Radiologic landmarks

On this page
🎯 Radiologic Landmark Mastery: Your Imaging Navigation System
Radiologic landmarks transform chaotic shadows on imaging into precise anatomical coordinates, enabling you to navigate the body with confidence across every plane and modality. You'll master the vertebral markers that anchor spinal localization, decode thoracic structures on chest films, map abdominal viscera through reliable reference points, and identify pelvic architecture that grounds lower body imaging. By integrating these landmarks across CT, MRI, and plain radiographs, you'll build the spatial fluency that separates novice image-gazers from clinicians who see pathology in context and communicate findings with surgical precision.
📌 Remember: SLAP - Skeletal, Lines, Angles, Planes - The four fundamental categories of radiologic landmarks that organize every imaging interpretation
Essential Landmark Categories
- Skeletal Landmarks
- Bony prominences: C7 spinous process (vertebra prominens)
- Joint spaces: L4-L5 disc at iliac crest level
- Growth plates: Visible until age 16-18 years in long bones
- Epiphyseal fusion timing varies by location
- Delayed closure indicates endocrine disorders
- Soft Tissue Lines
- Fascial planes: Prevertebral soft tissue <7mm at C2
- Organ boundaries: Psoas muscle margins on abdominal CT
- Vascular contours: Aortic knob prominence on chest X-ray
- Normal aortic diameter: <3.5cm at root level
- Age-related dilatation: 1mm per decade after age 40
| Landmark Type | Location | Normal Measurement | Clinical Significance | Age Variation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Atlantodental Interval | C1-C2 | <3mm adults, <5mm children | Cervical instability screening | Decreases with age |
| Iliopectineal Line | Pelvis | Smooth continuous arc | Acetabular fracture assessment | Unchanged |
| Spinolaminar Line | Cervical spine | Smooth lordotic curve | Ligamentous injury detection | Straightens with age |
| Cardiac Silhouette | Chest | <50% thoracic width | Cardiomegaly screening | Increases slightly |
| Bowel Gas Pattern | Abdomen | <3cm small bowel | Obstruction evaluation | Unchanged |
Systematic Landmark Recognition Framework
- Primary Survey Landmarks
- ABC approach: Airways, Bones, Cardiac silhouette
- Symmetry assessment: Bilateral comparison of paired structures
- Alignment evaluation: Continuous lines and smooth curves
- Cervical spine: 4 lordotic curves must be intact
- Thoracic spine: Posterior vertebral line alignment
- Secondary Survey Details
- Soft tissue analysis: Swelling patterns and fat pad displacement
- Joint space evaluation: Uniform width and parallel surfaces
- Trabecular patterns: Bone density and architectural integrity
- Normal trabecular spacing: 1-2mm intervals
- Osteoporotic changes: >30% bone loss before radiographic detection
💡 Master This: Every radiologic interpretation follows the "Lines, Angles, Spaces" principle - disruption of normal geometric relationships indicates pathology with >85% diagnostic accuracy
⭐ Clinical Pearl: The teardrop sign on lateral cervical spine represents the anteroinferior corner of the vertebral body - its absence indicates >95% probability of compression fracture
Connect these foundational landmark principles through systematic pattern recognition to understand how anatomical relationships guide diagnostic accuracy.
🎯 Radiologic Landmark Mastery: Your Imaging Navigation System
🗺️ Spinal Navigation: The Vertebral Roadmap System
📌 Remember: C3-4-5 Keeps the Diaphragm Alive - Critical cervical levels for respiratory function, with C4 as the primary phrenic nerve origin
Cervical Spine Landmark Hierarchy
- Upper Cervical Complex (C1-C2)
- Atlas (C1): No vertebral body, lateral masses only
- Axis (C2): Odontoid process extends superiorly 15-20mm
- Atlantodental interval: <3mm adults, <5mm children
- Increased distance indicates transverse ligament rupture
- Associated with >50% mortality in acute trauma
- Mid-Cervical Region (C3-C6)
- Uniform vertebral body height: 12-15mm anterior dimension
- Facet joint orientation: 45-degree angle to horizontal
- Uncovertebral joints: Unique to cervical spine, C3-C7
- Degenerative changes cause foraminal stenosis
- >2mm osteophyte formation clinically significant
| Cervical Level | Key Landmark | Normal Measurement | Clinical Correlation | Pathology Threshold |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1-C2 | Atlantodental interval | <3mm | Ligamentous stability | >5mm unstable |
| C2-C3 | First disc space | 4-6mm height | Degenerative changes | <2mm collapse |
| C3-C4 | Phrenic nerve origin | 45° facet angle | Respiratory function | Subluxation risk |
| C6-C7 | Cricoid cartilage level | 6-8mm prevertebral | Airway assessment | >10mm hematoma |
| C7-T1 | Vertebra prominens | Prominent spinous | Level identification | Transition zone |
Thoracolumbar Landmark Correlations
- Thoracic Reference Points
- T3 level: Aortic arch and carina bifurcation
- T6 level: Xiphoid process and right atrium border
- T10 level: Esophagogastric junction passage through diaphragm
- Hiatal hernia assessment reference point
- T10-T11: Most common thoracic compression fracture site
- Lumbar Identification System
- L4-L5 disc: Iliac crest line intersection (Tuffier's line)
- L5-S1 junction: Posterior superior iliac spine level
- Conus medullaris: Terminates at L1-L2 level in adults
- >L3 termination indicates tethered cord syndrome
- Lumbar puncture safety: Below L3-L4 level only

💡 Master This: The thoracolumbar junction (T12-L1) represents the transition from kyphotic to lordotic curvature - the most biomechanically stressed region with 40% of all spinal fractures
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Chance fractures occur predominantly at L1-L2 level in seatbelt injuries, with >80% association with intra-abdominal organ damage requiring immediate surgical evaluation
Connect spinal landmark mastery through thoracic imaging principles to understand how chest radiography builds upon vertebral reference systems.
🗺️ Spinal Navigation: The Vertebral Roadmap System
📸 Thoracic Imaging Architecture: The Chest X-Ray Blueprint
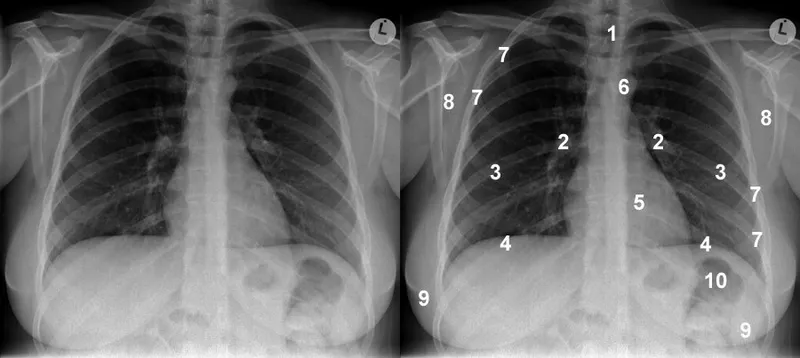
📌 Remember: ABCDEFGHI - Airway, Bones, Cardiac, Diaphragm, Effusion, Fields, Gastric, Hila, Implants - Systematic chest X-ray evaluation sequence
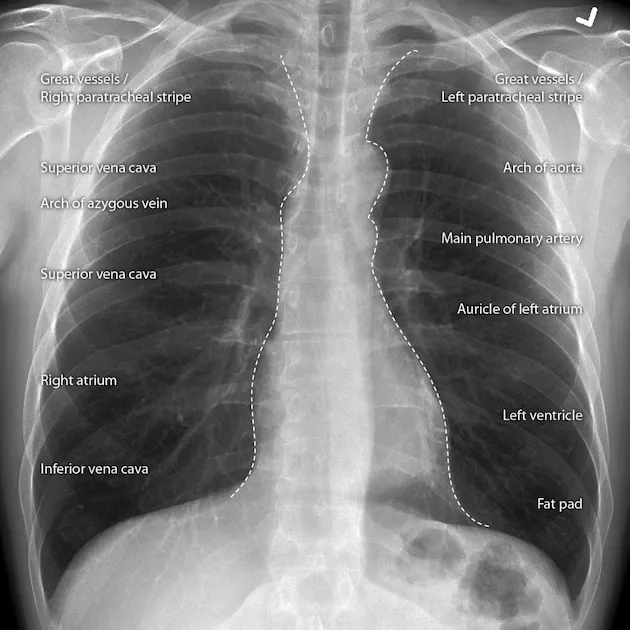
Cardiac Silhouette Landmark System
- Right Heart Border Components
- Superior segment: Superior vena cava - straight vertical line
- Middle segment: Right atrium - gentle convex curve
- Inferior segment: Inferior vena cava - short vertical segment
- Right atrial enlargement: Increased convexity >50% thoracic width
- Cardiothoracic ratio: Normal <50% on PA view
- Left Heart Border Architecture
- Aortic knob: T4 level, <4cm diameter in adults
- Pulmonary artery segment: Concave in normal adults
- Left atrial appendage: Not visible when normal size
- Straightening indicates left atrial enlargement
- Double density sign: >95% specific for LA dilation
| Cardiac Structure | Normal Appearance | Measurement Threshold | Enlargement Pattern | Clinical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Right Atrium | Gentle convex curve | <50% CT ratio | Increased convexity | Tricuspid disease |
| Left Atrium | Concave border | <7cm on lateral | Double density sign | Mitral valve disease |
| Left Ventricle | Rounded apex | <5.5cm from midline | Downward displacement | Systolic dysfunction |
| Aortic Arch | Prominent knob | <4cm diameter | Increased prominence | Hypertension/aging |
| Pulmonary Artery | Concave segment | <2.7cm diameter | Convex bulging | Pulmonary hypertension |
Mediastinal Contour Recognition
- Superior Mediastinum Landmarks
- Aortopulmonary window: Concave interface between aorta and pulmonary artery
- Azygos vein: <10mm diameter on upright PA view
- Paratracheal stripe: <4mm width, right-sided
- Widening >5mm indicates lymphadenopathy or edema
- Loss of definition: >90% sensitive for mediastinal pathology
- Hilar Architecture Assessment
- Left hilum: 1-2cm higher than right hilum normally
- Hilar overlay sign: Vessels visible through hilar masses
- Silhouette sign: Loss of normal borders indicates adjacent pathology
- Right heart border loss: Right middle lobe pathology
- Left heart border loss: Lingular or left lower lobe disease
💡 Master This: The silhouette sign principle - loss of normal anatomical borders occurs only when pathology is anatomically contiguous with the structure, enabling precise lobar localization of pulmonary disease
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Hilar enlargement >3cm in diameter has >85% specificity for malignancy in patients over 40 years, requiring immediate CT evaluation for staging
Connect thoracic landmark expertise through abdominal imaging principles to understand how organ localization builds upon systematic anatomical correlation.
📸 Thoracic Imaging Architecture: The Chest X-Ray Blueprint
🎯 Abdominal Terrain Mapping: The Visceral Coordinate System
📌 Remember: LIVER - L1 (Celiac), I2 (SMA), V3 (Renal), E4 (Bifurcation), R5 (Iliac) - Major vascular landmarks by vertebral level
Vertebral Level Organ Correlations
- Upper Abdominal Landmarks (T12-L2)
- T12-L1 level: Celiac trunk origin, liver hilum
- L1 level: Pancreatic body, splenic hilum
- L1-L2 level: Superior mesenteric artery origin
- SMA-aorta angle: Normal 38-65 degrees
- <25 degrees: Superior mesenteric artery syndrome
- Aortomesenteric distance: Normal 10-28mm
- Mid-Abdominal Reference Points (L2-L4)
- L2 level: Renal vessel origins, inferior vena cava formation
- L3 level: Umbilicus surface landmark
- L3-L4 level: Iliac crest line (Tuffier's line)
- Lumbar puncture safe zone below this level
- Retroperitoneal bleeding assessment reference
| Vertebral Level | Vascular Landmark | Organ Correlation | Surface Anatomy | Clinical Application |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T12-L1 | Celiac trunk | Liver hilum | Xiphoid process | Hepatic surgery planning |
| L1-L2 | SMA origin | Pancreatic neck | L1 spinous process | Pancreaticoduodenectomy |
| L2 | Renal vessels | Renal hilum | 2cm above umbilicus | Nephrectomy approach |
| L3-L4 | IMA origin | Sigmoid colon | Umbilicus level | Colorectal surgery |
| L4-L5 | Aortic bifurcation | Iliac vessels | Iliac crest | Vascular surgery access |
Anatomical Plane Reference System
- Transpyloric Plane (L1)
- Pylorus, duodenal bulb, pancreatic neck
- Renal hilum, splenic hilum, hepatic flexure
- Gallbladder fundus: 9th costal cartilage intersection
- Murphy's sign examination point
- Cholecystitis tenderness localization
- Subcostal Plane (L3)
- Inferior costal margin connection
- Duodenojejunal junction, splenic flexure
- Lower pole kidneys: Normal position reference
- Nephroptosis: >5cm descent with inspiration
- Renal mobility: 2-3cm normal respiratory excursion
💡 Master This: The transpyloric plane intersects 8 major anatomical structures at the L1 level - mastering this single reference enables rapid organ localization across the entire upper abdomen
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Retroperitoneal hematoma extends along fascial planes - the anterior pararenal space communicates with the pelvis, enabling >2 liters of blood loss without peritoneal signs
Connect abdominal landmark mastery through pelvic imaging principles to understand how reproductive and urological anatomy builds upon systematic reference systems.
🎯 Abdominal Terrain Mapping: The Visceral Coordinate System
🏛️ Pelvic Architecture: The Foundation Framework
📌 Remember: SHIP - Sacroiliac, Hip joint, Ischial spine, Pubic symphysis - The four cardinal pelvic reference points for surgical navigation
Bony Pelvic Landmark Architecture
- Pelvic Inlet Measurements
- Anteroposterior diameter: 11-12cm (obstetric conjugate)
- Transverse diameter: 13-14cm (widest pelvic dimension)
- Sacral promontory: S1 vertebral body anterior edge
- Gynecoid pelvis: >90% of female population
- Android pelvis: Heart-shaped inlet, difficult delivery
- Mid-Pelvic Reference Points
- Ischial spines: Narrowest pelvic dimension (10-11cm)
- Sacrospinous ligament: 3-4cm length, surgical landmark
- Arcus tendineus: Fascial condensation supporting pelvic floor
- Level I support: Uterosacral-cardinal ligament complex
- Level II support: Arcus tendineus fasciae pelvis
| Pelvic Landmark | Normal Measurement | Clinical Significance | Surgical Relevance | Pathology Indicator |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pelvic Inlet | 11-12cm AP | Obstetric assessment | Cesarean planning | <10cm cephalopelvic disproportion |
| Ischial Spines | 10-11cm distance | Labor progression | Pudendal block | Station 0 reference |
| Pubic Arch | 90-100° angle | Delivery mechanism | Episiotomy angle | <80° android pelvis |
| Acetabular Angle | 35-45° inclination | Hip stability | Arthroplasty planning | >50° dysplasia |
| Sacroiliac Joint | 2-4mm width | Pelvic stability | Fusion assessment | >6mm diastasis |
Soft Tissue Pelvic Correlations
- Fascial Plane Organization
- Denonvilliers fascia: Rectovesical separation in males
- Rectovaginal septum: 2-3mm thickness in females
- Presacral space: S2-S4 level, 2-3cm depth
- Total mesorectal excision surgical plane
- Presacral bleeding: Thumbtack hemostasis technique
- Vascular Landmark Correlations
- Internal iliac artery: L5-S1 level bifurcation
- Uterine artery: Crosses ureter at cervical level
- Superior vesical artery: Bladder dome vascular supply
- "Water under the bridge": Ureter passes under uterine artery
- Surgical injury risk: 1-2% in hysterectomy procedures
💡 Master This: The cardinal-uterosacral ligament complex provides Level I support - understanding this three-dimensional suspension system enables precise pelvic organ prolapse reconstruction with >85% success rates
⭐ Clinical Pearl: MRI pelvic floor imaging at rest, strain, and evacuation phases reveals dynamic dysfunction patterns - >2cm organ descent indicates significant prolapse requiring surgical intervention
Connect pelvic landmark expertise through advanced imaging integration to understand how multi-planar correlation enhances diagnostic precision across all body systems.
🏛️ Pelvic Architecture: The Foundation Framework
🔬 Advanced Integration: The Multi-Planar Mastery Matrix
📌 Remember: SPACE - Sagittal (spine), Parasagittal (organs), Axial (cross-section), Coronal (frontal), Endoscopic (3D) - Complete spatial orientation framework
Cross-Sectional Correlation Mastery
- Axial Plane Landmark Integration
- Vertebral level correlation: Every slice referenced to spine
- Symmetry assessment: Bilateral comparison for asymmetric pathology
- Organ boundary definition: Fascial plane identification
- Retroperitoneal spaces: 4 distinct compartments
- Peritoneal reflections: Surgical plane guidance
- Sagittal Plane Advantages
- Spinal alignment: Lordotic/kyphotic curve assessment
- Organ relationships: Anterior-posterior spatial correlation
- Pathology extent: Craniocaudal dimension measurement
- Tumor staging: T-stage determination accuracy >95%
- Surgical margins: 1-2cm clearance verification
| Imaging Plane | Primary Application | Landmark Advantage | Pathology Detection | Measurement Accuracy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Axial | Cross-sectional anatomy | Bilateral symmetry | Asymmetric lesions | ±1mm |
| Sagittal | Spinal alignment | Vertebral relationships | Disc pathology | ±0.5mm |
| Coronal | Joint assessment | Articular surfaces | Ligament tears | ±1mm |
| Oblique | Specialized views | Specific structures | Hidden pathology | ±2mm |
| 3D Reconstruction | Surgical planning | Spatial relationships | Complex anatomy | ±0.5mm |
Advanced Reconstruction Techniques
- Volume Rendering Applications
- CT angiography: Sub-millimeter vascular detail
- Virtual endoscopy: Internal surface visualization
- Surgical simulation: Pre-operative planning accuracy >90%
- Bone tumor resection: Margin planning precision
- Vascular reconstruction: Graft length calculation
- Functional Imaging Integration
- Dynamic contrast enhancement: Perfusion patterns analysis
- Diffusion-weighted imaging: Cellular density assessment
- Spectroscopy correlation: Metabolic activity mapping
- Tumor characterization: Malignancy prediction >85% accuracy
- Treatment response: Early detection of therapeutic effects
💡 Master This: Multi-planar reformation (MPR) enables unlimited viewing angles from a single acquisition - mastering oblique plane reconstruction reveals hidden pathology in 15-20% of cases missed on standard views
⭐ Clinical Pearl: Dual-energy CT separates calcium from contrast material with >99% accuracy, enabling virtual non-contrast images and advanced material decomposition for precise tissue characterization
Connect multi-planar mastery through rapid assessment protocols to understand how systematic landmark recognition enables efficient, accurate diagnostic workflows in clinical practice.
🔬 Advanced Integration: The Multi-Planar Mastery Matrix
⚡ Rapid Assessment Arsenal: The Clinical Decision Toolkit
📌 Remember: ABCDEFGHI - Airway, Breathing, Circulation, Disability, Exposure, Focused assessment, Get vitals, History, Imaging - Emergency assessment priority sequence
Critical Landmark Rapid Recognition
- Trauma Assessment Priorities
- Cervical spine: 3-line assessment in <30 seconds
- Anterior vertebral line: Smooth lordotic curve
- Posterior vertebral line: Continuous alignment
- Spinolaminar line: Intact posterior elements
- Chest trauma: 6-point evaluation in <60 seconds
- Pneumothorax: Pleural line displacement >2cm
- Hemothorax: Costophrenic angle blunting >200ml
- Aortic injury: Mediastinal width >8cm
- Cervical spine: 3-line assessment in <30 seconds
| Assessment Priority | Time Target | Critical Landmark | Pathology Threshold | Miss Rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| C-spine stability | <30 sec | Spinolaminar line | >2mm displacement | <1% |
| Pneumothorax | <15 sec | Pleural line | Absent lung sliding | <2% |
| Aortic injury | <45 sec | Mediastinal contour | >8cm width | <5% |
| Pelvic fracture | <30 sec | Iliopectineal line | Discontinuity | <3% |
| Abdominal bleeding | <60 sec | Fascial planes | Fluid collections | <8% |
Systematic Efficiency Protocols
- Primary Survey Checklist
- Image quality: Adequate penetration and positioning
- Life-threatening findings: Immediate communication required
- Systematic coverage: No anatomical region overlooked
- "Satisfaction of search": Continue evaluation after finding pathology
- Multiple injury rule: >85% of trauma patients have >1 injury
- Secondary Survey Optimization
- Pattern recognition: Common injury associations
- Anatomical correlation: Mechanism-specific injury patterns
- Quantitative thresholds: Measurement-based severity assessment
- Splenic laceration: Grade I-V classification system
- Liver injury: Depth >3cm indicates Grade III or higher
💡 Master This: Gestalt pattern recognition develops after interpreting >10,000 cases - systematic landmark assessment provides consistent accuracy regardless of experience level, achieving >95% diagnostic confidence
⭐ Clinical Pearl: "Aunt Minnie" signs - pathognomonic findings requiring immediate recognition - include pneumoperitoneum (football sign), tension pneumothorax (mediastinal shift), and aortic transection (pseudocoarctation contour)
⚡ Rapid Assessment Arsenal: The Clinical Decision Toolkit
Practice Questions: Radiologic landmarks
Test your understanding with these related questions
A 27-year-old male presents to the Emergency Room as a code trauma after being shot in the neck. En route, the patient's blood pressure is 127/73 mmHg, pulse is 91/min, respirations are 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 100% on room air with GCS of 15. On physical exam, the patient is in no acute distress; however, there is an obvious entry point with oozing blood near the left lateral neck above the cricoid cartilage with a small hematoma that is non-pulsatile and stable since arrival. The rest of the physical exam is unremarkable. Rapid hemoglobin returns back at 14.1 g/dL. After initial resuscitation, what is the next best step in management?










