Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 1: A 4-year-old girl is brought to the physician for a painless lump on her neck. She has no history of serious illness and her vital signs are within normal limits. On examination, there is a firm, 2-cm swelling at the midline just below the level of the hyoid bone. The mass moves cranially when she is asked to protrude her tongue. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Cystic hygroma
- B. Thyroglossal cyst (Correct Answer)
- C. Ranula
- D. Dermoid cyst
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: Thyroglossal cyst
- A midline neck mass that moves cranially with tongue protrusion is the classic presentation of a thyroglossal duct cyst.
- These cysts arise from the remnant of the thyroglossal duct, the embryonic tract along which the thyroid gland descends from the foramen cecum to its final position [1].
Cystic hygroma
- This is a lymphatic malformation typically appearing as a soft, compressible, transilluminant mass, often in the posterior triangle of the neck.
- It does not move with tongue protrusion and is usually not midline.
Ranula
- A ranula is a mucocele that forms in the floor of the mouth, usually due to obstruction of a sublingual salivary gland.
- It presents as a swelling in the oral cavity, below the tongue, and not as an external neck mass.
Dermoid cyst
- A dermoid cyst in the neck is typically a painless, doughy, subcutaneous mass that is also usually midline but does not move with tongue protrusion.
- These cysts are often found above the hyoid bone, unlike the typical position of a thyroglossal cyst.
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 2: A 20-year-old man presents with a painless neck mass that has gradually increased in size. The mass is anteromedial to the right sternocleidomastoid muscle and has been present for 3 years. The mass increased in size and became more tender following an upper respiratory infection. An ultrasound of the neck identifies a single, round cystic mass with uniform, low echogenicity, and no internal septations. A contrast-enhanced CT scan of the neck shows a homogeneous mass with low attenuation centrally and with smooth rim enhancement. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. First branchial cleft cyst
- B. Sternomastoid tumor
- C. Second branchial cleft cyst (Correct Answer)
- D. Ectopic thyroid tissue
- E. Cervical lymphadenopathy
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: **Second branchial cleft cyst**
- The **location** (anteromedial to the sternocleidomastoid muscle), **painless** nature, and history of **gradual enlargement** becoming tender after an URI are classic presentations.
- **Imaging findings** (single, round cystic mass with uniform low echogenicity on ultrasound; homogeneous mass with low attenuation centrally and smooth rim enhancement on CT) are highly characteristic of an infected branchial cleft cyst.
*First branchial cleft cyst*
- Typically presents with a mass located near the **external auditory canal** or **angle of the mandible**, often causing otorrhea or recurrent infections.
- The presented mass is in a different anatomical location, **anteromedial** to the sternocleidomastoid.
*Sternomastoid tumor*
- This condition usually presents as a **fibrotic mass** within the sternocleidomastoid muscle in **neonates or infants**, associated with **congenital muscular torticollis**.
- The patient's age (20 years old) and the **cystic nature** of the mass make this diagnosis unlikely.
*Ectopic thyroid tissue*
- While possible in the neck, ectopic thyroid tissue would typically present as a **solid mass** and would show **iodine uptake** on nuclear imaging, not a cystic appearance on ultrasound and CT.
- It is more commonly located in the **midline** of the neck (e.g., lingual thyroid) rather than anteromedial to the sternocleidomastoid.
*Cervical lymphadenopathy*
- Enlarged lymph nodes typically present with **multiple, often tender, solid masses** or a single mass with typical lymph node morphology (e.g., hilar fat, oval shape), especially after an infection.
- The **cystic nature** described by imaging, with uniform low echogenicity and rim enhancement, is not typical for uncomplicated lymphadenopathy.
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 3: A 1-year-old boy presents to pediatrics clinic for a well-child visit. He has no complaints. He has a cleft palate and an abnormal facial appearance. He has been riddled with recurrent infections and is followed by cardiology for a ventricular septal defect (VSD). Vital signs are stable, and the patient's physical exam is benign. If this patient's medical history is part of a larger syndrome, what might one also discover that is consistent with the manifestations of this syndrome?
- A. Kidney stones
- B. A positive Chvostek's sign (Correct Answer)
- C. B-cell deficiency
- D. Hypoactive deep tendon reflexes
- E. A shortened QT Interval
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***A positive Chvostek's sign***
- The constellation of **cleft palate**, **abnormal facial appearance**, **recurrent infections**, and a **ventricular septal defect (VSD)** strongly suggests **DiGeorge syndrome**.
- In DiGeorge syndrome, hypoparathyroidism leads to **hypocalcemia**, which can manifest as neuromuscular irritability, including a positive **Chvostek's sign** (facial muscle twitching upon tapping the facial nerve).
*Kidney stones*
- **Kidney stones** are typically associated with **hypercalcemia** or other metabolic disorders, not hypocalcemia seen in DiGeorge syndrome.
- While DiGeorge patients can have renal anomalies, **nephrolithiasis** is not a characteristic feature of the syndrome.
*B-cell deficiency*
- DiGeorge syndrome is characterized by **T-cell deficiency** due to thymic hypoplasia or aplasia, not primarily B-cell deficiency.
- While **B cells** may be secondarily affected due to lack of T-cell help, the primary immunodeficiency is related to T-lymphocytes.
*Hypoactive deep tendon reflexes*
- **Hypocalcemia** typically causes **hyperactive deep tendon reflexes** and increased neuromuscular excitability, not hypoactivity.
- **Hypoactive reflexes** might suggest conditions like hypothyroidism or certain neurological disorders.
*A shortened QT Interval*
- **Hypocalcemia** is associated with a **prolonged QT interval** on an electrocardiogram, not a shortened one.
- A **shortened QT interval** can occur in conditions like hypercalcemia or genetic channelopathies.
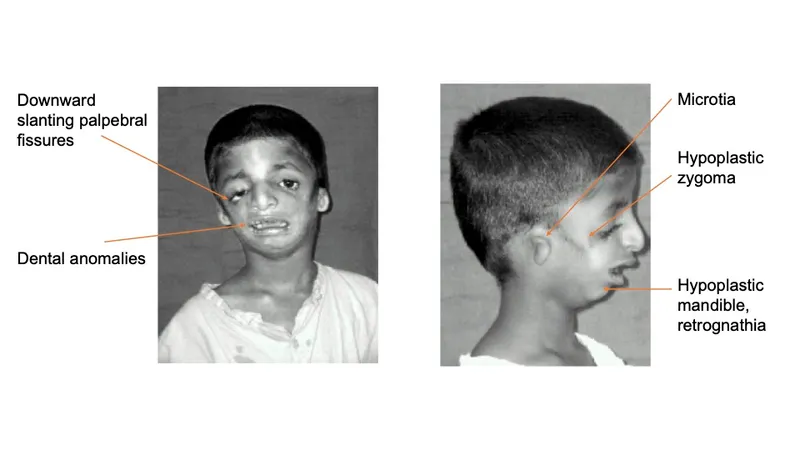
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 4: A 10-year-old boy comes for a post-operative clinic visit with his ENT surgeon three months after airway reconstruction surgery and placement of a tracheostomy tube. Since the surgery, he says that he has been able to breathe better and is now getting used to tracheostomy care and tracheostomy tube changes. In addition to this surgery, he has had over twenty surgeries to implant hearing aids, reconstruct his cheekbones, and support his jaw to enable him to swallow. He was born with these abnormalities and had difficult breathing, hearing, and eating throughout his childhood. Fortunately, he is now beginning to feel better and is able to attend public school where he is one of the best students in the class. Abnormal development of which of the following structures is most likely responsible for this patient's malformations?
- A. Second branchial cleft
- B. First branchial pouch
- C. Third and fourth branchial pouches
- D. First branchial arch (Correct Answer)
- E. Second branchial arch
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***First branchial arch***
- The clinical presentation describes features consistent with **Treacher Collins syndrome** (TCS), also known as mandibulofacial dysostosis, which results from maldevelopment of **both the first and second branchial arches**.
- However, the **predominant and most characteristic features** arise from **first branchial arch** abnormalities: **mandibular hypoplasia** (requiring jaw support for swallowing), **malar/zygomatic hypoplasia** (reconstructed cheekbones), and **maxillary hypoplasia**.
- These first arch skeletal abnormalities cause the **airway obstruction** (requiring tracheostomy) and feeding difficulties.
- The first branchial arch gives rise to: **mandible, maxilla, zygomatic bone, incus, malleus, muscles of mastication, and CN V** (trigeminal nerve).
- While hearing issues may involve second arch structures (stapes), the **overwhelming majority** of this patient's clinical problems stem from first arch malformations.
*Second branchial cleft*
- The second branchial cleft typically forms the **cervical sinus**, which normally obliterates. Persistence can lead to **cervical cysts or fistulas**, presenting as neck masses.
- Abnormalities of the second branchial cleft do not explain the extensive craniofacial malformations, hearing deficits, or airway compromise seen in this patient.
*First branchial pouch*
- The first branchial pouch gives rise to the **auditory (eustachian) tube** and the **tympanic cavity** (middle ear).
- While isolated first pouch defects could contribute to hearing problems, they would **not explain** the severe facial bone malformations (mandibular and malar hypoplasia), airway obstruction, or feeding difficulties.
- The pouch is distinct from the arch, which forms the skeletal and muscular structures.
*Third and fourth branchial pouches*
- The third branchial pouch contributes to the **inferior parathyroid glands** and the **thymus**. The fourth branchial pouch contributes to the **superior parathyroid glands** and the **ultimobranchial body** (parafollicular C cells of the thyroid).
- Abnormalities in these pouches, such as in **DiGeorge syndrome (22q11.2 deletion)**, lead to **T-cell immunodeficiency, hypocalcemia, and cardiac defects** but do not account for the craniofacial and hearing abnormalities described.
*Second branchial arch*
- The second branchial arch gives rise to the **stapes**, **styloid process**, **lesser horn and upper body of hyoid bone**, **stapedius muscle**, and **CN VII** (facial nerve).
- While Treacher Collins syndrome involves both first and second arch abnormalities, the **second arch contributions** are less prominent clinically.
- Second arch defects could contribute to **conductive hearing loss** (via stapes abnormalities) and **facial nerve issues**, but these are not the predominant features in this case.
- The critical skeletal malformations causing airway compromise, feeding difficulties, and facial dysmorphism are primarily **first arch** derivatives.
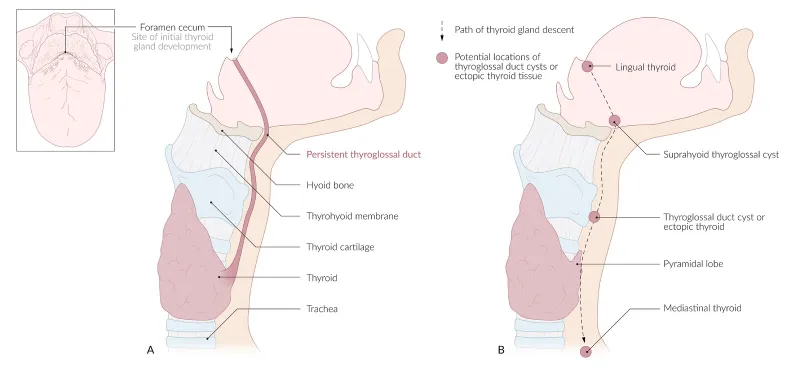
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 5: A six year-old female presents for evaluation of dry skin, fatigue, sensitivity to cold and constipation. The patient’s mother recalls that the patient had surgery to remove a “benign mass” at the base of her tongue 3 months ago because of trouble swallowing. What was the likely cause of the surgically removed mass?
- A. Failed caudal migration of the thyroid gland (Correct Answer)
- B. Iodine deficiency
- C. Failed fusion of the palatine shelves with the nasal septum
- D. Radiation exposure
- E. Maternal Diabetes Mellitus
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***Failed caudal migration of the thyroid gland***
- The symptoms of **dry skin, fatigue, cold sensitivity, and constipation** are classic signs of **hypothyroidism**.
- A mass at the **base of the tongue** that is later removed and leads to hypothyroidism strongly suggests a **lingual thyroid**, which results from the thyroid gland's **failure to descend** from its embryonic origin at the foramen cecum.
*Iodine deficiency*
- While iodine deficiency can cause **hypothyroidism** and **goiter**, it typically does not present as a **discrete mass** at the base of the tongue requiring surgical removal.
- It would usually result in a more generalized **enlargement of the thyroid gland**, often in the neck.
*Failed fusion of the palatine shelves with the nasal septum*
- This developmental anomaly leads to a **cleft palate**, affecting the **roof of the mouth**.
- It has no direct association with thyroid function or masses at the base of the tongue.
*Radiation exposure*
- Radiation exposure can increase the risk of thyroid cancer or hypothyroidism later in life, but it typically doesn't cause a congenital benign mass at the base of the tongue that presents in early childhood.
- Furthermore, the specific presentation points to a developmental anomaly rather than an acquired condition.
*Maternal Diabetes Mellitus*
- Maternal diabetes can lead to various congenital anomalies in the fetus, such as **macrosomia, caudal regression syndrome, or cardiac defects**.
- However, it is not a recognized cause of a lingual thyroid or a failure of thyroid migration.
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 6: A 2850-g (6-lb 5-oz) newborn is delivered at term to a 19-year-old primigravid woman via normal spontaneous vaginal delivery. The mother has had no prenatal care. Examination of the newborn in the delivery room shows malformed external ears, facial nerve palsy, and absence of the stapes bone on audiological testing. This patient's condition is most likely caused by abnormal development of the structure that also gives rise to which of the following?
- A. Muscles of mastication (Correct Answer)
- B. Maxillary process
- C. Meckel's cartilage
- D. Palatine tonsil
- E. Trigeminal nerve (CN V)
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***Muscles of mastication***
- The patient's presentation with **malformed external ears, facial nerve palsy (CN VII), and absence of the stapes** is characteristic of **second pharyngeal arch** abnormalities (seen in conditions like hemifacial microsomia or other branchial arch syndromes).
- The **second pharyngeal arch** (Reichert's cartilage) gives rise to the stapes, muscles of facial expression, styloid process, and is associated with CN VII (facial nerve).
- However, this question asks what else derives from "the structure" causing these findings. Since the **muscles of mastication derive from the first pharyngeal arch**, this appears to test understanding that they are NOT from the same arch as the stapes.
- **NOTE:** If this represents a combined first and second arch syndrome, then muscles of mastication (first arch) could be co-affected, making this the correct answer in that clinical context.
*Maxillary process*
- The maxillary process is derived from the **first pharyngeal arch** and forms the maxilla, zygoma, and part of the temporal bone.
- This is not derived from the second pharyngeal arch, which is primarily affected in this patient based on the stapes absence and facial nerve palsy.
*Meckel's cartilage*
- **Meckel's cartilage** is the cartilaginous component of the **first pharyngeal arch** and gives rise to the malleus, incus, anterior ligament of malleus, and sphenomandibular ligament.
- The **stapes** originates from the **second pharyngeal arch** (Reichert's cartilage), not Meckel's cartilage, making this an incorrect association.
*Palatine tonsil*
- The palatine tonsil develops from the **second pharyngeal pouch** (endoderm), not from the pharyngeal arches (mesoderm).
- Pouch derivatives are distinct from arch derivatives and are not involved in the skeletal and nerve malformations described.
*Trigeminal nerve (CN V)*
- The trigeminal nerve is the nerve of the **first pharyngeal arch** and provides sensory innervation to the face and motor innervation to the muscles of mastication.
- The **facial nerve (CN VII)** is the nerve of the **second pharyngeal arch**, which is the arch primarily affected in this clinical presentation.
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 7: A group of investigators studying embryological defects in mice knock out a gene that is responsible for the development of the ventral wing of the third branchial pouch. A similar developmental anomaly in a human embryo is most likely to result in which of the following findings after birth?
- A. Cleft palate
- B. Discharging neck sinus (Correct Answer)
- C. Carpopedal spasm
- D. Conductive hearing loss
- E. White oral patches
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***Discharging neck sinus***
- The **ventral wing of the third pharyngeal pouch** gives rise to the **thymus**
- During embryonic development, the thymus descends from the pharynx into the anterior mediastinum via the **thymopharyngeal duct**
- Normally, this duct obliterates completely, but **failure of obliteration** can result in a **cervical thymic cyst** or **persistent thymic tract**
- This presents as a **discharging neck sinus** along the lateral neck (anterior border of sternocleidomastoid), which may drain clear fluid or become infected
- This is a classic presentation of a **third pharyngeal pouch anomaly** affecting the thymic descent pathway
*Carpopedal spasm*
- **Carpopedal spasm** is a sign of **hypocalcemia** due to **hypoparathyroidism**
- The **dorsal wing** (not ventral wing) of the third pharyngeal pouch forms the **inferior parathyroid glands**
- Since the question specifically identifies a defect in the **ventral wing** (thymus), hypoparathyroidism would not result
- A dorsal wing defect would cause absent inferior parathyroid glands and hypocalcemia
*Cleft palate*
- Results from failure of **palatine shelf fusion** during weeks 8-12 of development
- Associated with **maxillary prominence** derivatives (first pharyngeal arch) and secondary palate formation
- Not related to third pharyngeal pouch development
*Conductive hearing loss*
- Associated with **first and second pharyngeal arch** derivatives affecting the middle ear structures
- First arch: malleus, incus (in part); Second arch: stapes (in part)
- The **third pharyngeal pouch** does not contribute to auditory structures
*White oral patches*
- Typically represent **mucosal lesions** (leukoplakia, candidiasis, lichen planus)
- Not associated with embryological defects of the pharyngeal apparatus
- Unrelated to third pharyngeal pouch derivatives
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 8: A 25-year-old woman gives birth to a male child at 30 weeks of gestation. Pregnancy was complicated by polyhydramnios diagnosed on ultrasonography at 26 weeks of gestation. The baby is born vaginally weighing 1.2 kg (2.64 lb). Because he does not cry immediately after birth, endotracheal intubation is attempted to secure the airway. However, the vocal cords cannot be visualized because there is only a single opening corresponding to the esophagus. He is transferred to the NICU under bag and mask ventilation, where intubation is attempted once again by passing the endotracheal tube in the visualized opening, after which his oxygen saturation begins to improve. His temperature is 37.0ºC (98.6°F), pulse is 120/min, and respiratory rate is 42/min. On physical examination, no abnormalities are noted. Chest radiography is suggestive of respiratory distress syndrome. Which of the following most likely failed to develop in this patient?
- A. Second branchial arch
- B. Mesonephric duct
- C. Fourth and sixth branchial arches (Correct Answer)
- D. First branchial arch
- E. Third branchial arch
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***Fourth and sixth branchial arches***
- The clinical presentation of **inability to visualize the vocal cords** and the presence of only a **single opening** suggests **laryngeal atresia** or severe laryngotracheal malformation. While the laryngotracheal structures primarily develop from the laryngotracheal diverticulum (an outgrowth of the foregut), the **fourth and sixth pharyngeal arches** are critical for the development of **laryngeal cartilages** and **innervation**:
- **Fourth arch**: Contributes to the thyroid cartilage, cricothyroid muscle, and superior laryngeal nerve
- **Sixth arch**: Forms the cricoid cartilage, arytenoid cartilages, and provides the recurrent laryngeal nerve (innervating all intrinsic laryngeal muscles except cricothyroid)
- Failure of proper development of these arches results in **absence or malformation of the larynx**, preventing normal vocal cord formation and airway development.
- The **polyhydramnios** occurs because the fetus cannot swallow amniotic fluid effectively due to airway obstruction.
*Second branchial arch*
- The **second branchial arch** (hyoid arch) contributes to the **stapes**, styloid process, stylohyoid ligament, lesser horn and upper body of the hyoid bone, and muscles of facial expression (via facial nerve).
- Defects in this arch typically lead to conditions like **Treacher Collins syndrome** or hemifacial microsomia, not laryngeal agenesis.
*Mesonephric duct*
- The **mesonephric duct (Wolffian duct)** is an embryonic structure crucial for the development of male internal reproductive organs including the **epididymis**, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, and ejaculatory duct.
- Failure of this duct to develop would result in male reproductive anomalies, not respiratory tract malformations.
*First branchial arch*
- The **first branchial arch** (mandibular arch) gives rise to the **maxilla, mandible, malleus, incus**, muscles of mastication, and trigeminal nerve branches.
- Malformations of this arch are associated with conditions like **Pierre Robin sequence** or mandibulofacial dysostosis, presenting with micrognathia and facial abnormalities, which are not described in this case.
*Third branchial arch*
- The **third branchial arch** forms the **greater horn and lower body of the hyoid bone**, stylopharyngeus muscle, and glossopharyngeal nerve.
- Anomalies of this arch may present with swallowing difficulties or glossopharyngeal nerve deficits, but do not cause the complete absence of laryngeal structures described in this scenario.
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 9: A patient was admitted with skull base trauma. The doctor was testing the marked structure in the pharyngeal region. Which of the following nerves was being tested?
- A. Trigeminal nerve
- B. Facial nerve
- C. Glossopharyngeal nerve (Correct Answer)
- D. Vagus
- E. Hypoglossal nerve
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***Glossopharyngeal nerve***
- The image shows a probe stimulating the posterior part of the **pharynx**, which elicits the **gag reflex**.
- The afferent limb of the **gag reflex** is mediated primarily by the **glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)**, which detects sensation from the posterior tongue and pharynx.
*Trigeminal nerve*
- The **trigeminal nerve (CN V)** primarily mediates sensation from the face, teeth, and anterior two-thirds of the tongue, and motor control of the **muscles of mastication**.
- It does not have a primary role in the sensation or reflex of the posterior pharyngeal wall.
*Facial nerve*
- The **facial nerve (CN VII)** is responsible for the **muscles of facial expression**, taste from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, and parasympathetic innervation to several glands.
- While it contributes to some aspects of swallowing, it is not the main sensory nerve for the gag reflex from the posterior pharynx.
*Vagus*
- The **vagus nerve (CN X)** provides the efferent limb of the gag reflex, causing pharyngeal muscle contraction.
- However, the sensory input from the posterior pharynx (the afferent limb being tested by the probe) is primarily carried by the **glossopharyngeal nerve**.
*Hypoglossal nerve*
- The **hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)** provides motor innervation to the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue.
- While it is relevant in skull base trauma, it does not mediate sensation from the pharynx or the gag reflex being tested in the image.
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG Question 10: A 29-year-old mother brings in her 2-week-old baby boy to a pediatrician because he has been having difficulty feeding. The mother reveals that she had no prenatal care during her pregnancy and gave birth at home without complications. She says that her son seems to be having difficulty sucking, and she occasionally sees breast milk coming out of the infant’s nose. Physical exam reveals that this patient has a gap between his oral and nasal cavities behind the incisive foramen. He is therefore prescribed specialized bottles and his mom is taught positional techniques to ensure better feeding. Failure to fuse which of the following structures is most likely responsible for this patient's disorder?
- A. Maxillary and medial nasal prominences
- B. Nasal septum with primary plates
- C. Maxillary and lateral nasal prominences
- D. Palatine shelves with primary plates
- E. Palatine shelves with nasal septum (Correct Answer)
Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives Explanation: ***Palatine shelves with nasal septum***
- A **cleft palate** results from the **failure of fusion of the palatine shelves** with each other and/or with the **nasal septum**, creating an abnormal communication between the oral and nasal cavities.
- This anatomical defect explains the infant's **feeding difficulties** and the leakage of breast milk into the nose, as well as the observed **gap behind the incisive foramen**.
*Maxillary and medial nasal prominences*
- The failure of fusion between the maxillary and medial nasal prominences results in a **cleft lip**, which is an anterior defect and does not explain the posterior gap described.
- While cleft lip can coexist with cleft palate, the symptoms here specifically point to a palatal defect, not primarily a lip defect.
*Nasal septum with primary plates*
- The primary palate forms from the fusion of the medial nasal prominences, anterior to the incisive foramen.
- While crucial for normal development, the specific clinical presentation (gap *behind* the incisive foramen and feeding difficulties) is more characteristic of a secondary palate defect involving the palatine shelves.
*Maxillary and lateral nasal prominences*
- The fusion of these structures contributes to the formation of the **nasolacrimal groove** and parts of the cheek, not the palate.
- Deficiencies in this fusion would lead to defects in the lateral facial region, not an oro-nasal communication related to feeding.
*Palatine shelves with primary plates*
- The **primary palate** fuses with the anterior part of the secondary palate (formed by the palatine shelves) at the incisive foramen.
- However, the more common and clinically relevant defect leading to an open communication between the oral and nasal cavities, especially *behind* the incisive foramen, involves the failure of fusion of the **palatine shelves** with each other and the **nasal septum**.
More Congenital anomalies of pharyngeal arch derivatives US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.