Urinary system histology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Urinary system histology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Urinary system histology US Medical PG Question 1: Which region of the nephron reabsorbs the highest percentage of filtered bicarbonate?
- A. Collecting duct
- B. Thick ascending limb
- C. Distal tubule
- D. Proximal tubule (Correct Answer)
Urinary system histology Explanation: ***Proximal tubule***
- The **proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)** reabsorbs approximately 80-90% of the **filtered bicarbonate** through a process involving **carbonic anhydrase** and the **Na+/H+ exchanger**.
- This vital function ensures that the majority of bicarbonate, a key buffer, is returned to the blood to maintain **acid-base balance**.
*Collecting duct*
- While the collecting duct does have the ability to reabsorb and secrete bicarbonate, its contribution is minor compared to the PCT, primarily for fine-tuning acid-base balance.
- Cells in the collecting duct, particularly **Type A intercalated cells**, are important for secreting acid (H+) in acidosis and therefore reabsorbing bicarbonate, but not the bulk of it.
*Thick ascending limb*
- The primary role of the **thick ascending limb** is the reabsorption of **sodium**, **potassium**, and **chloride** to create a concentrated interstitium, not significant bicarbonate reabsorption.
- It is largely impermeable to water and is relatively impermeable to bicarbonate.
*Distal tubule*
- The **distal convoluted tubule (DCT)** reabsorbs a small percentage of filtered bicarbonate, but its main role is regulated reabsorption of **sodium** and **calcium**, and secretion of **potassium** and **hydrogen ions**.
- Its contribution to bicarbonate reabsorption is much less significant than that of the proximal tubule.
Urinary system histology US Medical PG Question 2: A 56-year-old man undergoes a cystoscopy for the evaluation of macroscopic hematuria. During the procedure, an opening covered with a mucosal flap is visualized at the base of the trigone. Which of the following best describes this structure?
- A. Ejaculatory duct opening
- B. Ureteric orifice (Correct Answer)
- C. Diverticular opening
- D. Prostatic utricle
- E. Internal urethral orifice
Urinary system histology Explanation: ***Ureteric orifice***
- The description of an opening covered with a **mucosal flap** specifically at the **base of the trigone** is characteristic of a normal ureteric orifice, which prevents reflux of urine.
- The trigone is a triangular area at the base of the bladder formed by the two ureteric orifices and the internal urethral orifice.
*Ejaculatory duct opening*
- The ejaculatory ducts open into the **prostatic urethra**, not directly into the bladder trigone.
- They are typically located on the **verumontanum** within the prostatic urethra, posterior to the bladder neck.
*Diverticular opening*
- A diverticulum is an **outpouching** of the bladder wall, and its opening can appear anywhere, not specifically at the base of the trigone with a mucosal flap.
- While it's an opening, it would represent a pathological condition, not a normal anatomical structure.
*Prostatic utricle*
- The prostatic utricle is a small blind-ending pouch located in the **prostatic urethra**, often on the verumontanum.
- It is an embryonic remnant and is not found at the base of the bladder trigone.
*Internal urethral orifice*
- This is the opening of the **urethra** from the bladder, located at the **apex of the trigone**, not covered by a mucosal flap in the same way as a ureteric orifice.
- It marks the junction between the bladder and the urethra.
Urinary system histology US Medical PG Question 3: On cardiology service rounds, your team sees a patient admitted with an acute congestive heart failure exacerbation. In congestive heart failure, decreased cardiac function leads to decreased renal perfusion, which eventually leads to excess volume retention. To test your knowledge of physiology, your attending asks you which segment of the nephron is responsible for the majority of water absorption. Which of the following is a correct pairing of the segment of the nephron that reabsorbs the majority of all filtered water with the means by which that segment absorbs water?
- A. Distal convoluted tubule via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption
- B. Distal convoluted tubule via aquaporin channels
- C. Thick ascending loop of Henle via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption
- D. Proximal convoluted tubule via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption (Correct Answer)
- E. Collecting duct via aquaporin channels
Urinary system histology Explanation: ***Proximal convoluted tubule via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption***
- The **proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)** is responsible for reabsorbing approximately **65-70% of filtered water**, making it the primary site of water reabsorption in the nephron.
- This water reabsorption primarily occurs **passively**, following the active reabsorption of solutes (especially **sodium ions**), which creates an osmotic gradient.
*Distal convoluted tubule via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption*
- The **distal convoluted tubule (DCT)** reabsorbs a much smaller percentage of filtered water (around 5-10%) and its water reabsorption is largely **regulated by ADH**, not primarily simple passive diffusion following bulk ion reabsorption.
- While some passive water movement occurs, it is not the main mechanism or location for the majority of water reabsorption.
*Distal convoluted tubule via aquaporin channels*
- While aquaporin channels do play a role in water reabsorption in the DCT, particularly under the influence of **ADH**, the DCT is not the segment responsible for the **majority of all filtered water absorption**.
- The bulk of water reabsorption occurs earlier in the nephron, independently of ADH for the most part.
*Thick ascending loop of Henle via passive diffusion following ion reabsorption*
- The **thick ascending loop of Henle** is primarily involved in reabsorbing ions like Na+, K+, and Cl- but is largely **impermeable to water**.
- Its impermeability to water is crucial for creating the **osmotic gradient** in the renal medulla, which is necessary for later water reabsorption.
*Collecting duct via aquaporin channels*
- The **collecting duct** is critically important for **regulated water reabsorption** via **aquaporin-2 channels** under the influence of **ADH**, allowing for fine-tuning of urine concentration.
- However, it reabsorbs only a variable portion (typically 5-19%) of the remaining filtered water, not the **majority of all filtered water**.
Urinary system histology US Medical PG Question 4: Which transport mechanism is primarily responsible for calcium reabsorption in the proximal tubule?
- A. Paracellular transport (Correct Answer)
- B. Facilitated diffusion
- C. Active transport
- D. Antiport with sodium
Urinary system histology Explanation: ***Paracellular transport***
- In the **proximal tubule**, approximately 60-70% of filtered calcium is reabsorbed primarily through the **paracellular pathway**, driven by the electrochemical gradient and solvent drag.
- This transport occurs between cells, moving through the **tight junctions**, and is passive, following the reabsorption of water.
*Facilitated diffusion*
- While a type of passive transport, **facilitated diffusion** typically involves membrane proteins and occurs across the cell membrane, not primarily between cells in the proximal tubule for calcium.
- This mechanism is prominent for calcium reabsorption in other nephron segments like the **distal convoluted tubule** via **TRPV5/6 channels**, but not the main route in the proximal tubule.
*Active transport*
- **Active transport** of calcium, mainly via **calcium ATPase** and the **Na+/Ca2+ exchanger**, occurs across the luminal and basolateral membranes, respectively, in specific nephron segments.
- However, in the **proximal tubule**, the bulk of calcium reabsorption is passive and paracellular, not ATP-dependent active transport across cell membranes.
*Antiport with sodium*
- The **Na+/Ca2+ exchanger (NCX)** is an antiport mechanism that plays a crucial role in extruding calcium from the cell into the interstitium, particularly in the basolateral membrane of the distal tubule.
- However, it is not the primary mechanism for overall tubular reabsorption of calcium in the **proximal tubule**, where paracellular movement dominates.
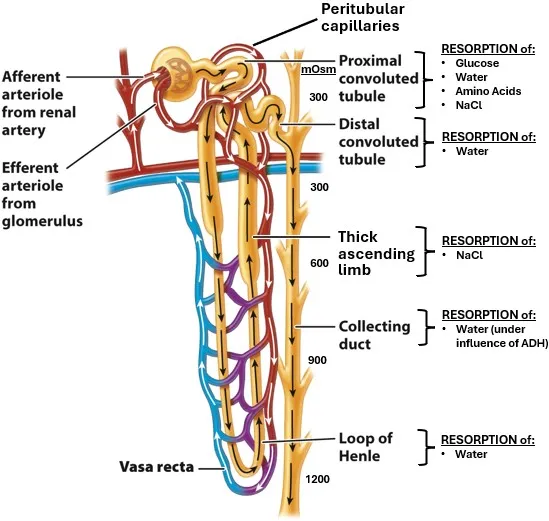
Urinary system histology US Medical PG Question 5: An investigator is studying physiologic renal responses to common medical conditions. She measures urine osmolalities in different parts of the nephron of a human subject in the emergency department. The following values are obtained:
Portion of nephron Osmolality (mOsmol/kg)
Proximal convoluted tubule 300
Loop of Henle, descending limb 1200
Loop of Henle, ascending limb 250
Distal convoluted tubule 100
Collecting duct 1200
These values were most likely obtained from an individual with which of the following condition?
- A. Gitelman syndrome
- B. Psychogenic polydipsia
- C. Furosemide overdose
- D. Dehydration (Correct Answer)
- E. Diabetes insipidus
Urinary system histology Explanation: ***Dehydration***
- The high osmolality in the **collecting duct (1200 mOsmol/kg)** indicates the kidney is actively conserving water, a normal physiological response to **dehydration**.
- In dehydration, **antidiuretic hormone (ADH)** levels are high, leading to increased water reabsorption in the collecting ducts and thus a concentrated urine.
*Gitelman syndrome*
- This condition involves a defect in the **NaCl cotransporter** in the **distal convoluted tubule**, leading to impaired sodium reabsorption.
- Patients typically present with significant **hypokalemia**, metabolic alkalosis, and a relatively dilute urine, which is not consistent with the given osmolality values.
*Psychogenic polydipsia*
- Individuals with psychogenic polydipsia consume excessive amounts of water, leading to **dilute urine** (low urine osmolality) as a compensatory mechanism to excrete the excess water.
- This would result in much lower osmolality values throughout the nephron, particularly in the collecting duct, compared to the values provided.
*Furosemide overdose*
- Furosemide is a **loop diuretic** that inhibits the reabsorption of sodium and chloride in the **thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle**.
- This would impair the kidney's ability to concentrate urine, leading to a much **lower osmolality in the collecting duct** than observed in this scenario.
*Diabetes insipidus*
- Diabetes insipidus (DI) is characterized by either a deficiency in ADH (central DI) or unresponsiveness to ADH (nephrogenic DI).
- In both types, the kidney cannot concentrate urine effectively, resulting in the production of a **large volume of very dilute urine** (low urine osmolality, typically <300 mOsmol/kg), which contradicts the high collecting duct osmolality.
Urinary system histology US Medical PG Question 6: To reduce the hemolysis that occurs with dialysis, researchers have developed an organic filtration membrane for dialysis that is believed to mimic the physiologic filtering apparatus of the human glomerulus. The permeability characteristics of this membrane are believed to be identical to those of the glomerular filtering membrane. Which of the following substances should be absent in the filtrate produced by this membrane?
- A. Amino acids
- B. Albumin (Correct Answer)
- C. Urea
- D. Creatinine
- E. Sodium
Urinary system histology Explanation: ***Albumin***
- The **glomerular filtration barrier** prevents passage of large proteins, especially **albumin (MW ~66 kDa)**, into the filtrate due to both **size selectivity** (fenestrated endothelium, basement membrane, slit diaphragms) and **charge selectivity** (negative charges repel anionic proteins).
- Albumin absence in filtrate indicates proper membrane function mimicking a healthy glomerulus.
- Normal albumin filtration is <30 mg/day; albuminuria indicates glomerular damage.
*Amino acids*
- Small molecules (MW ~100-200 Da) that are **freely filtered** by the glomerulus.
- Normally >95% reabsorbed in proximal tubule, but their presence in initial filtrate is expected and normal.
*Urea*
- Small waste product (MW 60 Da) that is **readily filtered** by the glomerulus.
- Primary uremic toxin removed during dialysis; freely passes through glomerular barrier.
*Creatinine*
- Small waste product (MW 113 Da) that is **freely filtered** and minimally reabsorbed.
- Used clinically to estimate GFR (creatinine clearance); must be present in filtrate.
*Sodium*
- Small cation (MW 23 Da) that is **freely filtered** by the glomerulus.
- Essential for fluid and electrolyte balance; normal presence in filtrate with subsequent tubular reabsorption (~99%).
Urinary system histology US Medical PG Question 7: A 67-year-old man comes to the physician because of urinary frequency, dysuria, and blood in his urine. He has also had a 4.5-kg (10-lb) weight loss over the past 3 months and has been feeling more fatigued than usual. He smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 40 years but quit 2 years ago. A urinalysis shows 3+ blood. Cystoscopy shows an irregular mass on the bladder wall; a biopsy is taken. Which of the following histologic findings would indicate the worst survival prognosis?
- A. Disordered urothelium lined with papillary fronds
- B. Dysplastic cells extending into the lamina propria
- C. Infiltrating nests of cells with squamous differentiation
- D. Nests of atypical cells in the urothelium
- E. Tubular glands with mucin secretions (Correct Answer)
Urinary system histology Explanation: ***Tubular glands with mucin secretions***
- The presence of **tubular glands with mucin secretions** indicates a diagnosis of **adenocarcinoma of the bladder**.
- Bladder adenocarcinoma is a rare and aggressive form of bladder cancer with a **significantly worse prognosis** compared to urothelial carcinoma, comprising <2% of bladder cancers and often presenting at advanced stages with limited treatment options.
*Dysplastic cells extending into the lamina propria*
- This description refers to **high-grade urothelial carcinoma** that has invaded the **lamina propria** (stage T1).
- While it's an invasive cancer with significant risk, it generally has a better prognosis than adenocarcinoma when treated appropriately.
*Disordered urothelium lined with papillary fronds*
- This suggests a **papillary urothelial neoplasm**, which could be low-grade or high-grade.
- Early-stage papillary tumors generally have a favorable prognosis, especially low-grade variants.
*Nests of atypical cells in the urothelium*
- This finding describes **carcinoma in situ (CIS)**, a high-grade, flat, non-invasive form of urothelial carcinoma.
- Although it has a high risk of progression to invasive cancer, it does not inherently indicate a worse prognosis than invasive adenocarcinoma at the time of diagnosis.
*Infiltrating nests of cells with squamous differentiation*
- This describes **squamous cell carcinoma of the bladder**, which accounts for 3-5% of bladder cancers.
- While aggressive and often associated with chronic irritation or schistosomiasis, it generally has a better prognosis than adenocarcinoma when detected and treated early.
Urinary system histology US Medical PG Question 8: A 17-year-old boy is brought to the physician by his father because of a 7-month history of fatigue, recurrent leg cramps, and increased urinary frequency. His pulse is 94/min and blood pressure is 118/85 mm Hg. Physical examination shows dry mucous membranes. Laboratory studies show:
Serum
Na+ 130 mEq/L
K+ 2.8 mEq/L
Cl- 92 mEq/L
Mg2+ 1.1 mEq/L
Ca2+ 10.6 mg/dL
Albumin 5.2 g/dL
Urine
Ca2+ 70 mg/24 h
Cl- 375 mEq/24h (N = 110–250)
Arterial blood gas analysis on room air shows a pH of 7.55 and an HCO3- concentration of 45 mEq/L. Impaired function of which of the following structures is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Ascending loop of Henle
- B. Collecting duct
- C. Distal convoluted tubule (Correct Answer)
- D. Descending loop of Henle
- E. Proximal convoluted tubule
Urinary system histology Explanation: ***Distal convoluted tubule***
- The patient presents with **hypokalemia**, **metabolic alkalosis**, **hypomagnesemia**, and **hypocalciuria** (24-hour urine Ca2+ 70 mg, normal up to 250 mg), which are characteristic findings of **Gitelman syndrome**.
- **Gitelman syndrome** is caused by a loss-of-function mutation in the **thiazide-sensitive Na-Cl cotransporter (NCC)**, located in the **distal convoluted tubule**, leading to impaired reabsorption of Na+ and Cl- at this segment.
*Ascending loop of Henle*
- Impaired function of the **Na-K-2Cl cotransporter (NKCC2)** in the **thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle** causes **Bartter syndrome**.
- Bartter syndrome typically presents with **hypercalciuria**, in contrast to the hypocalciuria seen in this patient.
*Collecting duct*
- Dysfunction of the **collecting duct** can lead to various conditions, such as **renal tubular acidosis** or **diabetes insipidus**, depending on which channels or receptors are affected.
- However, the specific combination of **hypokalemia**, **metabolic alkalosis**, **hypomagnesemia**, and **hypocalciuria** points away from primary collecting duct dysfunction.
*Descending loop of Henle*
- The **descending loop of Henle** is primarily permeable to **water** and has a limited role in electrolyte reabsorption.
- Impairment here would primarily affect **urine concentration** and dilution but would not account for the specific electrolyte imbalances observed.
*Proximal convoluted tubule*
- The **proximal convoluted tubule** is responsible for reabsorbing a large fraction of filtered electrolytes, glucose, and amino acids.
- Dysfunction here (e.g., **Fanconi syndrome**) would typically present with **generalized aminoaciduria**, **glycosuria**, **phosphaturia**, and **proximal renal tubular acidosis**, which are not seen in this patient.
Urinary system histology US Medical PG Question 9: A male newborn is born at 37 weeks' gestation after spontaneous vaginal delivery. The mother had no prenatal care. Physical examination shows a urethral opening on the dorsal aspect of the penis, 4 mm proximal to the glans. There is a 3-cm defect in the midline abdominal wall superior to the pubic symphysis with exposure of moist, erythematous mucosa. Which of the following is the most likely underlying cause of this patient's findings?
- A. Abnormal development of the gubernaculum
- B. Persistence of the urogenital membrane
- C. Failed fusion of the urethral folds
- D. Incomplete union of the labioscrotal swellings
- E. Malpositioning of the genital tubercle (Correct Answer)
Urinary system histology Explanation: ***Malpositioning of the genital tubercle***
- This condition describes **epispadias** (urethral opening on the dorsal aspect) and **bladder exstrophy** (abdominal wall defect with exposed bladder mucosa), which are frequently co-occurring and caused by a **ventral displacement of the genital tubercle**.
- A defect in the **abdominal wall closure** allows the bladder to remain exposed, and the abnormal positioning of the genital tubercle leads to an improperly formed urethra.
*Abnormal development of the gubernaculum*
- The gubernaculum is crucial for **testicular descent**; abnormal development would typically lead to **cryptorchidism** (undescended testes).
- It does not explain the urethral opening on the dorsal penis or the abdominal wall defect.
*Persistence of the urogenital membrane*
- Persistent urogenital membrane typically results in conditions like an **imperforate hymen** in females or **urogenital sinus anomalies**, but not epispadias or bladder exstrophy.
- This membrane normally ruptures, creating the definitive openings for the urethra and vagina.
*Failed fusion of the urethral folds*
- Failed fusion of the urethral folds in males can lead to **hypospadias**, where the urethral opening is on the **ventral** aspect of the penis.
- It does not account for the **dorsal urethral opening (epispadias)** described or the associated bladder exstrophy.
*Incomplete union of the labioscrotal swellings*
- Incomplete union of the labioscrotal swellings in males results in **bifid scrotum** or **hypospadias**.
- This doesn't explain the characteristic dorsal urethral defect of epispadias or the large abdominal wall defect associated with bladder exstrophy.
Urinary system histology US Medical PG Question 10: An investigator is studying the effects of an antihypertensive drug during pregnancy. Follow-up studies show that the drug can adversely affect differentiation of the ureteric bud into its direct derivatives in fetuses exposed during the first trimester. Which of the following structures is most likely to develop incorrectly in the affected fetus?
- A. Collecting ducts (Correct Answer)
- B. Proximal convoluted tubule
- C. Loop of Henle
- D. Bladder
- E. Distal convoluted tubule
Urinary system histology Explanation: ***Collecting ducts***
- The **ureteric bud** is an outgrowth of the **mesonephric (Wolffian) duct** that directly gives rise to the **collecting ducts**, minor and major calyces, renal pelvis, and ureter.
- An adverse effect on the differentiation of the ureteric bud during the first trimester would directly impact the development of these structures, potentially leading to renal dysplasia or collecting system abnormalities.
- **Clinical correlation**: ACE inhibitors and ARBs are contraindicated in pregnancy due to their teratogenic effects on fetal renal development.
*Proximal convoluted tubule*
- The **proximal convoluted tubule** develops from the **metanephric mesenchyme**, not from the ureteric bud.
- This structure is part of the nephron proper, which forms when the metanephric mesenchyme is induced by the ureteric bud to differentiate.
*Loop of Henle*
- The **loop of Henle** also develops from the **metanephric mesenchyme**.
- While its formation depends on inductive signals from the ureteric bud, it is not a direct derivative of the ureteric bud itself.
*Bladder*
- The **bladder** develops from the **urogenital sinus**, which is derived from the ventral part of the **cloaca** after partitioning by the urorectal septum.
- Its development is distinct from the derivatives of the ureteric bud, though they are functionally connected.
*Distal convoluted tubule*
- The **distal convoluted tubule** develops from the **metanephric mesenchyme**.
- It is a component of the nephron and connects to the collecting duct but is not a direct derivative of the ureteric bud.
More Urinary system histology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.