Pharyngeal pouches US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Pharyngeal pouches. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Pharyngeal pouches US Medical PG Question 1: A 7-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department with a high fever and oxygen desaturation. He had a tracheostomy placed as an infant and has been placed on mechanical ventilation intermittently. Since then, he has had several bouts of pneumonia similar to his current presentation. In addition, he has been deaf since birth but is able to communicate through sign language. He attends school and performs above average for his grade. Physical exam reveals underdeveloped cheekbones, hypoplasia of the mandible, and malformed ears. Abnormal development of which of the following structures is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
- A. Branchial cleft 1
- B. Branchial pouch 3
- C. Branchial arch 2
- D. Branchial arch 1 (Correct Answer)
- E. Branchial pouch 1
Pharyngeal pouches Explanation: ***Branchial arch 1***
- **Branchial arch 1** (mandibular arch) derivatives include the **mandible**, zygoma, part of the maxilla, incus, malleus, and facial muscles of mastication. Abnormal development leads to features like **underdeveloped cheekbones**, **mandibular hypoplasia**, and ear malformations, consistent with **Treacher Collins syndrome**.
- **Treacher Collins syndrome** is characterized by craniofacial anomalies resulting from improper development of structures derived from the **first and second pharyngeal arches**, specifically affecting the mandible, maxilla, zygoma, and ears. These malformations lead to airway difficulties requiring tracheostomy, chronic pneumonia due to aspiration, and conductive hearing loss.
*Branchial cleft 1*
- **Branchial cleft 1** anomalies typically present as **cysts** or **fistulas** in the periauricular or submandibular region, which are not described in this patient.
- While they can be associated with ear malformations, they do not typically cause the extensive **skeletal hypoplasia** of the face seen in this case.
*Branchial pouch 3*
- **Branchial pouch 3** develops into the **inferior parathyroid glands** and the **thymus**. Abnormalities here are associated with **DiGeorge syndrome**, characterized by hypocalcemia, T-cell immunodeficiency, and cardiac defects.
- These clinical features (hypocalcemia, immunodeficiency, heart defects) are distinct from the patient's presentation of craniofacial anomalies and recurrent respiratory issues related to airway compromise.
*Branchial arch 2*
- **Branchial arch 2** (hyoid arch) contributes to the development of the **stapes**, styloid process, lesser horn of the hyoid, and facial expression muscles. Dysfunction primarily leads to disorders like **facial nerve paralysis** or specific ear ossicle anomalies.
- While **Treacher Collins syndrome** also affects **branchial arch 2** derivatives, the primary skeletal and severe airway issues stem from the **first arch** involvement. The prominent features presented (mandibular and zygomatic hypoplasia) are more directly linked to the first arch.
*Branchial pouch 1*
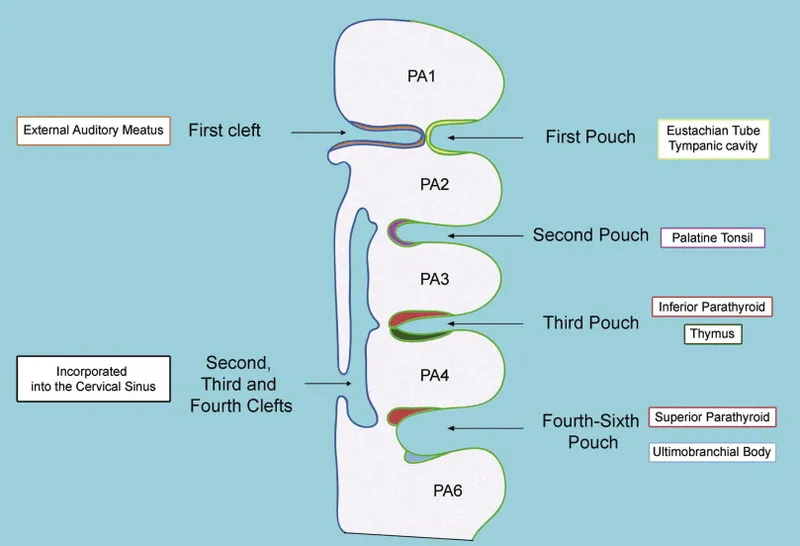
- **Branchial pouch 1** gives rise to the **Eustachian tube** and the **middle ear cavity**. Abnormalities here can cause middle ear effusions or conductive hearing loss but do not explain the extensive craniofacial bony deformities and related airway issues.
- While the patient has deafness, the entire constellation of symptoms, including mandibular and zygomatic hypoplasia, points to structural development beyond just the middle ear.
Pharyngeal pouches US Medical PG Question 2: A 10-year-old boy comes for a post-operative clinic visit with his ENT surgeon three months after airway reconstruction surgery and placement of a tracheostomy tube. Since the surgery, he says that he has been able to breathe better and is now getting used to tracheostomy care and tracheostomy tube changes. In addition to this surgery, he has had over twenty surgeries to implant hearing aids, reconstruct his cheekbones, and support his jaw to enable him to swallow. He was born with these abnormalities and had difficult breathing, hearing, and eating throughout his childhood. Fortunately, he is now beginning to feel better and is able to attend public school where he is one of the best students in the class. Abnormal development of which of the following structures is most likely responsible for this patient's malformations?
- A. Second branchial cleft
- B. First branchial pouch
- C. Third and fourth branchial pouches
- D. First branchial arch (Correct Answer)
- E. Second branchial arch
Pharyngeal pouches Explanation: ***First branchial arch***
- The clinical presentation describes features consistent with **Treacher Collins syndrome** (TCS), also known as mandibulofacial dysostosis, which results from maldevelopment of **both the first and second branchial arches**.
- However, the **predominant and most characteristic features** arise from **first branchial arch** abnormalities: **mandibular hypoplasia** (requiring jaw support for swallowing), **malar/zygomatic hypoplasia** (reconstructed cheekbones), and **maxillary hypoplasia**.
- These first arch skeletal abnormalities cause the **airway obstruction** (requiring tracheostomy) and feeding difficulties.
- The first branchial arch gives rise to: **mandible, maxilla, zygomatic bone, incus, malleus, muscles of mastication, and CN V** (trigeminal nerve).
- While hearing issues may involve second arch structures (stapes), the **overwhelming majority** of this patient's clinical problems stem from first arch malformations.
*Second branchial cleft*
- The second branchial cleft typically forms the **cervical sinus**, which normally obliterates. Persistence can lead to **cervical cysts or fistulas**, presenting as neck masses.
- Abnormalities of the second branchial cleft do not explain the extensive craniofacial malformations, hearing deficits, or airway compromise seen in this patient.
*First branchial pouch*
- The first branchial pouch gives rise to the **auditory (eustachian) tube** and the **tympanic cavity** (middle ear).
- While isolated first pouch defects could contribute to hearing problems, they would **not explain** the severe facial bone malformations (mandibular and malar hypoplasia), airway obstruction, or feeding difficulties.
- The pouch is distinct from the arch, which forms the skeletal and muscular structures.
*Third and fourth branchial pouches*
- The third branchial pouch contributes to the **inferior parathyroid glands** and the **thymus**. The fourth branchial pouch contributes to the **superior parathyroid glands** and the **ultimobranchial body** (parafollicular C cells of the thyroid).
- Abnormalities in these pouches, such as in **DiGeorge syndrome (22q11.2 deletion)**, lead to **T-cell immunodeficiency, hypocalcemia, and cardiac defects** but do not account for the craniofacial and hearing abnormalities described.
*Second branchial arch*
- The second branchial arch gives rise to the **stapes**, **styloid process**, **lesser horn and upper body of hyoid bone**, **stapedius muscle**, and **CN VII** (facial nerve).
- While Treacher Collins syndrome involves both first and second arch abnormalities, the **second arch contributions** are less prominent clinically.
- Second arch defects could contribute to **conductive hearing loss** (via stapes abnormalities) and **facial nerve issues**, but these are not the predominant features in this case.
- The critical skeletal malformations causing airway compromise, feeding difficulties, and facial dysmorphism are primarily **first arch** derivatives.
Pharyngeal pouches US Medical PG Question 3: During a thyroidectomy, a surgeon must carefully identify and preserve the parathyroid glands. These glands are most commonly located posterior to which part of the thyroid gland?
- A. Superior poles
- B. Inferior poles (Correct Answer)
- C. Pyramidal lobe
- D. Middle third
Pharyngeal pouches Explanation: Detailed anatomical knowledge is crucial during thyroidectomy to ensure preservation of vital structures [1].
***Inferior poles***
- The **inferior parathyroid glands** (parathyroid IV) are most commonly located posterior to the **inferior poles** of the thyroid gland [1].
- While they are more variable in position than superior glands and can descend into the thymus or mediastinum, the **most common location** is still posterior to the inferior poles [1].
- During thyroidectomy, these glands are frequently encountered in the inferior pole region and must be carefully preserved [1].
*Superior poles*
- The **superior parathyroid glands** (parathyroid III) are typically found at the **middle-to-upper third** of the thyroid, near the cricothyroid junction, rather than directly at the superior poles.
- While their position is more constant than inferior glands, they are not specifically located at the superior poles themselves.
*Pyramidal lobe*
- The **pyramidal lobe** is an embryological remnant extending superiorly from the thyroid isthmus.
- It is not associated with parathyroid gland location, as parathyroids are distinct endocrine structures located on the posterior thyroid surface.
*Middle third*
- The **superior parathyroid glands** are often found near the middle third of the thyroid posteriorly.
- However, when considering all four parathyroid glands (both superior and inferior pairs), the **inferior glands** at the inferior poles represent the most common overall location pattern.
Pharyngeal pouches US Medical PG Question 4: A 35-year-old man comes to the physician for evaluation of a neck mass and hoarseness. He has no history of major medical illness. Physical examination shows a 2.5-cm fixed, irregular thyroid nodule. His serum calcitonin concentration is elevated. The nodule is most likely comprised of cells that are embryologically derived from which of the following structures?
- A. Second branchial pouch
- B. Fourth branchial arch
- C. Surface ectoderm
- D. Third branchial pouch
- E. Neural crest cells (Correct Answer)
Pharyngeal pouches Explanation: ***Neural crest cells***
- The elevated **serum calcitonin** in the presence of a thyroid nodule is highly suggestive of **medullary thyroid carcinoma (MTC)**.
- **MTC** originates from the **parafollicular C cells** of the thyroid, which are embryologically derived from **neural crest cells** that migrate to the **ultimobranchial body** (from the 4th/5th pharyngeal pouch) during development and subsequently integrate into the thyroid gland.
- This is the definitive embryological origin of calcitonin-producing C cells.
*Second branchial pouch*
- The second branchial pouch typically gives rise to the **palatine tonsil crypts** and **tonsillar fossa**.
- It is not associated with the development of the **parafollicular C cells** or thyroid malignancies.
*Fourth branchial arch*
- The fourth branchial arch gives rise to the **superior laryngeal nerve** and associated laryngeal cartilages.
- While the **ultimobranchial body** (from the 4th/5th pharyngeal pouch) does contribute C cells to the thyroid, these cells themselves are derived from **neural crest cells** that migrate to this structure, not from the pouch itself.
- Therefore, the embryological origin is neural crest, not the branchial arch/pouch.
*Surface ectoderm*
- Surface ectoderm forms structures such as the **epidermis of the skin**, **hair**, **nails**, and **lens of the eye**.
- It does not contribute to the development of the **C cells** or the thyroid gland.
*Third branchial pouch*
- The third branchial pouch gives rise to the **inferior parathyroid glands** and the majority of the **thymus**.
- While it contributes to endocrine tissues, it does not form the **parafollicular C cells** of the thyroid.
Pharyngeal pouches US Medical PG Question 5: A 5-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department by her mother with seizures. The blood glucose is 94 mg/dl and the serum calcium is 5.3 mg/dl; however, the PTH levels are low. The medical history includes a delay in achieving developmental milestones. Her mother also says she needs frequent hospital visits due to recurrent bouts with the flu. The cardiovascular examination is within normal limits. What is the most likely cause underlying this presentation?
- A. Deletion of the chromosome 22q11 (Correct Answer)
- B. Mutation in the WAS gene
- C. B cell development failure
- D. B cell maturation failure
- E. Lysosomal trafficking regulator gene defect
Pharyngeal pouches Explanation: ***Deletion of the chromosome 22q11***
- The combination of **hypocalcemia with low PTH** (due to **parathyroid hypoplasia**), recurrent infections (due to **thymic hypoplasia** leading to T-cell deficiency), and developmental delay is classic for **DiGeorge syndrome**.
- **DiGeorge syndrome** is caused by a **microdeletion on chromosome 22q11.2**, affecting the development of structures derived from the **third and fourth pharyngeal pouches**.
*Mutation in the WAS gene*
- A mutation in the **WAS gene** causes **Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome**, characterized by **thrombocytopenia**, **eczema**, and **recurrent infections**.
- It does not directly explain the **hypocalcemia with low PTH** or developmental delay present in this patient.
*B cell development failure*
- **B-cell development failure**, as seen in conditions like **X-linked agammaglobulinemia**, leads to recurrent bacterial infections due to absent antibodies.
- However, it does not account for the **hypocalcemia** or developmental delay observed.
*B cell maturation failure*
- **B-cell maturation failure** results in impaired antibody production and recurrent infections but typically does not present with **hypocalcemia and low PTH** or developmental delay.
- Conditions like **Common Variable Immunodeficiency (CVID)** involve mature B cells failing to differentiate into plasma cells.
*Lysosomal trafficking regulator gene defect*
- A defect in the **lysosomal trafficking regulator gene (LYST)** is associated with **Chediak-Higashi syndrome**, which involves impaired lysosomal function, leading to immunodeficiency, **partial albinism**, and neurological abnormalities.
- This condition does not typically present with **hypocalcemia** or the specific constellation of symptoms seen in this case.
Pharyngeal pouches US Medical PG Question 6: A 64-year-old woman presents to an endocrinologist after her second time having a kidney stone in the last year. The patient reports no other symptoms except overall fatigue. On evaluation, the patient’s temperature is 98.4°F (36.9°C), blood pressure is 120/76 mmHg, pulse is 72/min, and respirations are 12/min. The patient has no neck masses and no tenderness to palpation in the abdomen. On laboratory workup, the endocrinologist finds that the patient has elevated parathyroid hormone levels and serum calcium. For surgical planning, the patient undergoes a sestamibi scan, which localizes disease to an area near the superior aspect of the thyroid in the right neck. Which of the following is the embryologic origin of this tissue?
- A. Fourth branchial arch
- B. Fourth branchial pouch (Correct Answer)
- C. Third branchial arch
- D. Dorsal wings of the third branchial pouch
- E. Ventral wings of the third branchial pouch
Pharyngeal pouches Explanation: ***Fourth branchial pouch***
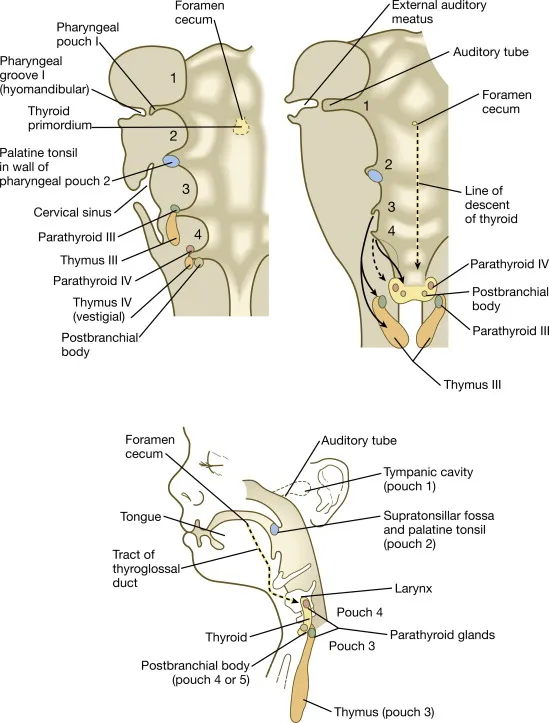
- The superior parathyroid glands, generally located near the superior aspect of the thyroid, develop from the **fourth branchial pouch (dorsal wing)**.
- The **ultimobranchial body (C-cells)** also originates from the fourth branchial pouch.
*Fourth branchial arch*
- The fourth branchial arch forms structures like the **cricothyroid muscle**, pharyngeal constrictors, and laryngeal cartilages.
- It does not give rise to the parathyroid glands.
*Third branchial arch*
- The third branchial arch forms structures including the **stylopharyngeus muscle**, greater horn of the hyoid, and parts of the pharynx.
- It does not contribute to the formation of the parathyroid glands.
*Dorsal wings of the third branchial pouch*
- The **dorsal wings of the third branchial pouch** give rise to the inferior parathyroid glands.
- In this case, the diseased tissue was localized to the superior aspect nearest the superior parathyroid glands, not the inferior glands.
*Ventral wings of the third branchial pouch*
- The **ventral wings of the third branchial pouch** give rise to the thymus.
- This structure is not involved in parathyroid gland development.
Pharyngeal pouches US Medical PG Question 7: A 26-year-old woman presents to your clinic with complaints of increasing muscle fatigue that worsens after periods of sustained activity. She also reports both ptosis and diplopia that make reading in the late afternoon and evenings difficult. An edrophonium test is performed and is positive, demonstrating resolution of the patient's weakness. One organ in particular, when abnormal, is associated with this patient's condition. Which of the following embryologic structures gives rise to this organ?
- A. 3rd branchial arch
- B. 4th branchial pouch
- C. 1st branchial pouch
- D. 2nd branchial cleft
- E. 3rd branchial pouch (Correct Answer)
Pharyngeal pouches Explanation: ***3rd branchial pouch***
- The clinical presentation (muscle fatigue worsening with activity, ptosis, diplopia, positive edrophonium test) indicates **myasthenia gravis**. Myasthenia gravis is commonly associated with **thymic abnormalities**, such as thymoma or thymic hyperplasia.
- The **thymus** develops from the **third pharyngeal (branchial) pouch**.
*3rd branchial arch*
- The 3rd branchial arch gives rise to structures such as the common **carotid artery**, proximal internal carotid artery, **stylopharyngeus muscle**, and **glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)**.
- It does not contribute to the development of the thymus or structures related to myasthenia gravis.
*4th branchial pouch*
- The 4th branchial pouch gives rise to the **superior parathyroid glands** and the **parafollicular C cells** of the thyroid gland.
- It is not involved in the embryological development of the thymus.
*1st branchial pouch*
- The 1st branchial pouch gives rise to the **eustachian tube**, **middle ear cavity**, and part of the mastoid air cells.
- These structures are unrelated to the thymus or myasthenia gravis.
*2nd branchial cleft*
- The 2nd, 3rd, and 4th branchial clefts typically merge and obliterate to form the **cervical sinus**.
- Persistence of these clefts or their incomplete obliteration can lead to **branchial cleft cysts or fistulas**, which are distinct from thymic development.
Pharyngeal pouches US Medical PG Question 8: A six year-old female presents for evaluation of dry skin, fatigue, sensitivity to cold and constipation. The patient’s mother recalls that the patient had surgery to remove a “benign mass” at the base of her tongue 3 months ago because of trouble swallowing. What was the likely cause of the surgically removed mass?
- A. Failed caudal migration of the thyroid gland (Correct Answer)
- B. Iodine deficiency
- C. Failed fusion of the palatine shelves with the nasal septum
- D. Radiation exposure
- E. Maternal Diabetes Mellitus
Pharyngeal pouches Explanation: ***Failed caudal migration of the thyroid gland***
- The symptoms of **dry skin, fatigue, cold sensitivity, and constipation** are classic signs of **hypothyroidism**.
- A mass at the **base of the tongue** that is later removed and leads to hypothyroidism strongly suggests a **lingual thyroid**, which results from the thyroid gland's **failure to descend** from its embryonic origin at the foramen cecum.
*Iodine deficiency*
- While iodine deficiency can cause **hypothyroidism** and **goiter**, it typically does not present as a **discrete mass** at the base of the tongue requiring surgical removal.
- It would usually result in a more generalized **enlargement of the thyroid gland**, often in the neck.
*Failed fusion of the palatine shelves with the nasal septum*
- This developmental anomaly leads to a **cleft palate**, affecting the **roof of the mouth**.
- It has no direct association with thyroid function or masses at the base of the tongue.
*Radiation exposure*
- Radiation exposure can increase the risk of thyroid cancer or hypothyroidism later in life, but it typically doesn't cause a congenital benign mass at the base of the tongue that presents in early childhood.
- Furthermore, the specific presentation points to a developmental anomaly rather than an acquired condition.
*Maternal Diabetes Mellitus*
- Maternal diabetes can lead to various congenital anomalies in the fetus, such as **macrosomia, caudal regression syndrome, or cardiac defects**.
- However, it is not a recognized cause of a lingual thyroid or a failure of thyroid migration.
Pharyngeal pouches US Medical PG Question 9: A 29-year-old mother brings in her 2-week-old baby boy to a pediatrician because he has been having difficulty feeding. The mother reveals that she had no prenatal care during her pregnancy and gave birth at home without complications. She says that her son seems to be having difficulty sucking, and she occasionally sees breast milk coming out of the infant’s nose. Physical exam reveals that this patient has a gap between his oral and nasal cavities behind the incisive foramen. He is therefore prescribed specialized bottles and his mom is taught positional techniques to ensure better feeding. Failure to fuse which of the following structures is most likely responsible for this patient's disorder?
- A. Maxillary and medial nasal prominences
- B. Nasal septum with primary plates
- C. Maxillary and lateral nasal prominences
- D. Palatine shelves with primary plates
- E. Palatine shelves with nasal septum (Correct Answer)
Pharyngeal pouches Explanation: ***Palatine shelves with nasal septum***
- A **cleft palate** results from the **failure of fusion of the palatine shelves** with each other and/or with the **nasal septum**, creating an abnormal communication between the oral and nasal cavities.
- This anatomical defect explains the infant's **feeding difficulties** and the leakage of breast milk into the nose, as well as the observed **gap behind the incisive foramen**.
*Maxillary and medial nasal prominences*
- The failure of fusion between the maxillary and medial nasal prominences results in a **cleft lip**, which is an anterior defect and does not explain the posterior gap described.
- While cleft lip can coexist with cleft palate, the symptoms here specifically point to a palatal defect, not primarily a lip defect.
*Nasal septum with primary plates*
- The primary palate forms from the fusion of the medial nasal prominences, anterior to the incisive foramen.
- While crucial for normal development, the specific clinical presentation (gap *behind* the incisive foramen and feeding difficulties) is more characteristic of a secondary palate defect involving the palatine shelves.
*Maxillary and lateral nasal prominences*
- The fusion of these structures contributes to the formation of the **nasolacrimal groove** and parts of the cheek, not the palate.
- Deficiencies in this fusion would lead to defects in the lateral facial region, not an oro-nasal communication related to feeding.
*Palatine shelves with primary plates*
- The **primary palate** fuses with the anterior part of the secondary palate (formed by the palatine shelves) at the incisive foramen.
- However, the more common and clinically relevant defect leading to an open communication between the oral and nasal cavities, especially *behind* the incisive foramen, involves the failure of fusion of the **palatine shelves** with each other and the **nasal septum**.
More Pharyngeal pouches US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.