Spleen and pancreas US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Spleen and pancreas. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Spleen and pancreas US Medical PG Question 1: A researcher is tracing the fate of C-peptide, a product of preproinsulin cleavage. Which of the following is a true statement regarding the fate of C-peptide?
- A. C-peptide exits the cells via a protein channel
- B. C-peptide is further cleaved into insulin
- C. C-peptide is packaged with insulin in secretory vesicles (Correct Answer)
- D. C-peptide is immediately degraded by the proteasome
- E. C-peptide activates an intracellular signaling cascade
Spleen and pancreas Explanation: ***C-peptide is packaged with insulin in secretory vesicles***
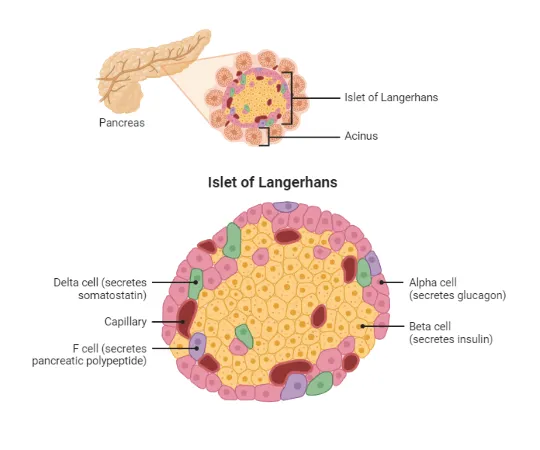
- Preproinsulin is cleaved in the **endoplasmic reticulum** to proinsulin (signal peptide removal), which is then transported to the **Golgi apparatus**.
- In the Golgi, proinsulin is cleaved by **prohormone convertases** into **insulin** and **C-peptide**, and both are stored together in **secretory vesicles** within the pancreatic beta cells.
- Upon stimulation, both insulin and C-peptide are **co-secreted** via exocytosis in equimolar amounts, making C-peptide a useful marker of endogenous insulin secretion.
*C-peptide exits the cells via a protein channel*
- C-peptide exits the beta cells via **exocytosis** of secretory granules, not through specific protein channels.
- It is **co-secreted with insulin** when secretory vesicles fuse with the plasma membrane.
- Its presence in the bloodstream in equimolar amounts with insulin makes it an indirect measure of **insulin secretion**.
*C-peptide is further cleaved into insulin*
- **C-peptide** is a product of proinsulin cleavage, alongside insulin; it is not further processed into insulin.
- Insulin itself is composed of two **peptide chains (A and B)** linked by disulfide bonds, formed after C-peptide is removed from proinsulin.
*C-peptide is immediately degraded by the proteasome*
- C-peptide is not immediately degraded by the **proteasome** upon synthesis.
- After secretion, it circulates in the blood with a **longer half-life** than insulin (approximately 30 minutes versus 4-6 minutes), allowing it to be a useful marker of endogenous insulin production.
- Its degradation occurs primarily in the **kidney**.
*C-peptide activates an intracellular signaling cascade*
- While there is some research suggesting C-peptide may have independent **biological activity** and activate certain signaling pathways extracellularly, its primary role in the context of the insulin synthesis pathway is as a **byproduct** of proinsulin processing.
- Its clinical utility is primarily as a **biomarker** of endogenous insulin secretion, particularly useful in distinguishing between endogenous and exogenous insulin in diabetic patients.
Spleen and pancreas US Medical PG Question 2: A 52-year-old woman presents to the urgent care center with several hours of worsening abdominal discomfort with radiation to the back. The patient also complains of malaise, chills, nausea, and vomiting. Social history is notable for alcoholism. On physical exam, she is febrile to 39.5°C (103.1°F), and she is diffusely tender to abdominal palpation. Complete blood count is notable for 13,500 white blood cells, bilirubin 2.1, lipase 842, and amylase 3,210. Given the following options, what is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Choledocholithiasis
- B. Ascending cholangitis
- C. Gallstone pancreatitis (Correct Answer)
- D. Cholelithiasis
- E. Acute cholecystitis
Spleen and pancreas Explanation: ***Gallstone pancreatitis***
- The patient presents with classic symptoms of **acute pancreatitis**: severe abdominal pain radiating to the back, nausea, vomiting, and markedly elevated **lipase (842)** and **amylase (3,210)**.
- The **key differentiating feature** is the elevated **bilirubin (2.1 mg/dL)**, which indicates biliary obstruction from a gallstone passing through or obstructing the ampulla of Vater.
- **Gallstone pancreatitis** is the most common cause of acute pancreatitis in women, and the combination of pancreatitis with hyperbilirubinemia strongly suggests a biliary etiology rather than alcoholic pancreatitis (which typically does not cause elevated bilirubin).
- While the patient has a history of alcoholism, the elevated bilirubin makes **gallstone pancreatitis** the most likely diagnosis.
*Choledocholithiasis*
- This refers to a stone in the **common bile duct**, which can cause biliary obstruction and elevated bilirubin.
- However, choledocholithiasis alone does not explain the **markedly elevated lipase and amylase**, which indicate pancreatic inflammation.
- Choledocholithiasis may be present as part of the pathophysiology, but the clinical picture is acute pancreatitis caused by the stone (gallstone pancreatitis).
*Ascending cholangitis*
- This serious bile duct infection presents with **Charcot's triad** (fever, jaundice, right upper quadrant pain) or **Reynolds' pentad** (adds altered mental status and hypotension).
- While the patient is febrile, she lacks **jaundice**, hypotension, or altered mental status.
- The **extremely elevated lipase and amylase** point to pancreatitis rather than cholangitis as the primary process.
*Cholelithiasis*
- This simply means **gallstones in the gallbladder**, which are often asymptomatic.
- The patient's acute presentation with fever, systemic symptoms, and markedly elevated pancreatic enzymes indicates a complication of gallstones (pancreatitis), not just their presence.
*Acute cholecystitis*
- This is **gallbladder inflammation**, typically presenting with right upper quadrant pain, fever, positive Murphy's sign, and leukocytosis.
- The **diffuse abdominal tenderness** (not localized to RUQ), pain radiating to the back, and **extremely elevated lipase and amylase** are characteristic of pancreatitis, not cholecystitis.
- Acute cholecystitis does not cause such dramatic elevations in pancreatic enzymes.
Spleen and pancreas US Medical PG Question 3: A 46-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with complaints of increasing left upper quadrant discomfort. She has a known history of type 1 Gaucher disease. On physical examination, her spleen is palpable 8 cm below the costal margin. Routine laboratory work reveals severe pancytopenia. After consultation with the patient on the risks of her condition, the patient decides to undergo a splenectomy. Which of the following is more likely to occur as a consequence of splenectomy in this patient?
- A. Thrombocytopenia
- B. Leukopenia
- C. Pneumococcal septicemia (Correct Answer)
- D. Staphylococcal septicemia
- E. Anemia
Spleen and pancreas Explanation: ***Pneumococcal septicemia***
- Patients who undergo splenectomy are at significantly increased risk of **overwhelming post-splenectomy infection (OPSI)**, particularly from **encapsulated bacteria** like *Streptococcus pneumoniae*.
- The spleen plays a crucial role in filtering encapsulated bacteria and producing opsonizing antibodies, and its removal compromises this immune function.
*Thrombocytopenia*
- **Thrombocytopenia** is typically a symptom *before* splenectomy in Gaucher disease due to hypersplenism.
- After splenectomy, the platelet count often **increases**, not decreases, due to the removal of the organ that sequesters platelets and destroys them.
*Leukopenia*
- **Leukopenia** (specifically neutropenia) is a pre-existing condition in severe Gaucher disease due to hypersplenism and bone marrow involvement.
- Post-splenectomy, the white blood cell count, particularly neutrophils, generally **increases** as the sequestration and destruction in the spleen are eliminated.
*Staphylococcal septicemia*
- While *Staphylococcus* can cause serious infections, it is **not the primary pathogen** associated with OPSI in asplenic patients.
- Encapsulated bacteria like *Streptococcus pneumoniae* are the most common and dangerous cause of post-splenectomy sepsis.
*Anemia*
- **Anemia** is a common finding in Gaucher disease due to hypersplenism and bone marrow infiltration.
- Splenectomy typically **improves** anemia by removing the site of red blood cell destruction and reducing abnormal cytokine production that inhibits erythropoiesis.
Spleen and pancreas US Medical PG Question 4: A 45-year-old male is brought to the emergency department by emergency medical services after sustaining a gunshot wound to the abdomen. He is unresponsive. His temperature is 99.0°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 95/58 mmHg, pulse is 115/min, and respirations are 20/min. Physical examination reveals an entry wound in the left abdominal quadrant just inferior to the left lateral costal border. Abdominal CT shows the bullet trajectory through the left abdominal cavity. Which of the following structures has the bullet most likely penetrated?
- A. Transverse colon
- B. Ascending colon
- C. Descending colon (Correct Answer)
- D. Sigmoid colon
- E. Superior duodenum
Spleen and pancreas Explanation: ***Descending colon***
- The **descending colon** is located in the left abdominal cavity, specifically in the left upper quadrant and extending into the left lower quadrant, making it highly susceptible to injury from a gunshot wound in the **left abdominal quadrant** just inferior to the left lateral costal border.
- Its position aligns directly with the described entry point and bullet trajectory.
*Transverse colon*
- The **transverse colon** lies more centrally in the upper abdomen, spanning from the right to the left upper quadrants.
- While possible to be hit by a left-sided entry wound, the trajectory described as "inferior to the left lateral costal border" makes the descending colon a more direct and likely target.
*Ascending colon*
- The **ascending colon** is located in the **right abdominal cavity**, specifically in the right upper and lower quadrants.
- A wound inferior to the left lateral costal border would be on the opposite side of the abdomen and thus unlikely to penetrate the ascending colon.
*Sigmoid colon*
- The **sigmoid colon** is located more inferiorly in the **left lower quadrant** and pelvis.
- While on the left side, the entry wound described as "inferior to the left lateral costal border" is generally higher than the typical location of the sigmoid colon.
*Superior duodenum*
- The **superior duodenum** is located in the **right upper quadrant** of the abdomen, anterior to the head of the pancreas.
- Its position on the right side makes it highly unlikely to be penetrated by a gunshot wound to the left abdominal quadrant.
Spleen and pancreas US Medical PG Question 5: A 54-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with a 2-month-history of diarrhea. He says that he feels the urge to defecate 3-4 times per day and that his stools have changed in character since the diarrhea began. Specifically, they now float, stick to the side of the toilet bowl, and smell extremely foul. His past medical history is significant for several episodes of acute pancreatitis secondary to excessive alcohol consumption. His symptoms are found to be due to a deficiency in an enzyme. Which of the following enzymes is most likely deficient in this patient?
- A. Enterokinase
- B. Amylase
- C. Colipase
- D. Lipase (Correct Answer)
- E. Chymotrypsin
Spleen and pancreas Explanation: ***Lipase***
- The patient's history of **recurrent pancreatitis** likely led to **exocrine pancreatic insufficiency**, reducing the production of digestive enzymes, particularly **lipase**.
- **Steatorrhea** (foul-smelling, floating, sticky stools) is a classic symptom of **fat malabsorption**, which occurs due to insufficient lipase for triglyceride digestion.
*Enterokinase*
- **Enterokinase** is an enzyme produced in the **duodenum** that activates trypsinogen to trypsin, which then activates other pancreatic proteases.
- A deficiency would primarily cause **protein malabsorption**, not the pronounced fat malabsorption (steatorrhea) seen in this patient.
*Amylase*
- **Amylase** is responsible for **carbohydrate digestion**.
- While chronic pancreatitis can lead to amylase deficiency, the primary symptom of this patient's diarrhea, steatorrhea, points more directly to **fat malabsorption** rather than carbohydrate malabsorption.
*Colipase*
- **Colipase** is a co-enzyme that helps **lipase** bind to the fat-water interface to digest triglycerides.
- While essential for fat digestion, lipase itself is the primary enzyme responsible, and a direct deficiency in colipase alone is less commonly implicated as the sole cause of severe steatorrhea than a general pancreatic enzyme insufficiency affecting lipase production.
*Chymotrypsin*
- **Chymotrypsin** is a **protease** primarily involved in **protein digestion**.
- A deficiency would lead to **protein malabsorption**, which typically presents with symptoms like muscle wasting and edema, rather than the prominent steatorrhea described.
Spleen and pancreas US Medical PG Question 6: A 27-year-old woman presented to the clinic with recurrent abdominal swelling and stunted growth relative to her siblings. She has a history of multiple blood transfusions in her childhood. She has a family history of jaundice in her father who was operated on for multiple gallbladder stones. The physical examination reveals a pale, icteric, small and short-statured young lady. On abdominal examination, the spleen was enlarged by 6 cm below the right costal margin, but the liver was not palpable. The ultrasound of the abdomen reveals multiple gallbladder stones. The laboratory test results are as follows:
Hb 9 g/dL
Hct 27%
WBC 6,200/mm3
Platelets 200,000/mm3
MCV 75 um3
MCHC 37 gm/dL
Reticulocytes 6.5%
A peripheral blood smear is presented in the image. The direct Coombs test was negative. The osmotic fragility test was increased. What is the most likely cause of her condition?
- A. Anemia of chronic disease
- B. Aplastic anemia
- C. Blood loss
- D. Vitamin B12 deficiency
- E. Hereditary spherocytosis (Correct Answer)
Spleen and pancreas Explanation: ***Hereditary spherocytosis***
- The patient's history of **recurrent abdominal swelling**, **stunted growth**, prior **multiple blood transfusions**, **family history of jaundice** and gallbladder stones, along with current findings of **palpable splenomegaly**, **increased osmotic fragility test**, and **elevated MCHC (37 g/dL)** with **spherocytes** on peripheral smear, all point to hereditary spherocytosis.
- **Hereditary spherocytosis** is caused by defects in red blood cell membrane proteins (spectrin, ankyrin, band 3), leading to fragile, spherical red blood cells that lose membrane surface area and are prematurely destroyed in the spleen, resulting in **hemolytic anemia**, **splenomegaly**, **jaundice**, and increased risk of **pigment gallstones** from chronic hemolysis.
- The **elevated MCHC** (concentration of hemoglobin) and **reduced MCV** (75 fL) reflect the spherical shape with decreased surface area-to-volume ratio characteristic of spherocytes.
- **Increased osmotic fragility test** is pathognomonic for hereditary spherocytosis, as spherocytes lyse more readily in hypotonic solutions.
*Anemia of chronic disease*
- This typically presents as **normocytic, normochromic anemia** or **microcytic, hypochromic anemia** with **low reticulocyte count**, elevated ferritin, and low transferrin saturation.
- The patient's **elevated reticulocyte count (6.5%)**, evidence of significant hemolysis (jaundice, splenomegaly, gallstones), **elevated MCHC**, and **increased osmotic fragility** are inconsistent with anemia of chronic disease.
*Aplastic anemia*
- Characterized by **pancytopenia** (low red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets) due to bone marrow failure with **low reticulocyte count**.
- The patient has **normal white blood cell and platelet counts**, along with **elevated reticulocytes (6.5%)**, which is contrary to aplastic anemia where reticulocytes would be markedly decreased.
*Blood loss*
- Acute blood loss would present with **normocytic, normochromic anemia** and eventually an **elevated reticulocyte count**. Chronic blood loss leads to **iron deficiency anemia** (microcytic, hypochromic with **low MCHC**).
- The patient's presentation includes significant **signs of hemolysis** (jaundice, splenomegaly, pigment gallstones), **elevated MCHC**, and **increased osmotic fragility test**, which are not features of anemia due to blood loss.
*Vitamin B12 deficiency*
- This causes **megaloblastic anemia**, characterized by **macrocytic red blood cells (MCV >100 fL)**, hypersegmented neutrophils, and **low reticulocyte count**.
- The patient's **MCV is 75 fL (microcytic)**, she has an **elevated reticulocyte count (6.5%)**, and **elevated MCHC**, all contradicting B12 deficiency.
Spleen and pancreas US Medical PG Question 7: A 23-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with 3 days of fatigue and back pain after she started a drug for malaria prophylaxis. She says that her urine has also been darker over the same time period. Her past medical history is significant for allergies as well as a broken elbow that was treated in a cast 10 years ago. She does not take any medications, does not smoke, and drinks socially. Peripheral blood smear reveals both red blood cells with dark intracellular inclusions as well as abnormally shaped red blood cells. The immune cells responsible for the shape of these red blood cells are located in which of the following places?
- A. Lymph nodes
- B. Red pulp of the spleen (Correct Answer)
- C. Bone marrow
- D. White pulp of the spleen
- E. Blood vessels
Spleen and pancreas Explanation: ***Red pulp of the spleen***
- The patient's symptoms (fatigue, back pain, dark urine after malaria prophylaxis) and lab findings (**dark intracellular inclusions** and abnormally shaped red blood cells) suggest **G6PD deficiency**, leading to **hemolytic anemia**.
- The **red pulp of the spleen** is where old or damaged red blood cells, including those with Heinz bodies (intracellular inclusions) or abnormal shapes, are **phagocytosed** by macrophages, thus "shaping" them or removing severely affected cells.
*Lymph nodes*
- **Lymph nodes** are primarily involved in filtering lymph and are major sites for adaptive immune responses, housing B and T lymphocytes.
- They are not the primary sites for the destruction or "shaping" of red blood cells.
*Bone marrow*
- The **bone marrow** is the primary site of **hematopoiesis**, where red blood cells are produced, not where they are destroyed or undergo physical shaping due to immune cell action in hemolysis.
- While macrophages are present, their main role in marrow is related to erythropoiesis (e.g., central macrophage in erythroblastic islands) and debris clearance, not erythrocyte shaping in peripheral circulation.
*White pulp of the spleen*
- The **white pulp of the spleen** is rich in lymphocytes and is the site of immune responses, similar to lymph nodes.
- It is involved in adaptive immunity and not directly engaged in the physical destruction or "shaping" of red blood cells during hemolysis.
*Blood vessels*
- **Blood vessels** are conduits for blood transport and are not primary sites for the physical destruction or shaping of red blood cells by immune cells.
- While some hemolysis can occur intravascularly, the immune cells responsible for removing and "shaping" damaged red blood cells (like macrophages) are predominantly organ-resident.
Spleen and pancreas US Medical PG Question 8: A 55-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-week history of intermittent burning epigastric pain. His pain improves with antacid use and eating but returns approximately 2 hours following meals. He has a history of chronic osteoarthritis and takes ibuprofen daily. Upper endoscopy shows a deep ulcer located on the posterior wall of the duodenal bulb. This ulcer is most likely to erode into which of the following structures?
- A. Splenic vein
- B. Descending aorta
- C. Pancreatic duct
- D. Gastroduodenal artery (Correct Answer)
- E. Transverse colon
Spleen and pancreas Explanation: ***Gastroduodenal artery***
- A deep ulcer on the **posterior wall of the duodenal bulb** is anatomically very close to the **gastroduodenal artery**.
- Erosion into this artery can lead to **life-threatening upper gastrointestinal bleeding**, a severe complication of peptic ulcer disease.
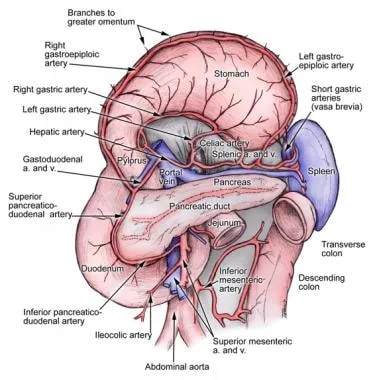
*Splenic vein*
- The **splenic vein** is located more posteriorly and superiorly, primarily in relation to the pancreas and spleen, making it less likely to be eroded by a duodenal bulb ulcer.
- While erosion into major vessels can occur, the gastroduodenal artery is in a much more direct and immediate proximity to the posterior duodenal bulb.
*Descending aorta*
- The **descending aorta** is a retroperitoneal structure located much more posteriorly and medially, far from the duodenal bulb.
- Erosion into the aorta is an extremely rare and catastrophic event, not typically associated with duodenal ulcers.
*Pancreatic duct*
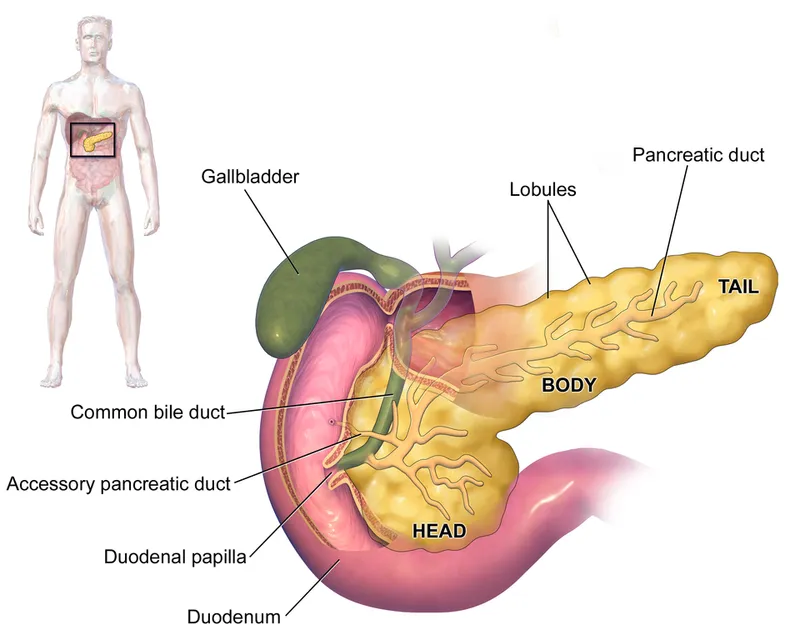
- The **pancreatic duct** (Wirsung's duct) is located within the pancreas, which lies posterior to the duodenum. While a *deep* ulcer could hypothetically penetrate the pancreas, the primary structure at risk for hemorrhage from a posterior duodenal bulb ulcer is the gastroduodenal artery.
- Erosion into the pancreatic duct would likely cause **pancreatitis** or **fistula formation**, rather than acute hemorrhage.
*Transverse colon*
- The **transverse colon** is located inferior to the duodenum, separated by the greater omentum.
- Ulcers would typically erode anteriorly or directly posteriorly, not inferiorly into the transverse colon, which would involve fistula formation rather than arterial erosion.
Spleen and pancreas US Medical PG Question 9: What is the most common site of congenital diaphragmatic hernia?
- A. Central tendon
- B. Posterolateral (Correct Answer)
- C. Crural
- D. Anterolateral
- E. Esophageal hiatus
Spleen and pancreas Explanation: ***Posterolateral***
- The **posterolateral** region, specifically the foramen of Bochdalek, is the most common site for congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH).
- This type of hernia accounts for approximately 80-90% of all CDH cases and usually occurs on the **left side**.
*Central tendon*
- Hernias through the **central tendon** are extremely rare and are distinct from the more common forms of CDH.
- Defects in the central tendon are often associated with **pericardial defects** rather than typical diaphragmatic hernias which allow abdominal contents into the thoracic cavity.
*Crural*
- Hernias involving the **crura** of the diaphragm are typically **hiatal hernias** (e.g., sliding or paraesophageal), which are different in origin and presentation from CDH.
- These are usually acquired and involve the stomach moving into the mediastinum, rather than a congenital defect leading to abdominal viscera migrating into the chest.
*Anterolateral*
- While congenital diaphragmatic hernias can occur **anterolaterally** through the foramen of Morgagni, these are much less common than posterolateral hernias.
- Morgagni hernias account for a small percentage of CDH cases (around 2-5%) and are typically located on the right side, often containing omentum or colon.
*Esophageal hiatus*
- The **esophageal hiatus** is the normal opening in the diaphragm through which the esophagus passes.
- While hiatal hernias can occur at this site, these are typically **acquired hernias** in adults, not congenital diaphragmatic hernias.
- Congenital CDH refers to developmental defects in the diaphragm itself, not enlargement of normal openings.
Spleen and pancreas US Medical PG Question 10: Identify the labeling correctly

- A. A - Ascending aorta, B - Pulmonary trunk, C - Superior vena cava, D - Descending aorta (Correct Answer)
- B. A - Ascending aorta, B - Superior vena cava, C - Pulmonary trunk, D - Descending aorta
- C. A - Superior vena cava, B - Pulmonary trunk, C - Ascending aorta, D - Descending aorta
- D. A - Pulmonary trunk, B - Ascending aorta, C - Superior vena cava, D - Descending aorta
- E. A - Ascending aorta, B - Pulmonary trunk, C - Descending aorta, D - Superior vena cava
Spleen and pancreas Explanation: ***A - Ascending aorta, B - Pulmonary trunk, C - Superior vena cava, D - Descending aorta***
- **A** points to the **ascending aorta**, the initial segment of the aorta emerging from the left ventricle.
- **B** indicates the **pulmonary trunk**, which originates from the right ventricle and carries deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
- **C** correctly identifies the **superior vena cava**, responsible for draining deoxygenated blood from the upper body into the right atrium.
- **D** is correctly labeled as the **descending aorta**, the portion of the aorta that descends through the thorax and abdomen.
*A - Ascending aorta, B - Superior vena cava, C - Pulmonary trunk, D - Descending aorta*
- This option incorrectly identifies **B as superior vena cava** and **C as pulmonary trunk**. B is clearly emerging from the right ventricle, characteristic of the pulmonary trunk, while C is positioned where the superior vena cava would be.
- The superior vena cava (C) would be located to the right and anterior to the ascending aorta, while the pulmonary trunk (B) is anterior to the ascending aorta, emerging from the right ventricle.
*A - Superior vena cava, B - Pulmonary trunk, C - Ascending aorta, D - Descending aorta*
- This option incorrectly labels **A as superior vena cava** and **C as ascending aorta**. A is clearly the large vessel emerging from the left side of the heart, consistent with the ascending aorta.
- The ascending aorta (A) would be the largest vessel emerging from the left ventricle, and the superior vena cava (C) would be entering the right atrium.
*A - Pulmonary trunk, B - Ascending aorta, C - Superior vena cava, D - Descending aorta*
- This option incorrectly identifies **A as pulmonary trunk** and **B as ascending aorta**. A is the large vessel originating from the left ventricle, which is the ascending aorta.
- The pulmonary trunk (B) arises from the right ventricle and is usually anterior to the ascending aorta (A).
*A - Ascending aorta, B - Pulmonary trunk, C - Descending aorta, D - Superior vena cava*
- This option incorrectly swaps **C and D**, labeling C as descending aorta and D as superior vena cava. C is positioned in the superior mediastinum where the superior vena cava enters the right atrium, not in the posterior mediastinum where the descending aorta would be located.
- The descending aorta (D) runs posteriorly in the thorax, while the superior vena cava (C) is an anterior structure draining into the right atrium.
More Spleen and pancreas US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.