Abdominal surface landmarks US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Abdominal surface landmarks. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Abdominal surface landmarks US Medical PG Question 1: During a surgical procedure to repair an abdominal aortic aneurysm, the surgeon must be careful to avoid injury to which of the following arterial structures that originates near the level of the renal vessels?
- A. Left renal artery (Correct Answer)
- B. Celiac trunk
- C. Right renal artery
- D. Superior mesenteric artery
Abdominal surface landmarks Explanation: ***Left renal artery***
- The **left renal artery** arises from the aorta usually just below the superior mesenteric artery, making it susceptible to injury during an **abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) repair** if the aneurysm extends proximally.
- Its proximity to the typical location of AAA, often near or involving the **infrarenal aorta**, necessitates careful identification and protection during clamping or graft placement.
*Celiac trunk*
- The **celiac trunk** originates higher up from the aorta, typically at the level of **T12-L1 vertebrae**, well above the common infrarenal AAA repair site.
- While important, it is generally less directly threatened during a typical infrarenal AAA repair compared to arteries immediately adjacent to or within the aneurysm sac.
*Right renal artery*
- The **right renal artery** also originates from the aorta near the level of the renal veins, but it is typically located more posteriorly and usually passes behind the inferior vena cava.
- Although it can be at risk, the left renal artery's course is often more anterior and directly in the field of dissection for the **aortic neck** during AAA repair.
*Superior mesenteric artery*
- The **superior mesenteric artery (SMA)** originates from the aorta proximal to the renal arteries, typically around the L1 vertebral level.
- While crucial, its origin is usually cephalad to the infrarenal aneurysm neck, making it generally less prone to direct injury during infrarenal AAA repair, though flow must be monitored.
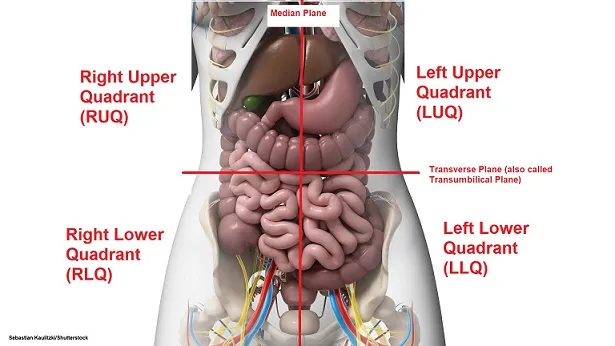
Abdominal surface landmarks US Medical PG Question 2: A 24-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of abdominal pain, fever, nausea, and vomiting for 12 hours. Her abdominal pain was initially dull and diffuse but has progressed to a sharp pain on the lower right side. Two years ago she had to undergo right salpingo-oophorectomy after an ectopic pregnancy. Her temperature is 38.7°C (101.7°F). Physical examination shows severe right lower quadrant tenderness with rebound tenderness; bowel sounds are decreased. Laboratory studies show leukocytosis with left shift. An abdominal CT scan shows a distended, edematous appendix. The patient is taken to the operating room for an appendectomy. During the surgery, the adhesions from the patient's previous surgery make it difficult for the resident physician to identify the appendix. Her attending mentions that she should use a certain structure for guidance to locate the appendix. The attending is most likely referring to which of the following structures?
- A. Epiploic appendages
- B. Right ureter
- C. Deep inguinal ring
- D. Ileocolic artery
- E. Teniae coli (Correct Answer)
Abdominal surface landmarks Explanation: ***Teniae coli***
- The **teniae coli** are three distinct longitudinal bands of smooth muscle that run along the length of the cecum and colon, converging at the base of the **appendix**.
- Following these bands inferiorly from the ascending colon or cecum during surgery is a reliable method to locate the **vermiform appendix**, especially in the presence of adhesions.
*Epiploic appendages*
- These are small, fat-filled sacs that protrude from the surface of the **large intestine** but are not directly used as a reliable landmark for locating the appendix.
- While present in the vicinity, they do not consistently lead to the base of the appendix like the teniae coli.
*Right ureter*
- The **right ureter** is located retroperitoneally, deep to the cecum and appendix, and is not a direct anatomical landmark used for identifying the appendix during an appendectomy.
- Identifying the ureter is important to avoid injury, but not for localizing the appendix.
*Deep inguinal ring*
- The **deep inguinal ring** is an opening in the transversalis fascia, involved in the formation of the inguinal canal, and is located far anterior and inferior to the region of the appendix.
- It has no anatomical relationship that would guide a surgeon to locate the appendix.
*Ileocolic artery*
- The **ileocolic artery** branches from the superior mesenteric artery and supplies the terminal ileum, cecum, and appendix. While it provides blood supply to the appendix, it is not a direct or consistent surface landmark for locating the appendix itself, especially in complex cases with adhesions.
- Locating the artery would be more complex and less reliable for initial identification compared to the teniae coli.
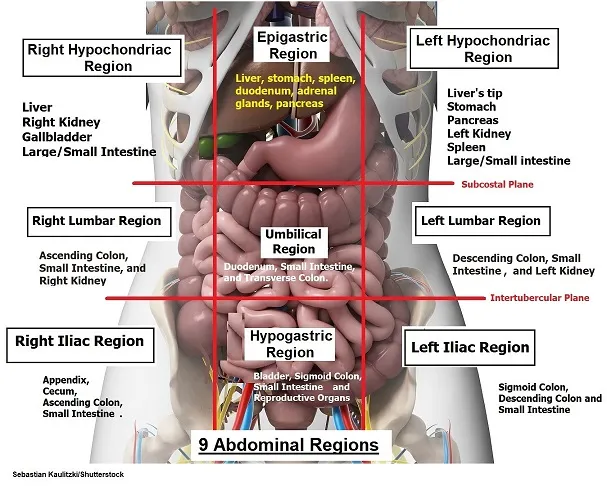
Abdominal surface landmarks US Medical PG Question 3: A 48-year-old woman presents to the emergency department because of increasingly severe right upper abdominal pain, fever, and non-bloody vomiting for the last 5 hours. The pain is dull, intermittent, and radiates to her right shoulder. During the past 3 months, she has had recurring abdominal discomfort after meals. The patient underwent an appendectomy more than 30 years ago. She has hypertension, diabetes mellitus type 2, and chronic back pain. She takes bisoprolol, metformin, and ibuprofen daily. She is 171 cm (5 ft 6 in) tall and weighs 99 kg (218 lb). Her BMI is 35.2 kg/m2. She appears uncomfortable and is clutching her abdomen. Her temperature is 38.5°C (101.3°F), pulse is 108/min, and blood pressure is 150/82 mm Hg. Abdominal examination shows right upper quadrant abdominal tenderness and guarding. Upon deep palpation of the right upper quadrant, the patient pauses during inspiration. Laboratory studies show the following:
Blood
Hemoglobin 13.1 g/dL
Leukocyte count 10,900/mm3
Platelet count 236,000/mm3
Mean corpuscular volume 89/µm3
Serum
Urea nitrogen 28 mg/dL
Glucose 89 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.7 mg/dL
Bilirubin
Total 1.6 mg/dL
Direct 1.1 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase 79 U/L
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT, GPT) 28 U/L
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST, GOT) 32 U/L
An X-ray of the abdomen shows no abnormalities. Further evaluation of the patient is most likely to reveal which of the following?
- A. History of recent travel to Indonesia
- B. Frequent, high-pitched bowel sounds on auscultation
- C. History of multiple past pregnancies (Correct Answer)
- D. Elevated carbohydrate-deficient transferrin
- E. History of recurrent sexually transmitted infections
Abdominal surface landmarks Explanation: ***History of multiple past pregnancies***
- This patient's symptoms (right upper quadrant pain radiating to the shoulder, guarding, positive Murphy's sign on deep palpation) along with fever and leukocytosis are highly suggestive of **acute cholecystitis**, likely due to gallstones.
- The "5 F's" risk factors for gallstones include **fat, female, forty, fertile (multiple pregnancies), and fair**, making a history of multiple pregnancies a highly relevant finding in this clinical context.
*History of recent travel to Indonesia*
- Recent travel to certain regions, including Indonesia, might increase the risk of certain **infectious diarrheal diseases** or **parasitic infections** that could cause abdominal pain.
- However, the classic symptoms and signs presented in the patient (RUQ pain, radiation to shoulder, positive Murphy's, fever, leukocytosis) are not typical for travel-related infections and point more strongly to biliary pathology.
*Frequent, high-pitched bowel sounds on auscultation*
- **High-pitched bowel sounds** are often associated with **bowel obstruction**, indicating hyperperistalsis above the obstruction point trying to push contents forward.
- This patient's presentation is consistent with acute cholecystitis, not bowel obstruction, and her abdominal X-ray was normal, making bowel obstruction less likely.
*Elevated carbohydrate-deficient transferrin*
- **Carbohydrate-deficient transferrin (CDT)** is a biomarker primarily used to detect **chronic excessive alcohol consumption**.
- While chronic alcohol use can contribute to various gastrointestinal issues (e.g., pancreatitis, liver disease), this patient's presentation is not typical of alcohol-related illness, and elevated CDT would not directly explain her acute cholecystitis symptoms.
*History of recurrent sexually transmitted infections*
- A history of recurrent sexually transmitted infections (STIs) might be relevant for conditions like **pelvic inflammatory disease (PID)**, which can sometimes cause right upper quadrant pain if it leads to **Fitz-Hugh-Curtis syndrome** (perihepatitis).
- However, the patient's presentation with classic signs of cholecystitis (Murphy's sign, radiation to shoulder, risk factors) along with elevated total and direct bilirubin, is much more indicative of biliary disease than an STI-related complication.
Abdominal surface landmarks US Medical PG Question 4: A 42-year-old woman presents to the emergency department complaining of abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting for the last 4 hours. She says that symptoms onset right after she had 2 generous portions of pizza. She notes that she had prior similar episodes which resolved spontaneously within an hour. However, the pain today has persisted for 5 hours and is much more severe. She says the pain is located in the right upper quadrant of her abdomen and radiates to her upper back. She describes the pain as dull and cramping. She has had hypertension for the past 10 years, managed medically. Her vital signs are a blood pressure of 148/96 mm Hg, a pulse of 108/min, a respiratory rate of 18/min, and a temperature of 37.7°C (99.9°F). Her BMI is 28 kg/m2. On physical examination, the patient appears uncomfortable and is clutching her abdomen in pain. Abdominal exam reveals severe tenderness to palpation in the right upper quadrant with guarding. A positive Murphy’s sign is present. Her serum chemistry levels, including amylase, lipase, bilirubin, and liver function tests and urinalysis are normal. Urine hCG level is < 0.5 IU/L. Abdominal ultrasound reveals a large stone lodged in the neck of the gallbladder. Which of the following is the most likely pathway for referred pain in this patient?
- A. Right thoraco-abdominal intercostal nerves
- B. The phrenic nerve
- C. Greater splanchnic nerves to the spinal cord (Correct Answer)
- D. Left greater splanchnic nerve
- E. The pain endings of the visceral peritoneum
Abdominal surface landmarks Explanation: ***Greater splanchnic nerves to the spinal cord***
- The **greater splanchnic nerves** (T5-T9) carry **visceral afferent fibers** from the gallbladder, transmitting pain to the spinal cord segments corresponding to the upper back (T5-T9).
- This explains the **dull, cramping right upper quadrant pain** that **radiates to the upper back**, characteristic of visceral pain from the gallbladder.
*Right thoraco-abdominal intercostal nerves*
- These nerves primarily innervate the **parietal peritoneum** and abdominal wall, responsible for sharp, localized somatic pain.
- While they could be involved in localized pain, they don't typically account for the **referred dull, cramping pain to the back** originating from a visceral organ like the gallbladder.
*The phrenic nerve*
- The **phrenic nerve** innervates the diaphragm and carries pain from the **diaphragmatic pleura and peritoneum**, often resulting in referred pain to the shoulder tip.
- Gallbladder pain can sometimes irritate the diaphragm, but the primary referral to the **upper back** is more characteristic of splanchnic nerve involvement.
*Left greater splanchnic nerve*
- The **left greater splanchnic nerve** primarily innervates organs on the left side of the upper abdomen, such as the stomach and spleen.
- Since the gallbladder is on the **right side**, its afferent pain signals travel via the right greater splanchnic nerves.
*The pain endings of the visceral peritoneum*
- The **visceral peritoneum** itself is generally insensitive to pain from cutting or burning; it senses stretch and inflammation.
- However, the pain signals from the stretched or inflamed gallbladder are transmitted via **visceral afferent fibers within the splanchnic nerves**, not directly by the visceral peritoneum's own pain endings.
Abdominal surface landmarks US Medical PG Question 5: An epidemiologist is evaluating the efficacy of Noxbinle in preventing HCC deaths at the population level. A clinical trial shows that over 5 years, the mortality rate from HCC was 25% in the control group and 15% in patients treated with Noxbinle 100 mg daily. Based on this data, how many patients need to be treated with Noxbinle 100 mg to prevent, on average, one death from HCC?
- A. 20
- B. 73
- C. 10 (Correct Answer)
- D. 50
- E. 100
Abdominal surface landmarks Explanation: ***10***
- The **number needed to treat (NNT)** is calculated by first finding the **absolute risk reduction (ARR)**.
- **ARR** = Risk in control group - Risk in treatment group = 25% - 15% = **10%** (or 0.10).
- **NNT = 1 / ARR** = 1 / 0.10 = **10 patients**.
- This means that **10 patients must be treated with Noxbinle to prevent one death from HCC** over 5 years.
*20*
- This would result from an ARR of 5% (1/0.05 = 20), which is not supported by the data.
- May arise from miscalculating the risk difference or incorrectly halving the actual ARR.
*73*
- This value does not correspond to any standard calculation of NNT from the given mortality rates.
- May result from confusion with other epidemiological measures or calculation error.
*50*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 2% (1/0.02 = 50), which significantly underestimates the actual risk reduction.
- Could result from incorrectly calculating the difference as a proportion rather than absolute percentage points.
*100*
- This would correspond to an ARR of 1% (1/0.01 = 100), grossly underestimating the treatment benefit.
- May result from confusing ARR with relative risk reduction or other calculation errors.
Abdominal surface landmarks US Medical PG Question 6: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Abdominal surface landmarks Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Abdominal surface landmarks US Medical PG Question 7: A 31-year-old woman presents to the emergency room with high-grade fever and abdominal pain for the past 2 days. She also complains of malaise and has vomited several times since last night. The past medical history is benign. The vital signs include: temperature 40.0°C (104.0°F), pulse 120/min, respiratory rate 28/min, and blood pressure 120/89 mm Hg. On physical examination, severe costovertebral angle tenderness is noted. She is admitted to the medical floor and blood is drawn. The laboratory testing reveals leukocytosis with predominant neutrophilia and increased C-reactive protein and ferritin levels. She is suspected to have a retroperitoneal organ infection. Which of the following best describes the involved organ?
- A. It is the most common site of Meckel's diverticulum.
- B. It is composed of white pulp and red pulp.
- C. It is composed of tubules and parenchyma. (Correct Answer)
- D. It stores and concentrates bile.
- E. It produces hydrochloric acid.
Abdominal surface landmarks Explanation: ***It is composed of tubules and parenchyma.***
- The patient's symptoms of **high-grade fever**, **abdominal pain**, and **costovertebral angle (CVA) tenderness** are highly suggestive of **pyelonephritis**, an infection of the kidney.
- The **kidney** is a retroperitoneal organ composed of millions of **nephrons**, which include **renal tubules** and surrounding **parenchyma**.
*It is the most common site of Meckel's diverticulum.*
- **Meckel's diverticulum** is a remnant of the vitelline duct and is typically found in the **ileum** (small intestine), an intraperitoneal organ, not a retroperitoneal one.
- Its presence is not associated with costovertebral angle tenderness or the described systemic symptoms.
*It is composed of white pulp and red pulp.*
- The **spleen** is composed of white pulp (lymphoid tissue) and red pulp (vascular sinuses), but it is an **intraperitoneal organ** and its infection typically does not present with costovertebral angle tenderness.
- Splenic infection (e.g., abscess) is less common and usually presents with left upper quadrant pain, not the retroperitoneal symptoms described.
*It stores and concentrates bile.*
- The **gallbladder** stores and concentrates bile, and while it is partially retroperitoneal or intraperitoneal depending on its location, an infection (cholecystitis) typically causes right upper quadrant pain, not costovertebral angle tenderness.
- Its function is unrelated to the described symptoms of a kidney infection.
*It produces hydrochloric acid.*
- The **stomach** produces hydrochloric acid, but it is an **intraperitoneal organ**, and its infection or inflammation (gastritis, peptic ulcer) would cause epigastric pain, not costovertebral angle tenderness.
- The clinical picture does not align with symptoms related to the stomach.
Abdominal surface landmarks US Medical PG Question 8: A 45-year-old male is brought to the emergency department by emergency medical services after sustaining a gunshot wound to the abdomen. He is unresponsive. His temperature is 99.0°F (37.2°C), blood pressure is 95/58 mmHg, pulse is 115/min, and respirations are 20/min. Physical examination reveals an entry wound in the left abdominal quadrant just inferior to the left lateral costal border. Abdominal CT shows the bullet trajectory through the left abdominal cavity. Which of the following structures has the bullet most likely penetrated?
- A. Transverse colon
- B. Ascending colon
- C. Descending colon (Correct Answer)
- D. Sigmoid colon
- E. Superior duodenum
Abdominal surface landmarks Explanation: ***Descending colon***
- The **descending colon** is located in the left abdominal cavity, specifically in the left upper quadrant and extending into the left lower quadrant, making it highly susceptible to injury from a gunshot wound in the **left abdominal quadrant** just inferior to the left lateral costal border.
- Its position aligns directly with the described entry point and bullet trajectory.
*Transverse colon*
- The **transverse colon** lies more centrally in the upper abdomen, spanning from the right to the left upper quadrants.
- While possible to be hit by a left-sided entry wound, the trajectory described as "inferior to the left lateral costal border" makes the descending colon a more direct and likely target.
*Ascending colon*
- The **ascending colon** is located in the **right abdominal cavity**, specifically in the right upper and lower quadrants.
- A wound inferior to the left lateral costal border would be on the opposite side of the abdomen and thus unlikely to penetrate the ascending colon.
*Sigmoid colon*
- The **sigmoid colon** is located more inferiorly in the **left lower quadrant** and pelvis.
- While on the left side, the entry wound described as "inferior to the left lateral costal border" is generally higher than the typical location of the sigmoid colon.
*Superior duodenum*
- The **superior duodenum** is located in the **right upper quadrant** of the abdomen, anterior to the head of the pancreas.
- Its position on the right side makes it highly unlikely to be penetrated by a gunshot wound to the left abdominal quadrant.
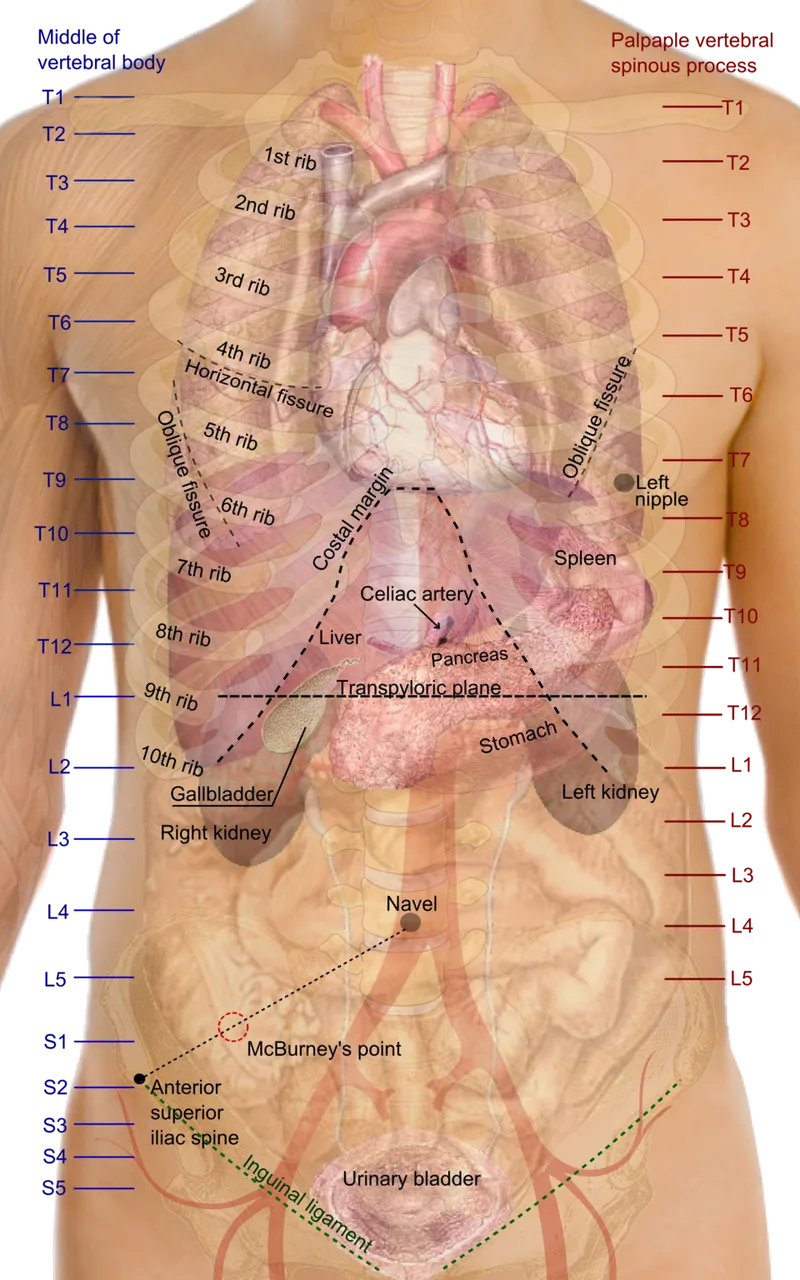
Abdominal surface landmarks US Medical PG Question 9: A researcher is investigating the blood supply of the adrenal gland. While performing an autopsy on a patient who died from unrelated causes, he identifies a vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the inferior aspect of the right adrenal gland. Which of the following vessels most likely gave rise to the vessel in question?
- A. Inferior phrenic artery
- B. Abdominal aorta
- C. Renal artery (Correct Answer)
- D. Superior mesenteric artery
- E. Common iliac artery
Abdominal surface landmarks Explanation: ***Renal artery***
- The **inferior suprarenal artery**, which supplies the inferior part of the adrenal gland, typically arises from the **renal artery**.
- The adrenal glands receive a rich blood supply from three main arterial sources: superior, middle, and inferior suprarenal arteries.
*Inferior phrenic artery*
- The **superior suprarenal arteries** typically arise from the **inferior phrenic arteries** and supply the superior aspect of the adrenal glands.
- While critical for adrenal blood supply, they do not typically contribute to the inferior aspect directly.
*Abdominal aorta*
- The **middle suprarenal artery** usually arises directly from the **abdominal aorta**.
- This vessel supplies the central part of the adrenal gland, but not primarily the inferior aspect.
*Superior mesenteric artery*
- The **superior mesenteric artery** primarily supplies structures of the midgut (e.g., small intestine, ascending colon) and does not typically give rise to vessels supplying the adrenal glands.
- It is located inferior to the origin of the renal arteries and the adrenal glands.
*Common iliac artery*
- The **common iliac arteries** supply the lower limbs and pelvic organs, originating from the abdominal aorta bifurcation.
- These arteries are located much too far inferior to supply the adrenal glands, which are retroperitoneal structures in the upper abdomen.
Abdominal surface landmarks US Medical PG Question 10: A 72-year-old male presents to a cardiac surgeon for evaluation of severe aortic stenosis. He has experienced worsening dyspnea with exertion over the past year. The patient also has a history of poorly controlled hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and hyperlipidemia. An echocardiogram revealed a thickened calcified aortic valve. The surgeon is worried that the patient will be a poor candidate for open heart surgery and decides to perform a less invasive transcatheter aortic valve replacement. In order to perform this procedure, the surgeon must first identify the femoral pulse just inferior to the inguinal ligament and insert a catheter into the vessel in order to gain access to the arterial system. Which of the following structures is immediately lateral to this structure?
- A. Lymphatic vessels
- B. Femoral vein
- C. Sartorius muscle
- D. Pectineus muscle
- E. Femoral nerve (Correct Answer)
Abdominal surface landmarks Explanation: ***Femoral nerve***
- The **femoral nerve** lies lateral to the **femoral artery** within the **femoral triangle**.
- The order of structures from **lateral to medial** under the inguinal ligament is remembered by the mnemonic **NAVEL**: **N**erve, **A**rtery, **V**ein, **E**mpty space, **L**ymphatics.
*Lymphatic vessels*
- **Lymphatic vessels** and nodes are located most medially within the femoral triangle, medial to the femoral vein.
- This position is not immediately lateral to the femoral artery.
*Femoral vein*
- The **femoral vein** is located immediately medial to the **femoral artery**.
- It would not be found immediately lateral to the femoral artery.
*Sartorius muscle*
- The **sartorius muscle** forms the lateral boundary of the **femoral triangle** but is not immediately adjacent and lateral to the femoral artery within the triangle itself.
- The femoral nerve is enclosed within the iliopsoas fascial compartment, which runs deep to the sartorius.
*Pectineus muscle*
- The **pectineus muscle** forms part of the floor of the **femoral triangle**, but it is deep to the neurovascular structures.
- It is not immediately lateral to the femoral artery.
More Abdominal surface landmarks US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.