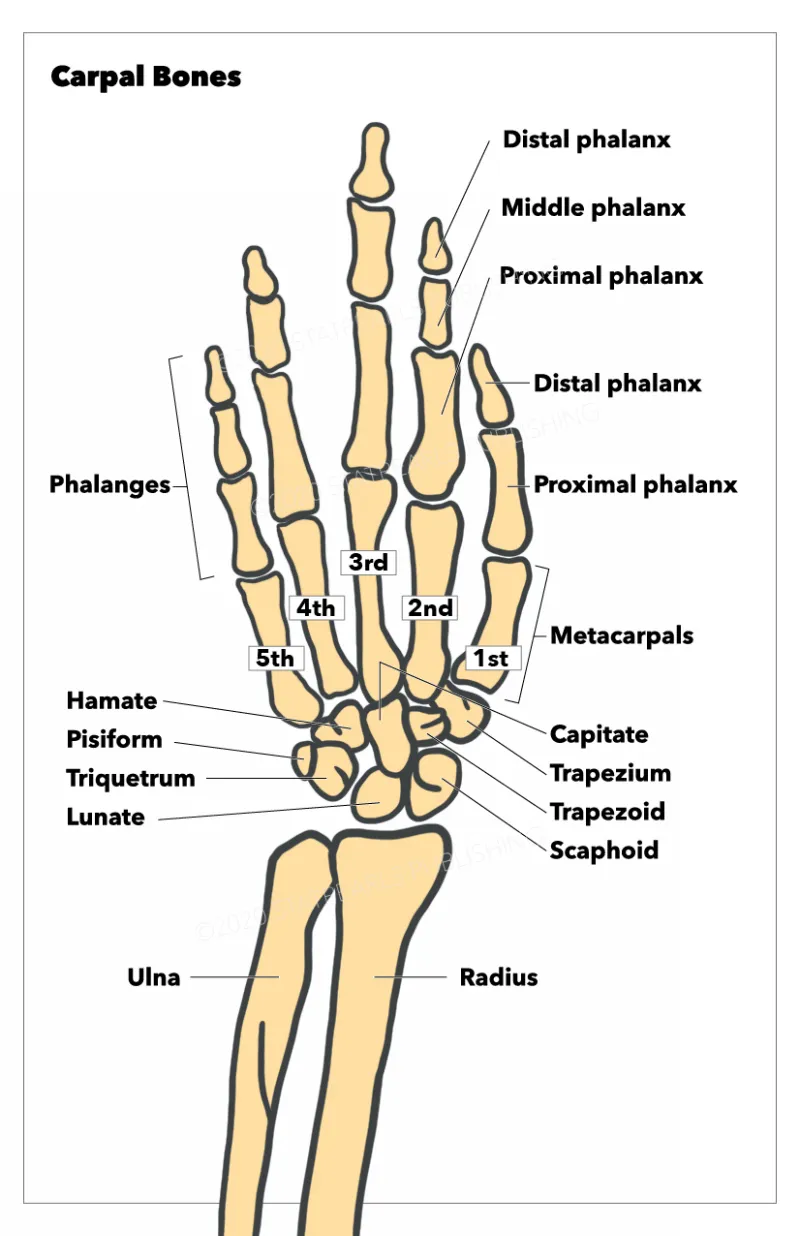
Bones and joints of upper limb US Medical PG Question 5: A 33-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with pain in her right wrist. She says she was walking on the sidewalk a few hours ago when she suddenly slipped and landed forcefully on her outstretched right hand with her palm facing down. The patient is afebrile, and vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination of her right wrist shows mild edema and tenderness on the lateral side of the right hand with a decreased range of motion. Sensation is intact. The patient is able to make a fist and OK sign with her right hand. A plain radiograph of her right wrist is shown in the image. Which of the following bones is most likely fractured in this patient?
- A. Bone labeled 'A'
- B. Bone labeled 'D' (Correct Answer)
- C. Bone labeled 'C'
- D. Bone labeled 'E'
- E. Bone labeled 'B'
Bones and joints of upper limb Explanation: ***Bone labeled 'D'***
- The clinical presentation of a fall on an **outstretched hand (FOOSH)** with pain on the **lateral aspect** of the wrist suggests a **scaphoid fracture**.
- Bone 'D' is the **scaphoid bone**, which is commonly fractured in this mechanism due to its position and poor blood supply, making it prone to **avascular necrosis** if untreated.
*Bone labeled 'A'*
- Bone 'A' is the **ulna**, which is less commonly fractured due to FOOSH injuries unless there is a direct impact or significant rotational force.
- While it articulates with the wrist, a fracture of the ulna would typically present with pain more medially and potentially forearm instability.
*Bone labeled 'C'*
- Bone 'C' is the first **metacarpal**, part of the thumb, which is distal to the wrist joint.
- A fracture here would cause pain more specifically localised to the thumb base rather than the general wrist area as described.
*Bone labeled 'E'*
- Bone 'E' is the **hamate bone**, located in the distal carpal row.
- Fractures of the hamate are less common than scaphoid fractures via FOOSH and are often associated with direct impact (e.g., from a golf club) or forceful gripping.
*Bone labeled 'B'*
- Bone 'B' represents the **radius**, specifically its distal portion. While a **Colles fracture** of the distal radius is common with FOOSH, the tenderness being on the "lateral side of the right hand" specifically points away from a general distal radius fracture and more towards the carpal bones, particularly the scaphoid.
- A Colles fracture often results in a **"dinner fork" deformity**, which is not mentioned in the presentation, and tenderness would be more widespread over the distal forearm.
Bones and joints of upper limb US Medical PG Question 6: A 7-year-old child is brought to the emergency room by his parents in severe pain. They state that he fell on his outstretched right arm while playing with his friends. He is unable to move his right arm which is being supported by his left. On exam, his vitals are normal. His right extremity reveals normal pulses without swelling in any compartments, but there is crepitus above the elbow upon movement. The child is able to flex and extend his wrist, but this is limited by pain. The child has decreased sensation along his thumb and is unable to make the "OK" sign with his thumb and index finger. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Scaphoid fracture
- B. Distal ulnar fracture
- C. Supracondylar humerus fracture (Correct Answer)
- D. Distal radius fracture
- E. Midhumerus fracture
Bones and joints of upper limb Explanation: ***Supracondylar humerus fracture***
- The classic presentation of a **fall on an outstretched arm** with **crepitus above the elbow** is highly indicative of a supracondylar humerus fracture.
- **Decreased sensation along the thumb** and inability to make an **"OK" sign** points to **anterior interosseous nerve (AIN)** palsy, a common complication of this fracture type due to compression or injury.
*Scaphoid fracture*
- This fracture typically presents with **pain in the anatomical snuffbox** and occurs at the wrist, not above the elbow.
- While it can result from a fall on an outstretched hand, it does not explain the crepitus above the elbow or the specific nerve palsy described.
*Distal ulnar fracture*
- This injury would cause pain and swelling at the **distal forearm/wrist**, not crepitus above the elbow.
- Nerve involvement, if present, would typically affect the **ulnar nerve**, not the anterior interosseous nerve.
*Distal radius fracture*
- Also known as a **Colles fracture** when dorsal displacement is present, this injury occurs at the wrist and presents with pain and deformity there.
- It does not account for the crepitus above the elbow or the specific AIN palsy symptoms.
*Midhumerus fracture*
- While a midhumerus fracture can occur from a fall on an outstretched arm and cause crepitus, it would be located in the **middle third of the upper arm**, not specifically above the elbow joint.
- The specific AIN palsy is less commonly associated with mid-shaft humeral fractures, which are more likely to involve the **radial nerve**.
Bones and joints of upper limb US Medical PG Question 7: A previously healthy 2-year-old boy is brought to the emergency room by his mother because of persistent crying and refusal to move his right arm. The episode began 30 minutes ago after the mother lifted him up by the arms. He appears distressed and is inconsolable. On examination, his right arm is held close to his body in a flexed and pronated position. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Proximal ulnar fracture
- B. Radial head subluxation (Correct Answer)
- C. Anterior shoulder dislocation
- D. Supracondylar fracture of the humerus
- E. Olecranon fracture
Bones and joints of upper limb Explanation: ***Radial head subluxation***
- This presentation is classic for **radial head subluxation** (nursemaid's elbow), which typically occurs when a child is pulled or lifted by the hand or wrist, causing the **annular ligament** to slip over the radial head.
- The child usually presents with immediate pain, refusal to use the affected arm, and the arm held in a characteristic **flexed and pronated position**.
*Proximal ulnar fracture*
- A proximal ulnar fracture would typically present with more generalized pain, swelling, and **point tenderness** over the ulna, which are not described.
- The mechanism of injury (lifting by arms) is less consistent with an isolated proximal ulnar fracture and more suggestive of a traction injury at the elbow.
*Anterior shoulder dislocation*
- An anterior shoulder dislocation typically results from a fall or direct blow, not a traction injury to the arm, and the arm would be held in **abduction and external rotation**.
- This injury is also much less common in toddlers compared to radial head subluxation.
*Supracondylar fracture of the humerus*
- A supracondylar fracture usually results from a fall onto an outstretched hand and is associated with significant pain, swelling, and often a **visible deformity** or **neurovascular compromise**.
- The specific injury mechanism described does not fit the typical cause of a supracondylar fracture.
*Olecranon fracture*
- An olecranon fracture usually results from direct trauma or a fall onto the elbow, presenting with localized pain, swelling, and inability to extend the elbow against resistance.
- The "lifting by the arms" mechanism is unlikely to cause an olecranon fracture, and the classic presentation of a pronated arm is not characteristic of this injury.
Bones and joints of upper limb US Medical PG Question 8: A 4-year-old boy is brought to the pediatrician by his mother for a routine medical examination. His medical history is relevant for delayed gross motor milestones. The mother is concerned about a growth delay because both of his brothers were twice his size at this age. Physical examination reveals a well-groomed and healthy boy with a prominent forehead and short stature, in addition to shortened upper and lower extremities with a normal vertebral column. The patient’s vitals reveal: temperature 36.5°C (97.6°F); pulse 60/min; and respiratory rate 17/min and a normal intelligence quotient (IQ). A mutation in which of the following genes is the most likely cause underlying the patient’s condition?
- A. Runt-related transcription factor 2
- B. Alpha-1 type I collagen
- C. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (Correct Answer)
- D. Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor
- E. Fibrillin-1
Bones and joints of upper limb Explanation: ***Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3***
- The constellation of **short stature**, prominent forehead, and **shortened upper and lower extremities** with a normal vertebral column in a child with normal intelligence is characteristic of **achondroplasia**.
- Achondroplasia is caused by a gain-of-function mutation in the **fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3)** gene, which inhibits chondrocyte proliferation and differentiation, leading to impaired endochondral ossification.
*Runt-related transcription factor 2*
- Mutations in **Runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2)** are associated with **cleidocranial dysplasia**, a condition characterized by absent or hypoplastic clavicles, delayed closure of fontanelles, and dental abnormalities, which are not described in this patient.
- While it affects bone development, the specific features of achondroplasia, such as rhizomelic dwarfism and a prominent forehead, are not typical of RUNX2 mutations.
*Alpha-1 type I collagen*
- Mutations in **collagen genes**, particularly type I collagen (COL1A1, COL1A2), are linked to **osteogenesis imperfecta**, characterized by **fragile bones**, blue sclera, and hearing loss.
- The patient's presentation does not include these features, and the primary issue is disproportionate short stature due to impaired cartilage growth, not bone fragility.
*Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor*
- Mutations in the **insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF1R)** can lead to **pre- and postnatal growth retardation** and microcephaly, often associated with developmental delay and feeding difficulties.
- While IGF1R mutations cause short stature, the specific skeletal dysmorphology (e.g., prominent forehead, shortened limbs) and normal intelligence are much more suggestive of achondroplasia.
*Fibrillin-1*
- Mutations in **fibrillin-1** are responsible for **Marfan syndrome**, which typically presents with **tall stature**, long limbs (dolichostenomelia), joint hypermobility, and cardiovascular abnormalities such as aortic root dilation.
- The patient's short stature and shortened limbs directly contradict the clinical picture of Marfan syndrome.
Bones and joints of upper limb US Medical PG Question 9: A 42-year-old woman comes to the physician because of increasing pain in the right hip for 2 months. The pain is intermittent, presenting at the lateral side of the hip and radiating towards the thigh. It is aggravated while climbing stairs or lying on the right side. Two weeks ago, the patient was treated with a course of oral prednisone for exacerbation of asthma. Her current medications include formoterol-budesonide and albuterol inhalers. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows tenderness to palpation over the upper lateral part of the right thigh. There is no swelling. The patient is placed in the left lateral decubitus position. Abducting the extended right leg against the physician's resistance reproduces the pain. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. An x-ray of the pelvis shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Osteoarthritis of the hip
- B. Osteonecrosis of femoral head
- C. Lumbosacral radiculopathy
- D. Greater trochanteric pain syndrome (Correct Answer)
- E. Iliotibial band syndrome
Bones and joints of upper limb Explanation: ***Greater trochanteric pain syndrome***
- The patient's symptoms of **lateral hip pain** radiating to the thigh, aggravated by activity and lying on the affected side, and **tenderness over the greater trochanter** are classic for **greater trochanteric pain syndrome** (GTPS).
- Pain reproduction with **abduction against resistance** (a specific test for GTPS) and normal X-rays further support this diagnosis.
*Osteoarthritis of the hip*
- Typically causes **groin pain** that can radiate to the buttock or knee, not primarily lateral hip pain.
- X-rays would likely show signs of **joint space narrowing**, osteophytes, or subchondral sclerosis, which are absent here.
*Osteonecrosis of femoral head*
- While **corticosteroid use** is a risk factor, osteonecrosis usually presents with **groin or buttock pain** and would likely show abnormalities on X-ray (advanced stages) or MRI (early stages).
- The specific tenderness and pain reproduction with abduction against resistance are not typical for osteonecrosis.
*Lumbosacral radiculopathy*
- Would typically present with pain radiating **down the leg** in a dermatomal pattern, often accompanied by **neurological deficits** such as sensory loss, weakness, or reflex changes.
- The examination findings of isolated lateral hip tenderness and pain with resisted abduction do not support radiculopathy.
*Iliotibial band syndrome*
- More commonly affects **runners** or cyclists and causes pain along the **lateral aspect of the knee**, although it can present as lateral hip pain.
- While it can manifest with lateral hip pain, the focal tenderness over the greater trochanter and pain on resisted abduction make **GTPS** a more precise diagnosis.
Bones and joints of upper limb US Medical PG Question 10: A 44-year-old woman comes to the physician for the evaluation of right knee pain for 1 week. The pain began after the patient twisted her knee during basketball practice. At the time of the injury, she felt a popping sensation and her knee became swollen over the next few hours. The pain is exacerbated by walking up or down stairs and worsens throughout the day. She also reports occasional locking of the knee. She has been taking acetaminophen during the past week, but the pain is worse today. Her mother has rheumatoid arthritis. The patient is 155 cm (4 ft 11 in) tall and weighs 75 kg (165 lb); BMI is 33 kg/m2. Vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows effusion of the right knee; range of motion is limited by pain. There is medial joint line tenderness. Knee extension with rotation results in an audible snap. Further evaluation is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Hyperintense line in the meniscus on MRI (Correct Answer)
- B. Trabecular loss in the proximal femur on x-ray
- C. Posterior tibial translation on examination
- D. Erosions and synovial hyperplasia on MRI
- E. Anterior tibial translation on examination
Bones and joints of upper limb Explanation: ***Hyperintense line in the meniscus on MRI***
- This patient's symptoms of a **popping sensation**, rapid swelling, pain with stairs, and **locking of the knee** after a twisting injury are highly suggestive of a **meniscal tear**.
- An MRI with a **hyperintense line within the substance of the meniscus extending to the articular surface** is the classic finding for a meniscal tear.
*Trabecular loss in the proximal femur on x-ray*
- **Trabecular loss** in the proximal femur on X-ray is characteristic of **osteoporosis**, a condition affecting bone density.
- While this patient is a woman, there are no other clinical signs pointing to osteoporosis, and it would not explain the acute knee injury symptoms.
*Posterior tibial translation on examination*
- **Posterior tibial translation** on examination (positive posterior drawer test) indicates damage to the **posterior cruciate ligament (PCL)**.
- While a knee injury, the symptoms of initial popping, rapid swelling, and locking are more characteristic of a meniscal tear or ACL injury than an isolated PCL tear.
*Erosions and synovial hyperplasia on MRI*
- **Erosions and synovial hyperplasia** on MRI are classic findings in **inflammatory arthropathies** like **rheumatoid arthritis**, which primarily affect the joint lining (synovium).
- Although the patient's mother has rheumatoid arthritis, there is no indication of chronic inflammatory arthritis, and the patient's acute injury symptoms are not consistent with this.
*Anterior tibial translation on examination*
- **Anterior tibial translation** on examination (positive anterior drawer test or Lachman test) indicates damage to the **anterior cruciate ligament (ACL)**.
- While an ACL injury can cause a pop and swelling, the prominent symptom of **locking** is more specifically associated with meniscal tears where a torn piece of cartilage intermittently blocks joint movement.
More Bones and joints of upper limb US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.