Skin histology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Skin histology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
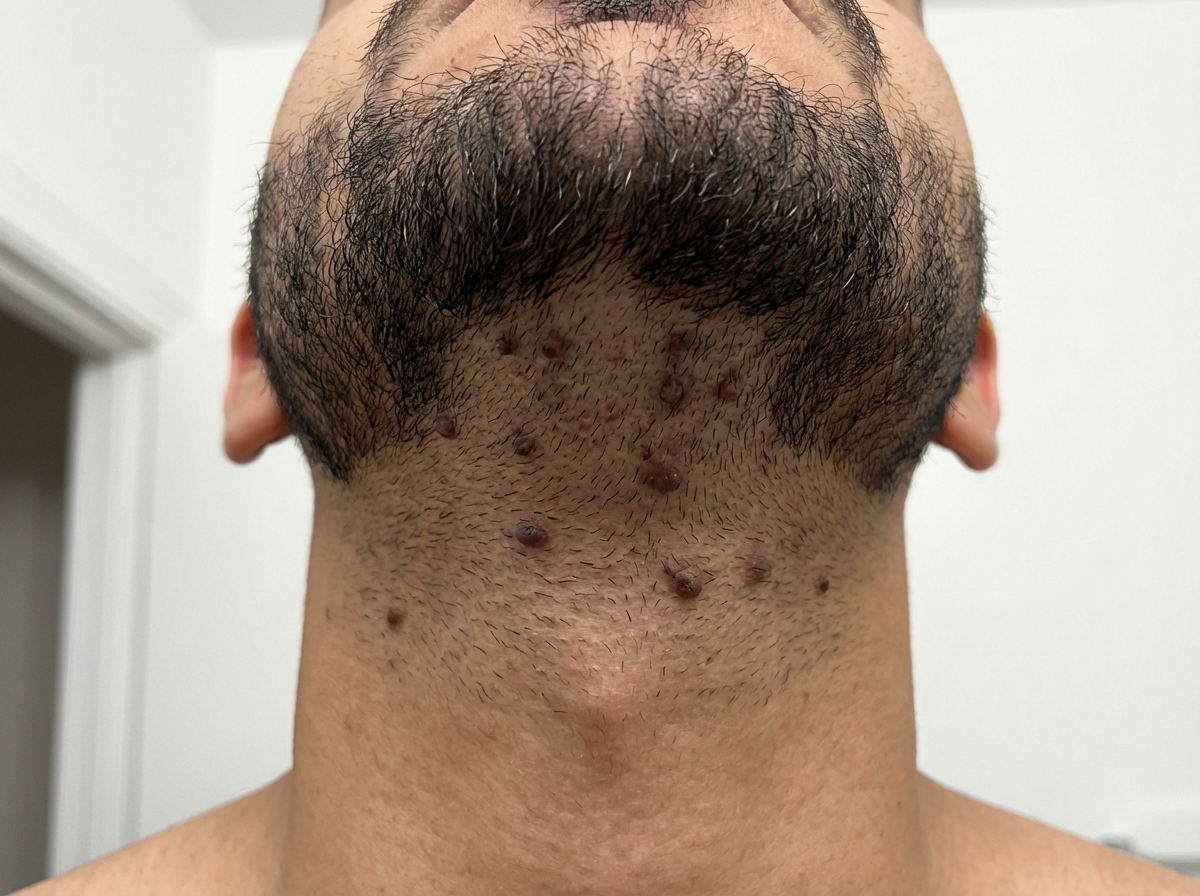
Skin histology US Medical PG Question 1: A 21-year-old man comes to the physician because of painful, firm, dark bumps on his neck and jawline. He has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. His brother had a similar rash. A photograph of the rash is shown. Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of this patient's condition?
- A. Trichophyton infection of the superficial hair follicle
- B. Interfollicular penetration of the skin by distal end of hair (Correct Answer)
- C. Bacterial infection of the superficial or deep hair follicle
- D. Follicular obstruction with subsequent duct rupture
- E. Cutibacterium acnes colonization of the pilosebaceous unit
Skin histology Explanation: ***Interfollicular penetration of the skin by distal end of hair***
- The description of painful, firm, dark bumps on the neck and jawline, particularly in a young man, is classic for **pseudofolliculitis barbae**, often caused by the distal end of hair penetrating the skin after shaving.
- This condition is common in individuals with **curly hair** where shaved hairs re-enter the skin, causing a foreign body inflammatory reaction.
*Trichophyton infection of the superficial hair follicle*
- This would typically present as **tinea barbae** or **tinea capitis**, characterized by scaling, erythema, and pustules, often with hair breakage, not firm dark bumps from embedded hairs.
- While fungal infections can cause folliculitis, the clinical presentation and family history of improvement with erythromycin (an antibacterial) make this less likely.
*Bacterial infection of the superficial or deep hair follicle*
- **Bacterial folliculitis** (e.g., *Staphylococcus aureus*) usually presents as pustules, papules, and sometimes carbuncles, which are typically red, inflamed, and often pus-filled.
- The family history of improvement with erythromycin might suggest a bacterial component, but the primary mechanism described (firm, dark bumps) points away from primary bacterial infection and more towards a physical cause like pseudofolliculitis barbae, which can then become secondarily infected.
*Follicular obstruction with subsequent duct rupture*
- This mechanism is characteristic of **acne vulgaris** (comedones, papules, pustules, cysts) or **hidradenitis suppurativa** (deep-seated nodules, abscesses affecting intertriginous areas), which are different in appearance and location from the described lesions.
- While related to follicular issues, the specific description of "dark bumps" and the context of shaving make embedded hairs more likely than a primary obstruction and rupture.
*Cutibacterium acnes colonization of the pilosebaceous unit*
- This is the primary bacterial contributor to **acne vulgaris**, leading to comedones, inflamed papules, and pustules, often affecting the face, chest, and back.
- Although the jawline is a common area for acne, the "firm, dark bumps" are less typical of classic acne and more consistent with ingrown hairs.
Skin histology US Medical PG Question 2: A 65-year-old man presents with a slowly growing, hyperkeratotic lesion on his right temple. The lesion has been present for approximately 8 months. He has a history of significant sun exposure. Examination reveals a 1.5 cm scaly, erythematous plaque with adherent scale. Biopsy shows atypical keratinocytes extending from the epidermis into the dermis. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Actinic keratosis
- B. Keratoacanthoma
- C. Squamous cell carcinoma (Correct Answer)
- D. Basal cell carcinoma
Skin histology Explanation: ***Squamous cell carcinoma***
- The description of a **slowly growing, hyperkeratotic lesion** on a **sun-exposed area** (right temple) in an elderly man is highly suggestive of **squamous cell carcinoma (SCC)**. The lesion being a **scaly, erythematous plaque with adherent scale** further supports this.
- The biopsy finding of **atypical keratinocytes extending from the epidermis into the dermis** is the definitive histological hallmark of invasive SCC.
*Actinic keratosis*
- While actinic keratosis is a **premalignant lesion** that can progress to SCC, it typically presents as smaller, rough, sandpaper-like papules or patches.
- The key differentiating factor here is the biopsy finding of **atypical keratinocytes extending into the dermis**, which denotes invasion and thus a diagnosis of SCC, not just actinic keratosis.
*Keratoacanthoma*
- **Keratoacanthomas** are rapidly growing, dome-shaped nodules with a central keratin plug, often resolving spontaneously.
- Although they are a variant of SCC, the description of a **slowly growing lesion present for 8 months** and the plaque-like appearance are less typical for a classic keratoacanthoma.
*Basal cell carcinoma*
- **Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)** usually presents as a **pearly nodule with telangiectasias**, a rodent ulcer, or a waxy papule.
- The biopsy demonstrating **atypical keratinocytes** (which originate from the spinous layer of the epidermis) extending into the dermis is characteristic of SCC, not BCC, which originates from the basal layer of the epidermis.
Skin histology US Medical PG Question 3: A 46-year-old woman presents to your office with oral lesions as shown in Image A. On examination, you find that her back has flaccid bullae that spread when you apply lateral pressure with your fingertips. This patient most likely has autoantibodies directed against which of the following?
- A. Type VII collagen
- B. Lamina densa
- C. Hemidesmosomes
- D. Lamina lucida
- E. Desmosomes (Correct Answer)
Skin histology Explanation: ***Desmosomes***
- The presence of **flaccid bullae**, a positive **Nikolsky sign (spread with lateral pressure)**, and **oral lesions** are characteristic features of **pemphigus vulgaris**.
- **Pemphigus vulgaris** is an autoimmune disease where autoantibodies target **desmogleins 1 and 3**, which are components of desmosomes, leading to the loss of cell-to-cell adhesion within the epidermis.
*Type VII collagen*
- Autoantibodies against **type VII collagen** are associated with **epidermolysis bullosa acquisita**, which typically presents with **tense bullae** and scarring, unlike the flaccid bullae seen here.
- This condition involves the **dermal-epidermal junction**, leading to subepidermal blistering.
*Lamina densa*
- The **lamina densa** is a component of the **basement membrane zone**, and antibodies targeting it are characteristic of certain types of **bullous pemphigoid** or some forms of **epidermolysis bullosa**.
- However, typical bullous pemphigoid presents with **tense bullae** and, unlike pemphigus, usually spares the oral mucosa.
*Hemidesmosomes*
- Autoantibodies targeting **hemidesmosomes** (specifically **BP180 and BP230 antigens**) are typical of **bullous pemphigoid**, which is characterized by **tense bullae** and often pruritus.
- These antibodies lead to blistering at the **dermal-epidermal junction**, but the bullae are typically firm and do not show a positive Nikolsky sign.
*Lamina lucida*
- The **lamina lucida** is another component of the **basement membrane zone** where blistering occurs in some autoimmune bullous diseases, specifically **bullous pemphigoid**.
- However, the clinical presentation of flaccid bullae with oral involvement and a positive Nikolsky sign strongly points away from bullous pemphigoid and towards pemphigus vulgaris, which primarily involves intercellular adhesion.
Skin histology US Medical PG Question 4: A 15-year-old boy comes to the physician because of skin changes on his face, chest, and back over the past year. Treatment with over-the-counter benzoyl peroxide has been ineffective. Physical examination shows numerous open comedones, inflammatory papules, and pustules on his face, chest, and back. Which of the following is the most likely underlying mechanism of this patient’s skin condition?
- A. Hyperkeratinization of hair follicles (Correct Answer)
- B. Type IV hypersensitivity reaction
- C. Formation of superficial epidermal inclusion cyst
- D. Excess androgen production
- E. Hyperplasia of pilosebaceous glands
Skin histology Explanation: **Hyperkeratinization of hair follicles**
- The primary event in the pathogenesis of **acne vulgaris** is the **shedding of hyperkeratinized corneocytes** into the lumen of the hair follicle, which then combines with sebum to form a microcomedone.
- This process leads to the **obstruction of the pilosebaceous unit**, creating an anaerobic environment conducive to the proliferation of *Cutibacterium acnes* and the development of inflammatory lesions like papules and pustules.
*Type IV hypersensitivity reaction*
- This mechanism involves **T-cell mediated delayed hypersensitivity**, leading to conditions like **allergic contact dermatitis** or **tuberculosis**.
- Acne vulgaris is not primarily an allergic reaction mediated by T cells; its pathogenesis involves follicular obstruction, sebum production, bacterial colonization, and inflammation.
*Formation of superficial epidermal inclusion cyst*
- Epidermal inclusion cysts (also known as epidermoid cysts) are typically solitary, slow-growing cysts that result from the **implantation of epidermal cells into the dermis**, often due to trauma or blocked hair follicles, but they are not the underlying mechanism for widespread acne.
- While some severe acne lesions can rarely lead to cyst formation, the presence of numerous **comedones, papules, and pustules** indicates typical acne vulgaris, not primarily cyst formation.
*Excess androgen production*
- While **androgens stimulate sebum production**, which is a contributing factor to acne, they are not the initiating mechanism for the follicular obstruction itself.
- Most adolescents with acne have **normal androgen levels**; the skin's sebaceous glands are simply more sensitive to circulating androgens, leading to increased sebum.
*Hyperplasia of pilosebaceous glands*
- **Sebaceous gland hyperplasia** refers to an increase in the number and size of sebaceous glands, leading to an overproduction of sebum, which contributes to acne.
- However, the fundamental initiating event for comedone formation in acne is the **follicular hyperkeratinization and obstruction**, rather than simply the glands being hyperplastic.
Skin histology US Medical PG Question 5: A 37-year-old man presents to the clinic because of painful, severe blistering over his buttocks for the past week. About a year ago, he noticed a similar outbreak on his inner thighs, but it receded within a few days on its own. Physical examination shows the blisters are tense, and rubbing the affected skin does not result in ‘popping’ of the blisters. A biopsy shows the entire epidermis lifting away from the basal lamina with extensive inflammatory infiltrates abundant with eosinophils. Immunofluorescence shows a linear pattern of immune complex deposits. Which of the following cellular structures, if defective, is most likely involved in the formation of these blisters?
- A. Gap junctions
- B. Hemidesmosomes (Correct Answer)
- C. Lamellar bodies
- D. Zonula occludens
- E. Macula adherens
Skin histology Explanation: ***Hemidesmosomes***
- The clinical picture of **tense blisters** that do not pop with rubbing (**negative Nikolsky sign**), along with the histological finding of the **entire epidermis lifting away from the basal lamina** (subepidermal blistering), strongly suggests **bullous pemphigoid**.
- **Immunofluorescence showing linear deposits** along the basement membrane zone is characteristic of bullous pemphigoid, which is caused by autoantibodies targeting proteins within the hemidesmosomes.
*Gap junctions*
- **Gap junctions** are involved in **intercellular communication** and the passage of small molecules between cells.
- Defects in gap junctions do not typically lead to blistering skin disorders.
*Lamellar bodies*
- **Lamellar bodies** are organelles in **keratinocytes** that release lipids to form the **skin barrier**.
- Defects in lamellar bodies are associated with disorders like **ichthyosis**, not blistering as described.
*Zonula occludens*
- **Zonula occludens**, also known as **tight junctions**, are crucial for forming a **seal between epithelial cells**, regulating paracellular transport.
- Dysfunctional tight junctions can lead to increased permeability but are not directly involved in the formation of subepidermal blisters.
*Macula adherens*
- **Macula adherens**, or **desmosomes**, are cell-to-cell adhesion structures that provide strong mechanical attachments between keratinocytes.
- Defects in desmosomes are associated with **pemphigus vulgaris** and **pemphigus foliaceus**, which typically present with **flaccid blisters** that show a **positive Nikolsky sign** and involve intraepidermal cleavage.
Skin histology US Medical PG Question 6: A 59-year-old man comes to the physician for evaluation of a progressively enlarging, 8-mm skin lesion on the right shoulder that developed 1 month ago. The patient has a light-skinned complexion and has had several dysplastic nevi removed in the past. A photograph of the lesion is shown. The lesion is most likely derived from cells that are also the embryological origin of which of the following tumors?
- A. Adrenal adenoma
- B. Liposarcoma
- C. Basal cell carcinoma
- D. Neuroblastoma (Correct Answer)
- E. Medullary thyroid cancer
Skin histology Explanation: ***Neuroblastoma***
- The skin lesion described, with history of dysplastic nevi and progressive growth, is highly suggestive of **melanoma**. Melanoma arises from **melanocytes**, which are derived from the **neural crest**.
- **Neuroblastoma** is a tumor of the **sympathetic nervous system** that also originates from **neural crest cells**, making it the correct embryological match.
- Neuroblastoma is the **classic example** of a neural crest-derived tumor taught alongside melanoma in medical education.
*Adrenal adenoma*
- **Adrenal adenomas** are benign tumors of the adrenal cortex, which is derived from the **mesoderm**.
- This embryological origin is distinct from the neural crest origin of melanocytes.
*Liposarcoma*
- **Liposarcomas** are malignant tumors of adipose tissue, which arises from the **mesoderm**.
- This origin does not match the neural crest origin of melanocytes.
*Basal cell carcinoma*
- **Basal cell carcinoma** originates from the **basal layer of the epidermis**, which is derived from **surface ectoderm** (not neural crest).
- While it's an ectodermal derivative, it does not share the neural crest origin of melanocytes.
*Medullary thyroid cancer*
- **Medullary thyroid cancer** originates from the **parafollicular C cells** of the thyroid gland, which are also derived from the **neural crest**.
- While this shares the same embryological origin as melanoma, **neuroblastoma** is the more commonly tested and classic pairing with melanoma in standard medical examinations when discussing neural crest-derived tumors.
Skin histology US Medical PG Question 7: A 65-year-old man comes to the physician because he is worried about a mole on his right forearm. He has had the mole for several years, but it has grown in size in the past 3 months. Physical examination shows a hyperpigmented plaque with irregular borders and small area of ulceration. Histopathologic analysis of a full-thickness excisional biopsy confirms the diagnosis of malignant melanoma. Invasion of which of the following layers of skin carries the highest risk of mortality for this patient?
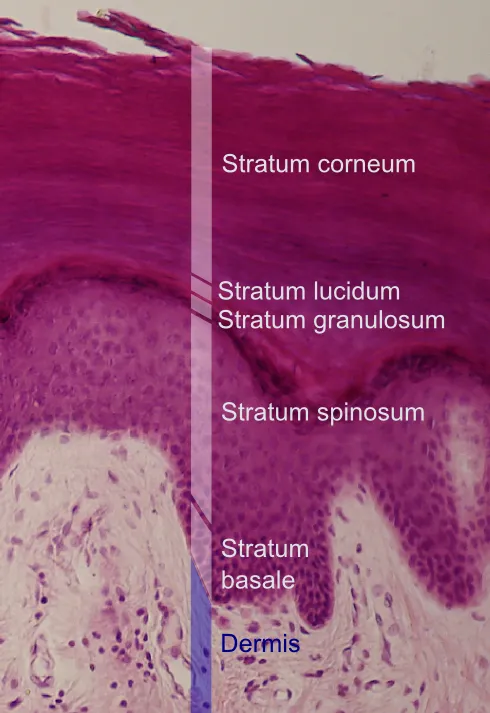
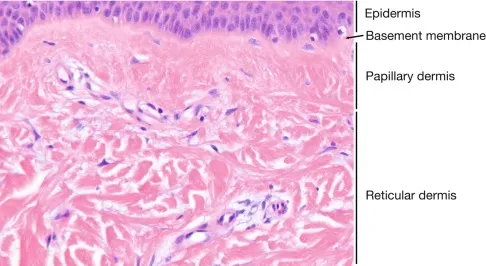
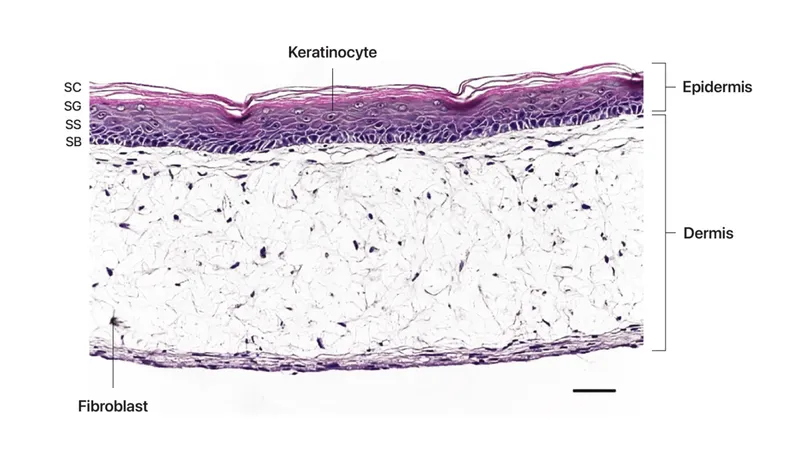
- A. Reticular dermis
- B. Papillary dermis
- C. Stratum basale
- D. Stratum corneum
- E. Hypodermis (Correct Answer)
Skin histology Explanation: ***Hypodermis***
- Invasion into the **hypodermis (subcutaneous tissue)** indicates the deepest penetration of the melanoma, correlated with the **greatest tumor thickness** (Breslow depth).
- Deeper invasion significantly increases the likelihood of **lymphatic and hematogenous spread**, leading to the highest risk of **metastasis** and mortality.
- This represents the **worst prognosis** among the layers listed.
*Stratum corneum*
- The **stratum corneum** is the outermost, dead keratinized layer of the epidermis.
- Melanoma cells limited to this layer would indicate **melanoma in situ** or a very superficial lesion.
- This represents the most superficial involvement, carrying the **lowest risk of mortality** and metastasis.
*Stratum basale*
- The **stratum basale** is the deepest layer of the epidermis at the dermal-epidermal junction.
- Melanoma confined to or near this level represents early invasion just beyond the basement membrane.
- This level of invasion is still relatively superficial and is associated with a **better prognosis** than deeper dermal or subcutaneous invasion.
*Papillary dermis*
- Invasion into the **papillary dermis** signifies invasive melanoma but represents an early stage of dermal invasion.
- The risk of distant metastasis and mortality is present but lower compared to invasion into deeper dermal layers or the hypodermis.
*Reticular dermis*
- Invasion into the **reticular dermis** indicates deeper penetration and a more advanced tumor with greater Breslow depth.
- Metastatic risk is significantly increased compared to papillary dermis invasion but is still lower than invasion into the subcutaneous tissue (hypodermis).
Skin histology US Medical PG Question 8: Research is being conducted on embryoblasts. The exact date of fertilization is unknown. There is the presence of a cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast, marking the time when implantation into the uterus would normally occur. Within the embryoblast, columnar and cuboidal cells are separated by a membrane. Which of these cell layers begins to line the yolk sac cavity?
- A. Hypoblast (Correct Answer)
- B. Epiblast
- C. Syncytiotrophoblast
- D. Inner cell mass
- E. Endoderm
Skin histology Explanation: ***Hypoblast***
- The **hypoblast** is a layer of cuboidal cells that forms from the inner cell mass around day 8 post-fertilization.
- It plays a crucial role in forming the **primary yolk sac** by migrating to line the exocoelomic cavity.
*Epiblast*
- The **epiblast** is composed of columnar cells located dorsal to the hypoblast and forms the floor of the **amniotic cavity**.
- It is the source of the **three primary germ layers** during gastrulation (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm), not the yolk sac lining itself.
*Syncytiotrophoblast*
- The **syncytiotrophoblast** is the outer, invasive layer of the trophoblast that facilitates implantation and forms the fetal component of the placenta.
- It is not involved in lining the yolk sac cavity but rather in **invading the uterine endometrium** and producing hCG.
*Inner cell mass*
- The **inner cell mass (ICM)** is the cluster of cells within the blastocyst that gives rise to the embryoblast (which further differentiates into epiblast and hypoblast).
- The ICM itself does not line the yolk sac; rather, its derivative, the hypoblast, does.
*Endoderm*
- The **endoderm** is one of the three primary germ layers that forms during gastrulation from the epiblast derivative.
- It ultimately forms the linings of the **gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts**, not the primary yolk sac lining.
Skin histology US Medical PG Question 9: A 52-year-old woman sees you in your office with a complaint of new-onset headaches over the past few weeks. On exam, you find a 2 x 2 cm dark, irregularly shaped, pigmented lesion on her back. She is concerned because her father recently passed away from skin cancer. What tissue type most directly gives rise to the lesion this patient is experiencing?
- A. Neural crest cells (Correct Answer)
- B. Endoderm
- C. Mesoderm
- D. Ectoderm
- E. Neuroectoderm
Skin histology Explanation: ***Neural crest cells***
- The suspected lesion, given its description and the patient's family history of skin cancer, is likely a **melanoma**.
- Melanoma originates from **melanocytes**, which are derived from **neural crest cells** during embryonic development.
*Endoderm*
- The endoderm gives rise to the **lining of the gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts**, as well as organs such as the liver and pancreas.
- It is not involved in the formation of melanocytes or skin lesions like melanoma.
*Mesoderm*
- The mesoderm forms tissues such as **muscle, bone, cartilage, connective tissue**, and the circulatory system.
- It does not directly give rise to melanocytes, which are the cells of origin for melanoma.
*Ectoderm*
- The ectoderm gives rise to the **epidermis, nervous system**, and sensory organs.
- While melanocytes are found in the epidermis, they are specifically derived from the **neural crest (a sub-population of ectoderm)**, not the general ectoderm.
*Neuroectoderm*
- Neuroectoderm specifically refers to the ectoderm that develops into the **nervous system**.
- While neural crest cells originate from the neuroectoderm, "neural crest cells" is a more precise answer for the origin of melanocytes.
Skin histology US Medical PG Question 10: A 32-year-old woman presents with amenorrhea and galactorrhea. MRI shows a pituitary adenoma. Histological examination of the surgical specimen shows cells arranged in cords and nests with sinusoidal capillaries. Special staining reveals three distinct cell types: chromophobes (50%), acidophils (40%), and basophils (10%). Immunohistochemistry shows the tumor cells staining strongly for prolactin. Evaluate the relationship between normal pituitary architecture and tumor development to determine which cell type most likely gave rise to this neoplasm.
- A. Somatotrophs (acidophils producing growth hormone)
- B. Lactotrophs (acidophils producing prolactin) (Correct Answer)
- C. Corticotrophs (basophils producing ACTH)
- D. Gonadotrophs (basophils producing FSH/LH)
- E. Chromophobes (null cells with no secretory granules)
Skin histology Explanation: ***Lactotrophs (acidophils producing prolactin)***
- These cells are classified as **acidophils** based on their staining characteristics and are responsible for the secretion of **prolactin**, consistent with the patient's **amenorrhea** and **galactorrhea**.
- Although the tumor specimen contains various cell types, the **immunohistostaining** specifically identifying **prolactin** confirms these cells as the source of the neoplasm.
*Somatotrophs (acidophils producing growth hormone)*
- While these are also **acidophilic** cells, they secrete **Growth Hormone (GH)**, and a tumor of this type would present with **acromegaly** or gigantism rather than galactorrhea.
- They do not typically stain for **prolactin**, unless the tumor is a rare plurihormonal adenoma, which is not indicated here.
*Corticotrophs (basophils producing ACTH)*
- These cells are **basophils** and produce **ACTH**; an adenoma arising from them would lead to **Cushing's disease** due to hypercortisolism.
- Histologically, they would not correspond to the strong **prolactin** staining observed in this immunohistochemical evaluation.
*Gonadotrophs (basophils producing FSH/LH)*
- These are **basophilic** cells that produce **FSH** and **LH**, and tumors originating from them are usually non-functional or present with mass effects rather than hormonal excess.
- They are clinically and histologically distinct from **prolactin-producing** lactotrophs.
*Chromophobes (null cells with no secretory granules)*
- **Chromophobes** lack significant cytoplasmic staining due to a lack of hormone granules; they often represent cells that have depleted their secretory stores.
- While they occupy 50% of the specimen, the **strong prolactin staining** identifies the active neoplastic process as originating from the hormone-producing lineage.
More Skin histology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.