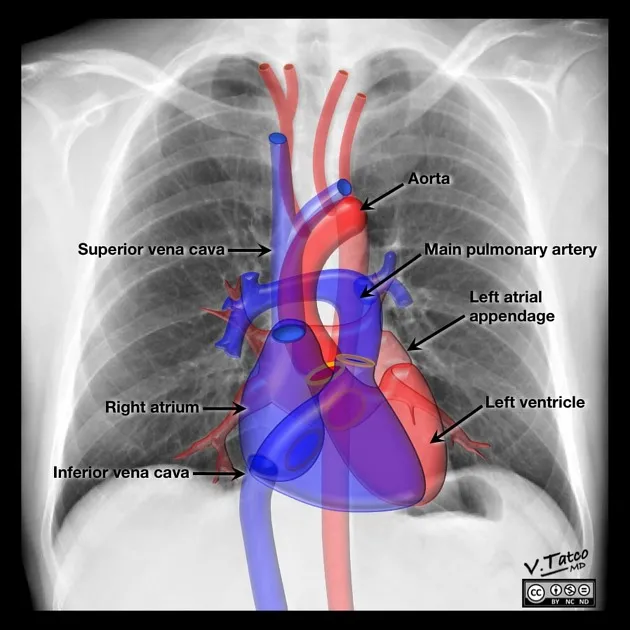
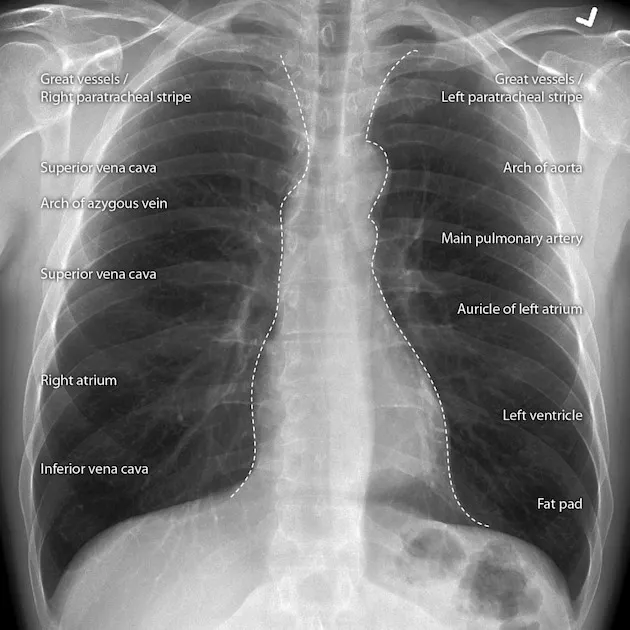
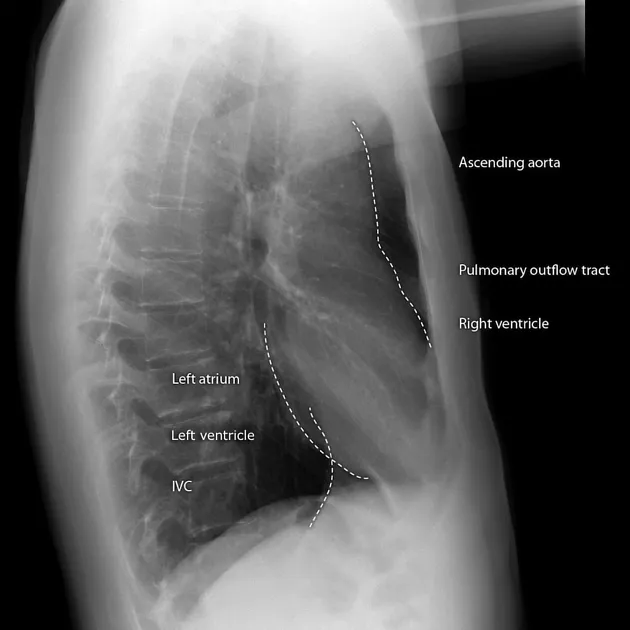
Cardiac radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Cardiac radiologic landmarks. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Cardiac radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 1: A 52-year-old man presents to a medical clinic to establish care. He has no known chronic illnesses but has not seen a physician in over 20 years. He generally feels well but occasionally has shortness of breath when he jogs and exercises. He smokes 2-5 cigarettes per day and uses IV heroin “now and then.” Physical exam is unremarkable. ECG shows prominent QRS voltage and left axis deviation. Trans-thoracic echocardiogram shows mild concentric left ventricular hypertrophy but is otherwise normal. Which of the following is the most likely etiology of the echocardiogram findings?
- A. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- B. Pulmonary hypertension
- C. Aortic regurgitation
- D. Systemic hypertension (Correct Answer)
- E. Mitral stenosis
Cardiac radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Systemic hypertension***
- Chronic **systemic hypertension** is a common cause of **concentric left ventricular hypertrophy** due to increased afterload, which the left ventricle must overcome.
- The ECG findings of **prominent QRS voltage** and **left axis deviation** are also consistent with left ventricular hypertrophy, supporting chronic hypertension as the most likely cause.
*Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease*
- COPD primarily affects the lungs and typically leads to **right ventricular hypertrophy** (cor pulmonale) due to increased pulmonary vascular resistance, not left ventricular hypertrophy.
- While smoking is a risk factor for COPD, the patient's echocardiogram shows left, not right, heart changes.
*Pulmonary hypertension*
- Pulmonary hypertension causes increased afterload on the **right ventricle**, leading to **right ventricular hypertrophy**, not left ventricular hypertrophy.
- The echocardiogram specifically reports **left ventricular hypertrophy**.
*Aortic regurgitation*
- **Aortic regurgitation** leads to **volume overload** of the left ventricle, causing **eccentric left ventricular hypertrophy** (dilation along with thickening), not concentric hypertrophy.
- The echocardiogram finding of **concentric** (symmetric thickening without significant dilation) hypertrophy points away from aortic regurgitation.
*Mitral stenosis*
- **Mitral stenosis** causes increased pressure in the **left atrium** and **pulmonary circulation**, which can eventually lead to **right ventricular hypertrophy**, not left ventricular hypertrophy.
- It would not explain the **concentric left ventricular hypertrophy** noted in the echocardiogram.
Cardiac radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 2: A 42-year-old woman comes to the physician because of 2 episodes of loss of consciousness over the past week. She recovered immediately and was not confused following the episodes. During the past 5 months, she has also had increased shortness of breath and palpitations. She has been unable to carry out her daily activities. She also reports some chest tightness that resolves with rest. She has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. She immigrated with her family from India 10 years ago. Her temperature is 37.3°C (99.1°F), pulse is 115/min and irregular, and blood pressure is 108/70 mm Hg. Examination shows jugular venous distention and pitting edema below the knees. Bilateral crackles are heard at the lung bases. Cardiac examination shows an accentuated and split S2. There is an opening snap followed by a low-pitched diastolic murmur in the fifth left intercostal space at the midclavicular line. An ECG shows atrial fibrillation and right axis deviation. Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of these findings?
- A. Increased left ventricular end diastolic pressure
- B. Increased left to right shunting
- C. Increased systemic arterial resistance
- D. Increased left atrial pressure (Correct Answer)
- E. Decreased left ventricular contractility
Cardiac radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Increased left atrial pressure***
- The patient's symptoms (dyspnea, palpitations, chest tightness, volume overload signs like JVD, edema, crackles) and cardiac findings (**accentuated S2, opening snap, diastolic murmur**) are highly suggestive of **mitral stenosis**.
- **Mitral stenosis** causes obstruction of blood flow from the left atrium to the left ventricle, leading to a significant increase in **left atrial pressure** to maintain cardiac output, which can then cause atrial fibrillation and pulmonary hypertension.
*Increased left ventricular end diastolic pressure*
- This is typically seen in conditions like **aortic stenosis**, **aortic regurgitation**, or **decompensated heart failure** where the left ventricle is distended or failing.
- The patient's presentation with an **opening snap** and **diastolic murmur** points away from primary left ventricular pathology causing elevated LVEDP, and more towards a valvular issue upstream.
*Increased left to right shunting*
- This typically occurs in **septal defects** (e.g., VSD, ASD, PDA) and would lead to symptoms of pulmonary hypertension and right heart strain, but the specific murmur and opening snap are not characteristic of a shunt.
- While it can cause right ventricular hypertrophy and pulmonary hypertension, the classic auscultatory findings are distinct from those described here.
*Increased systemic arterial resistance*
- This is characteristic of **hypertension** or conditions causing systemic vasoconstriction, which primarily affect afterload on the left ventricle.
- While it can lead to left ventricular hypertrophy over time, it does not explain the specific findings of an **opening snap** and **diastolic murmur**, or the symptoms of pulmonary congestion in this context.
*Decreased left ventricular contractility*
- This would lead to **systolic heart failure** with reduced ejection fraction, causing symptoms like fatigue and dyspnea, and often a **S3 gallop** with a systolic murmur if mitral regurgitation develops.
- However, it does not explain the specific auscultatory findings of an **opening snap** and **diastolic murmur** that are pathognomonic for mitral stenosis.
Cardiac radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 3: A tall, slender 32-year-old man comes to the emergency room because of sudden chest pain, cough, and shortness of breath. On physical examination, he has decreased breath sounds on the right. Chest radiography shows translucency on the right side of his chest. His pCO2 is elevated and pO2 is decreased. What is the most likely cause of his symptoms?
- A. Spontaneous pneumothorax (Correct Answer)
- B. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
- C. Tension pneumothorax
- D. Asthma
- E. Pneumonia
Cardiac radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Spontaneous pneumothorax***
- The patient's presentation with **sudden chest pain**, **cough**, and **shortness of breath** in a **tall, slender young man** is classic for a primary spontaneous pneumothorax.
- **Decreased breath sounds** on the affected side and **translucency on chest X-ray** (indicating air in the pleural space) further support this diagnosis.
*Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease*
- COPD typically affects older individuals with a history of smoking and presents with **chronic progressive dyspnea**, not sudden onset.
- While COPD can lead to secondary spontaneous pneumothorax, the patient's age and lack of pre-existing lung disease make this less likely as the primary cause.
*Tension pneumothorax*
- A tension pneumothorax is a **life-threatening condition causing mediastinal shift** and severe hemodynamic compromise (e.g., hypotension, tracheal deviation) which are not described.
- While it shares some features, the absence of these critical signs means a simple spontaneous pneumothorax is more likely first.
*Asthma*
- Asthma presents with **episodic wheezing**, cough, and shortness of breath, often triggered by allergens or exercise.
- The sudden onset of symptoms with **decreased localized breath sounds** and radiological findings of transparencies do not align with typical asthma exacerbations.
*Pneumonia*
- Pneumonia usually involves **fever, productive cough, and localized crackles** or bronchial breath sounds on examination.
- Chest X-rays in pneumonia show **infiltrates or consolidation**, which contrast with the translucency seen in this case.
Cardiac radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 4: A 64-year-old man presents to the office for an annual physical examination. He has no complaints at this visit. His chart states that he has a history of hypertension, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (emphysema), Raynaud’s disease, and glaucoma. He is a 30 pack-year smoker. His medications included lisinopril, tiotropium, albuterol, nifedipine, and latanoprost. The blood pressure is 139/96 mm Hg, the pulse is 86/min, the respiration rate is 16/min, and the temperature is 37.2°C (99.1°F). On physical examination, his pupils are equal, round, and reactive to light. The cardiac auscultation reveals an S4 gallop without murmur, and the lungs are clear to auscultation bilaterally. However, the inspection of the chest wall shows an enlarged anterior to posterior diameter. Which of the following is the most appropriate screening test for this patient?
- A. Low-dose CT (Correct Answer)
- B. Bronchoalveolar lavage with cytology
- C. Magnetic resonance imaging
- D. Pulmonary function tests
- E. Chest radiograph
Cardiac radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Low-dose CT***
- This patient, a 64-year-old with a 30 pack-year smoking history and current emphysema (COPD), falls precisely within the **high-risk criteria** for lung cancer screening.
- The **USPSTF guidelines** recommend annual **low-dose computed tomography (LDCT)** for individuals aged 50-80 years with a 20 pack-year smoking history who currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years.
*Bronchoalveolar lavage with cytology*
- This is an **invasive diagnostic procedure** used to collect cells and fluid directly from the airways, typically performed when there is already suspicion of a lung malignancy or infection.
- It is not a recommended **screening test** for asymptomatic individuals due to its invasiveness and the absence of clear evidence of benefit as a primary screening tool.
*Magnetic resonance imaging*
- **MRI** is primarily used for evaluating soft tissue structures, defining tumor extent, and assessing metastatic disease, but it is **not the preferred imaging modality for lung cancer screening** due to its lower spatial resolution for pulmonary nodules compared to CT and higher cost.
- It involves longer scan times and is not routinely used for primary lung screening.
*Pulmonary function tests*
- **PFTs** are used to assess lung function, diagnose and monitor respiratory conditions like COPD, and evaluate the severity of airflow obstruction.
- While important for managing his **emphysema**, PFTs do not directly screen for **lung cancer**; they measure how well the lungs work.
*Chest radiograph*
- A **chest X-ray** is less sensitive than LDCT for detecting small lung nodules and early-stage lung cancer due to its two-dimensional nature and potential for superimposition of structures.
- While readily available and less expensive, it is **not recommended for lung cancer screening** as it has not shown a mortality benefit in randomized controlled trials compared to no screening.
Cardiac radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 5: A young researcher is responsible for graphing laboratory data involving pulmonary blood flow and ventilation pattern obtained from a healthy volunteer who was standing in an upright position. After plotting the following graph, the researcher realizes he forgot to label the curves and the x-axis (which represents the position in the lung). Which of the following is the appropriate label for each point on the graph?
- A. A: Ventilation B: Blood flow C: Base of the lung D: Apex of the lung (Correct Answer)
- B. A: Ventilation B: Blood flow C: Mid-portion of the lung D: Apex of the lung
- C. A: Dead Space B: Shunt C: Base of the lung D: Apex of the lung
- D. A: Blood flow B: Ventilation C: Base of the lung D: Lung hilum
- E. A: Blood flow B: Ventilation C: Apex of the lung D: Lung hilum
Cardiac radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***A: Ventilation B: Blood flow C: Base of the lung D: Apex of the lung***
- In an upright individual, both **ventilation** and **blood flow** are greater at the **base of the lung** than at the apex due to gravity.
- However, the increase in **perfusion** from apex to base (curve B) is proportionally much greater than the increase in **ventilation** (curve A), leading to a higher V/Q ratio at the apex and a lower V/Q ratio at the base.
*A: Ventilation B: Blood flow C: Mid-portion of the lung D: Apex of the lung*
- This option correctly identifies curves A and B but incorrectly labels C as the **mid-portion of the lung** instead of the base.
- The x-axis represents the lung from base to apex or vice-versa, and the curve indicates the highest values at C.
*A: Dead Space B: Shunt C: Base of the lung D: Apex of the lung*
- This option incorrectly identifies curves A and B; they represent **ventilation** and **blood flow**, not dead space and shunt, which are concepts related to V/Q mismatch.
- **Dead space** refers to ventilated but unperfused areas, while a **shunt** is perfused but unventilated.
*A: Blood flow B: Ventilation C: Base of the lung D: Lung hilum*
- This option incorrectly reverses the labels for curves A and B, as **blood flow** increases more steeply than **ventilation** towards the base.
- The x-axis represents the lung position from base to apex, not the **hilum**, which is a specific anatomical region.
*A: Blood flow B: Ventilation C: Apex of the lung D: Lung hilum*
- This option incorrectly reverses the labels for curves A and B, in addition to mislabeling C as the **apex of the lung**, where values are lowest, not highest.
- The X-axis represents the lung position from base to apex, not focusing on the **hilum**.
Cardiac radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 6: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Cardiac radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
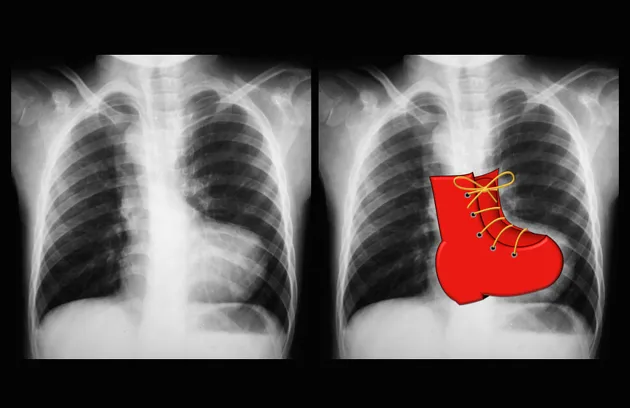
Cardiac radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 7: A 2-year-old child is brought to the emergency department with rapid breathing and a severe cyanotic appearance of his lips, fingers, and toes. He is known to have occasional episodes of mild cyanosis, especially when he is extremely agitated. This is the worst episode of this child’s life, according to his parents. He was born with an APGAR score of 8 via a normal vaginal delivery. His development is considered delayed compared to children of his age. History is significant for frequent squatting after strenuous activity. On auscultation, there is evidence of a systolic ejection murmur at the left sternal border. On examination, his oxygen saturation is 71%, blood pressure is 81/64 mm Hg, respirations are 42/min, pulse is 129/min, and temperature is 36.7°C (98.0°F). Which of the following will most likely be seen on chest x-ray (CXR)?
- A. Egg on a string
- B. Boot-shaped heart (Correct Answer)
- C. Increased pulmonary vascular markings
- D. Cardiomegaly with globular heart
- E. Figure-3 sign
Cardiac radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Boot-shaped heart***
- The patient's presentation with **cyanosis**, **squatting spells**, and a **systolic ejection murmur** is classic for **Tetralogy of Fallot** (TOF).
- A **boot-shaped heart** (Coeur en sabot) on chest X-ray is a characteristic finding in TOF, caused by **right ventricular hypertrophy** and an upturned cardiac apex, leading to a concave pulmonary artery segment.
*Egg on a string*
- This CXR finding is characteristic of **Transposition of the Great Arteries (TGA)**, where the aorta and pulmonary artery are switched, creating an "egg" outline with a narrow vascular pedicle ("string").
- TGA typically presents with severe **cyanosis** from birth and does not usually involve squatting spells or a loud systolic murmur from a prominent **right ventricular outflow tract obstruction**.
*Increased pulmonary vascular markings*
- This finding is common in conditions with **left-to-right shunting** or **increased pulmonary blood flow**, such as a **ventricular septal defect (VSD)** or **patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)**.
- In Tetralogy of Fallot, there is typically **decreased pulmonary blood flow** due to **pulmonic stenosis**, leading to *decreased* pulmonary vascular markings.
*Cardiomegaly with globular heart*
- A **globular heart** is a non-specific finding often associated with **pericardial effusion** or **dilated cardiomyopathy**, where the heart appears enlarged and rounded.
- While TOF can cause cardiomegaly (specifically **right ventricular hypertrophy**), the characteristic shape is "boot-shaped," not globally enlarged or globular.
*Figure-3 sign*
- The **figure-3 sign** on CXR is pathognomonic for **aortic coarctation**, caused by indentation of the aorta at the coarctation site and post-stenotic dilation.
- This condition presents with signs of **heart failure**, **differential cyanosis** (if preductal), and **blood pressure discrepancies** between upper and lower extremities, not the cyanotic spells and squatting seen in this case.
Cardiac radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 8: A 55-year-old man visits the clinic with his wife. He has had difficulty swallowing solid foods for the past 2 months. His wife adds that his voice is getting hoarse but they thought it was due to his recent flu. His medical history is significant for type 2 diabetes mellitus for which he is on metformin. He suffered from many childhood diseases due to lack of medical care and poverty. His blood pressure is 125/87 mm Hg, pulse 95/min, respiratory rate 14/min, and temperature 37.1°C (98.7°F). On examination, an opening snap is heard over the cardiac apex. An echocardiogram shows an enlarged cardiac chamber pressing into his esophagus. Changes in which of the following structures is most likely responsible for this patient’s symptoms?
- A. Patent ductus arteriosus
- B. Right ventricle
- C. Left ventricle
- D. Left atrium (Correct Answer)
- E. Right atrium
Cardiac radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Left atrium***
- The patient's symptoms of **dysphagia (difficulty swallowing)** and **hoarseness** suggest compression of anatomical structures by an enlarged cardiac chamber, which the echocardiogram confirms.
- An enlarged **left atrium**, typically due to **mitral stenosis**, can compress the esophagus (leading to dysphagia) and the **recurrent laryngeal nerve** (leading to hoarseness, known as Ortner's syndrome). The **opening snap** at the apex is also highly characteristic of mitral stenosis.
*Patent ductus arteriosus*
- A **patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)** is a congenital heart defect that typically causes a **continuous murmur** and may lead to pulmonary hypertension or heart failure, but not direct compression of the esophagus or recurrent laryngeal nerve.
- The symptoms of PDA are usually present earlier in life, though uncorrected large PDAs can cause symptoms in adulthood, they do not cause dysphagia or hoarseness through direct esophageal compression.
*Right ventricle*
- An enlarged **right ventricle** usually causes symptoms related to right heart failure like **peripheral edema** or **dyspnea** due to pulmonary hypertension.
- It is not anatomically positioned to compress the esophagus or recurrent laryngeal nerve in a way that would cause dysphagia or hoarseness.
*Left ventricle*
- An enlarged **left ventricle** (e.g., due to hypertension or aortic stenosis) primarily causes symptoms like **dyspnea on exertion** or **angina**.
- While a severely dilated left ventricle can displace other structures, it does not typically cause direct esophageal compression leading to dysphagia or recurrent laryngeal nerve compression leading to hoarseness.
*Right atrium*
- An enlarged **right atrium** might be seen in conditions like tricuspid regurgitation or right heart failure but can manifest as **edema** or **jugular venous distention**.
- It is not anatomically positioned to cause dysphagia or hoarseness from esophageal or recurrent laryngeal nerve compression.
Cardiac radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 9: A 45-year-old woman comes to the physician because of progressive difficulty swallowing solids and liquids over the past 4 months. She has lost 4 kg (9 lb) during this period. There is no history of serious illness. She emigrated to the US from Panama 7 years ago. She does not smoke cigarettes or drink alcohol. Cardiopulmonary examination shows a systolic murmur and an S3 gallop. A barium radiograph of the chest is shown. Histopathologic examination of the esophageal wall is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Presence of intranuclear basophilic inclusions
- B. Atrophy of esophageal smooth muscle cells
- C. Infiltration of eosinophils in the epithelium
- D. Presence of metaplastic columnar epithelium
- E. Absence of myenteric plexus neurons (Correct Answer)
Cardiac radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Absence of myenteric plexus neurons***
- This finding is pathognomonic for **Chagas disease** (American trypanosomiasis), caused by *Trypanosoma cruzi*, endemic to Central and South America including Panama.
- The parasite destroys the **myenteric (Auerbach's) plexus neurons** in the esophageal wall, disrupting normal peristalsis and leading to **megaesophagus**.
- This results in **progressive dysphagia for both solids and liquids** and weight loss, as seen in this patient.
- The **cardiac findings** (systolic murmur and S3 gallop) indicate associated **chagasic cardiomyopathy**, another manifestation of chronic Chagas disease.
*Presence of intranuclear basophilic inclusions*
- Suggestive of **cytomegalovirus (CMV) esophagitis**, typically seen in immunocompromised patients (HIV/AIDS, transplant recipients).
- This patient has no immunocompromised state, and CMV does not cause the cardiac manifestations or chronic megaesophagus seen here.
*Atrophy of esophageal smooth muscle cells*
- Not characteristic of Chagas disease or achalasia; these conditions typically show **smooth muscle hypertrophy** due to chronic obstruction.
- Muscle atrophy would not explain the dysphagia, megaesophagus, or cardiac findings.
*Infiltration of eosinophils in the epithelium*
- Indicates **eosinophilic esophagitis**, an allergic condition usually presenting with food impaction and dysphagia mainly for solids.
- Would not explain the cardiac manifestations or the epidemiological connection to Panama.
*Presence of metaplastic columnar epithelium*
- Represents **Barrett's esophagus**, a complication of chronic gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD).
- The patient's presentation with dysphagia for both solids and liquids, cardiac disease, and megaesophagus on barium study points to a **motility disorder** (Chagas disease), not reflux disease.
Cardiac radiologic landmarks US Medical PG Question 10: A 70-year-old woman presents with substernal chest pain. She says that the symptoms began 2 hours ago and have not improved. She describes the pain as severe, episodic, and worse with exertion. She reports that she has had multiple similar episodes that have worsened and increased in frequency over the previous 4 months. Past medical history is significant for diabetes and hypertension, both managed medically. The vital signs include temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), blood pressure 150/100 mm Hg, pulse 80/min, and respiratory rate 15/min. Her serum total cholesterol is 280 mg/dL and high-density lipoprotein (HDL) is 30 mg/dL. The electrocardiogram (ECG) shows ST-segment depression on multiple chest leads. Coronary angiography reveals 75% narrowing of her left main coronary artery. In which of the following anatomical locations is a mural thrombus most likely to form in this patient?
- A. Left ventricle (Correct Answer)
- B. Left atrium
- C. Aorta
- D. Right atrium
- E. Right ventricle
Cardiac radiologic landmarks Explanation: ***Left ventricle***
- The patient presents with symptoms and ECG findings consistent with **unstable angina** or **non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI)**, indicating myocardial ischemia.
- With **75% left main coronary artery stenosis**, there is high risk of progression to **transmural myocardial infarction (STEMI)**, particularly affecting the anterior wall and septum.
- Mural thrombi in the left ventricle typically form **3-7 days post-infarction** in areas of **dyskinetic or akinetic myocardium** due to blood stasis, endocardial injury, and hypercoagulability (Virchow's triad).
- Left main disease affecting such a large territory makes the **left ventricle the most likely site** for mural thrombus formation.
*Left atrium*
- Mural thrombi in the left atrium are most commonly associated with **atrial fibrillation** due to blood stasis in the **left atrial appendage**.
- This patient's symptoms are characteristic of coronary artery disease affecting the left ventricle, not an atrial arrhythmia.
*Aorta*
- While thrombi can form in the aorta (e.g., in the setting of **atherosclerosis** or **aneurysms**), they are typically mural thrombi associated with specific vascular pathologies.
- The symptoms of **chest pain, ST depression**, and **coronary artery narrowing** point toward a myocardial event, making the left ventricle the most likely site for mural thrombus in this clinical context.
*Right atrium*
- Thrombi in the right atrium are usually associated with conditions leading to **venous stasis, such as deep vein thrombosis**, **central venous catheters**, or **right-sided heart failure**.
- The patient's presentation with exertional chest pain and left main coronary artery narrowing is unrelated to right atrial thrombosis.
*Right ventricle*
- The right ventricle is **much less commonly** affected by ischemic events leading to mural thrombi compared to the left ventricle, due to its **lower oxygen demand** and **different blood supply** (right coronary artery).
- While right ventricular infarction can occur (usually with inferior MI), the **left main coronary artery** supplies the left ventricle, making it the primary concern for mural thrombus formation in this patient.
More Cardiac radiologic landmarks US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.