Thoracic radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Thoracic radiologic landmarks. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Thoracic radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 1: A 3-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department by her parents with sudden onset shortness of breath. They tell the emergency physician that their daughter was lying on the bed watching television when she suddenly began gasping for air. They observed a bowl of peanuts lying next to her when they grabbed her up and brought her to the emergency department. Her respirations are 25/min, the pulse is 100/min and the blood pressure is 90/65 mm Hg. The physical findings as of now are apparently normal. She is started on oxygen and is sent in for a chest X-ray. Based on her history and physical exam findings, the cause of her current symptoms would be seen on the X-ray at which of the following sites?
- A. The superior segment of the right lower lobe
- B. The posterior segment of the right lower lobe (Correct Answer)
- C. The lingula of the left upper lobe
- D. The apical segment of the right upper lobe
- E. The apical segment of the left upper lobe
Thoracic radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***The posterior segment of the right lower lobe***
- This is the **most common site for foreign body aspiration in a supine or lying down position** due to gravity and anatomical orientation.
- The history explicitly states the child was **"lying on the bed watching television"** when aspiration occurred, making the **posterior segment of the right lower lobe** the most gravity-dependent and therefore most likely location.
- The **right main bronchus** is wider, shorter, and more vertical than the left, making the right lung the predominant site for aspiration, and in supine position, the posterior segment is most dependent [1, 2].
*The superior segment of the right lower lobe*
- The **superior segment of the right lower lobe** is the most common site for aspiration in **upright, standing, or semi-upright positions**, not in a supine position.
- Since the child was lying down (supine), gravity would direct the aspirated peanut to the **posterior segment** rather than the superior segment.
- This would be correct if the child had aspirated while sitting upright.
*The lingula of the left upper lobe*
- The **lingula** is an uncommon site for aspiration because the **left main bronchus** has a sharper angle and smaller diameter compared to the right bronchus [2].
- The anatomical differences make aspiration into the right lung significantly more common than the left lung [2].
- The lingula is not a gravity-dependent area in the supine position.
*The apical segment of the right upper lobe*
- The **apical segment of the right upper lobe** is associated with aspiration when the patient is in **Trendelenburg position** (head lower than feet) or in extreme head-down positions.
- The described scenario of lying flat on the bed does not favor aspiration into apical segments, which are non-gravity-dependent in supine position.
- This location would be contra-gravity in the supine position.
*The apical segment of the left upper lobe*
- Aspiration into the **left upper lobe** is less frequent than the right lung due to the sharper angle of the left main bronchus [2].
- The **apical segment** would require head-down positioning (Trendelenburg) that is not described in this clinical scenario.
- This is the least likely location given both the supine position and left-sided anatomy.
Thoracic radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 2: A 57-year-old man presents to the emergency department with shortness of breath. He was eating dinner with his family during the holidays and felt very short of breath, thus prompting him to come in. The patient has a past medical history of diabetes, hypertension, 2 myocardial infarctions, and obesity. Physical exam is notable for bilateral pulmonary crackles and a jugular venous distension. Chest radiography reveals an enlarged cardiac silhouette and blunting of the costophrenic angles. The patient is started on a medication for his acute symptoms. Two hours later, he states his symptoms have vastly improved and repeat chest radiography is notable for an enlarged cardiac silhouette. Which of the following is a property of the medication most likely given?
- A. Increases cardiac contractility and decreases afterload
- B. Chronic use leads to long-term nephrogenic adaptations (Correct Answer)
- C. Increases cardiac contractility and afterload
- D. Can lead to respiratory depression
- E. Causes venodilation and a decrease in preload
Thoracic radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Chronic use leads to long-term nephrogenic adaptations***
- The patient's presentation with acute shortness of breath, crackles, JVD, enlarged cardiac silhouette, and blunting of costophrenic angles is classic for **acute decompensated heart failure** with **pulmonary edema**. The prompt improvement of symptoms and resolution of pulmonary edema suggests a **loop diuretic** like **furosemide** was administered.
- **Chronic use of loop diuretics** can lead to long-term **nephrogenic adaptations**, such as hypertrophy of the distal nephron and increased counter-regulatory hormone production (renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system), which can contribute to diuretic resistance over time.
*Increases cardiac contractility and decreases afterload*
- Medications that increase cardiac contractility (positive inotropes) and decrease afterload (vasodilators) are sometimes used in heart failure, but they are not the primary treatment for **acute pulmonary edema** leading to rapid resolution of fluid overload.
- While improved contractility might benefit cardiac output, the immediate goal in pulmonary edema is **volume reduction** and **preload reduction**.
*Increases cardiac contractility and afterload*
- Medications that increase both cardiac contractility and afterload (e.g., some vasopressors) would be detrimental in this setting, as increased afterload would further burden the failing heart and worsen pulmonary congestion.
- This combination is not used to treat acute decompensated heart failure with pulmonary edema.
*Can lead to respiratory depression*
- **Opioids** like morphine can cause respiratory depression and are sometimes used in acute heart failure to reduce preload and anxiety, but they are not the primary cause of the rapid resolution of pulmonary edema and would not be considered the "most likely" medication in this scenario without other indicators.
- While they might provide some symptomatic relief, the *main* intervention for pulmonary edema here points to diuresis.
*Causes venodilation and a decrease in preload*
- **Nitroglycerin** causes venodilation and a decrease in preload, which is beneficial in acute heart failure. However, while it helps alleviate pulmonary congestion via preload reduction, the rapid and significant improvement in pulmonary edema (as suggested by "blunting of costophrenic angles" being mentioned in the initial presentation and the overall improvement in symptoms) points more strongly to the potent fluid removal action of a loop diuretic.
- Though nitroglycerin is often used in combination with diuretics in acute heart failure, a diuretic is the most effective single agent for rapidly addressing the **fluid overload** evident in pulmonary edema.
Thoracic radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 3: A 32-year-old man who recently emigrated from Somalia comes to the physician because of a 4-week history of fever, cough, and chest pain. He has had a 5-kg (11-lb) weight loss over the last 3 months despite no changes in appetite. His temperature is 38.1°C (100.6°F). Physical examination shows enlarged cervical lymph nodes. The lungs are clear to auscultation. The results of an interferon-γ release assay are positive. An x-ray of the chest shows bilateral mediastinal lymphadenopathy. A transbronchial needle aspiration biopsy of a mediastinal lymph node is performed; a photomicrograph of the specimen is shown. The structure indicated by the arrow is most likely comprised of which of the following types of cells?
- A. Natural killer cells
- B. B cells
- C. Fibroblasts
- D. Neutrophils
- E. Macrophages (Correct Answer)
Thoracic radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Macrophages***
- The photomicrograph shows a **granuloma**, characterized by collections of **epithelioid histiocytes** (modified macrophages) and **multinucleated giant cells**, which are essentially fused macrophages.
- This morphology, coupled with the clinical picture of fever, cough, weight loss, positive interferon-γ release assay, and mediastinal lymphadenopathy in a patient from an endemic area, is highly suggestive of **tuberculosis**, a classic granulomatous disease.
*Natural killer cells*
- Natural killer cells are part of the innate immune system and are primarily involved in **killing virally infected cells** and **tumor cells**.
- They are not the primary cellular component forming the characteristic structure of a granuloma.
*B cells*
- B cells are responsible for **antibody production** and antigen presentation.
- While B cells may be present in the periphery of a granuloma, they do not form the core epithelioid and giant cell components.
*Fibroblasts*
- Fibroblasts produce **collagen** and the extracellular matrix, playing a role in **scar formation** and the fibrotic wall that can surround chronic granulomas.
- They do not constitute the primary cellular components of the inflammatory core of a granuloma.
*Neutrophils*
- Neutrophils are typically associated with **acute inflammation** and bacterial infections, characterized by pus formation.
- They are not the predominant cell type in the organized structure of a **granuloma** found in tuberculosis.
Thoracic radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 4: During a thoracotomy procedure, a surgeon needs to access the posterior mediastinum. Which of the following structures forms the anterior boundary of the posterior mediastinum?
- A. Descending thoracic aorta
- B. Pericardial sac (Correct Answer)
- C. Azygos vein
- D. Thoracic vertebrae
- E. Sternum
Thoracic radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Pericardial sac***
- The **pericardial sac** (and the diaphragm, inferiorly) forms the anterior boundary of the **posterior mediastinum** [1].
- This anatomical relationship is crucial for surgeons during thoracotomy to distinguish between the middle and posterior mediastinal compartments [1].
*Descending thoracic aorta*
- The **descending thoracic aorta** is a large vessel located *within* the posterior mediastinum itself, typically running along its left side [2].
- Therefore, it is a content of the posterior mediastinum, not a boundary.
*Azygos vein*
- The **azygos vein** is also a major structure *within* the posterior mediastinum, running along the right side of the vertebral column.
- It is a content, not a boundary, of this compartment.
*Thoracic vertebrae*
- The **thoracic vertebrae** form the *posterior* boundary of the posterior mediastinum [1].
- This anatomical landmark gives the posterior mediastinum its name and defines its dorsal limit.
Thoracic radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 5: A 72-year-old retired shipyard worker received a chest x-ray as part of a routine medical work-up. The radiologist reported incidental findings suggestive of an occupational lung disease. Which of the following descriptions is most consistent with this patient's film?
- A. Hyperinflated lungs with a loss of lung markings
- B. Enlarged hilar lymph nodes
- C. Nodular calcium lesions in the apex of the lung
- D. Fibrocalcific parietal pleural plaques on the diaphragm (Correct Answer)
- E. No specific radiographic findings
Thoracic radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Fibrocalcific parietal pleural plaques on the diaphragm***
- A retired **shipyard worker** has a high likelihood of **asbestos exposure**, which often leads to the development of **pleural plaques**, especially on the diaphragm and parietal pleura.
- These plaques are **fibrocalcific** and are the most common radiographic manifestation of prior asbestos exposure, often found incidentally.
*Hyperinflated lungs with a loss of lung markings*
- This description is characteristic of **emphysema**, specifically the destruction of alveolar walls leading to air trapping and reduced vascular markings.
- While smoking could be common among shipyard workers, this finding does not directly indicate an **occupational lung disease** specific to asbestos exposure.
*Enlarged hilar lymph nodes*
- **Enlarged hilar lymph nodes** are a prominent feature in conditions like **sarcoidosis**, tuberculosis, or certain lymphomas.
- It is not a typical or specific finding for asbestos-related lung disease in the absence of other complications like malignancy.
*Nodular calcium lesions in the apex of the lung*
- **Nodular calcium lesions in the apex of the lung** are highly suggestive of **granulomatous disease**, most commonly **healed primary tuberculosis**.
- This finding is not directly associated with asbestos exposure or other common occupational lung diseases.
*No specific radiographic findings*
- A **chest x-ray** is highly effective in detecting significant asbestos-related changes due to their characteristic appearance.
- Given the patient's occupational history, the absence of specific findings would be less likely if there were any significant asbestos-related changes.
Thoracic radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 6: A 45-year-old man presents for a follow-up visit as part of his immigration requirements into the United States. Earlier this week, he was administered the Mantoux tuberculin skin test (TST). Today’s reading, 3 days after being administered the test, he shows an induration of 10 mm. Given his recent immigration from a country with a high prevalence of tuberculosis, he is requested to obtain a radiograph of the chest, which is shown in the image. Which of the following is true regarding this patient’s chest radiograph (CXR)?
- A. Posterior ribs 9 and 10 are visible only in an expiratory film.
- B. The right lower boundary of the mediastinal silhouette belongs to the right ventricle.
- C. If the spinous process is not in-between the two clavicular heads, the image is repeated. (Correct Answer)
- D. The film is taken in a supine position.
- E. The view is anteroposterior (AP).
Thoracic radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***If the spinous process is not in-between the two clavicular heads, the image is repeated.***
- Proper patient positioning is crucial for an accurate chest X-ray; **rotation of the patient** can distort the appearance of the heart and lungs, simulating pathology or obscuring real findings.
- Symmetrical positioning, indicated by the **spinous process being equidistant from the medial ends of the clavicles**, ensures an ideal posteroanterior (PA) view for interpretation.
*Posterior ribs 9 and 10 are visible only in an expiratory film.*
- In a properly **inspired chest X-ray**, at least 9 or 10 posterior ribs (or 5-6 anterior ribs) should be visible above the diaphragm.
- If fewer ribs are visible on a standard PA film, it indicates a **poor inspiratory effort**, which can compress lung fields and mimic pathology.
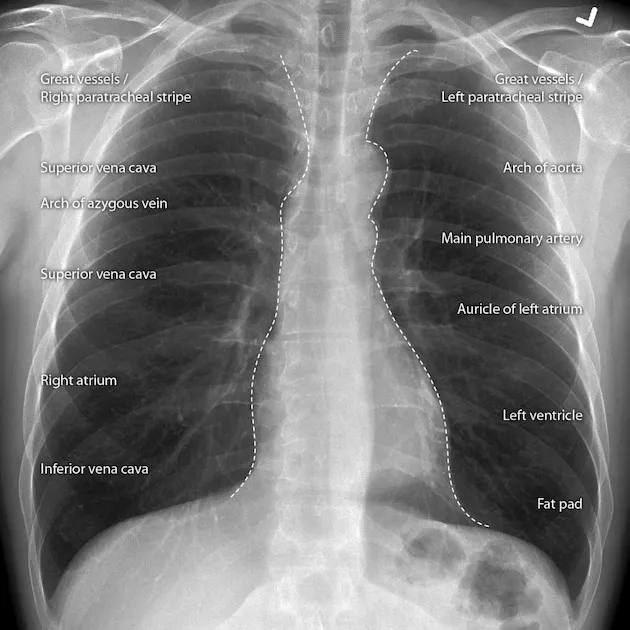
*The right lower boundary of the mediastinal silhouette belongs to the right ventricle.*
- The **right lower boundary of the mediastinal silhouette** is formed by the right atrium, not the right ventricle.
- The right ventricle forms part of the **anterior cardiac border** and is typically not seen as a distinct border on a standard PA chest X-ray.
*The film is taken in a supine position.*
- The presence of the **gastric bubble visible below the left hemidiaphragm** confirms an upright position, as gas rises in the stomach.
- A supine film would typically result in a **magnified cardiac silhouette** and less prominent gastric air.
*The view is anteroposterior (AP).*
- In an AP view, the **medial ends of the clavicles overlay the lung apices**, and the scapulae are often within the lung fields; this image shows the scapulae largely clear of the lung fields, consistent with a PA view.
- AP films also tend to **magnify the heart shadow** due to the divergent X-ray beam, which is not evident here.
Thoracic radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 7: A 72-year-old man is brought to the emergency department after an episode of hemoptysis. He has a chronic cough that is productive of copious sputum. Six years ago, he had a stroke that left him with difficulty swallowing. He smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 40 years, but quit 2 years ago. His respirations are 25/min and labored. Physical examination shows digital clubbing. An x-ray of the chest shows tram track opacities in the lower lung fields. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Aspiration pneumonia
- B. Bronchiectasis (Correct Answer)
- C. Emphysema
- D. Lung cancer
- E. Chronic bronchitis
Thoracic radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Bronchiectasis***
- The combination of **chronic cough with copious sputum**, **hemoptysis**, **digital clubbing**, and **tram track opacities** on chest x-ray is highly characteristic of bronchiectasis.
- The patient's history of difficulty swallowing following a stroke suggests a risk factor for recurrent aspirations leading to chronic infection and airway damage characteristic of bronchiectasis.
*Aspiration pneumonia*
- While the patient has a risk factor for aspiration due to difficulty swallowing, aspiration pneumonia typically presents as an acute infection with fever and infiltrates, rather than chronic symptoms and specific radiographic findings like **tram track opacities** and **digital clubbing**.
- Aspiration pneumonia may lead to bronchiectasis if chronic, but it is not the most definitive diagnosis given the full constellation of findings described.
*Emphysema*
- Emphysema is a form of COPD characterized by destruction of alveolar walls and presents with **dyspnea**, **barrel chest**, and often a history of smoking, but does not typically cause **hemoptysis** or **tram track opacities**.
- Chest x-rays in emphysema usually show **hyperinflation** and **flattened diaphragms**, not specific airway dilation.
*Lung cancer*
- While **hemoptysis** and **chronic cough** can be symptoms of lung cancer, and the patient has a significant smoking history, lung cancer does not typically cause **copious sputum** or **tram track opacities**.
- Although digital clubbing can occur with lung cancer as a paraneoplastic syndrome, the presence of **tram track opacities** is pathognomonic for bronchiectasis and points strongly to this diagnosis.
*Chronic bronchitis*
- Chronic bronchitis is defined by a **chronic productive cough** for at least three months in two consecutive years and is associated with smoking.
- However, it does not typically cause **hemoptysis**, **digital clubbing**, or the specific **tram track opacities** seen on x-ray, which indicate bronchial wall thickening and dilation.
Thoracic radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 8: A 2-year-old child is brought to the emergency department with rapid breathing and a severe cyanotic appearance of his lips, fingers, and toes. He is known to have occasional episodes of mild cyanosis, especially when he is extremely agitated. This is the worst episode of this child’s life, according to his parents. He was born with an APGAR score of 8 via a normal vaginal delivery. His development is considered delayed compared to children of his age. History is significant for frequent squatting after strenuous activity. On auscultation, there is evidence of a systolic ejection murmur at the left sternal border. On examination, his oxygen saturation is 71%, blood pressure is 81/64 mm Hg, respirations are 42/min, pulse is 129/min, and temperature is 36.7°C (98.0°F). Which of the following will most likely be seen on chest x-ray (CXR)?
- A. Egg on a string
- B. Boot-shaped heart (Correct Answer)
- C. Increased pulmonary vascular markings
- D. Cardiomegaly with globular heart
- E. Figure-3 sign
Thoracic radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Boot-shaped heart***
- The patient's presentation with **cyanosis**, **squatting spells**, and a **systolic ejection murmur** is classic for **Tetralogy of Fallot** (TOF).
- A **boot-shaped heart** (Coeur en sabot) on chest X-ray is a characteristic finding in TOF, caused by **right ventricular hypertrophy** and an upturned cardiac apex, leading to a concave pulmonary artery segment.
*Egg on a string*
- This CXR finding is characteristic of **Transposition of the Great Arteries (TGA)**, where the aorta and pulmonary artery are switched, creating an "egg" outline with a narrow vascular pedicle ("string").
- TGA typically presents with severe **cyanosis** from birth and does not usually involve squatting spells or a loud systolic murmur from a prominent **right ventricular outflow tract obstruction**.
*Increased pulmonary vascular markings*
- This finding is common in conditions with **left-to-right shunting** or **increased pulmonary blood flow**, such as a **ventricular septal defect (VSD)** or **patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)**.
- In Tetralogy of Fallot, there is typically **decreased pulmonary blood flow** due to **pulmonic stenosis**, leading to *decreased* pulmonary vascular markings.
*Cardiomegaly with globular heart*
- A **globular heart** is a non-specific finding often associated with **pericardial effusion** or **dilated cardiomyopathy**, where the heart appears enlarged and rounded.
- While TOF can cause cardiomegaly (specifically **right ventricular hypertrophy**), the characteristic shape is "boot-shaped," not globally enlarged or globular.
*Figure-3 sign*
- The **figure-3 sign** on CXR is pathognomonic for **aortic coarctation**, caused by indentation of the aorta at the coarctation site and post-stenotic dilation.
- This condition presents with signs of **heart failure**, **differential cyanosis** (if preductal), and **blood pressure discrepancies** between upper and lower extremities, not the cyanotic spells and squatting seen in this case.
Thoracic radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 9: A 55-year-old man visits the clinic with his wife. He has had difficulty swallowing solid foods for the past 2 months. His wife adds that his voice is getting hoarse but they thought it was due to his recent flu. His medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus for which he is on metformin. He suffered from many childhood diseases due to lack of medical care and poverty. His blood pressure is 125/87 mm Hg, pulse 95/min, respiratory rate 14/min, and temperature 37.1°C (98.7°F). On examination, an opening snap is heard over the cardiac apex. An echocardiogram shows an enlarged cardiac chamber pressing into his esophagus. Changes in which of the following structures is most likely responsible for this patient’s symptoms?
- A. Patent ductus arteriosus
- B. Right ventricle
- C. Left ventricle
- D. Left atrium (Correct Answer)
- E. Right atrium
Thoracic radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Left atrium***
- The patient's symptoms of **dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)** and **hoarseness** suggest compression of anatomical structures by an enlarged cardiac chamber, which the echocardiogram confirms.
- An enlarged **left atrium**, typically due to **mitral stenosis**, can compress the esophagus (leading to dysphagia) and the **recurrent laryngeal nerve** (leading to hoarseness, known as Ortner's syndrome). The **opening snap** at the apex is also highly characteristic of mitral stenosis.
*Patent ductus arteriosus*
- A **patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)** is a congenital heart defect that typically causes a **continuous murmur** and may lead to pulmonary hypertension or heart failure, but not direct compression of the esophagus or recurrent laryngeal nerve.
- The symptoms of PDA are usually present earlier in life, though uncorrected large PDAs can cause symptoms in adulthood, they do not cause dysphagia or hoarseness through direct esophageal compression.
*Right ventricle*
- An enlarged **right ventricle** usually causes symptoms related to right heart failure like **peripheral edema** or **dyspnea** due to pulmonary hypertension.
- It is not anatomically positioned to compress the esophagus or recurrent laryngeal nerve in a way that would cause dysphagia or hoarseness.
*Left ventricle*
- An enlarged **left ventricle** (e.g., due to hypertension or aortic stenosis) primarily causes symptoms like **dyspnea on exertion** or **angina**.
- While a severely dilated left ventricle can displace other structures, it does not typically cause direct esophageal compression leading to dysphagia or recurrent laryngeal nerve compression leading to hoarseness.
*Right atrium*
- An enlarged **right atrium** might be seen in conditions like tricuspid regurgitation or right heart failure but can manifest as **edema** or **jugular venous distention**.
- It is not anatomically positioned to cause dysphagia or hoarseness from esophageal or recurrent laryngeal nerve compression.
Thoracic radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 10: An 18-year-old man is brought to the emergency department 30 minutes after being stabbed in the chest during a fight. He has no other injuries. His pulse is 120/min, blood pressure is 90/60 mm Hg, and respirations are 22/min. Examination shows a 4-cm deep, straight stab wound in the 4th intercostal space 2 cm medial to the right midclavicular line. The knife most likely passed through which of the following structures?
- A. Serratus anterior muscle, pleura, inferior vena cava
- B. External oblique muscle, superior epigastric artery, azygos vein
- C. Pectoralis minor muscle, dome of the diaphragm, right lobe of the liver
- D. Intercostal muscles, internal thoracic artery, right heart
- E. Pectoral fascia, transversus thoracis muscle, right lung (Correct Answer)
Thoracic radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Pectoral fascia, transversus thoracis muscle, right lung***
* The stab wound is in the **4th intercostal space**, 2 cm medial to the right midclavicular line, placing it over the anterior chest wall. This trajectory would first penetrate the **pectoral fascia**.
* Deeper structures in this region include the **transversus thoracis muscle** and, given the depth, the **right lung** as it extends superiorly behind the anterior chest wall.
* *Serratus anterior muscle, pleura, inferior vena cava*
* The **serratus anterior muscle** is more laterally positioned, typically covering the side of the rib cage.
* The **inferior vena cava** is located more medially and posteriorly within the mediastinum, deep to the diaphragm, making it an unlikely target for an anterior 4th intercostal stab.
* *External oblique muscle, superior epigastric artery, azygos vein*
* The **external oblique muscle** is part of the abdominal wall and would not be penetrated in the 4th intercostal space.
* The **superior epigastric artery** is lower, typically extending into the abdominal wall, and the **azygos vein** is in the posterior mediastinum, not in the path of this superficial anterior stab wound.
* *Pectoralis minor muscle, dome of the diaphragm, right lobe of the liver*
* The **pectoralis minor muscle** is located deep to the pectoralis major, which would be penetrated. However, a stab at the 4th intercostal space would be too high to directly involve the **dome of the diaphragm** or the **right lobe of the liver**, which are typically below the 5th intercostal space, especially in forced expiration.
* *Intercostal muscles, internal thoracic artery, right heart*
* The **intercostal muscles** would certainly be traversed.
* However, the **internal thoracic artery** runs paramedially (about 1-2 cm from the sternum), and getting to the **right heart** would require a more medial and deeper trajectory, potentially causing immediate tamponade or severe hemorrhage.
More Thoracic radiologic landmarks US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.