Male reproductive histology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Male reproductive histology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Male reproductive histology US Medical PG Question 1: A 13-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his parents for evaluation of severe groin pain for the past 4 hours. His symptoms began while he was participating in a basketball game. On arrival to the ED, the resident on call notes a swollen, tender, and elevated left testicle with absence of the cremasteric reflex. A urology consult is requested and the patient is scheduled for surgery. An abnormality in which of the following anatomical structures is most likely responsible for this patient’s condition?
- A. Tunica vaginalis (Correct Answer)
- B. Cremasteric muscle
- C. Tunica dartos
- D. Tunica vasculosa
- E. Tunica albuginea
Male reproductive histology Explanation: ***Tunica vaginalis***
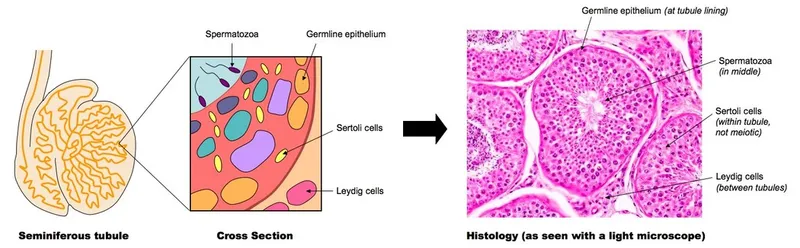
- This patient presents with symptoms highly suggestive of **testicular torsion**, characterized by acute scrotal pain, testicular elevation, and absence of the cremasteric reflex.
- In most cases of testicular torsion, the *tunica vaginalis* has an abnormally high attachment, which allows the testis to rotate freely within the scrotum (bell-clapper deformity).
*Cremasteric muscle*
- The cremasteric muscle is responsible for elevating the testis; its absence of reflex is a *symptom* of torsion, not the underlying cause of the anatomical predisposition.
- While its function is important for testicular positioning, an abnormality in the muscle itself is not the primary anatomical defect leading to torsion.
*Tunica dartos*
- The tunica dartos is a layer of smooth muscle beneath the scrotal skin that helps regulate testicular temperature by contracting and relaxing the scrotal skin.
- Abnormalities in the tunica dartos do not predispose to testicular torsion.
*Tunica albuginea*
- The tunica albuginea is a dense, fibrous capsule directly surrounding the testis, providing its structural integrity.
- While it encases the testis, its abnormal attachment is not the main reason for the increased mobility that leads to torsion; rather, it is the relationship of the *tunica vaginalis* to the testis.
Male reproductive histology US Medical PG Question 2: A pathologist examining a tissue sample notes the presence of pseudostratified columnar epithelium with goblet cells and cilia. This tissue was most likely obtained from which of the following locations?
- A. Bronchi (Correct Answer)
- B. Small intestine
- C. Skin
- D. Esophagus
- E. Urinary bladder
Male reproductive histology Explanation: ***Bronchi***
- The **bronchi**, as part of the respiratory tract, are lined with **pseudostratified columnar epithelium** that contains abundant **goblet cells** and **cilia** [1].
- **Cilia** help propel mucus and trapped particles out of the respiratory system, while **goblet cells** produce mucus to trap foreign substances [1].
*Small intestine*
- The small intestine is lined with **simple columnar epithelium** with **microvilli** (forming a brush border) and goblet cells, but it lacks **cilia**.
- Its primary function is nutrient absorption, not particulate clearance.
*Skin*
- The skin is covered by **stratified squamous epithelium**, specifically **keratinized stratified squamous epithelium**, which provides protection against abrasion and dehydration.
- It does not contain **goblet cells**, **cilia**, or **pseudostratified columnar epithelium**.
*Esophagus*
- The esophagus is lined with **non-keratinized stratified squamous epithelium**, designed to protect against mechanical abrasion during food passage.
- It lacks **goblet cells**, **cilia**, and **pseudostratified columnar epithelium**.
Male reproductive histology US Medical PG Question 3: A 34-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-week history of left testicular swelling. He has no pain. He underwent a left inguinal hernia repair as a child. He takes no medications. He appears healthy. His vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows an enlarged, nontender left testicle. When the patient is asked to cough, there is no bulge present in the scrotum. When a light is held behind the scrotum, it does not shine through. There is no inguinal lymphadenopathy. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 14.5 g/dL
Leukocyte count 8,800/mm3
Platelet count 345,000/mm3
Serum
Glucose 88 mg/dL
Creatinine 0.8 mg/dL
Total bilirubin 0.7 mg/dL
Alkaline phosphatase 35 U/L
AST 15 U/L
ALT 14 U/L
Lactate dehydrogenase 60 U/L
β-Human chorionic gonadotropin 80 mIU/mL (N < 5)
α-Fetoprotein 6 ng/mL (N < 10)
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Seminoma (Correct Answer)
- B. Leydig cell tumor
- C. Choriocarcinoma
- D. Spermatocele of testis
- E. Yolk sac tumor
Male reproductive histology Explanation: **Seminoma**
- The elevated **beta-human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG)** in the presence of a normal alpha-fetoprotein (α-FP) is highly suggestive of seminoma, especially in a painless testicular mass in a young man.
- While AFP is typically not elevated in pure seminomas, β-hCG can be mildly to moderately elevated in approximately 10-30% of cases, consistent with this presentation.
*Leydig cell tumor*
- These tumors often produce androgens or estrogens, leading to symptoms like **precocious puberty** in boys or **gynecomastia** in adult men, which are not described.
- Serum tumor markers like β-hCG and α-FP are typically **not elevated** in Leydig cell tumors.
*Choriocarcinoma*
- This highly aggressive germ cell tumor is characterized by **markedly elevated β-hCG levels**, often much higher than 80 mIU/mL, and can also elevate α-FP.
- Given the relatively mild β-hCG elevation and normal α-FP, choriocarcinoma is less likely.
*Spermatocele of testis*
- A spermatocele is a **benign cyst** that typically transilluminates (light shines through), which is absent in this case.
- Tumor markers like β-hCG and α-FP would be **normal** in a spermatocele, ruling it out.
*Yolk sac tumor*
- Yolk sac tumors are characterized by **elevated alpha-fetoprotein (α-FP)** levels, which are normal in this patient.
- While they can also elevate β-hCG in some cases, the defining marker, α-FP, is not elevated here.
Male reproductive histology US Medical PG Question 4: A 31-year-old G2P2 female at 40 weeks gestation presents to the hospital following a rush of water that came from her vagina. She is 4 cm dilated and 80% effaced. Fetal heart tracing shows a pulse of 155/min with variable decelerations. About 12 hours after presentation, she gives birth to a 6 lb 15 oz baby boy with APGAR scores of 8 and 9 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. Which of the following structures is responsible for inhibition of female internal genitalia?
- A. Allantois
- B. Syncytiotrophoblast
- C. Leydig cells
- D. Spermatogonia
- E. Sertoli cells (Correct Answer)
Male reproductive histology Explanation: ***Sertoli cells***
- **Sertoli cells** in the male fetus produce **anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH)**, which is crucial for the regression of the **Müllerian ducts**.
- The **Müllerian ducts** are the precursors to the female internal genitalia (uterus, fallopian tubes, and upper vagina), so their inhibition is essential for male sexual development.
*Allantois*
- The **allantois** is a fetal membrane involved in waste storage and gas exchange, contributing to the formation of the **urachus** and parts of the bladder.
- It plays no direct role in the inhibition or development of internal genitalia.
*Syncytiotrophoblast*
- The **syncytiotrophoblast** is a layer of placental tissue that produces hormones vital for maintaining pregnancy, such as **human chorionic gonadotropin (hCG)**.
- It is not involved in the sexual differentiation of the internal genitalia.
*Leydig cells*
- **Leydig cells** produce **testosterone**, which stimulates the development of the **Wolffian ducts** into male internal genitalia (epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles).
- While essential for male development, they do not inhibit female internal genitalia; that function belongs to Sertoli cells.
*Spermatogonia*
- **Spermatogonia** are germ cells that differentiate into spermatozoa in the adult male.
- They are primordials of reproductive cells and do not have an endocrine role in embryonic sexual differentiation.
Male reproductive histology US Medical PG Question 5: A 65-year-old African American man presents for follow-up examination with a 6-month history of urinary hesitancy, weak stream, and terminal dribbling, which is refractory to a combination therapy of finasteride and tamsulosin. The patient’s past medical history is otherwise unremarkable. His father and brother were diagnosed with prostate cancer at the age of 55 years. His vital signs are within normal limits. The patient has a normal anal sphincter tone and a bulbocavernosus muscle reflex. Digital rectal exam (DRE) reveals a prostate size equivalent to 2 finger pads with a hard nodule and without fluctuance or tenderness. Serum prostate-specific antigen (PSA) level is 5 ng/mL. Which of the following investigations is most likely to establish a definitive diagnosis?
- A. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- B. 4Kscore test
- C. Prostate Health Index (PHI)
- D. Image-guided needle biopsy (Correct Answer)
- E. PSA in 3 months
Male reproductive histology Explanation: ***Image-guided needle biopsy***
- A definitive diagnosis of **prostate cancer** requires histological confirmation, which is achieved through a **biopsy**.
- The patient's presentation with a **hard nodule** on DRE, elevated PSA, and a strong family history of prostate cancer, despite treatment for BPH, strongly indicates the need for a biopsy.
*Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)*
- While MRI can help in **staging prostate cancer** and guiding biopsies, it does not provide a definitive diagnosis on its own.
- An MRI may identify suspicious lesions but **cannot confirm malignancy** without tissue sampling.
*4Kscore test*
- The 4Kscore test estimates the **risk of high-grade prostate cancer** but does not provide a definitive diagnosis.
- It uses a panel of four prostate-specific kallikrein proteins, along with patient age, DRE status, and prior biopsy results, to calculate a risk score.
*Prostate Health Index (PHI)*
- The PHI is a blood test that combines total PSA, free PSA, and [-2]proPSA to assess the **probability of prostate cancer**.
- It helps in deciding whether a biopsy is needed, but like the 4Kscore, it is not a diagnostic tool in itself.
*PSA in 3 months*
- Re-checking PSA in 3 months would **delay definitive diagnosis** and treatment for a potentially aggressive cancer, especially given the palpable nodule and family history.
- The current PSA of 5 ng/mL, although not extremely high, combined with the suspicious DRE finding, warrants more immediate action.
Male reproductive histology US Medical PG Question 6: A research team is studying certain congenital anomalies of the respiratory tract. The method consists of marking a certain germinal layer with an isotope, following its development stages in chicken embryos, and finally analyzing the specimen. A given specimen of tissue is presented in the exhibit. Which of the following germinal structures most likely gave rise to the epithelial lining of this specimen?
- A. Ectoderm
- B. Neural crest
- C. Mesoderm
- D. Endoderm (Correct Answer)
- E. Surface ectoderm
Male reproductive histology Explanation: ***Endoderm***
- The **epithelial lining** of the entire respiratory tract, including the larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs, is derived from the **endoderm**.
- The **laryngotracheal groove** develops from the ventral wall of the primitive foregut, which is endodermal in origin, further differentiating into the respiratory tree.
*Ectoderm*
- The **ectoderm** primarily forms the epidermis, hair, nails, and the nervous system (brain and spinal cord).
- It does not contribute to the internal epithelial lining of the respiratory tract.
*Neural crest*
- **Neural crest cells** contribute to a wide variety of structures, including components of the peripheral nervous system, head mesenchyme, and melanocytes.
- They are not involved in forming the epithelial lining of the respiratory system.
*Mesoderm*
- The **mesoderm** forms the connective tissue, cartilage, and muscle components of the respiratory tract, such as the smooth muscle and cartilage rings of the trachea and bronchi, and the visceral pleura.
- However, it does not form the epithelial lining itself.
*Surface ectoderm*
- **Surface ectoderm** specifically gives rise to the epidermis, hair, nails, and glands of the skin, as well as the oral cavity epithelium.
- It does not contribute to the internal epithelial structures of the respiratory tract.
Male reproductive histology US Medical PG Question 7: A 35-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of facial hair growth, acne, and irregular menses. Her friends have told her that her voice sounds lower than usual. Physical examination shows pustular acne and dark hair growth along the jawline. Serum studies show elevated testosterone levels and normal inhibin levels. An ultrasound of the pelvis shows a left-sided ovarian mass. Microscopic examination of the resected ovarian mass shows pale, testosterone-positive staining cells with cytoplasmic Reinke crystal inclusions. These abnormal cells are homologous to which of the following physiological cell type in females?
- A. Clue cells
- B. Theca interna cells (Correct Answer)
- C. Granulosa cells
- D. Germinal epithelial cells
- E. Sertoli cells
Male reproductive histology Explanation: ***Theca interna cells***
- This patient's presentation with **hirsutism**, **acne**, **virilization** (deepened voice), **irregular menses**, **elevated testosterone**, and an **ovarian mass** containing **Reinke crystal inclusions** is characteristic of a **Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor**.
- **Leydig cells** (the primary component of the tumor causing virilization) are the male homolog of female **theca interna cells**, both of which produce androgens.
*Clue cells*
- **Clue cells** are **vaginal epithelial cells** covered in bacteria, typically associated with **bacterial vaginosis**.
- They are not related to ovarian hormone production or tumor cells.
*Granulosa cells*
- **Granulosa cells** produce **estrogen** and are associated with estrogen-producing ovarian tumors, such as **granulosa cell tumors**, which would lead to signs of estrogen excess, not virilization.
- While granulosa cells are ovarian cells, they are primarily involved in estrogen synthesis, not androgen production.
*Germinal epithelial cells*
- **Germinal epithelial cells** are the surface epithelial cells of the ovary and are the origin of common **epithelial ovarian cancers**.
- These cells do not typically produce significant amounts of hormones or contain Reinke crystal inclusions.
*Sertoli cells*
- While **Sertoli cells** are part of the Sertoli-Leydig cell tumor and are the male homolog of female **granulosa cells**, they are primarily involved in supporting spermatogenesis in males and do not produce androgens themselves.
- The **virilizing effects** in this tumor are due to the **Leydig cell component**, which is homologous to the theca interna cells.
Male reproductive histology US Medical PG Question 8: A 51-year-old man presents to the emergency department with an episode of syncope. He was at a local farmer's market when he fainted while picking produce. He rapidly returned to his baseline mental status and did not hit his head. The patient has a past medical history of diabetes and hypertension but is not currently taking any medications. His temperature is 97.5°F (36.4°C), blood pressure is 173/101 mmHg, pulse is 82/min, respirations are 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam is notable for clear breath sounds and a S4 heart sound. Rectal exam reveals a firm and nodular prostate that is non-tender and a fecal-occult sample that is negative for blood. Which of the following is this patient's presentation most concerning for?
- A. Prostatitis
- B. Prostate abscess
- C. Benign prostatic hyperplasia
- D. Prostate cancer (Correct Answer)
- E. Normal physical exam
Male reproductive histology Explanation: ***Prostate cancer***
- A **firm**, **nodular**, and non-tender prostate on digital rectal examination is highly suspicious for prostate cancer, particularly in a 51-year-old male.
- The patient's presentation with **syncope** could indirectly be related to a paraneoplastic syndrome in advanced prostate cancer, although this is less common.
*Prostatitis*
- Prostatitis typically presents with **perineal pain**, **dysuria**, and **fever**, none of which are noted in this patient.
- The prostate would usually be **tender** and boggy, not firm and nodular.
*Prostate abscess*
- A prostate abscess is characterized by **severe pain**, **fever**, **chills**, and urinary symptoms, which are absent in this case.
- The prostate would be exquisitely **tender** and potentially fluctuant on examination.
*Benign prostatic hyperplasia*
- While BPH can cause urinary symptoms, it typically results in a **smooth**, enlarged, and rubbery prostate, not a firm and nodular one.
- It is not associated with syncope or the specific prostate findings described.
*Normal physical exam*
- A **firm** and **nodular** prostate on rectal exam is an abnormal finding that warrants further investigation, especially given the patient's age.
- While other findings may be normal, the prostate exam is highly concerning for pathology.
Male reproductive histology US Medical PG Question 9: A 55-year-old man comes to the physician because of difficulties achieving an erection for the past year. A medication is prescribed that inhibits cyclic GMP phosphodiesterase type 5. Which of the following is the most likely site of action of the prescribed drug?
- A. Corpus spongiosum
- B. Pelvic splanchnic nerves
- C. Pudendal nerve
- D. Prostate smooth muscle
- E. Corpus cavernosum (Correct Answer)
Male reproductive histology Explanation: ***Corpus cavernosum***
- **Erectile dysfunction** is primarily due to insufficient blood flow into the **corpus cavernosum**, which are the main erectile tissues of the penis.
- **cGMP phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors** like sildenafil work by increasing cGMP levels in the smooth muscle cells of the corpus cavernosum, leading to vessel relaxation and improved blood inflow.
*Corpus spongiosum*
- The **corpus spongiosum** primarily surrounds the urethra and prevents its compression during erection; it plays a secondary role in penile rigidity.
- While it does contain smooth muscle, it is not the primary target for medications aimed at enhancing penile rigidity.
*Pelvic splanchnic nerves*
- The **pelvic splanchnic nerves** are involved in the neural initiation of erection by releasing **nitric oxide (NO)**, which triggers cGMP production.
- However, the prescribed medication acts on the cGMP breakdown *within* the erectile tissue, not on the nerves that initiate the process.
*Pudendal nerve*
- The **pudendal nerve** is mainly responsible for carrying sensory information from the penis and innervating the external urethral sphincter and perineal muscles.
- It does not directly control the vascular smooth muscle relaxation necessary for erection, so it is not the site of action for PDE5 inhibitors.
*Prostate smooth muscle*
- While the **prostate** contains smooth muscle, it is not directly involved in the erectile process itself.
- Some PDE5 inhibitors are used for **benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)** symptoms by relaxing smooth muscle in the prostate and bladder neck, but this is a secondary effect distinct from their primary erectile function.
Male reproductive histology US Medical PG Question 10: A 35-year-old woman presents to a pre-operative evaluation clinic prior to an elective cholecystectomy. She has a 5 pack-year smoking history. The anesthesiologist highly recommends to discontinue smoking for at least 8 weeks prior to the procedure for which she is compliant. What is the most likely histology of her upper respiratory tract's epithelial lining at the time of her surgery?
- A. Simple squamous
- B. Simple columnar
- C. Pseudostratified columnar (Correct Answer)
- D. Stratified squamous
- E. Stratified columnar
Male reproductive histology Explanation: ***Pseudostratified columnar***
- The upper respiratory tract is normally lined by **pseudostratified ciliated columnar epithelium** with goblet cells, which is crucial for mucociliary clearance.
- While smoking can initially cause **squamous metaplasia**, discontinuing smoking for 8 weeks allows for significant, if not complete, **reversal of these changes** back to the normal pseudostratified columnar epithelium.
*Simple squamous*
- This type of epithelium is found in areas designed for efficient **gas exchange** (e.g., alveoli of the lungs) and is not typical for the conductive airways of the upper respiratory tract.
- It lacks the **cilia and goblet cells** necessary for clearing inhaled particles and pathogens.
*Simple columnar*
- **Simple columnar epithelium** is found in regions like the lining of the gastrointestinal tract (e.g., stomach, small and large intestines) and is not characteristic of the upper respiratory tract.
- While it can have goblet cells, it typically lacks **cilia** for respiratory clearance.
*Stratified squamous*
- **Stratified squamous epithelium** is found in areas subject to friction and abrasion, such as the oral cavity, pharynx, and esophagus.
- While chronic smoking can induce **squamous metaplasia** in the respiratory tract, an 8-week cessation period would likely result in the reversal of this change back to the normal type.
*Stratified columnar*
- **Stratified columnar epithelium** is a relatively rare type found in specific locations like parts of the male urethra and some large excretory ducts.
- It is not the normal or even a common metaplastic lining for the human upper respiratory tract.
More Male reproductive histology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.