Pancreas and salivary gland histology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Pancreas and salivary gland histology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Pancreas and salivary gland histology US Medical PG Question 1: A 45-year-old woman comes to the emergency department with recurrent episodes of shaking, sweating, and palpitations. The patient is confused and complains of hunger. One week ago, she had similar symptoms that improved after eating. She has hypertension and a history of biliary pancreatitis. She underwent cholecystectomy 1 year ago. She works as a nurse aide in a nursing care facility. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. She does not exercise. Her temperature is 36.7°C (98°F), pulse is 104/min, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure is 135/88 mm Hg. Examination shows tremors and diaphoresis. Laboratory studies show:
Blood glucose 50 mg/dL
Thyroid-stimulating hormone 1 mU/L
C-peptide 0.50 ng/mL (N=0.8–3.1)
Abdominal ultrasound reveals a 1-cm anechoic lesion in the head of the pancreas. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Pancreatic neoplasm
- B. Pancreatic pseudocyst
- C. Graves' disease
- D. Surreptitious insulin use (Correct Answer)
- E. Type 1 diabetes mellitus
Pancreas and salivary gland histology Explanation: ***Surreptitious insulin use***
- The patient's symptoms of **hypoglycemia** (shaking, sweating, palpitations, confusion, hunger) combined with a **low C-peptide level** (0.50 ng/mL) and a normal TSH strongly suggest **exogenous insulin administration**.
- As a nurse aide, she has access to insulin, and the normal pancreatic ultrasound (1 cm anechoic lesion is non-specific and unlikely to cause these symptoms) rules out an **insulinoma**, which would present with high C-peptide.
*Pancreatic neoplasm*
- While a pancreatic neoplasm can cause various symptoms, an **insulinoma** (a type of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor) would present with **hypoglycemia** but typically with **elevated C-peptide levels**, as it produces endogenous insulin.
- The ultrasound finding of a 1-cm anechoic lesion is **non-specific** and not definitively indicative of an insulinoma or any other functional neoplasm causing these specific symptoms.
*Pancreatic pseudocyst*
- Pancreatic pseudocysts are collections of fluid that can occur after **pancreatitis** or trauma, and while this patient has a history of biliary pancreatitis, pseudocysts generally cause symptoms like **abdominal pain, distension, and early satiety**, not hypoglycemia.
- They also do not explain the **low C-peptide** and recurrent episodes of neuroglycopenic symptoms.
*Graves' disease*
- Graves' disease is an **autoimmune hyperthyroid condition** that causes symptoms like palpitations, sweating, and tremors, but it is characterized by **low TSH** with elevated free T3/T4 due to negative feedback, not hypoglycemia or low C-peptide.
- The patient's **normal TSH** (1 mU/L) rules out Graves' disease as the cause of her current symptoms.
*Type 1 diabetes mellitus*
- Type 1 diabetes is characterized by **insulin deficiency** due to autoimmune destruction of pancreatic beta cells, leading to **hyperglycemia**, not hypoglycemia.
- While patients with type 1 diabetes may experience hypoglycemia if they administer too much insulin, the underlying disease itself causes high blood glucose, and the C-peptide would be very low or undetectable in a new diagnosis, but not as the cause of recurrent spontaneous hypoglycemia.
Pancreas and salivary gland histology US Medical PG Question 2: A 58-year-old woman with refractory gastrointestinal complaints undergoes a bowel biopsy. On histology, the pathologist observes that submucosal glands of Brunner are present in the specimen. Which portion of the bowel was most likely biopsied?
- A. Descending colon
- B. Ileum
- C. Jejunum
- D. Cecum
- E. Duodenum (Correct Answer)
Pancreas and salivary gland histology Explanation: ***Duodenum***
- The presence of **Brunner's glands** in the submucosa is a **histological hallmark** of the duodenum.
- These glands produce an **alkaline mucus** that helps protect the duodenal wall from acidic chyme entering from the stomach.
*Descending colon*
- The descending colon is part of the **large intestine** and does not contain Brunner's glands.
- Its histology is characterized by numerous **goblet cells** and the absence of villi.
*Ileum*
- The ileum is the final section of the small intestine, characterized by the presence of **Peyer's patches** (lymphoid aggregates) in the lamina propria and submucosa.
- It lacks Brunner's glands.
*Jejunum*
- The jejunum is the middle section of the small intestine, known for its tall, finger-like villi, but it **does not contain Brunner's glands**.
- It is primarily involved in nutrient absorption and has a reduced number of goblet cells compared to the ileum.
*Cecum*
- The cecum is the beginning of the **large intestine** and is characterized by a high density of **goblet cells** and lymphoid tissue, but no Brunner's glands.
- It plays a role in absorption of fluids and electrolytes.
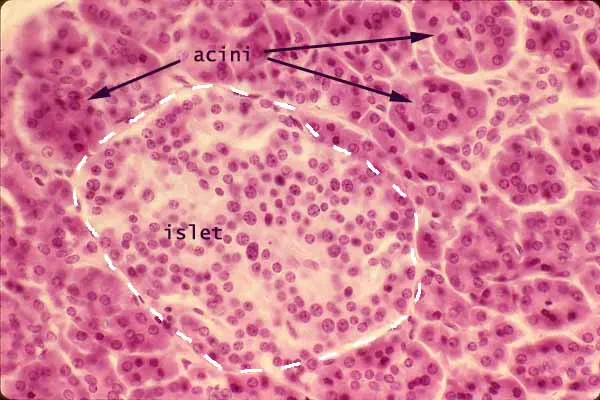
Pancreas and salivary gland histology US Medical PG Question 3: A histological examination of the carotid body reveals glomus cells containing dense-core vesicles. These cells function primarily as chemoreceptors for which of the following?
- A. Partial pressure of oxygen (Correct Answer)
- B. Blood pH
- C. Temperature
- D. Blood glucose levels
Pancreas and salivary gland histology Explanation: ***Partial pressure of oxygen***
- Carotid body **glomus cells** are highly specialized **chemoreceptors** that primarily sense changes in the **partial pressure of oxygen (PO2)** in arterial blood.
- When PO2 decreases (e.g., hypoxia), these cells are activated and stimulate the respiratory and cardiovascular systems to increase oxygen uptake.
*Blood pH*
- While carotid body chemoreceptors can sense large changes in blood pH, their primary and most sensitive role is in detecting changes in **PO2**.
- Central chemoreceptors in the brainstem are more crucial for routine regulation of respiration in response to changes in **pH and PCO2**.
*Temperature*
- **Thermoreceptors** located in the skin, hypothalamus, and other internal organs are responsible for sensing body temperature, not the carotid body.
- The carotid body's main function is related to blood gas homeostasis, not temperature regulation.
*Blood glucose levels*
- Blood glucose levels are regulated by specialized cells in the **pancreas** (islets of Langerhans) that secrete hormones like insulin and glucagon.
- The carotid body is not directly involved in sensing or regulating glucose homeostasis.
Pancreas and salivary gland histology US Medical PG Question 4: A 37-year-old man presents with dull, continuous epigastric pain that radiates to the back in a circumscribing fashion. The history is significant for 3 episodes of acute pancreatitis that were managed conservatively. He reports no history of such episodes in his relatives and denies a family history of any cardiovascular or gastrointestinal disorders. The vital signs include: blood pressure 105/70 mm Hg, heart rate 101/min, respiratory rate 17/min, and temperature 37.4℃ (99.3℉). The physical examination reveals epigastric tenderness, slight muscle guarding, a positive Mayo-Robson’s sign, and abdominal distention. Laboratory studies show the following findings:
Complete blood count
Erythrocytes 4.5 x 106/mm3
Hgb 14.7 g/dL
Hct 43%
Leukocytes 12,700/mm3
Segmented neutrophils 65%
Bands 4%
Eosinophils 1%
Basophils 0%
Lymphocytes 27%
Monocytes 3%
Biochemistry
Serum amylase 170 U/L
ALT 21 U/L
AST 19 U/L
Total serum cholesterol 139 mg/dL (3.6 mmol/L)
Serum triglycerides 127 mg/dL (1.4 mmol/L)
The magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography findings are shown in the exhibit. What embryogenic disruption could cause such anatomic findings?
- A. Duplication of the pancreatic bud of the midgut
- B. Failure of fusion of dorsal and ventral pancreatic duct anlages (Correct Answer)
- C. Ectopy of the developing bile duct
- D. Duplication of the embryonic pancreatic duct
- E. Improper rotation of the ventral pancreatic bud
Pancreas and salivary gland histology Explanation: ***Failure of fusion of dorsal and ventral pancreatic duct anlages***
- The patient's history of **recurrent pancreatitis**, dull epigastric pain radiating to the back, and the provided magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) findings are highly suggestive of **pancreas divisum**. Pancreas divisum results from the **failure of the dorsal and ventral pancreatic ducts to fuse** during embryological development.
- In pancreas divisum, the majority of the pancreatic drainage occurs through the **minor papilla** via the dorsal pancreatic duct, which can become stenotic or obstructed, leading to increased pressure in the dorsal duct and recurrent pancreatitis.
*Improper rotation of the anterior pancreatic bud*
- **Improper rotation of the ventral pancreatic bud** (not anterior) can lead to **annular pancreas**, where pancreatic tissue encircles the duodenum.
- While annular pancreas can cause duodenal obstruction, it does not typically present with the specific MRCP findings seen in pancreas divisum or recurrent pancreatitis as the primary symptom.
*Duplication of the pancreatic bud of the midgut*
- The pancreas develops from the **foregut**, not the midgut. Duplication of pancreatic buds is a rare condition and would likely manifest differently from the typical presentation of pancreas divisum.
- Pancreatic development involves dorsal and ventral buds, not a "midgut" bud, making this option anatomically incorrect in the context of typical pancreatic anomalies.
*Ectopy of the developing bile duct*
- **Ectopy of the bile duct** refers to the bile duct opening in an abnormal location. While bile duct anomalies can occur, they are distinct from pancreatic duct fusion abnormalities.
- This would primarily cause issues related to bile drainage, such as cholestasis or cholangitis, rather than the recurrent pancreatitis and specific ductal morphology associated with pancreas divisum.
*Duplication of the embryonic pancreatic duct*
- While congenital anomalies involving pancreatic ducts exist, **duplication of the entire embryonic pancreatic duct** is not a recognized cause of pancreas divisum.
- Pancreas divisum is specifically due to a *failure of fusion* rather than an extra ductal structure stemming from an initial duplication.
Pancreas and salivary gland histology US Medical PG Question 5: You have been asked to deliver a lecture to medical students about the effects of various body hormones and neurotransmitters on the metabolism of glucose. Which of the following statements best describes the effects of sympathetic stimulation on glucose metabolism?
- A. Norepinephrine causes increased glucose absorption within the intestines.
- B. Without epinephrine, insulin cannot act on the liver.
- C. Peripheral tissues require epinephrine to take up glucose.
- D. Epinephrine increases liver glycogenolysis. (Correct Answer)
- E. Sympathetic stimulation to alpha receptors of the pancreas increases insulin release.
Pancreas and salivary gland histology Explanation: ***Epinephrine increases liver glycogenolysis.***
- **Epinephrine**, released during sympathetic stimulation, primarily acts to increase **glucose availability** for immediate energy.
- It achieves this by stimulating **glycogenolysis** (breakdown of glycogen into glucose) in the liver via **beta-adrenergic receptors**.
*Norepinephrine causes increased glucose absorption within the intestines.*
- **Norepinephrine** primarily causes **vasoconstriction** and can *decrease* **intestinal motility** and nutrient absorption due to shunting blood away from the digestive tract during stress.
- Glucose absorption is mainly regulated by digestive enzymes and transport proteins, not directly increased by norepinephrine.
*Without epinephrine, insulin cannot act on the liver.*
- **Insulin** acts on the liver independent of epinephrine to promote **glucose uptake**, **glycogenesis**, and **lipid synthesis**.
- Epinephrine and insulin have **antagonistic effects** on liver glucose metabolism; epinephrine increases glucose output, while insulin decreases it.
*Peripheral tissues require epinephrine to take up glucose.*
- **Insulin** is the primary hormone required for **glucose uptake** by most peripheral tissues, especially **muscle** and **adipose tissue**, via **GLUT4 transporters**.
- Epinephrine generally *reduces* glucose uptake by peripheral tissues to preserve glucose for the brain during stress.
*Sympathetic stimulation to alpha receptors of the pancreas increases insulin release.*
- Sympathetic stimulation, primarily acting through **alpha-2 adrenergic receptors** on pancreatic beta cells, actually **inhibits** **insulin secretion**.
- This inhibition helps to increase blood glucose levels by reducing insulin's glucose-lowering effects.
Pancreas and salivary gland histology US Medical PG Question 6: A 21-year-old college student comes to the emergency department because of a two-day history of vomiting and epigastric pain that radiates to the back. He has a history of atopic dermatitis and Hashimoto thyroiditis. His only medication is levothyroxine. He has not received any routine vaccinations. He drinks 1–2 beers on the weekends and occasionally smokes marijuana. The patient appears distressed and is diaphoretic. His temperature is 37.9°C (100.3°F), pulse is 105/min, respirations are 16/min, and blood pressure is 130/78 mm Hg. Physical examination shows abdominal distention with tenderness to palpation in the epigastrium. There is no guarding or rebound tenderness. Skin examination shows several clusters of yellow plaques over the trunk and extensor surfaces of the extremities. Hemoglobin concentration is 15.2 g/dL and serum calcium concentration is 7.9 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in evaluation?
- A. Measure serum mumps IgM titer
- B. Measure serum lipid levels (Correct Answer)
- C. Obtain an upright x-ray of the abdomen
- D. Perform a pilocarpine-induced sweat test
- E. Measure stool elastase level
Pancreas and salivary gland histology Explanation: ***Measure serum lipid levels***
- This patient presents with **epigastric pain radiating to the back**, vomiting, and potential signs of systemic inflammation (fever, tachycardia), suggestive of **pancreatitis**. One of the most common causes of pancreatitis, especially in the absence of gallstones or significant alcohol abuse, is **severe hypertriglyceridemia**.
- The presence of **yellow plaques over the trunk and extensor surfaces** (likely **eruptive xanthomas**) is a strong indicator of **severe hypertriglyceridemia**, making serum lipid measurement the most appropriate next step to confirm this etiology for his pancreatitis.
*Measure serum mumps IgM titer*
- While mumps can cause pancreatitis, this patient has not received routine vaccinations, but there is no specific exposure history or other symptoms (like **parotitis**) to strongly suggest mumps as the primary cause.
- The more compelling physical finding of eruptive xanthomas points more directly to **hypertriglyceridemia** as the cause of pancreatitis.
*Obtain an upright x-ray of the abdomen*
- An upright abdominal x-ray is primarily used to look for **free air under the diaphragm** as an indicator of a perforated viscus, which would present with peritonitis and guarding. This patient has **no guarding or rebound tenderness**.
- While it can show signs of ileus, it is not the most targeted test for diagnosing the *cause* of pancreatitis or conditions indicated by eruptive xanthomas.
*Perform a pilocarpine-induced sweat test*
- A **pilocarpine-induced sweat test** is used to diagnose **cystic fibrosis (CF)**, which can cause pancreatic insufficiency and pancreatitis, especially in younger individuals.
- While CF could be considered in a young patient with pancreatic symptoms, his presentation with clear signs of **hyperlipidemia (eruptive xanthomas)** makes this a less direct or immediate next step.
*Measure stool elastase level*
- **Stool elastase** is a test for **exocrine pancreatic insufficiency**, indicating chronic damage to the pancreas.
- This patient is presenting with acute pancreatitis, not chronic insufficiency, and the prominent physical findings point to an **acute metabolic cause** rather than chronic pancreatic dysfunction as the primary differential at this stage.
Pancreas and salivary gland histology US Medical PG Question 7: A 38-year-old man comes to the clinic complaining of recurrent abdominal pain for the past 2 months. He reports a gnawing, dull pain at the epigastric region that improves with oral ingestion. He has been taking calcium carbonate for the past few weeks; he claims that “it used to help a lot but it’s losing its effects now.” Laboratory testing demonstrated increased gastrin levels after the administration of secretin. A push endoscopy visualized several ulcers at the duodenum and proximal jejunum. What characteristics distinguish the jejunum from the duodenum?
- A. Lack of goblet cells
- B. Crypts of Lieberkuhn
- C. Lack of submucosal Brunner glands (Correct Answer)
- D. Peyer patches
- E. Plicae circulares
Pancreas and salivary gland histology Explanation: ***Lack of submucosal Brunner glands***
- The **jejunum** lacks **Brunner glands**, which are characteristic of the **duodenum** and secrete alkaline mucus to neutralize acidic chyme from the stomach.
- The absence of these glands helps differentiate the jejunum from the duodenum histologically.
*Lack of goblet cells*
- **Goblet cells** are present throughout the small intestine, including both the duodenum and jejunum, though their density increases distally.
- Therefore, the **lack of goblet cells** does not distinguish the jejunum from the duodenum.
*Crypts of Lieberkuhn*
- **Crypts of Lieberkuhn** (intestinal crypts) are present throughout the entire small intestine, including both the **duodenum** and **jejunum**, where they house stem cells for epithelial renewal.
- Their presence is not a distinguishing feature between these two segments histologically.
*Peyer patches*
- **Peyer patches** are lymphoid aggregates primarily found in the **ileum**, not the jejunum or duodenum, and are involved in immune surveillance.
- They are a distinguishing feature of the ileum but not between the jejunum and duodenum.
*Plicae circulares*
- **Plicae circulares** (also known as valves of Kerckring or circular folds) are macroscopic folds of the mucosa and submucosa that are present in both the **duodenum** and **jejunum**.
- They are most prominent in the jejunum, but their mere presence does not distinguish the jejunum from the duodenum.
Pancreas and salivary gland histology US Medical PG Question 8: A 55-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of painful swelling on the right side of her face. The pain worsens when she eats. Examination of the face shows a right-sided, firm swelling that is tender to palpation. Oral examination shows no abnormalities. Ultrasonography shows a stone located in a duct that runs anterior to the masseter muscle and passes through the buccinator muscle. Sialoendoscopy is performed to remove the stone. At which of the following sites is the endoscope most likely to be inserted during the procedure?
- A. Lateral to the lingual frenulum
- B. Into the floor of the mouth
- C. Lateral to the superior labial frenulum
- D. Into the mandibular foramen
- E. Opposite the second upper molar tooth (Correct Answer)
Pancreas and salivary gland histology Explanation: ***Opposite the second upper molar tooth***
- The description of the duct running anterior to the **masseter muscle** and through the **buccinator muscle** is characteristic of the **parotid duct (Stensen's duct)**.
- The parotid duct opens into the oral cavity on the buccal mucosa **opposite the second upper molar tooth**, which is the most likely entry point for sialoendoscopy to remove a stone from this duct.
*Lateral to the lingual frenulum*
- This location is where the **submandibular duct (Wharton's duct)** opens into the oral cavity.
- While stones can occur in the submandibular duct, the patient's symptoms and the duct's anatomical description do not match this location.
*Into the floor of the mouth*
- The floor of the mouth is the general area where the submandibular and sublingual ducts open.
- However, the specific anatomical description of the duct in relation to the masseter and buccinator muscles points away from the submandibular/sublingual glands.
*Lateral to the superior labial frenulum*
- This area is associated with the openings of minor salivary glands in the upper lip.
- These glands are typically too small to be the source of such a prominent swelling or a large stone requiring sialoendoscopy.
*Into the mandibular foramen*
- The **mandibular foramen** is an opening on the medial surface of the mandibular ramus.
- It is an anatomical landmark for the **inferior alveolar nerve and vessels** and has no direct involvement in salivary gland duct openings.
Pancreas and salivary gland histology US Medical PG Question 9: An 87-year-old male presents to his neurologist for a follow-up visit. He is being followed for an inoperable tumor near his skull. He reports that he recently noticed that food has started to lose its taste. He also notes increasing difficulty with swallowing. He has a history of myocardial infarction, diabetes mellitus, hyperlipidemia, hypertension, and presbycusis. He takes aspirin, metoprolol, metformin, glyburide, atorvastatin, lisinopril, and hydrochlorothiazide. On examination, the patient is a frail-appearing male sitting in a wheelchair. He is oriented to person, place, and time. Gag reflex is absent on the right side. A taste evaluation is performed which demonstrates a decreased ability to detect sour and bitter substances on the right posterior tongue. The nerve responsible for this patient’s loss of taste sensation also has which of the following functions?
- A. Somatic sensory innervation to the roof of the pharynx
- B. Parasympathetic innervation to the trachea
- C. Somatic sensory innervation to the lower lip
- D. Parasympathetic innervation to the parotid gland (Correct Answer)
- E. Parasympathetic innervation to the submandibular gland
Pancreas and salivary gland histology Explanation: ***Parasympathetic innervation to the parotid gland***
- The patient's symptoms, including loss of taste on the **right posterior tongue**, difficulty swallowing, and an absent gag reflex, point to an issue with the **glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)**.
- The glossopharyngeal nerve provides **parasympathetic innervation to the parotid gland** via the otic ganglion, stimulating saliva production.
*Somatic sensory innervation to the roof of the pharynx*
- The glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) does provide somatic sensory innervation to the pharynx, but specifically the **posterior 1/3 of the tongue**, tonsils, and part of the pharynx, not primarily the roof.
- While related to the pharynx, this option is not the most precise or unique function associated with the primary nerve implicated here.
*Parasympathetic innervation to the trachea*
- **Parasympathetic innervation to the trachea** is primarily mediated by the **vagus nerve (CN X)**, which innervates the smooth muscle and glands of the trachea and bronchi.
- The glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) does not have a direct role in tracheal innervation.
*Somatic sensory innervation to the lower lip*
- **Somatic sensory innervation to the lower lip** is primarily provided by the **mental nerve**, a branch of the **trigeminal nerve (CN V)**.
- The glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) is not involved in sensory innervation of the lower lip.
*Parasympathetic innervation to the submandibular gland*
- **Parasympathetic innervation to the submandibular and sublingual glands** is provided by the **facial nerve (CN VII)** via the submandibular ganglion.
- This function is distinct from the glossopharyngeal nerve's role in innervating the parotid gland.
Pancreas and salivary gland histology US Medical PG Question 10: A 32-year-old woman presents with amenorrhea and galactorrhea. MRI shows a pituitary adenoma. Histological examination of the surgical specimen shows cells arranged in cords and nests with sinusoidal capillaries. Special staining reveals three distinct cell types: chromophobes (50%), acidophils (40%), and basophils (10%). Immunohistochemistry shows the tumor cells staining strongly for prolactin. Evaluate the relationship between normal pituitary architecture and tumor development to determine which cell type most likely gave rise to this neoplasm.
- A. Somatotrophs (acidophils producing growth hormone)
- B. Lactotrophs (acidophils producing prolactin) (Correct Answer)
- C. Corticotrophs (basophils producing ACTH)
- D. Gonadotrophs (basophils producing FSH/LH)
- E. Chromophobes (null cells with no secretory granules)
Pancreas and salivary gland histology Explanation: ***Lactotrophs (acidophils producing prolactin)***
- These cells are classified as **acidophils** based on their staining characteristics and are responsible for the secretion of **prolactin**, consistent with the patient's **amenorrhea** and **galactorrhea**.
- Although the tumor specimen contains various cell types, the **immunohistostaining** specifically identifying **prolactin** confirms these cells as the source of the neoplasm.
*Somatotrophs (acidophils producing growth hormone)*
- While these are also **acidophilic** cells, they secrete **Growth Hormone (GH)**, and a tumor of this type would present with **acromegaly** or gigantism rather than galactorrhea.
- They do not typically stain for **prolactin**, unless the tumor is a rare plurihormonal adenoma, which is not indicated here.
*Corticotrophs (basophils producing ACTH)*
- These cells are **basophils** and produce **ACTH**; an adenoma arising from them would lead to **Cushing's disease** due to hypercortisolism.
- Histologically, they would not correspond to the strong **prolactin** staining observed in this immunohistochemical evaluation.
*Gonadotrophs (basophils producing FSH/LH)*
- These are **basophilic** cells that produce **FSH** and **LH**, and tumors originating from them are usually non-functional or present with mass effects rather than hormonal excess.
- They are clinically and histologically distinct from **prolactin-producing** lactotrophs.
*Chromophobes (null cells with no secretory granules)*
- **Chromophobes** lack significant cytoplasmic staining due to a lack of hormone granules; they often represent cells that have depleted their secretory stores.
- While they occupy 50% of the specimen, the **strong prolactin staining** identifies the active neoplastic process as originating from the hormone-producing lineage.
More Pancreas and salivary gland histology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.