Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree US Medical PG Question 1: A 65-year-old man comes to the clinic complaining of abdominal pain for the past 2 months. He describes the pain as a dull, aching, 6/10 pain that is diffuse but worse in the right upper quadrant (RUQ). His past medical history is significant for diabetes controlled with metformin and a cholecystectomy 10 years ago. He reports fatigue and a 10-lb weight loss over the past month that he attributes to poor appetite; he denies fever, nausea/vomiting, palpitations, chest pain, or bowel changes. Physical examination is significant for mild scleral icterus and tenderness at the RUQ. Further workup reveals a high-grade malignant vascular neoplasm of the liver. What relevant detail would you expect to find in this patient’s history?
- A. Chronic alcohol abuse
- B. Heavy ingestion of acetaminophen
- C. Infection with the hepatitis B virus
- D. Obesity
- E. Prior occupation in a chemical plastics manufacturing facility (Correct Answer)
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree Explanation: ***Prior occupation in a chemical plastics manufacturing facility***
- This history suggests exposure to **vinyl chloride**, a known carcinogen associated with hepatic angiosarcoma, a rare but aggressive **vascular neoplasm of the liver**.
- **Hepatic angiosarcoma** often presents with vague symptoms like abdominal pain, weight loss, and fatigue, as seen in this patient, and can lead to liver failure and jaundice [1].
*Chronic alcohol abuse*
- While chronic alcohol abuse can lead to various liver diseases, including **alcoholic hepatitis**, **cirrhosis**, and **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)**, it is not typically associated with angiosarcomas.
- The patient's symptoms are more consistent with a rapidly progressing malignancy, and HCC typically presents in patients with underlying cirrhosis or hepatitis.
*Heavy ingestion of acetaminophen*
- Acute or chronic overdose of **acetaminophen** primarily causes **centrilobular necrosis** and liver failure, but it is not linked to the development of hepatic vascular neoplasms like angiosarcoma.
- The patient's presentation of a high-grade malignant vascular neoplasm points away from drug-induced liver injury as the primary cause.
*Infection with the hepatitis B virus*
- **Hepatitis B virus (HBV)** infection is a major risk factor for **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)**, a common primary liver cancer, but not for hepatic angiosarcoma.
- The patient's clinical picture of a "high-grade malignant vascular neoplasm" is less typical for HCC, which originates from hepatocytes, not vascular endothelial cells.
*Obesity*
- Obesity is a risk factor for **non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)**, which can progress to **non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)**, cirrhosis, and **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)** [2].
- However, obesity is not directly linked to the development of primary hepatic vascular neoplasms like angiosarcoma.
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree US Medical PG Question 2: During a surgical procedure to repair an abdominal aortic aneurysm, the surgeon must be careful to avoid injury to which of the following arterial structures that originates near the level of the renal vessels?
- A. Left renal artery (Correct Answer)
- B. Celiac trunk
- C. Right renal artery
- D. Superior mesenteric artery
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree Explanation: ***Left renal artery***
- The **left renal artery** arises from the aorta usually just below the superior mesenteric artery, making it susceptible to injury during an **abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) repair** if the aneurysm extends proximally.
- Its proximity to the typical location of AAA, often near or involving the **infrarenal aorta**, necessitates careful identification and protection during clamping or graft placement.
*Celiac trunk*
- The **celiac trunk** originates higher up from the aorta, typically at the level of **T12-L1 vertebrae**, well above the common infrarenal AAA repair site.
- While important, it is generally less directly threatened during a typical infrarenal AAA repair compared to arteries immediately adjacent to or within the aneurysm sac.
*Right renal artery*
- The **right renal artery** also originates from the aorta near the level of the renal veins, but it is typically located more posteriorly and usually passes behind the inferior vena cava.
- Although it can be at risk, the left renal artery's course is often more anterior and directly in the field of dissection for the **aortic neck** during AAA repair.
*Superior mesenteric artery*
- The **superior mesenteric artery (SMA)** originates from the aorta proximal to the renal arteries, typically around the L1 vertebral level.
- While crucial, its origin is usually cephalad to the infrarenal aneurysm neck, making it generally less prone to direct injury during infrarenal AAA repair, though flow must be monitored.
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree US Medical PG Question 3: A 65-year-old obese female presents to the emergency room complaining of severe abdominal pain. She reports pain localized to the epigastrium that radiates to the right scapula. The pain occurred suddenly after a fast food meal with her grandchildren. Her temperature is 100.9°F (38.2°C), blood pressure is 140/85 mmHg, pulse is 108/min, and respirations are 20/min. On examination, she demonstrates tenderness to palpation in the epigastrium. She experiences inspiratory arrest during deep palpation of the right upper quadrant but this exam finding is not present on the left upper quadrant. A blockage at which of the following locations is most likely causing this patient’s symptoms?
- A. Common hepatic duct
- B. Ampulla of Vater
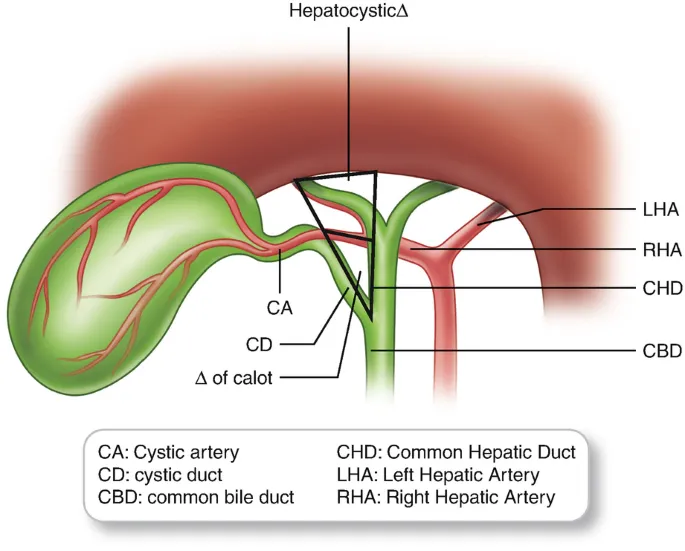
- C. Cystic duct (Correct Answer)
- D. Pancreatic duct of Wirsung
- E. Common bile duct
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree Explanation: ***Cystic duct***
- This patient presents with **fever**, **right upper quadrant pain with inspiratory arrest (Murphy's sign)**, and a history of fatty meal ingestion, all classic signs of **acute cholecystitis** due to a gallstone obstructing the cystic duct.
- Obstruction of the cystic duct leads to bile stasis, inflammation, and potential infection within the gallbladder, causing the characteristic symptoms.
*Common hepatic duct*
- Obstruction of the **common hepatic duct** would typically cause **jaundice**, as it would block bile flow from both the left and right hepatic ducts, leading to systemic bilirubin accumulation.
- While it can cause right upper quadrant pain, the presence of Murphy's sign points more specifically to gallbladder inflammation.
*Ampulla of Vater*
- Obstruction at the **Ampulla of Vater** would lead to both **obstructive jaundice** and **pancreatitis** (due to blockage of both bile and pancreatic ducts), which are not fully reflected in this patient's presentation.
- The patient's symptoms are more localized to the gallbladder rather than a diffuse obstruction of bile flow.
*Pancreatic duct of Wirsung*
- Obstruction of the **pancreatic duct of Wirsung** typically causes **acute pancreatitis**, characterized by severe epigastric pain often radiating to the back, elevated lipase and amylase, and potentially nausea/vomiting.
- While the patient has epigastric pain, the radiation to the right scapula and positive Murphy's sign are more indicative of biliary pathology.
*Common bile duct*
- Obstruction of the **common bile duct** (choledocholithiasis) would cause **jaundice** due to the blockage of bile flow from the liver to the small intestine.
- Although it can cause right upper quadrant pain and fever (if cholangitis develops), the prominent **Murphy's sign** makes acute cholecystitis from cystic duct obstruction a more direct diagnosis.
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree US Medical PG Question 4: A 48-year-old woman with a history of obesity presents with acute onset of diffuse epigastric pain that began a few hours ago and then localized to the right upper quadrant. Further questioning reveals that the pain has been exacerbated by eating but has otherwise been unchanged in nature. Physical exam reveals severe right upper quadrant pain that is accompanied by arrest of respiration with deep palpation of the right upper quadrant. Which of the following symptoms is associated with the most likely etiology of this patient's presentation?
- A. Crunching sound upon heart auscultation
- B. Pain with passive right leg raising
- C. Diffuse substernal pain
- D. Pain radiating to the right shoulder (Correct Answer)
- E. Hematemesis
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree Explanation: ***Pain radiating to the right shoulder***
- The patient's presentation with acute epigastric pain localizing to the **right upper quadrant**, exacerbation by eating, and a positive **Murphy's sign** (arrest of respiration with deep palpation of the RUQ) is highly suggestive of **acute cholecystitis**.
- **Referred pain** to the right shoulder or scapula is a classic symptom of cholecystitis due to irritation of the **diaphragm** and shared C3-C5 dermatomes with the phrenic nerve.
*Crunching sound upon heart auscultation*
- A crunching sound synchronous with the heartbeat (Hamman's sign) is indicative of **pneumomediastinum**, a condition unrelated to the patient's abdominal pain.
- This symptom suggests air in the mediastinum, typically due to esophageal rupture or severe asthma, not gallbladder inflammation.
*Pain with passive right leg raising*
- Pain with passive right leg raising (**Psoas sign**) is associated with irritation of the **psoas muscle**, often seen in conditions like **appendicitis** or retroperitoneal abscess.
- This finding is not characteristic of acute cholecystitis, which primarily affects the right upper quadrant.
*Diffuse substernal pain*
- Diffuse substernal pain is a hallmark symptom of **cardiac ischemia** or **gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)**.
- While it can sometimes be confused with epigastric pain, the localization to the RUQ and positive Murphy's sign differentiate the patient's condition from these causes.
*Hematemesis*
- **Hematemesis**, or vomiting blood, suggests **upper gastrointestinal bleeding** from conditions like peptic ulcers, esophageal varices, or Mallory-Weiss tears.
- This symptom is unrelated to acute cholecystitis, which involves inflammation of the gallbladder and not direct bleeding into the GI tract.
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree US Medical PG Question 5: A 26-year-old medical student who is preparing for Step 1 exams is woken up by her friend for breakfast. She realizes that she must have fallen asleep at her desk while attempting to study through the night. While walking with her friend to breakfast, she realizes that she has not eaten since breakfast the previous day. Using this as motivation to review some biochemistry, she pauses to consider what organs are responsible for allowing her to continue thinking clearly in this physiologic state. Which of the following sets of organs are associated with the major source of energy currently facilitating her cognition?
- A. Muscle only
- B. Liver and kidney (Correct Answer)
- C. Liver and muscle
- D. Liver, muscle, and kidney
- E. Liver only
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree Explanation: ***Liver and kidney***
- After an overnight fast (~16-24 hours without food), the **liver** is the **primary organ** responsible for maintaining blood glucose levels through **glycogenolysis** (initially) and **gluconeogenesis** (predominantly at this stage).
- The **kidney** also contributes to **gluconeogenesis** even during an overnight fast, providing approximately **10-15% of total glucose production**. While this contribution is relatively minor compared to the liver, it becomes increasingly important during more prolonged fasting states (>48-72 hours), where it can account for up to 40% of glucose production.
- Since the brain relies almost exclusively on glucose at this stage of fasting (ketone bodies are not yet a major fuel source), both organs that produce glucose for systemic use are correctly identified here.
*Muscle only*
- Muscle glycogen can only be used by the **muscle cells themselves** due to the absence of **glucose-6-phosphatase**, so muscle cannot release free glucose into the bloodstream for use by the brain.
- While muscle does provide amino acids (particularly alanine and glutamine) for gluconeogenesis in the liver and kidney, it does not directly supply glucose to support brain function.
*Liver and muscle*
- As explained above, muscle cannot directly supply glucose to the bloodstream to support brain function due to the lack of **glucose-6-phosphatase**.
- The liver is a major contributor, but muscle is not a direct source of blood glucose.
*Liver, muscle, and kidney*
- This option incorrectly includes muscle as a direct source of glucose for the brain. While liver and kidney both perform gluconeogenesis and release glucose into the bloodstream, muscle lacks this capability.
*Liver only*
- While the liver is indeed the **dominant source** of glucose during an overnight fast (contributing ~85-90% of gluconeogenesis), the **kidney also actively participates** in glucose production, contributing ~10-15% at this stage.
- Since the question asks which organs are "responsible" for maintaining cognition, and both organs contribute to systemic glucose production (even if disproportionately), "liver only" is incomplete.
- The kidney's contribution, though relatively minor during overnight fasting, becomes more substantial during prolonged fasting states.
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree US Medical PG Question 6: A 44-year-old woman presents to the emergency department with severe, fluctuating right upper quadrant abdominal pain. The pain was initially a 4/10 but has increased recently to a 6/10 prompting her to come in. The patient has a past medical history of type II diabetes mellitus, depression, anxiety, and irritable bowel syndrome. Her current medications include metformin, glyburide, escitalopram and psyllium husks. On exam you note an obese woman with pain upon palpation of the right upper quadrant. The patient's vital signs are a pulse of 95/min, blood pressure of 135/90 mmHg, respirations of 15/min and 98% saturation on room air. Initial labs are sent off and the results are below:
Na+: 140 mEq/L
K+: 4.0 mEq/L
Cl-: 100 mEq/L
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
AST: 100 U/L
ALT: 110 U/L
Amylase: 30 U/L
Alkaline phosphatase: 125 U/L
Bilirubin
Total: 2.5 mg/dL
Direct: 1.8 mg/dL
The patient is sent for a right upper quadrant ultrasound demonstrating an absence of stones, no pericholecystic fluid, a normal gallbladder contour and no abnormalities noted in the common bile duct. MRCP with secretin infusion is performed demonstrating patent biliary and pancreatic ductal systems. Her lab values and clinical presentation remain unchanged 24 hours later. Which of the following is the best next step in management?
- A. ERCP with manometry (Correct Answer)
- B. Laparoscopy
- C. Elective cholecystectomy
- D. Analgesics and await resolution of symptoms
- E. MRI of the abdomen
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree Explanation: ***ERCP with manometry***
- The patient's presentation with **biliary-type pain**, elevated liver enzymes (**AST, ALT, alkaline phosphatase**), and **conjugated hyperbilirubinemia** despite negative ultrasound and MRCP for gallstones or structural ductal abnormalities strongly suggests a **functional biliary disorder**, such as **sphincter of Oddi dysfunction (SOD)**.
- **ERCP with manometry** is the gold standard for diagnosing SOD by directly measuring the pressure within the sphincter of Oddi; this procedure can also offer therapeutic intervention via sphincterotomy.
*Laparoscopy*
- While laparoscopy can be used to perform a cholecystectomy for **acalculous cholecystitis** or **biliary dyskinesia**, these conditions are less likely given the **normal gallbladder contour** and lack of pericholecystic fluid, and would not directly address the possibility of sphincter of Oddi dysfunction.
- It is an invasive surgical procedure that would not provide diagnostic information about the patency or function of the biliary tree in the same way manometry does.
*Elective cholecystectomy*
- An **elective cholecystectomy** is not indicated as initial imaging (ultrasound, MRCP) has ruled out gallstones or significant structural gallbladder abnormalities, and the diagnosis of **biliary dyskinesia** has not been confirmed.
- Performing a cholecystectomy without a clear indication could lead to persistent symptoms if the underlying issue is **sphincter of Oddi dysfunction**.
*Analgesics and await resolution of symptoms*
- This approach is inappropriate given the **persistent pain**, **elevated liver enzymes**, and **hyperbilirubinemia**, which suggest an ongoing pathological process that requires diagnosis and definitive treatment.
- Simply masking the symptoms with analgesics would delay diagnosis and potentially lead to further complications.
*MRI of the abdomen*
- An **MRI of the abdomen** has already been performed in the form of an **MRCP** (Magnetic Resonance Cholangiopancreatography), which specifically visualizes the biliary and pancreatic ducts.
- Since the MRCP with secretin infusion was negative for structural abnormalities, a repeat or general MRI of the abdomen would likely not yield additional diagnostic information regarding the cause of the biliary pain and elevated liver enzymes.
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree US Medical PG Question 7: A 35-year-old female presents to her primary care physician complaining of right upper quadrant pain over the last 6 months. Pain is worst after eating and feels like intermittent squeezing. She also admits to lighter colored stools and a feeling of itchiness on her skin. Physical exam demonstrates a positive Murphy's sign. The vitamin level least likely to be affected by this condition is associated with which of the following deficiency syndromes?
- A. Rickets and osteomalacia
- B. Hemolytic anemia
- C. Night blindness
- D. Increased prothrombin time and easy bleeding
- E. Scurvy (Correct Answer)
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree Explanation: ***Scurvy***
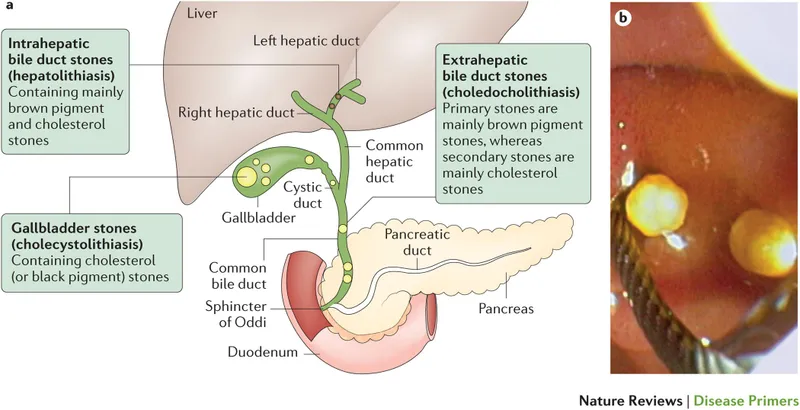
- This condition is likely **cholestasis** due to common bile duct obstruction, given the RUQ pain after eating, light-colored stools, itchiness, and **positive Murphy's sign**.
- Cholestasis impairs the absorption of **fat-soluble vitamins** (A, D, E, K), but not **water-soluble vitamins** like vitamin C, which prevents scurvy.
*Rickets and osteomalacia*
- These conditions are caused by **vitamin D deficiency**, which is a **fat-soluble vitamin**.
- Impaired fat absorption in cholestasis would significantly impact vitamin D levels, leading to increased risk of rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults.
*Hemolytic anemia*
- This can be caused by **vitamin E deficiency**, a **fat-soluble vitamin**.
- Cholestasis impairs vitamin E absorption, which can lead to increased red blood cell fragility and hemolytic anemia.
*Night blindness*
- This is a classic symptom of **vitamin A deficiency**, which is a **fat-soluble vitamin**.
- Impaired fat absorption in cholestasis would reduce vitamin A uptake, contributing to night blindness.
*Increased prothrombin time and easy bleeding*
- These symptoms are indicative of **vitamin K deficiency**, a **fat-soluble vitamin**.
- Vitamin K is essential for the synthesis of clotting factors, and its absorption is severely hindered in cholestasis, leading to coagulopathies.
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree US Medical PG Question 8: A CT scan of the abdomen reveals a mass in the pancreatic uncinate process. Which of the following structures is most likely to be compressed by this mass?
- A. Common bile duct
- B. Portal vein
- C. Splenic vein
- D. Superior mesenteric vein (Correct Answer)
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree Explanation: ***Superior mesenteric vein***
- The **uncinate process** of the pancreas hooks around the **superior mesenteric vessels**. Therefore, a mass in this region would most directly compress the **superior mesenteric vein (SMV)** and artery (SMA).
- Compression of the SMV can lead to **venous outflow obstruction** from the small intestine, potentially causing **bowel ischemia** or edema.
*Common bile duct*
- The **common bile duct** passes through the **head of the pancreas**, not typically the uncinate process.
- Compression of the common bile duct would more commonly be associated with masses in the **head of the pancreas**, leading to **jaundice**.
*Portal vein*
- The **portal vein** is formed by the union of the **splenic vein** and the **superior mesenteric vein**, generally posterior to the neck of the pancreas.
- While pancreatic masses can affect the portal vein, a mass specifically in the uncinate process would more directly impinge on the SMV before significantly affecting the main portal vein, which is superior and posterior to the uncinate process.
*Splenic vein*
- The **splenic vein** runs along the **posterior aspect of the body and tail of the pancreas**.
- A mass in the uncinate process, located at the inferior margin of the head, is relatively distant from the splenic vein.
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree US Medical PG Question 9: A 64-year-old man presents to the outpatient clinic because of abdominal pain. He reports that for the last few months, he has had postprandial pain that is worsened by spicy foods. He states that the pain is often located in the right upper portion of his abdomen and feels like it's traveling to his shoulder blade. These episodes are sporadic and unpredictable. He denies any fevers. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Abdominal ultrasound is shown. Which of the following is the best treatment for this condition?
- A. Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)
- B. Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)
- C. Cholecystectomy (Correct Answer)
- D. Ursodeoxycholic acid
- E. Ketorolac
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree Explanation: ***Cholecystectomy***
- The patient's symptoms of **postprandial right upper quadrant pain** radiating to the **shoulder blade**, exacerbated by spicy foods, strongly suggest **biliary colic** due to **cholelithiasis**.
- The ultrasound findings of **gallstones in the gallbladder neck** with **posterior acoustic shadowing** confirm the diagnosis, making surgical removal of the gallbladder (cholecystectomy) the definitive treatment.
*Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)*
- ERCP is primarily an **invasive therapeutic procedure** used to remove **choledocholithiasis** (stones in the common bile duct) or to stent strictures, not for symptomatic cholelithiasis confined to the gallbladder.
- It carries risks such as **pancreatitis** and perforation, making it inappropriate as a first-line treatment for uncomplicated cholelithiasis.
*Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP)*
- MRCP is a **non-invasive diagnostic imaging technique** primarily used to visualize the biliary and pancreatic ducts to detect stones or strictures, particularly in the common bile duct.
- While useful for diagnosis, it is **not a treatment** and is typically reserved for cases where common bile duct stones are suspected or when ERCP is contraindicated.
*Ursodeoxycholic acid*
- Ursodeoxycholic acid is a **bile acid** sometimes used to **dissolve small cholesterol gallstones** in patients who are not surgical candidates or for prevention in certain high-risk groups.
- It is **not effective for large or calcified stones**, and treatment can take months to years with a high recurrence rate, making it less suitable for symptomatic cholelithiasis requiring definitive treatment.
*Ketorolac*
- Ketorolac is a **non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID)** that can provide **symptomatic relief** for acute pain associated with biliary colic.
- However, it **does not treat the underlying cause** (gallstones) and is therefore not a definitive treatment for symptomatic cholelithiasis.
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree US Medical PG Question 10: A 51-year-old homeless man presents to the emergency department with severe abdominal pain and cramping for the past 3 hours. He endorses radiation to his back. He adds that he vomited multiple times. He admits having been hospitalized repeatedly for alcohol intoxication and abdominal pain. His temperature is 103.8° F (39.8° C), respiratory rate is 15/min, pulse is 107/min, and blood pressure is 100/80 mm Hg. He refuses a physical examination due to severe pain. Blood work reveals the following:
Serum:
Albumin: 3.2 gm/dL
Alkaline phosphatase: 150 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase: 76 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase: 155 U/L
Gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase: 202 U/L
Lipase: 800 U/L
What is the most likely diagnosis of this patient?
- A. Duodenal peptic ulcer
- B. Choledocholithiasis
- C. Pancreatitis (Correct Answer)
- D. Cholecystitis
- E. Gallbladder cancer
Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree Explanation: ***Pancreatitis***
- The patient's history of **repeated alcohol intoxication** and abdominal pain, combined with **severe abdominal pain radiating to the back**, vomiting, and significantly elevated **lipase (800 U/L)**, are highly indicative of **acute pancreatitis**.
- The elevated **liver enzymes (ALT, AST, GGT)** and **alkaline phosphatase** can be associated with cholestasis or liver involvement often seen in alcohol-induced pancreatitis or can be elevated due to a gallstone lodged in the common bile duct, which is also a common cause of pancreatitis.
*Duodenal peptic ulcer*
- While duodenal ulcers cause severe abdominal pain, they typically present with **epigastric pain** that may be relieved by food, and often cause **melena or hematemesis** if bleeding.
- The extremely high **lipase level** and pain radiating to the back are not characteristic of an uncomplicated duodenal ulcer.
*Choledocholithiasis*
- **Choledocholithiasis** (gallstones in the common bile duct) can cause severe right upper quadrant or epigastric pain and elevated liver enzymes, but it doesn't typically present with an isolated, dramatically high **lipase** level without concomitant pancreatitis.
- The main symptom is **biliary colic**, often post-prandial, and usually involves jaundice or cholangitis if infected.
*Cholecystitis*
- **Cholecystitis** presents with **right upper quadrant pain**, often radiating to the shoulder, associated with fever and nausea, and is usually triggered by fatty meals.
- Although there might be some elevation in liver enzymes and amylase/lipase, the **markedly elevated lipase** and pain radiating to the back are more suggestive of pancreatitis.
*Gallbladder cancer*
- **Gallbladder cancer** typically presents with more insidious symptoms, such as chronic right upper quadrant pain, weight loss, jaundice, and anorexia.
- It would not usually present with an acute episode of **severe abdominal pain and drastically high lipase** in this manner.
More Liver, gallbladder and biliary tree US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.