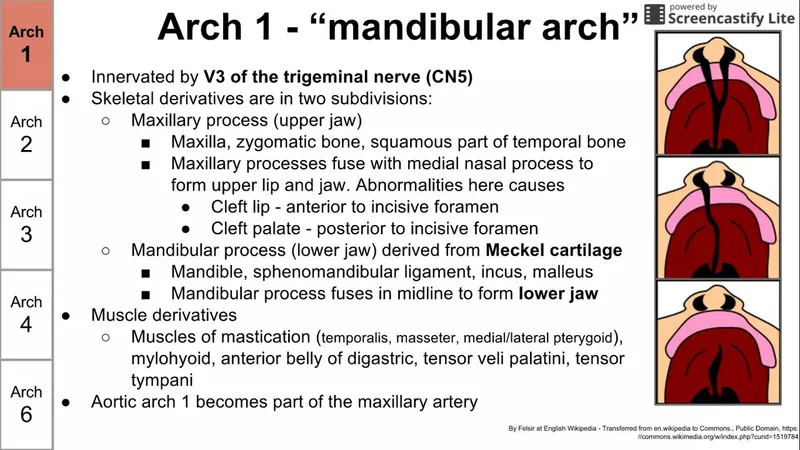
First pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for First pharyngeal arch derivatives. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
First pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 1: A 54-year-old woman comes to the emergency department because of drooping on the left side of her face since that morning. She also reports difficulty closing her eyes and chewing. During the neurologic examination, the physician asks the patient to open her jaw against resistance. Which of the following muscles is most likely activated in this movement?
- A. Hyoglossus
- B. Masseter
- C. Orbicularis oris
- D. Buccinator
- E. Lateral pterygoid (Correct Answer)
First pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***Lateral pterygoid***
- The **lateral pterygoid muscle** is the primary muscle responsible for **opening the jaw (depressing the mandible)** and protruding it.
- When opening the jaw against resistance, this muscle would be actively engaged and contracting to overcome the opposing force.
*Hyoglossus*
- The **hyoglossus muscle** is a muscle of the tongue, primarily involved in **depressing and retracting the tongue**.
- It does not play a role in the movement of the jaw itself.
*Masseter*
- The **masseter muscle** is one of the primary muscles of **mastication**, responsible for **closing the jaw (elevating the mandible)** and clenching the teeth.
- It would be active during jaw closure against resistance, not during jaw opening.
*Orbicularis oris*
- The **orbicularis oris muscle** surrounds the mouth and is responsible for **pursing the lips**, closing the mouth, and other facial expressions related to the mouth.
- It is not involved in the movement of the jaw itself.
*Buccinator*
- The **buccinator muscle** is a facial muscle that forms the wall of the cheek and is involved in **compressing the cheek** (e.g., during blowing or sucking) and keeping food pocketed during chewing.
- It does not directly participate in the opening or closing of the jaw joint.
First pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 2: A 7-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department with a high fever and oxygen desaturation. He had a tracheostomy placed as an infant and has been placed on mechanical ventilation intermittently. Since then, he has had several bouts of pneumonia similar to his current presentation. In addition, he has been deaf since birth but is able to communicate through sign language. He attends school and performs above average for his grade. Physical exam reveals underdeveloped cheekbones, hypoplasia of the mandible, and malformed ears. Abnormal development of which of the following structures is most likely responsible for this patient's symptoms?
- A. Branchial cleft 1
- B. Branchial pouch 3
- C. Branchial arch 2
- D. Branchial arch 1 (Correct Answer)
- E. Branchial pouch 1
First pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***Branchial arch 1***
- **Branchial arch 1** (mandibular arch) derivatives include the **mandible**, zygoma, part of the maxilla, incus, malleus, and facial muscles of mastication. Abnormal development leads to features like **underdeveloped cheekbones**, **mandibular hypoplasia**, and ear malformations, consistent with **Treacher Collins syndrome**.
- **Treacher Collins syndrome** is characterized by craniofacial anomalies resulting from improper development of structures derived from the **first and second pharyngeal arches**, specifically affecting the mandible, maxilla, zygoma, and ears. These malformations lead to airway difficulties requiring tracheostomy, chronic pneumonia due to aspiration, and conductive hearing loss.
*Branchial cleft 1*
- **Branchial cleft 1** anomalies typically present as **cysts** or **fistulas** in the periauricular or submandibular region, which are not described in this patient.
- While they can be associated with ear malformations, they do not typically cause the extensive **skeletal hypoplasia** of the face seen in this case.
*Branchial pouch 3*
- **Branchial pouch 3** develops into the **inferior parathyroid glands** and the **thymus**. Abnormalities here are associated with **DiGeorge syndrome**, characterized by hypocalcemia, T-cell immunodeficiency, and cardiac defects.
- These clinical features (hypocalcemia, immunodeficiency, heart defects) are distinct from the patient's presentation of craniofacial anomalies and recurrent respiratory issues related to airway compromise.
*Branchial arch 2*
- **Branchial arch 2** (hyoid arch) contributes to the development of the **stapes**, styloid process, lesser horn of the hyoid, and facial expression muscles. Dysfunction primarily leads to disorders like **facial nerve paralysis** or specific ear ossicle anomalies.
- While **Treacher Collins syndrome** also affects **branchial arch 2** derivatives, the primary skeletal and severe airway issues stem from the **first arch** involvement. The prominent features presented (mandibular and zygomatic hypoplasia) are more directly linked to the first arch.
*Branchial pouch 1*
- **Branchial pouch 1** gives rise to the **Eustachian tube** and the **middle ear cavity**. Abnormalities here can cause middle ear effusions or conductive hearing loss but do not explain the extensive craniofacial bony deformities and related airway issues.
- While the patient has deafness, the entire constellation of symptoms, including mandibular and zygomatic hypoplasia, points to structural development beyond just the middle ear.
First pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 3: An otherwise healthy 45-year-old man comes to the physician because of a painful ulcer on his tongue for 3 days. Examination shows a shallow, tender 5-mm wide ulcer on the lateral aspect of the tongue, adjacent to his left first molar. There is no induration surrounding the ulcer or cervical lymphadenopathy. A lesion of the cranial nerve responsible for the transmission of pain from this ulcer would most likely result in which of the following?
- A. Loss of taste from the supraglottic region
- B. Lateral deviation of the tongue
- C. Inability to wrinkle the forehead
- D. Decreased sensation in the upper lip
- E. Loss of sensation in the anterior two-thirds of the tongue (Correct Answer)
First pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***Loss of sensation in the anterior two-thirds of the tongue***
- The sensation of pain from the **anterior two-thirds of the tongue** is transmitted by the **lingual nerve**, which is a branch of the mandibular division (V3) of the **trigeminal nerve**. A lesion affecting this nerve would therefore cause loss of sensation in this region.
- The ulcer is located on the **lateral aspect of the tongue**, placing it within the distribution of the lingual nerve.
*Loss of taste from the supraglottic region*
- **Taste sensation** from the **supraglottic region** and epiglottis is primarily mediated by the **superior laryngeal nerve** (a branch of the vagus nerve, CN X), not the nerve responsible for pain sensation from the anterior tongue.
- A lesion of the lingual nerve would affect taste sensation from the **anterior two-thirds of the tongue** (carried by the chorda tympani, a branch of CN VII, which joins the lingual nerve), but not the supraglottic region.
*Lateral deviation of the tongue*
- **Lateral deviation of the tongue** (towards the side of the lesion) occurs due to damage to the **hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)**, which innervates the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue.
- This is a motor deficit, whereas the question describes a sensory issue related to pain transmission from an ulcer on the tongue.
*Inability to wrinkle the forehead*
- The **inability to wrinkle the forehead** (along with other facial expressions) results from damage to the **facial nerve (CN VII)**, specifically its temporal branch.
- This is a motor deficit affecting the muscles of facial expression, unrelated to pain sensation from the tongue.
*Decreased sensation in the upper lip*
- **Sensation in the upper lip** is supplied by the **infraorbital nerve**, a branch of the maxillary division (V2) of the **trigeminal nerve**.
- A lesion affecting the nerve responsible for pain from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue (lingual nerve, V3) would not directly impact sensation in the upper lip.
First pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 4: A 27-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-day history of right-sided facial weakness and sound intolerance. Three days ago, he hit the right side of his head in a motor vehicle collision. He neither lost consciousness nor sought medical attention. Physical examination shows drooping of the mouth on the right side. Sensation over the face is not impaired. Impedance audiometry shows an absence of the acoustic reflex in the right ear. Which of the following muscles is most likely paralyzed in this patient?
- A. Anterior belly of the digastric
- B. Stylopharyngeus
- C. Cricothyroid
- D. Tensor tympani
- E. Stylohyoid (Correct Answer)
First pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***Stylohyoid***
- The patient presents with **facial nerve (CN VII) injury** following head trauma, evidenced by **facial weakness** and **hyperacusis** (sound intolerance).
- The **absent acoustic reflex** indicates paralysis of the **stapedius muscle** (the primary muscle responsible for the acoustic reflex and sound dampening).
- Among the options provided, **stylohyoid** is the only muscle innervated by the **facial nerve (CN VII)**, making it the correct answer in this context.
- The stylohyoid is innervated by the **nerve to stylohyoid**, a branch of CN VII.
*Anterior belly of the digastric*
- The **anterior belly of the digastric** is innervated by the **mylohyoid nerve**, a branch of the **trigeminal nerve (CN V3)**.
- This would not be affected in facial nerve injury.
*Stylopharyngeus*
- The **stylopharyngeus muscle** is innervated by the **glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)**.
- Damage would cause **dysphagia** and **loss of taste** on the posterior third of the tongue, not facial weakness or hyperacusis.
*Cricothyroid*
- The **cricothyroid muscle** is innervated by the **external branch of the superior laryngeal nerve** (from **vagus nerve, CN X**).
- Its paralysis causes **voice changes** and difficulty with high-pitched phonation, not facial nerve symptoms.
*Tensor tympani*
- The **tensor tympani muscle** is innervated by the **nerve to tensor tympani**, a branch of the **trigeminal nerve (V3)**.
- Although it dampens sound, it would not be affected in facial nerve injury; the **stapedius muscle** (CN VII) is responsible for the acoustic reflex and hyperacusis when paralyzed.
First pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 5: A 45-year-old patient presents with difficulty speaking and swallowing following a stroke. MRI reveals an infarct in the medulla. Which of the following cranial nerve nuclei is most likely affected?
- A. Vestibulocochlear nucleus
- B. Trigeminal nerve nucleus
- C. Facial nerve nucleus
- D. Nucleus ambiguus (Correct Answer)
First pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***Nucleus ambiguus***
- The **nucleus ambiguus** is located in the **medulla** and contains motor neurons that innervate muscles involved in **speaking** and **swallowing**, specifically those of the pharynx, larynx, and soft palate via cranial nerves IX, X, and XI [1].
- An infarct in the medulla causing difficulty speaking and swallowing strongly implicates damage to this nucleus, leading to **dysarthria** and **dysphagia** [1].
*Vestibulocochlear nucleus*
- This nucleus is primarily involved in **hearing** and **balance**, which would manifest as dizziness, hearing loss, or nystagmus, not directly difficulty speaking and swallowing.
- While located in the brainstem, damage to this nucleus typically does not cause the specific symptoms of dysarthria and dysphagia described.
*Trigeminal nerve nucleus*
- The trigeminal nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the face, and motor innervation for **mastication** (chewing).
- Damage would primarily affect facial sensation or jaw movement, not the act of deglutition or phonation.
*Facial nerve nucleus*
- This nucleus, located in the **pons**, controls the muscles of **facial expression** and taste for the anterior two-thirds of the tongue.
- Damage would lead to facial weakness or paralysis, not the profound difficulty with speaking and swallowing affecting pharyngeal and laryngeal function.
First pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 6: A group of investigators studying embryological defects in mice knock out a gene that is responsible for the development of the ventral wing of the third branchial pouch. A similar developmental anomaly in a human embryo is most likely to result in which of the following findings after birth?
- A. Cleft palate
- B. Discharging neck sinus (Correct Answer)
- C. Carpopedal spasm
- D. Conductive hearing loss
- E. White oral patches
First pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***Discharging neck sinus***
- The **ventral wing of the third pharyngeal pouch** gives rise to the **thymus**
- During embryonic development, the thymus descends from the pharynx into the anterior mediastinum via the **thymopharyngeal duct**
- Normally, this duct obliterates completely, but **failure of obliteration** can result in a **cervical thymic cyst** or **persistent thymic tract**
- This presents as a **discharging neck sinus** along the lateral neck (anterior border of sternocleidomastoid), which may drain clear fluid or become infected
- This is a classic presentation of a **third pharyngeal pouch anomaly** affecting the thymic descent pathway
*Carpopedal spasm*
- **Carpopedal spasm** is a sign of **hypocalcemia** due to **hypoparathyroidism**
- The **dorsal wing** (not ventral wing) of the third pharyngeal pouch forms the **inferior parathyroid glands**
- Since the question specifically identifies a defect in the **ventral wing** (thymus), hypoparathyroidism would not result
- A dorsal wing defect would cause absent inferior parathyroid glands and hypocalcemia
*Cleft palate*
- Results from failure of **palatine shelf fusion** during weeks 8-12 of development
- Associated with **maxillary prominence** derivatives (first pharyngeal arch) and secondary palate formation
- Not related to third pharyngeal pouch development
*Conductive hearing loss*
- Associated with **first and second pharyngeal arch** derivatives affecting the middle ear structures
- First arch: malleus, incus (in part); Second arch: stapes (in part)
- The **third pharyngeal pouch** does not contribute to auditory structures
*White oral patches*
- Typically represent **mucosal lesions** (leukoplakia, candidiasis, lichen planus)
- Not associated with embryological defects of the pharyngeal apparatus
- Unrelated to third pharyngeal pouch derivatives
First pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 7: A 2850-g (6-lb 5-oz) newborn is delivered at term to a 19-year-old primigravid woman via normal spontaneous vaginal delivery. The mother has had no prenatal care. Examination of the newborn in the delivery room shows malformed external ears, facial nerve palsy, and absence of the stapes bone on audiological testing. This patient's condition is most likely caused by abnormal development of the structure that also gives rise to which of the following?
- A. Muscles of mastication (Correct Answer)
- B. Maxillary process
- C. Meckel's cartilage
- D. Palatine tonsil
- E. Trigeminal nerve (CN V)
First pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***Muscles of mastication***
- The patient's presentation with **malformed external ears, facial nerve palsy (CN VII), and absence of the stapes** is characteristic of **second pharyngeal arch** abnormalities (seen in conditions like hemifacial microsomia or other branchial arch syndromes).
- The **second pharyngeal arch** (Reichert's cartilage) gives rise to the stapes, muscles of facial expression, styloid process, and is associated with CN VII (facial nerve).
- However, this question asks what else derives from "the structure" causing these findings. Since the **muscles of mastication derive from the first pharyngeal arch**, this appears to test understanding that they are NOT from the same arch as the stapes.
- **NOTE:** If this represents a combined first and second arch syndrome, then muscles of mastication (first arch) could be co-affected, making this the correct answer in that clinical context.
*Maxillary process*
- The maxillary process is derived from the **first pharyngeal arch** and forms the maxilla, zygoma, and part of the temporal bone.
- This is not derived from the second pharyngeal arch, which is primarily affected in this patient based on the stapes absence and facial nerve palsy.
*Meckel's cartilage*
- **Meckel's cartilage** is the cartilaginous component of the **first pharyngeal arch** and gives rise to the malleus, incus, anterior ligament of malleus, and sphenomandibular ligament.
- The **stapes** originates from the **second pharyngeal arch** (Reichert's cartilage), not Meckel's cartilage, making this an incorrect association.
*Palatine tonsil*
- The palatine tonsil develops from the **second pharyngeal pouch** (endoderm), not from the pharyngeal arches (mesoderm).
- Pouch derivatives are distinct from arch derivatives and are not involved in the skeletal and nerve malformations described.
*Trigeminal nerve (CN V)*
- The trigeminal nerve is the nerve of the **first pharyngeal arch** and provides sensory innervation to the face and motor innervation to the muscles of mastication.
- The **facial nerve (CN VII)** is the nerve of the **second pharyngeal arch**, which is the arch primarily affected in this clinical presentation.
First pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 8: A newborn male is evaluated in the hospital nursery two hours after birth. The patient was born at 39 weeks of gestation to a 30-year-old primigravid via vaginal delivery. The patient’s mother received routine prenatal care, and the pregnancy was uncomplicated. The patient’s anatomy ultrasound at 20 weeks of gestation was unremarkable. The patient’s mother denies any family history of genetic diseases. The patient’s Apgar scores were notable for poor muscle tone at both one and five minutes of life. The patient’s birth weight is 2.6 kg (5 lb 11 oz), which is at the 5th percentile. His height and head circumference are in the 15th and 3rd percentile, respectively. On physical exam, the patient has a wide nasal bridge, downslanting palpebral fissures, and widely spaced eyes. He has good respiratory effort with a high-pitched cry. This patient is most likely to have experienced a deletion on which of the following chromosomes?
- A. 4p
- B. 5q
- C. 7q
- D. 15q
- E. 5p (Correct Answer)
First pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***5p***
- The constellation of findings, including **low birth weight**, **microcephaly**, **hypotonia**, **widely spaced eyes**, **downslanting palpebral fissures**, **wide nasal bridge**, and a **high-pitched cry**, is highly characteristic of **Cri-du-chat syndrome**.
- **Cri-du-chat syndrome** is caused by a **deletion of the short arm of chromosome 5 (5p)**.
*4p*
- A deletion on **4p** is associated with **Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome**, which presents with **microcephaly**, a distinct **"Greek helmet" facial appearance**, and often severe intellectual disability, which are not perfectly aligned with all features described.
- While there can be overlapping features like growth restriction and developmental delay, the specific craniofacial features and the characteristic cry of Cri-du-chat are not typical for Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome.
*5q*
- A deletion on **5q** is associated with various conditions, including some forms of **myelodysplastic syndromes** (particularly 5q- syndrome), which are hematologic disorders and not typically presenting with the described birth defects.
- While deletions can occur on the long arm of chromosome 5, they do not cause Cri-du-chat syndrome; that is specifically a 5p deletion.
*7q*
- Deletions on **7q** are associated with conditions like **Williams syndrome** (a microdeletion on 7q11.23, characterized by "elfin" facies, supravalvular aortic stenosis, and unique personality traits) or **Silver-Russell syndrome** (associated with some 7q deletions, causing growth restriction and characteristic facial features).
- The described presentation does not match the typical features of conditions linked to 7q deletions.
*15q*
- Deletions on **15q** are linked to conditions such as **Prader-Willi syndrome** (paternal deletion of 15q11-q13, causing hypotonia, feeding difficulties in infancy followed by hyperphagia, and intellectual disability) and **Angelman syndrome** (maternal deletion or mutation on 15q11-q13, presenting with severe intellectual disability, ataxia, and inappropriate laughter).
- The clinical features presented do not align with the characteristic presentation of either Prader-Willi or Angelman syndrome.
First pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 9: A 10-year-old boy comes for a post-operative clinic visit with his ENT surgeon three months after airway reconstruction surgery and placement of a tracheostomy tube. Since the surgery, he says that he has been able to breathe better and is now getting used to tracheostomy care and tracheostomy tube changes. In addition to this surgery, he has had over twenty surgeries to implant hearing aids, reconstruct his cheekbones, and support his jaw to enable him to swallow. He was born with these abnormalities and had difficult breathing, hearing, and eating throughout his childhood. Fortunately, he is now beginning to feel better and is able to attend public school where he is one of the best students in the class. Abnormal development of which of the following structures is most likely responsible for this patient's malformations?
- A. Second branchial cleft
- B. First branchial pouch
- C. Third and fourth branchial pouches
- D. First branchial arch (Correct Answer)
- E. Second branchial arch
First pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***First branchial arch***
- The clinical presentation describes features consistent with **Treacher Collins syndrome** (TCS), also known as mandibulofacial dysostosis, which results from maldevelopment of **both the first and second branchial arches**.
- However, the **predominant and most characteristic features** arise from **first branchial arch** abnormalities: **mandibular hypoplasia** (requiring jaw support for swallowing), **malar/zygomatic hypoplasia** (reconstructed cheekbones), and **maxillary hypoplasia**.
- These first arch skeletal abnormalities cause the **airway obstruction** (requiring tracheostomy) and feeding difficulties.
- The first branchial arch gives rise to: **mandible, maxilla, zygomatic bone, incus, malleus, muscles of mastication, and CN V** (trigeminal nerve).
- While hearing issues may involve second arch structures (stapes), the **overwhelming majority** of this patient's clinical problems stem from first arch malformations.
*Second branchial cleft*
- The second branchial cleft typically forms the **cervical sinus**, which normally obliterates. Persistence can lead to **cervical cysts or fistulas**, presenting as neck masses.
- Abnormalities of the second branchial cleft do not explain the extensive craniofacial malformations, hearing deficits, or airway compromise seen in this patient.
*First branchial pouch*
- The first branchial pouch gives rise to the **auditory (eustachian) tube** and the **tympanic cavity** (middle ear).
- While isolated first pouch defects could contribute to hearing problems, they would **not explain** the severe facial bone malformations (mandibular and malar hypoplasia), airway obstruction, or feeding difficulties.
- The pouch is distinct from the arch, which forms the skeletal and muscular structures.
*Third and fourth branchial pouches*
- The third branchial pouch contributes to the **inferior parathyroid glands** and the **thymus**. The fourth branchial pouch contributes to the **superior parathyroid glands** and the **ultimobranchial body** (parafollicular C cells of the thyroid).
- Abnormalities in these pouches, such as in **DiGeorge syndrome (22q11.2 deletion)**, lead to **T-cell immunodeficiency, hypocalcemia, and cardiac defects** but do not account for the craniofacial and hearing abnormalities described.
*Second branchial arch*
- The second branchial arch gives rise to the **stapes**, **styloid process**, **lesser horn and upper body of hyoid bone**, **stapedius muscle**, and **CN VII** (facial nerve).
- While Treacher Collins syndrome involves both first and second arch abnormalities, the **second arch contributions** are less prominent clinically.
- Second arch defects could contribute to **conductive hearing loss** (via stapes abnormalities) and **facial nerve issues**, but these are not the predominant features in this case.
- The critical skeletal malformations causing airway compromise, feeding difficulties, and facial dysmorphism are primarily **first arch** derivatives.
First pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 10: A 52-year-old woman sees you in your office with a complaint of new-onset headaches over the past few weeks. On exam, you find a 2 x 2 cm dark, irregularly shaped, pigmented lesion on her back. She is concerned because her father recently passed away from skin cancer. What tissue type most directly gives rise to the lesion this patient is experiencing?
- A. Neural crest cells (Correct Answer)
- B. Endoderm
- C. Mesoderm
- D. Ectoderm
- E. Neuroectoderm
First pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***Neural crest cells***
- The suspected lesion, given its description and the patient's family history of skin cancer, is likely a **melanoma**.
- Melanoma originates from **melanocytes**, which are derived from **neural crest cells** during embryonic development.
*Endoderm*
- The endoderm gives rise to the **lining of the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts**, as well as organs such as the liver and pancreas.
- It is not involved in the formation of melanocytes or skin lesions like melanoma.
*Mesoderm*
- The mesoderm forms tissues such as **muscle, bone, cartilage, connective tissue**, and the circulatory system.
- It does not directly give rise to melanocytes, which are the cells of origin for melanoma.
*Ectoderm*
- The ectoderm gives rise to the **epidermis, nervous system**, and sensory organs.
- While melanocytes are found in the epidermis, they are specifically derived from the **neural crest (a sub-population of ectoderm)**, not the general ectoderm.
*Neuroectoderm*
- Neuroectoderm specifically refers to the ectoderm that develops into the **nervous system**.
- While neural crest cells originate from the neuroectoderm, "neural crest cells" is a more precise answer for the origin of melanocytes.
More First pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.