Pulse points and vascular access US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Pulse points and vascular access. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Pulse points and vascular access US Medical PG Question 1: A 47-year-old woman comes to the emergency department after coughing up 2 cups of bright red blood. A CT angiogram of the chest shows active extravasation from the right bronchial artery. A coil embolization is planned to stop the bleeding. During this procedure, a catheter is first inserted into the right femoral artery. Which of the following represents the correct subsequent order of the catheter route?
- A. Thoracic aorta, right superior epigastric artery, right bronchial artery
- B. Thoracic aorta, right bronchial artery (Correct Answer)
- C. Thoracic aorta, left ventricle, left atrium, pulmonary artery, right bronchial artery
- D. Thoracic aorta, brachiocephalic trunk, right subclavian artery, right internal thoracic artery, right bronchial artery
- E. Thoracic aorta, right subclavian artery, right internal thoracic artery, right bronchial artery
Pulse points and vascular access Explanation: ***Thoracic aorta, right bronchial artery***
- The **femoral artery** leads directly into the **aorta**. From the aorta, the catheter can be navigated to the **thoracic aorta**, where the **bronchial arteries** typically originate.
- The **bronchial arteries** usually arise directly from the **descending thoracic aorta** (most commonly T5-T6 vertebral level) to supply the lung parenchyma and airways.
*Thoracic aorta, right superior epigastric artery, right bronchial artery*
- The **superior epigastric artery** is a terminal branch of the **internal thoracic artery**, supplying the anterior abdominal wall, and is not a direct path to the bronchial arteries.
- Navigating from the superior epigastric artery to the main bronchial artery without passing through intermediary large vessels would be anatomically incorrect and impractical.
*Thoracic aorta, left ventricle, left atrium, pulmonary artery, right bronchial artery*
- This path describes the venous and then pulmonary circulation (right heart, lungs), which is incorrect for reaching the **arterial system** of the bronchial arteries.
- A catheter inserted via the **femoral artery** remains within the arterial system and would not cross into the pulmonary circulation or the left heart chambers in this manner.
*Thoracic aorta, brachiocephalic trunk, right subclavian artery, right internal thoracic artery, right bronchial artery*
- This pathway involves ascending from the **thoracic aorta** to the **brachiocephalic trunk** and subsequently into the **right subclavian** and **internal thoracic arteries**, which is a route primarily to the upper limb and chest wall.
- While the internal thoracic artery can sometimes have small anastomoses, it is not the primary or direct route for embolizing a bronchial artery, which typically originates directly from the descending thoracic aorta.
*Thoracic aorta, right subclavian artery, right internal thoracic artery, right bronchial artery*
- Similar to the previous incorrect option, this route involves navigating through the **subclavian** and **internal thoracic arteries**, which is an indirect and unnecessarily complex path to the bronchial arteries.
- The **bronchial arteries** are direct branches of the **thoracic aorta**, making this a much more convoluted and less likely route for therapeutic embolization.
Pulse points and vascular access US Medical PG Question 2: A 14-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of acute left-sided chest pain and dyspnea following a motor vehicle accident. His pulse is 122/min and blood pressure is 85/45 mm Hg. Physical examination shows distended neck veins and tracheal displacement to the right side. The left chest is hyperresonant to percussion and there are decreased breath sounds. This patient would most benefit from needle insertion at which of the following anatomical sites?
- A. 5th left intercostal space along the midclavicular line
- B. 8th left intercostal space along the posterior axillary line
- C. 2nd left intercostal space along the midclavicular line (Correct Answer)
- D. Subxiphoid space in the left sternocostal margin
- E. 5th left intercostal space along the midaxillary line
Pulse points and vascular access Explanation: ***2nd left intercostal space along the midclavicular line***
- The patient's symptoms (chest pain, dyspnea, hypotension, distended neck veins, tracheal deviation, hyperresonance, and decreased breath sounds on the left) are classic signs of a **tension pneumothorax**.
- Immediate treatment for **tension pneumothorax** involves needle decompression at the **2nd intercostal space** in the midclavicular line to relieve pressure and restore hemodynamic stability.
*5th left intercostal space along the midclavicular line*
- This location is typically used for **chest tube insertion** in a more controlled setting, not for emergent needle decompression of a tension pneumothorax.
- While it's a safe location for pleural access, it is not the **first-line site** for immediate life-saving decompression.
*8th left intercostal space along the posterior axillary line*
- This site is too low and posterior for effective needle decompression of a tension pneumothorax, which requires rapid access to the **apex of the lung**.
- It is more commonly used for **thoracentesis** to drain fluid from the pleural cavity.
*Subxiphoid space in the left sternocostal margin*
- This location is primarily used for **pericardiocentesis** to drain fluid from the pericardial sac in cases of cardiac tamponade.
- It is not appropriate for addressing a **pneumothorax**, which involves air in the pleural space.
*5th left intercostal space along the midaxillary line*
- This site is a common alternative for **chest tube insertion** but is not the preferred or most immediate site for needle decompression of a tension pneumothorax.
- While it offers pleural access, the **2nd intercostal space** anteriorly is chosen for expediency and safety in an emergency.
Pulse points and vascular access US Medical PG Question 3: A 41-year-old man with a history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia is brought to the emergency department by his wife for difficulty breathing after choking on food at dinner. He is unconscious and pulseless on arrival. Despite appropriate life-saving measures, he dies. Examination of the heart shows a necrotic, pale yellow plaque in the left circumflex artery. Similar lesions are most likely to be found in which of the following locations?
- A. Thoracic aorta
- B. Superficial temporal artery
- C. Internal carotid artery (Correct Answer)
- D. Abdominal aorta
- E. Pulmonary artery
Pulse points and vascular access Explanation: ***Internal carotid artery***
- The description of a "necrotic, pale yellow plaque" in the **left circumflex artery** is characteristic of an **atherosclerotic plaque** that has likely led to a **myocardial infarction (MI)**.
- **Atherosclerosis** is a **systemic disease** that preferentially affects **medium-sized muscular arteries** at bifurcations and areas of turbulent flow.
- Given the patient's history of **hypertension** and **hyperlipidemia**, similar lesions are most likely to be found in the **internal carotid artery**, which is:
- A **medium-sized muscular artery** (like coronary arteries)
- A common site for **atherosclerotic plaque formation** leading to **thrombotic stroke**
- Subject to the same risk factors and pathophysiology as coronary arteries
- Prone to similar acute complications (plaque rupture, thrombosis, vessel occlusion)
*Thoracic aorta*
- While the **thoracic aorta** can develop **atherosclerotic plaques**, it is an **elastic artery** rather than a muscular artery.
- Atherosclerosis in the aorta is typically less obstructive and less prone to acute thrombotic events compared to medium-sized muscular arteries.
- The thoracic aorta is less frequently the site for clinically significant acute occlusive events like MI or stroke.
*Superficial temporal artery*
- The **superficial temporal artery** is typically involved in diseases like **giant cell arteritis**, an inflammatory vasculitis, rather than widespread **atherosclerosis**.
- It is a smaller, more distal artery and not a typical site for the type of clinically significant **atherosclerotic plaques** described in this case.
- Atherosclerotic disease causing acute events preferentially affects larger, proximal vessels.
*Abdominal aorta*
- The **abdominal aorta** is indeed a very common site for **atherosclerosis** and **aneurysm formation**.
- However, like the thoracic aorta, it is an **elastic artery** rather than a muscular artery, so the lesions may differ in character and clinical behavior.
- While atherosclerosis here is common, it is less directly linked to acute thrombotic occlusive events (like acute MI or stroke) compared to medium-sized muscular arteries supplying the heart and brain.
*Pulmonary artery*
- The **pulmonary artery** system is a **low-pressure system** and is generally spared from systemic **atherosclerosis**.
- **Atherosclerotic plaques** are exceedingly rare in the pulmonary arteries unless there is severe pre-existing **pulmonary hypertension**.
- This is not a typical site for systemic atherosclerotic disease.
Pulse points and vascular access US Medical PG Question 4: A 35-year-old male is brought into the emergency department for a trauma emergency. The emergency medical services states that the patient was wounded with a knife on his upper left thigh near the inguinal ligament. Upon examination in the trauma bay, the patient is awake and alert. His physical exam and FAST exam is normal other than the knife wound. Large bore intravenous lines are inserted into the patient for access and fluids are being administered. Pressure on the knife wound is being held by one of the physicians with adequate control of the bleeding, but the physician notices the blood was previously extravasating in a pulsatile manner. His vitals are BP 100/50, HR 110, T 97.8, RR 22. What is the next best step for this patient?
- A. CT lower extremities
- B. Radiograph lower extremities
- C. Coagulation studies and blood typing/crossmatch
- D. Tourniquet of proximal lower extremity
- E. Emergent surgery (Correct Answer)
Pulse points and vascular access Explanation: ***Emergent surgery***
- The pulsatile bleeding from a thigh wound near the inguinal ligament is highly suggestive of a major arterial injury, such as to the **femoral artery**.
- Given the potential for rapid blood loss and hemodynamic instability, **emergent surgical exploration and repair** are necessary to control the bleeding and prevent further compromise.
*CT lower extremities*
- While CT angiography could further delineate vascular injury, the presence of **active pulsatile bleeding** necessitates immediate surgical intervention rather than delaying for imaging.
- Delaying surgery for imaging risks **exsanguination** and worsening patient outcomes, especially with a blood pressure of **100/50 mmHg** and a heart rate of **110 bpm**, indicating early shock.
*Radiograph lower extremities*
- A radiograph would primarily visualize bone structures and foreign bodies but would not provide adequate information regarding the **vascular injury** and active bleeding.
- It would not change the urgent need for **surgical exploration** to address the pulsatile hemorrhage.
*Coagulation studies and blood typing/crossmatch*
- These are important preparatory steps for major surgery involving significant blood loss, but they should be carried out **concurrently with preparations for emergent surgery**, not instead of it.
- Delaying surgery to await these results would be inappropriate when facing **active arterial bleeding**.
*Tourniquet of proximal lower extremity*
- While a tourniquet can be used for temporary hemorrhage control, especially in an uncontrolled external hemorrhage, the current bleeding is being controlled by **direct pressure**.
- Applying a tourniquet could cause **ischemic damage** to the extremity if applied for too long, and for a deep stab wound, direct compression is often effective until surgical control can be achieved.
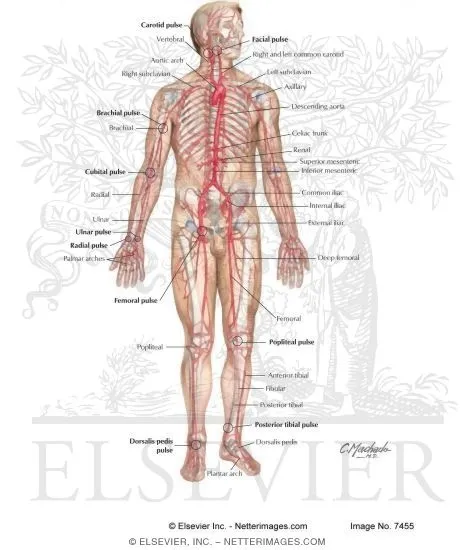
Pulse points and vascular access US Medical PG Question 5: A 72-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of severe, acute, right leg pain for 2 hours. The patient's symptoms started suddenly while he was doing household chores. He has no history of leg pain at rest or with exertion. Yesterday, he returned home after a 6-hour bus ride from his grandson's home. He has hypertension treated with ramipril. He appears uncomfortable. His temperature is 37.4°C (99.3°F), pulse is 105/min and irregular, and blood pressure is 146/92 mm Hg. The right lower extremity is cool and tender to touch. A photograph of the limb is shown. Femoral pulses are palpable bilaterally; popliteal and pedal pulses are decreased on the right side. Sensation to pinprick and light touch and muscle strength are decreased in the right lower extremity. Which of the following is most likely to confirm the underlying source of this patient's condition?
- A. Biopsy of a superficial vein
- B. Doppler ultrasonography of the legs
- C. Digital subtraction angiography
- D. Manometry
- E. Echocardiography (Correct Answer)
Pulse points and vascular access Explanation: ***Echocardiography***
- The patient's presentation with acute, severe leg pain, coolness, decreased pulses, and neurological deficits in the right lower extremity, along with an **irregular pulse** (suggesting **atrial fibrillation**), points to an **arterial embolism**.
- An **echocardiogram** is crucial to identify the source of the embolus, most commonly a **left atrial thrombus** due to atrial fibrillation, which would then confirm the underlying cause.
*Biopsy of a superficial vein*
- A biopsy of a superficial vein would be indicated for conditions like **vasculitis** or **thrombophlebitis**, which are not consistent with the acute, severe arterial occlusion observed.
- This test would not help in identifying the source of an arterial embolus causing acute limb ischemia.
*Doppler ultrasonography of the legs*
- While **Doppler ultrasonography** can confirm the presence of **arterial occlusion** and assess flow, it does not identify the **source** of an embolus.
- It is more useful for diagnosing deep vein thrombosis or chronic arterial insufficiency, which are not the primary concern here.
*Digital subtraction angiography*
- **Digital subtraction angiography** is an invasive procedure that can precisely map the arterial tree and identify the location of the **occlusion**.
- However, it primarily pinpoints the site of the blockage and doesn't reveal the **etiology** or the source of an embolus in the heart.
*Manometry*
- **Manometry** is used to measure pressures, typically in the gastrointestinal tract or for compartment syndrome, and is not relevant for diagnosing the source of an arterial embolus.
- This diagnostic tool has no role in the investigation of acute limb ischemia or its cardiac origin.
Pulse points and vascular access US Medical PG Question 6: A 55-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of left-sided chest pain and difficulty breathing for the past 30 minutes. His pulse is 88/min. He is pale and anxious. Serum studies show increased cardiac enzymes. An ECG shows ST-elevations in leads I, aVL, and V5-V6. A percutaneous coronary intervention is performed. In order to localize the site of the lesion, the catheter must pass through which of the following structures?
- A. Left coronary artery → left circumflex artery (Correct Answer)
- B. Right coronary artery → posterior descending artery
- C. Left coronary artery → left anterior descending artery
- D. Right coronary artery → right marginal artery
- E. Left coronary artery → posterior descending artery
Pulse points and vascular access Explanation: ***Left coronary artery → left circumflex artery***
- **ST-elevations** in leads I, aVL, and V5-V6 are indicative of a **lateral myocardial infarction**.
- The **left circumflex artery** primarily supplies the lateral wall of the left ventricle.
*Right coronary artery → posterior descending artery*
- The **posterior descending artery** (PDA) typically supplies the inferior wall and posterior interventricular septum.
- An occlusion here would cause **ST-elevations** in leads II, III, and aVF, which is not seen in this case.
*Left coronary artery → left anterior descending artery*
- The **left anterior descending** (LAD) artery supplies the anterior wall and apex of the left ventricle.
- Occlusion of the LAD would typically cause **ST-elevations** in leads V1-V4, indicating an anterior MI.
*Right coronary artery → right marginal artery*
- The **right marginal artery** is a branch of the right coronary artery and supplies part of the right ventricle.
- Occlusion here would primarily affect the **right ventricle**, and is not typically associated with the given ECG changes.
*Left coronary artery → posterior descending artery*
- While the **posterior descending artery** can sometimes originate from the left circumflex artery (**left dominant circulation**), it primarily supplies the inferior wall.
- The observed ECG changes in leads I, aVL, and V5-V6 are characteristic of a **lateral wall infarct**, which is supplied by the left circumflex artery.
Pulse points and vascular access US Medical PG Question 7: A 58-year-old man presents to the emergency department with severe right leg pain accompanied by tingling and weakness. His condition started suddenly 3 hours ago when he was watching a movie. His medical history is remarkable for type 2 diabetes mellitus and hypertension. He has been smoking 20–30 cigarettes per day for the past 35 years. His vital signs include a blood pressure of 149/85 mm Hg, a temperature of 36.9°C (98.4°F), and an irregular pulse of 96/min. On physical examination, his right popliteal and posterior tibial pulses are absent. His right leg is pale and cold. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Buerger's disease
- B. Leriche syndrome
- C. Acute limb ischemia (Correct Answer)
- D. CREST syndrome
- E. Deep vein thrombosis
Pulse points and vascular access Explanation: ***Acute limb ischemia***
- The sudden onset of **severe leg pain**, **tingling**, **weakness**, and the **six P's** (pain, pallor, pulselessness, paresthesias, poikilothermia, and paralysis) are classic signs of acute limb ischemia.
- The patient's history of **smoking**, **hypertension**, **diabetes**, and an **irregular pulse** (suggesting atrial fibrillation) are significant risk factors for **thromboembolism**, which is a common cause of acute limb ischemia.
*Buerger's disease*
- This condition primarily affects **small and medium-sized arteries and veins** in the limbs and is strongly associated with **heavy tobacco use**.
- However, it typically presents with **distal extremity ischemia**, superficial phlebitis, and Raynaud's phenomenon, rather than the sudden, severe, large vessel occlusion described here.
*Leriche syndrome*
- This syndrome involves **atherosclerotic occlusion of the distal aorta** at or just below the renal arteries, affecting both lower limbs.
- It classically presents with a triad of **bilateral buttock/thigh claudication**, **impotence**, and **absent femoral pulses**, which does not align with the unilateral symptoms and specific pulse deficits described in the case.
*CREST syndrome*
- CREST (Calcinosis, Raynaud's phenomenon, Esophageal dysmotility, Sclerodactyly, Telangiectasias) is a subtype of **systemic sclerosis**, a **connective tissue disease**.
- Its symptoms are unrelated to the acute vascular event presented, which involves sudden limb ischemia.
*Deep vein thrombosis*
- DVT primarily involves the formation of a **blood clot in a deep vein**, leading to symptoms like **swelling**, **pain**, and **redness** in the affected limb.
- It does not typically cause the **acute pallor**, **coldness**, **pulselessness**, and severe neurologic deficits (tingling, weakness) seen with arterial occlusion.
Pulse points and vascular access US Medical PG Question 8: A 33-year-old pregnant woman at 38 weeks gestation requires emergency cesarean section. The obstetrician must perform a perimortem procedure due to maternal cardiac arrest. She makes a Pfannenstiel incision but encounters significant bleeding. The patient has a history of previous cesarean section with documented bladder injury. Considering the surface anatomy and previous surgery, evaluate the most likely source of bleeding and the anatomical relationship that increases risk in this scenario.
- A. External iliac vessels exposed due to loss of normal tissue planes from adhesions
- B. Superficial epigastric vessels in the subcutaneous tissue
- C. Inferior epigastric vessels injured due to lateral extension of the incision (Correct Answer)
- D. Uterine vessels injured due to lower segment extension
- E. Superior vesical arteries injured due to abnormal bladder position from scarring
Pulse points and vascular access Explanation: ***Inferior epigastric vessels injured due to lateral extension of the incision***
- A **Pfannenstiel incision** is a transverse incision performed 2-3 cm above the symphysis pubis; extending this incision too far laterally increases the risk of transecting the **inferior epigastric vessels**.
- These vessels are located deep to the **rectus abdominis** muscle but lateral to its midline, making them susceptible during emergency procedures where rapid extension of the surgical field is required.
*Uterine vessels injured due to lower segment extension*
- The **uterine vessels** are located within the **broad ligament** and are typically injured during the hysterotomy (uterine incision) phase rather than the initial abdominal wall approach.
- While heavy bleeding occurs if the uterine incision extends laterally into the **vascular pedicle**, it does not correlate with superficial anatomical landmarks of a Pfannenstiel incision.
*External iliac vessels exposed due to loss of normal tissue planes from adhesions*
- The **external iliac vessels** are retroperitoneal structures and are generally too deep and lateral to be the primary source of bleeding in a standard **Pfannenstiel incision**.
- Although **adhesions** can distort anatomy, injury to these vessels is more common in extensive pelvic lymphadenectomy or oncological surgeries rather than a perimortem C-section.
*Superficial epigastric vessels in the subcutaneous tissue*
- The **superficial epigastric vessels** run in the **Camper's fascia** and are commonly transected during the initial skin incision, but they rarely cause "significant" or life-threatening bleeding compared to deeper vessels.
- Bleeding from these vessels is usually easily controlled with cautery or pressure and does not represent the primary anatomical risk of lateral **Pfannenstiel extension**.
*Superior vesical arteries injured due to abnormal bladder position from scarring*
- The **superior vesical arteries** supply the upper portion of the bladder; while at risk during dissection of a **scarred bladder flap**, they are not the source encountered during the abdominal wall incision.
- Previous **bladder injury** increases the risk of cystotomy, but the vascular supply to the bladder is located deep within the pelvic cavity, not at the level of the **rectus sheath**.
Pulse points and vascular access US Medical PG Question 9: A 71-year-old man with atrial fibrillation presents with sudden onset of severe abdominal pain out of proportion to physical findings. He has mild diffuse tenderness but no peritoneal signs. His lactate is 4.5 mmol/L. CT angiography shows occlusion of a major mesenteric vessel. The surgeon explains that the occluded vessel supplies the midgut from just distal to the second part of the duodenum to the proximal two-thirds of the transverse colon. Based on surface anatomy, at what vertebral level does this vessel originate?
- A. L3
- B. T12
- C. L1 (Correct Answer)
- D. L2
- E. T10
Pulse points and vascular access Explanation: ***L1***
- The clinical presentation describes **acute mesenteric ischemia** involving the **Superior Mesenteric Artery (SMA)**, which supplies the embryologic **midgut**.
- The SMA originates from the **abdominal aorta** behind the neck of the pancreas at the level of the **L1 vertebra**.
*T10*
- The **esophagus** passes through the diaphragm at the **T10 level** via the esophageal hiatus.
- No major abdominal vascular branches supplying the gastrointestinal tract originate at this specific thoracic level.
*T12*
- This is the level of the **celiac trunk**, which supplies the **foregut** structures including the stomach, liver, and spleen.
- It also marks the **aortic hiatus** where the aorta enters the abdominal cavity from the thorax.
*L2*
- This level corresponds to the origin of the **renal arteries** and the site where the **duodenojejunal flexure** is suspended by the ligament of Treitz.
- While the SMA is in close proximity, its distinct origin from the aorta is characteristically at the **L1 level**.
*L3*
- This is the level of origin for the **Inferior Mesenteric Artery (IMA)**, which supplies the **hindgut** including the distal third of the transverse colon.
- Clinical findings in this case point to midgut ischemia, which is associated with the **Superior Mesenteric Artery** rather than the IMA.
Pulse points and vascular access US Medical PG Question 10: A 25-year-old motorcyclist presents after a high-speed collision with facial trauma. Clinical examination reveals cerebrospinal fluid rhinorrhea, periorbital ecchymosis, and numbness over the cheek and upper teeth. CT shows a fracture extending through a foramen at the apex of the orbit. Based on the clinical presentation and surface anatomy, which foramen is most likely involved?
- A. Foramen rotundum (Correct Answer)
- B. Superior orbital fissure
- C. Infraorbital foramen
- D. Inferior orbital fissure
- E. Optic canal
Pulse points and vascular access Explanation: ***Foramen rotundum***
- The **foramen rotundum** transmits the **maxillary nerve (V2)**; trauma here explains the **numbness over the cheek** and **upper teeth** as these are within the V2 sensory distribution.
- Located at the **apex of the orbit**, this foramen communicates with the pterygopalatine fossa and is frequently involved in high-velocity fractures causing **middle cranial fossa** disruption and CSF rhinorrhea.
*Optic canal*
- The **optic canal** transmits the **optic nerve (CN II)** and the **ophthalmic artery**.
- Damage would result in **visual field defects** or blindness and an abnormal **pupillary light reflex**, rather than facial sensory loss.
*Superior orbital fissure*
- This fissure transmits **CN III, IV, VI** and the **ophthalmic nerve (V1)**; damage would cause **ophthalmoplegia** and forehead numbness.
- It does not carry the **V2 branch**, thus it cannot account for the loss of sensation in the **cheek and upper teeth**.
*Infraorbital foramen*
- While the **infraorbital nerve** (a branch of V2) passes here to supply the cheek, this foramen is on the **anterior surface of the maxilla**, not at the **apex of the orbit**.
- Trauma at this superficial site would not typically present with **CSF rhinorrhea**, which indicates a more deep-seated skull base fracture.
*Inferior orbital fissure*
- This fissure is located between the floor and lateral wall of the orbit but is not situated at the **apex** where the injury is described.
- While it transmits the **infraorbital nerve**, it is not a pathway through which a skull base injury leads to **CSF leakage** into the nasal cavity.
More Pulse points and vascular access US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.