Kidneys and suprarenal glands US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Kidneys and suprarenal glands. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Kidneys and suprarenal glands US Medical PG Question 1: A 19-year-old man presents to the emergency department after a motor vehicle accident. The patient reports left shoulder pain that worsens with deep inspiration. Medical history is significant for a recent diagnosis of infectious mononucleosis. His temperature is 99°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 80/55 mmHg, pulse is 115/min, and respiratory rate is 22/min. On physical exam, there is abdominal guarding, abdominal tenderness in the left upper quadrant, and rebound tenderness. The patient’s mucous membranes are dry and skin turgor is reduced. Which of the following most likely represents the acute changes in renal plasma flow (RPF) and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in this patient?
- A. No change in RPF and decreased GFR
- B. Decreased RPF and decreased GFR (Correct Answer)
- C. No change in RPF and increased GFR
- D. Decreased RPF and no change in GFR
- E. No change in RPF and GFR
Kidneys and suprarenal glands Explanation: ***Decreased RPF and decreased GFR***
- This patient presents with signs of **hypovolemic shock** (hypotension with BP 80/55 mmHg, tachycardia, dry mucous membranes, reduced skin turgor) likely due to **splenic rupture** from the motor vehicle accident, exacerbated by splenomegaly from **infectious mononucleosis**.
- With a blood pressure of 80/55 mmHg (MAP ~73 mmHg), the patient is at or below the **lower limit of renal autoregulation** (~80 mmHg MAP).
- In acute hypovolemic shock, **renal blood flow and RPF decrease** due to systemic hypotension and **sympathetic vasoconstriction**.
- Although **angiotensin II-mediated efferent arteriolar constriction** attempts to preserve GFR by maintaining glomerular capillary pressure, this compensation is **insufficient** when MAP falls below the autoregulatory range.
- Result: **Both RPF and GFR decrease**, though GFR may be relatively preserved compared to the magnitude of RPF decrease initially.
*No change in RPF and decreased GFR*
- This scenario would suggest decreased filtration despite normal renal perfusion, implying a primary glomerular barrier problem.
- In hypovolemic shock, **RPF is always decreased** due to reduced systemic blood flow and renal vasoconstriction.
*Decreased RPF and no change in GFR*
- While renal autoregulation attempts to maintain stable GFR despite changes in blood pressure, this mechanism works only within the **autoregulatory range (MAP 80-180 mmHg)**.
- At BP 80/55 mmHg, autoregulation is overwhelmed, and **GFR will decrease** along with RPF.
*No change in RPF and increased GFR*
- An **increased GFR** is inconsistent with hypovolemic shock and would require either increased RPF or enhanced glomerular filtration pressure.
- Maintaining normal RPF during severe hypotension is physiologically implausible.
*No change in RPF and GFR*
- This suggests normal renal function despite **severe hypotension and hypovolemia**, which contradicts basic renal physiology.
- The body's compensatory mechanisms cannot fully maintain both RPF and GFR when systemic blood pressure falls below the autoregulatory threshold.
Kidneys and suprarenal glands US Medical PG Question 2: A 20-year-old man is brought to the emergency room for evaluation of a back injury sustained while at work. A CT scan of the lumbar spine shows an incidental 2-cm mass adjacent to the inferior vena cava. Histologic examination of a biopsy specimen of the mass shows clusters of chromaffin cells. This mass is most likely to secrete which of the following substances?
- A. Aldosterone
- B. Dehydroepiandrosterone
- C. Norepinephrine (Correct Answer)
- D. Cortisol
- E. Estrogen
Kidneys and suprarenal glands Explanation: **Norepinephrine**
- The description of a mass with **clusters of chromaffin cells** is characteristic of a **pheochromocytoma**, a tumor typically arising from the **adrenal medulla**.
- **Pheochromocytomas** are known to secrete catecholamines, primarily **norepinephrine** and epinephrine.
*Aldosterone*
- **Aldosterone** is secreted by the **zona glomerulosa** of the **adrenal cortex** and is involved in blood pressure regulation.
- Tumors secreting aldosterone are usually **aldosteronomas** (Conn's syndrome) and do not arise from chromaffin cells.
*Dehydroepiandrosterone*
- **Dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA)** is an **adrenal androgen** secreted by the **zona reticularis** of the adrenal cortex.
- Its secretion is associated with cortical tumors or hyperplasia, not chromaffin cell tumors.
*Cortisol*
- **Cortisol** is a glucocorticoid produced by the **zona fasciculata** of the **adrenal cortex**.
- Elevated cortisol levels are usually due to **Cushing's syndrome**, often caused by adrenal adenomas or hyperplasia, not chromaffin cell tumors.
*Estrogen*
- While small amounts of **estrogen** can be produced by the adrenal glands, the primary sites of estrogen synthesis are the **ovaries** and **placenta**.
- A tumor composed of **chromaffin cells** is not typically associated with significant estrogen secretion.
Kidneys and suprarenal glands US Medical PG Question 3: A 45-year-old female is undergoing renal transplantation for management of chronic renal failure secondary to glomerulonephritis. The transplant surgeon placed the donor kidney in the recipient and anastomosed the donor renal artery to the recipient's external iliac artery as well as the donor ureter to the recipient's bladder. After removing the clamps on the external iliac artery, the recipient's blood is allowed to perfuse the transplanted kidney. Within 3 minutes, the surgeon notes that the kidney does not appear to be sufficiently perfused. Upon further investigation, an inflammatory reaction is noted that led to clotting off of the donor renal artery, preventing blood flow to the transplanted organ. Which of the following best describes the pathophysiology of this complication?
- A. Type III hypersensitivity reaction
- B. Type IV hypersensitivity reaction
- C. Graft-versus-host disease
- D. Type I hypersensitivity reaction
- E. Hyperacute rejection (Correct Answer)
Kidneys and suprarenal glands Explanation: ***Hyperacute rejection***
- This scenario describes **hyperacute rejection**, a **Type II hypersensitivity reaction** that occurs minutes to hours after transplantation due to pre-existing host antibodies (e.g., ABO or HLA antibodies) recognizing donor antigens on endothelial cells.
- The binding of these antibodies activates the complement system, leading to rapid **antibody-mediated cytotoxicity**, **thrombosis** of the graft vasculature, and ischemic necrosis.
- This represents the pathophysiologic mechanism causing the immediate graft failure observed.
*Type III hypersensitivity reaction*
- This reaction involves the formation of **immune complexes** (antigen-antibody complexes) that deposit in tissues, leading to inflammation.
- It typically manifests hours to days after exposure and is not characterized by immediate graft thrombosis.
*Type IV hypersensitivity reaction*
- This is a **delayed-type hypersensitivity** mediated by T lymphocytes and macrophages, rather than antibodies.
- It usually occurs days to weeks after transplantation (e.g., in acute cellular rejection) and does not cause rapid vascular occlusion.
*Graft-versus-host disease*
- **Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)** occurs when immunocompetent T cells from the donor (graft) recognize recipient (host) tissues as foreign and attack them.
- This complication is most common in **hematopoietic stem cell transplantation** and is unlikely to manifest minutes after solid organ transplantation.
*Type I hypersensitivity reaction*
- This is an immediate, **IgE-mediated allergic reaction** involving mast cell degranulation and release of inflammatory mediators.
- While rapid, it typically involves systemic allergic symptoms (e.g., anaphylaxis) or localized allergic responses, not specifically graft thrombosis in this context.
Kidneys and suprarenal glands US Medical PG Question 4: An 11-year-old girl is brought to the office by her mother due to complaint of intermittent and severe periumbilical pain for 1 day. She does not have any significant past medical history. She provides a history of a recent school trip to the suburbs. On physical examination, there is a mild tenderness around the umbilicus without any distension or discharge. There is no rebound tenderness. Bowel sounds are normal. An abdominal imaging shows enlarged mesenteric lymph nodes, and she is diagnosed with mesenteric lymphadenitis. However, incidentally, a mass of tissue was seen joining the inferior pole of both kidneys as shown in the image. Which of the following best describes this renal anomaly?
- A. Fused kidneys ascend beyond superior mesenteric artery.
- B. Rapid progression to acute renal failure
- C. Kidneys are usually non-functional.
- D. Increased risk of developing renal vein thrombosis
- E. Association with ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO) (Correct Answer)
Kidneys and suprarenal glands Explanation: ***Association with ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO)***
- **Horseshoe kidney** is characterized by the fusion of the lower poles (most common) or upper poles of the kidneys, forming a U-shape. This anomaly is associated with an increased incidence of **ureteropelvic junction obstruction (UPJO)** due to the abnormal course of the ureters over the isthmus.
- The abnormal ascent of the fused kidneys can also lead to an increased incidence of other anomalies such as **vesicoureteral reflux**, **renal calculi**, and recurrent urinary tract infections.
*Fused kidneys ascend beyond superior mesenteric artery.*
- The **horseshoe kidney** typically **fails to ascend** completely during development because its isthmus (the fused part) can get trapped under the **inferior mesenteric artery**.
- Therefore, fused kidneys in horseshoe kidney are often found in a **lower position** than normal, not ascended beyond the superior mesenteric artery.
*Rapid progression to acute renal failure*
- While horseshoe kidney can be associated with an increased risk of complications (like UPJO, stones, infections), it does not inherently lead to **rapid progression to acute renal failure**.
- Many individuals with a horseshoe kidney have **normal renal function** without significant clinical manifestations.
*Kidneys are usually non-functional.*
- The presence of a horseshoe kidney **does not typically mean the kidneys are non-functional**.
- In most cases, both renal units of a horseshoe kidney are **functional**, although they may be at increased risk for complications that could impact function over time.
*Increased risk of developing renal vein thrombosis*
- There is **no established increased risk** of developing **renal vein thrombosis** specifically associated with horseshoe kidney.
- The primary vascular anomalies associated with horseshoe kidney relate to the arterial supply and variations in the number and origin of renal arteries, not typically venous thrombosis.
Kidneys and suprarenal glands US Medical PG Question 5: A 37-year-old woman presents to the Emergency Department after 8 hours of left sided flank pain that radiates to her groin and pelvic pain while urinating. Her medical history is relevant for multiple episodes of urinary tract infections, some requiring hospitalization, and intravenous antibiotics. In the hospital, her blood pressure is 125/83 mm Hg, pulse of 88/min, a respiratory rate of 28/min, and a body temperature of 36.5°C (97.7°F). On physical examination, she has left costovertebral tenderness and lower abdominal pain. Laboratory studies include a negative pregnancy test, mild azotemia, and a urinary dipstick that is positive for blood. Which of the following initial tests would be most useful in the diagnosis of this case?
- A. Urine osmolality
- B. Fractional excretion of sodium (FeNa+)
- C. Renal ultrasonography (Correct Answer)
- D. Contrast abdominal computed tomography
- E. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN): serum creatinine (SCr) ratio
Kidneys and suprarenal glands Explanation: ***Renal ultrasonography***
- This is the most appropriate initial imaging test to evaluate for **kidney stones** (given the flank pain radiating to groin and hematuria) and **hydronephrosis** (which can indicate obstruction) and assess for signs of **pyelonephritis** (given the history of recurrent UTIs and CVA tenderness).
- It is **non-invasive**, readily available, and avoids radiation exposure, making it suitable as a first-line diagnostic tool in this setting.
*Urine osmolality*
- This test primarily assesses the kidney's ability to **concentrate urine**, which is more relevant for evaluating fluid balance, diabetes insipidus, or other renal tubular disorders.
- It would not directly diagnose the cause of acute flank pain or urinary tract obstruction.
*Fractional excretion of sodium (FeNa+)*
- FeNa+ is used to differentiate between **prerenal azotemia** and **acute tubular necrosis**, indicating the kidney's response to hypoperfusion.
- While the patient has mild azotemia, FeNa+ would not identify the underlying cause of the flank pain, hematuria, or potential obstruction.
*Contrast abdominal computed tomography*
- While highly sensitive for diagnosing kidney stones and other renal pathologies, **contrast CT** exposes the patient to **ionizing radiation** and risks associated with contrast agents (e.g., contrast-induced nephropathy), especially with pre-existing azotemia.
- It is often reserved for cases where ultrasound is inconclusive or more detailed anatomical information is needed.
*Blood urea nitrogen (BUN): serum creatinine (SCr) ratio*
- This ratio is primarily used to differentiate between **prerenal** causes of acute kidney injury (high ratio, e.g., >20:1) and **intrinsic renal** causes (lower ratio, e.g., <15:1).
- While it can provide insight into the etiology of azotemia, it does not directly identify the cause of the patient's acute flank pain or potential urinary tract obstruction.
Kidneys and suprarenal glands US Medical PG Question 6: A 2-day-old infant dies of severe respiratory distress following a gestation complicated by persistent oligohydramnios. Upon examination at autopsy, the left kidney is noted to selectively lack cortical and medullary collecting ducts. From which of the following embryological structures do the cortical and medullary collecting ducts arise?
- A. Mesonephros
- B. Pronephros
- C. Ureteric bud (Correct Answer)
- D. Paramesonephric duct
- E. Metanephric mesenchyme
Kidneys and suprarenal glands Explanation: ***Ureteric bud***
- The **ureteric bud** is an outgrowth of the mesonephric duct that gives rise to the **collecting ducts**, major and minor calyces, renal pelvis, and ureter.
- Absence or anomaly of the ureteric bud's development leads to conditions like **renal agenesis** or **renal hypoplasia**, which can cause oligohydramnios and Potter sequence due to insufficient urine production.
*Mesonephros*
- The **mesonephros** is a temporary kidney that functions early in development but largely degenerates.
- Its tubules, in males, contribute to the **epididymis**, **vas deferens**, and **ejaculatory duct**.
*Pronephros*
- The **pronephros** is the first and most primitive kidney structure, forming early in embryonic development.
- It rapidly **degenerates** and has no functional role in human development beyond inducing mesonephros development.
*Paramesonephric duct*
- The **paramesonephric (Müllerian) duct** is critical for the development of the female reproductive tract.
- It forms the **fallopian tubes**, **uterus**, and **upper vagina**.
*Metanephric mesenchyme*
- The **metanephric mesenchyme** (or metanephric blastema) differentiates into the structures involved in urine filtration and initial processing.
- This includes the **glomeruli**, Bowman's capsule, proximal convoluted tubules, loops of Henle, and distal convoluted tubules.
Kidneys and suprarenal glands US Medical PG Question 7: A 42-year-old man comes to the physician for a health maintenance examination. He has had generalized fatigue and muscle aches since his previous visit 6 months ago. He has hypertension and gastroesophageal reflux disease. Current medications include amlodipine and omeprazole. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.1°F), pulse is 88/min and blood pressure is 156/102 mm Hg. Physical examination shows no abnormalities. Serum studies show:
Na+ 143 mEq/L
K+ 2.3 mEq/L
Cl- 100 mEq/L
HCO3- 31 mEq/L
Urea nitrogen 14 mg/dL
Creatinine 1 mg/dL
His blood pressure medication is discontinued. One week later his plasma aldosterone concentration is 35 ng/dL (N=3.6 - 24.0 ng/dL) and plasma renin activity is 0.4 ng/mL/h (N=0.3 to 4.2 ng/mL/h). An oral sodium loading test over 3 days fails to reduce aldosterone. A contrast-enhanced CT scan of the abdomen and pelvis shows a 3-cm, homogenous, right-sided adrenal mass with rapid contrast washout. He is counseled about his treatment options and chooses to pursue surgery. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Right adrenalectomy
- B. Fludrocortisone suppression test
- C. Adrenal vein sampling (Correct Answer)
- D. Spironolactone therapy
- E. Bilateral adrenalectomy
Kidneys and suprarenal glands Explanation: ***Adrenal vein sampling***
- This patient presents with **hypokalemia**, **hypertension**, elevated **plasma aldosterone concentration** with suppressed **plasma renin activity**, and unsuppressed aldosterone after a sodium loading test, all highly suggestive of **primary hyperaldosteronism**.
- Given the **3-cm adrenal mass** on the right side and the patient's choice for surgery, **adrenal vein sampling (AVS)** is crucial to confirm that the right adrenal gland is the sole source of excess aldosterone production, ensuring that surgery will be curative.
*Right adrenalectomy*
- Although surgery on the right adrenal gland is the desired outcome, performing a **right adrenalectomy** without prior adrenal vein sampling is premature and potentially harmful.
- AVS is essential to differentiate between a unilateral aldosterone-producing adenoma and bilateral adrenal hyperplasia, as the latter would not be cured by unilateral surgery.
*Fludrocortisone suppression test*
- The **fludrocortisone suppression test** is used to confirm the diagnosis of primary hyperaldosteronism, but the diagnosis in this patient is already strongly supported by the elevated aldosterone-to-renin ratio and lack of suppression with the oral sodium loading test.
- This test would not help in localizing the source of aldosterone excess.
*Spironolactone therapy*
- **Spironolactone** is an **aldosterone antagonist** that can be used to manage primary hyperaldosteronism, especially in cases of bilateral adrenal hyperplasia or if surgery is contraindicated or declined.
- However, given the patient's desire for surgery and the presence of a unilateral mass, the goal is curative resection, which requires further localization with AVS.
*Bilateral adrenalectomy*
- **Bilateral adrenalectomy** is generally reserved for rare cases of bilateral adrenal hyperplasia that are unresponsive to medical therapy or when AVS confirms bilateral disease and surgery is absolutely necessary.
- Performing a bilateral adrenalectomy would lead to permanent **adrenal insufficiency**, requiring lifelong corticosteroid replacement, which is a major drawback.
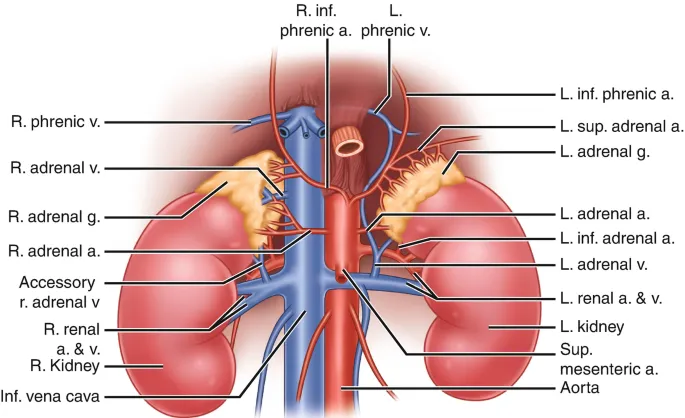
Kidneys and suprarenal glands US Medical PG Question 8: A researcher is investigating the blood supply of the adrenal gland. While performing an autopsy on a patient who died from unrelated causes, he identifies a vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the inferior aspect of the right adrenal gland. Which of the following vessels most likely gave rise to the vessel in question?
- A. Inferior phrenic artery
- B. Abdominal aorta
- C. Renal artery (Correct Answer)
- D. Superior mesenteric artery
- E. Common iliac artery
Kidneys and suprarenal glands Explanation: ***Renal artery***
- The **inferior suprarenal artery**, which supplies the inferior part of the adrenal gland, typically arises from the **renal artery**.
- The adrenal glands receive a rich blood supply from three main arterial sources: superior, middle, and inferior suprarenal arteries.
*Inferior phrenic artery*
- The **superior suprarenal arteries** typically arise from the **inferior phrenic arteries** and supply the superior aspect of the adrenal glands.
- While critical for adrenal blood supply, they do not typically contribute to the inferior aspect directly.
*Abdominal aorta*
- The **middle suprarenal artery** usually arises directly from the **abdominal aorta**.
- This vessel supplies the central part of the adrenal gland, but not primarily the inferior aspect.
*Superior mesenteric artery*
- The **superior mesenteric artery** primarily supplies structures of the midgut (e.g., small intestine, ascending colon) and does not typically give rise to vessels supplying the adrenal glands.
- It is located inferior to the origin of the renal arteries and the adrenal glands.
*Common iliac artery*
- The **common iliac arteries** supply the lower limbs and pelvic organs, originating from the abdominal aorta bifurcation.
- These arteries are located much too far inferior to supply the adrenal glands, which are retroperitoneal structures in the upper abdomen.
Kidneys and suprarenal glands US Medical PG Question 9: A 63-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-month history of difficulty swallowing, low-grade fever, and weight loss. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 30 years. An esophagogastroduodenoscopy shows an esophageal mass just distal to the upper esophageal sphincter. Histological examination confirms the diagnosis of locally invasive squamous cell carcinoma. A surgical resection is planned. Which of the following structures is at greatest risk for injury during this procedure?
- A. Bronchial branch of thoracic aorta
- B. Left gastric artery
- C. Left inferior phrenic artery
- D. Esophageal branch of thoracic aorta
- E. Inferior thyroid artery (Correct Answer)
Kidneys and suprarenal glands Explanation: **Inferior thyroid artery**
- The esophageal mass is located just distal to the **upper esophageal sphincter**, which is in the neck, close to the **thyroid gland**.
- During surgery for an esophageal tumor in this region, the **inferior thyroid artery**, which supplies the thyroid and adjacent structures, is at the greatest risk of injury due to its proximity.
*Bronchial branch of thoracic aorta*
- The **bronchial branches** of the thoracic aorta primarily supply the bronchi and lungs.
- These vessels are located deeper in the thorax, away from the **upper esophageal sphincter** and the initial surgical field for an upper esophageal tumor.
*Left gastric artery*
- The **left gastric artery** supplies the stomach and is a branch of the celiac trunk.
- This artery is located in the **abdomen**, far from the surgical site involving an esophageal mass near the upper esophageal sphincter.
*Left inferior phrenic artery*
- The **left inferior phrenic artery** primarily supplies the diaphragm.
- This vessel originates from the aorta in the **abdominal region**, which is distant from the upper esophageal sphincter.
*Esophageal branch of thoracic aorta*
- **Esophageal branches** directly supply the esophagus; however, the question refers to the **thoracic aorta branches**.
- Tumors near the **upper esophageal sphincter** are usually accessed via a cervical incision, making thoracic branches less likely to be injured compared to arteries located in the neck.
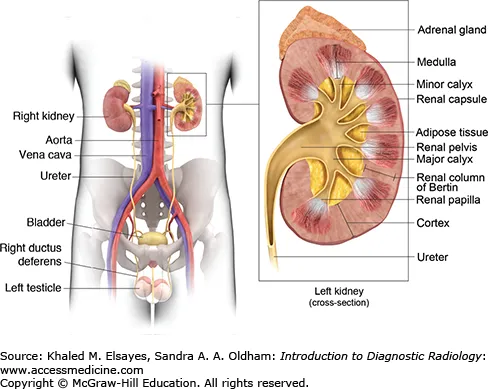
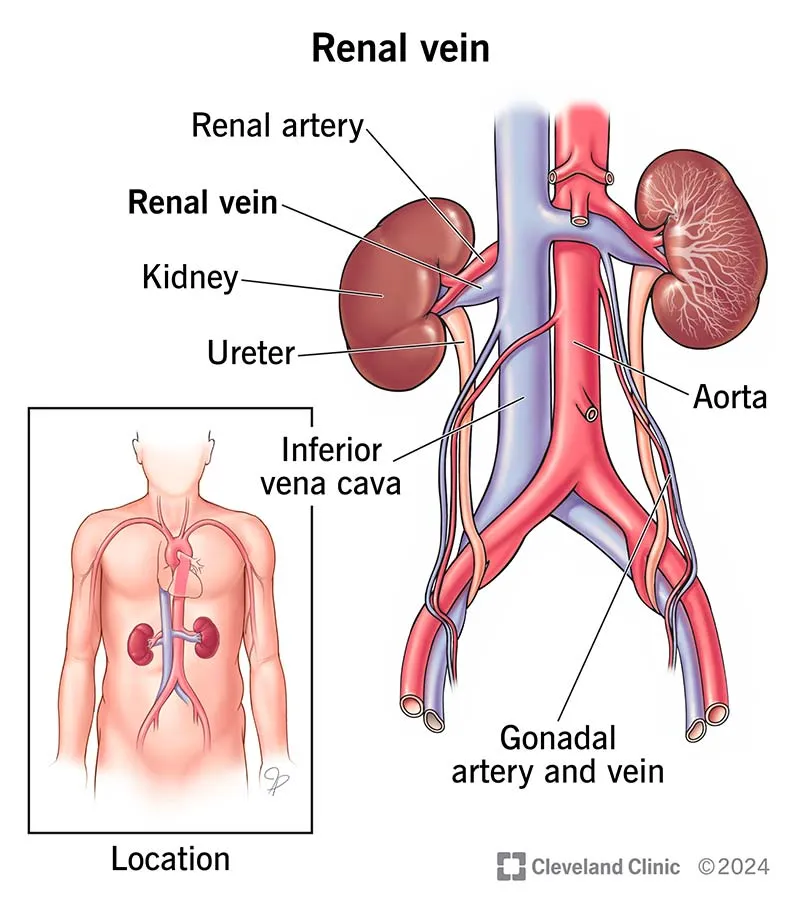
Kidneys and suprarenal glands US Medical PG Question 10: A 22-year-old Caucasian male is stabbed in his left flank, injuring his left kidney. As the surgeon undertakes operative repair, she reviews relevant renal anatomy. All of the following are correct regarding the left kidney EXCEPT?
- A. The left kidney has a longer renal vein than the right kidney
- B. The left kidney underlies the left 12th rib
- C. The left kidney moves vertically during deep breathing
- D. The left kidney has a longer renal artery than the right kidney (Correct Answer)
- E. The left kidney lies between T12 and L3
Kidneys and suprarenal glands Explanation: ***The left kidney has a longer renal artery than the right kidney***
- The **aorta** lies to the left of the midline, so the **right renal artery** must traverse a greater distance to reach the right kidney.
- Therefore, the right renal artery is longer than the left renal artery.
*The left kidney has a longer renal vein than the right kidney*
- The **inferior vena cava (IVC)** is positioned to the right of the midline, requiring the **left renal vein** to cross the aorta to drain.
- This anatomical arrangement makes the left renal vein longer than the right renal vein.
*The left kidney underlies the left 12th rib*
- The kidneys are retroperitoneal organs, and the 12th rib provides significant posterior protection for **both kidneys**.
- The superior pole of the left kidney typically extends to the level of the **11th and 12th ribs**.
*The left kidney moves vertically during deep breathing*
- The kidneys are surrounded by **perirenal fat** and are influenced by the diaphragm's movement.
- During **deep inspiration**, the diaphragm descends, causing both kidneys to move vertically by 2-3 cm.
*The left kidney lies between T12 and L3*
- The kidneys are situated in the retroperitoneum, generally extending from the level of the **T12 vertebra** to the **L3 vertebra**.
- The left kidney is typically positioned slightly higher than the right kidney.
More Kidneys and suprarenal glands US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.