Lymphoid tissue histology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Lymphoid tissue histology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Lymphoid tissue histology US Medical PG Question 1: A 24-year-old man, an information technology professional, gets himself tested for serum immunoglobulin M (IgM) levels because he wants to know more about his immunity. He knows that IgM levels reflect the status of his immunity, based on the internet. Although the laboratory report is normal, he consults a physician. The physician discusses human immunity and its important components. He also tells him that most circulating IgM antibodies in the blood of normal persons are produced by a specific type of B cell, which is present mostly in the peritoneal cavity and in mucosal tissues. He also mentions that these cells are components of innate immunity. Which of the following types of B cells is the physician referring to?
- A. Naïve B cells
- B. Marginal zone B cells
- C. Follicular B cells
- D. B-1 B cells (Correct Answer)
Lymphoid tissue histology Explanation: ***B-1 B cells***
- **B-1 B cells** are a distinct lymphocyte population found primarily in the **peritoneal and pleural cavities**, and mucosal tissues. They spontaneously secrete **IgM antibodies** without T cell help, which are important for initial defense against common pathogens.
- They are considered a component of the **innate immune system** due to their rapid, T-cell-independent response and limited receptor diversity, providing immediate protection.
*Naïve B cells*
- **Naïve B cells** circulate in the blood and secondary lymphoid organs, express both **IgM and IgD** on their surface, and have not yet encountered their specific antigen.
- They require activation by antigen and often **T cell help** to differentiate into plasma cells and produce antibodies.
*Marginal zone B cells*
- **Marginal zone (MZ) B cells** are located in the marginal zone of the spleen and respond rapidly to **blood-borne polysaccharide antigens**.
- While they can produce **IgM without T-cell help**, they are primarily found in the spleen, not predominantly the peritoneal cavity or mucosal tissues.
*Follicular B cells*
- **Follicular B cells** are the most abundant B cell population in secondary lymphoid organs, residing in **B cell follicles**.
- They require **T cell help** to mount robust immune responses, undergo class-switching, and affinity maturation, and are not primarily known for spontaneous IgM production in the peritoneal cavity.
Lymphoid tissue histology US Medical PG Question 2: A 24-year-old male with cystic fibrosis is brought to the emergency room by his mother after he had difficulty breathing. He previously received a lung transplant 6 months ago and was able to recover quickly from the operation. He is compliant with all of his medications and had been doing well with no major complaints until 2 weeks ago when he began to experience shortness of breath. Exam reveals a decreased FEV1/FVC ratio and biopsy reveals lymphocytic infiltration. Which of the following components is present in the airway zone characteristically affected by the most likely cause of this patient's symptoms?
- A. Pseudostratified columnar cells
- B. Goblet cells
- C. Simple cuboidal cells (Correct Answer)
- D. Stratified cuboidal cells
- E. Cartilage
Lymphoid tissue histology Explanation: ***Simple cuboidal cells***
- The patient's symptoms, history of a lung transplant, and biopsy findings of **lymphocytic infiltration** suggest **bronchiolitis obliterans**, a form of chronic lung allograft dysfunction.
- Bronchiolitis obliterans primarily affects the **small airways** (bronchioles), which are characterized by an epithelial lining of **simple cuboidal cells** and lack cartilage.
*Pseudostratified columnar cells*
- These cells line the **trachea** and **main bronchi** (larger airways), which are typically not the primary site of damage in bronchiolitis obliterans.
- They are part of the **mucociliary escalator** and are also associated with cartilage.
*Goblet cells*
- While present in the **larger airways** along with pseudostratified columnar cells, goblet cells are less prominent or absent in the small bronchioles primarily affected by bronchiolitis obliterans.
- Their characteristic function is mucus production, not the specific epithelial type of the affected bronchioles.
*Stratified cuboidal cells*
- This cell type is **rare** in the respiratory tract and is not characteristic of the small airways affected by bronchiolitis obliterans.
- Stratified epithelia are typically seen in ducts of glands or specialized transitional zones, not the functional bronchioles.
*Cartilage*
- Cartilage provides structural support to the **trachea and main bronchi**, but it is **absent** in the small airways (bronchioles) that are the primary target of bronchiolitis obliterans.
- The presence of cartilage would indicate a larger airway, contradicting the pathophysiology of this condition.
Lymphoid tissue histology US Medical PG Question 3: A 26-year-old woman presents to your clinic with complaints of increasing muscle fatigue that worsens after periods of sustained activity. She also reports both ptosis and diplopia that make reading in the late afternoon and evenings difficult. An edrophonium test is performed and is positive, demonstrating resolution of the patient's weakness. One organ in particular, when abnormal, is associated with this patient's condition. Which of the following embryologic structures gives rise to this organ?
- A. 3rd branchial arch
- B. 4th branchial pouch
- C. 1st branchial pouch
- D. 2nd branchial cleft
- E. 3rd branchial pouch (Correct Answer)
Lymphoid tissue histology Explanation: ***3rd branchial pouch***
- The clinical presentation (muscle fatigue worsening with activity, ptosis, diplopia, positive edrophonium test) indicates **myasthenia gravis**. Myasthenia gravis is commonly associated with **thymic abnormalities**, such as thymoma or thymic hyperplasia.
- The **thymus** develops from the **third pharyngeal (branchial) pouch**.
*3rd branchial arch*
- The 3rd branchial arch gives rise to structures such as the common **carotid artery**, proximal internal carotid artery, **stylopharyngeus muscle**, and **glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)**.
- It does not contribute to the development of the thymus or structures related to myasthenia gravis.
*4th branchial pouch*
- The 4th branchial pouch gives rise to the **superior parathyroid glands** and the **parafollicular C cells** of the thyroid gland.
- It is not involved in the embryological development of the thymus.
*1st branchial pouch*
- The 1st branchial pouch gives rise to the **eustachian tube**, **middle ear cavity**, and part of the mastoid air cells.
- These structures are unrelated to the thymus or myasthenia gravis.
*2nd branchial cleft*
- The 2nd, 3rd, and 4th branchial clefts typically merge and obliterate to form the **cervical sinus**.
- Persistence of these clefts or their incomplete obliteration can lead to **branchial cleft cysts or fistulas**, which are distinct from thymic development.
Lymphoid tissue histology US Medical PG Question 4: A 32-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 3-week history of cough, weight loss, and night sweats. He migrated from Sri Lanka 6 months ago. He appears emaciated. His temperature is 38.1°C (100.5°F). Physical examination shows enlargement of the right supraclavicular lymph node. Chest and abdominal examination show no abnormalities. An interferon-gamma assay is positive. A biopsy specimen of the cervical lymph node is most likely to show the causal organism in which of the following locations?
- A. Mantle zone
- B. Medullary sinus
- C. Germinal center
- D. Subcapsular sinus
- E. Paracortex (Correct Answer)
Lymphoid tissue histology Explanation: ***Paracortex***
- The patient's symptoms (cough, weight loss, night sweats, fever), recent migration from an endemic area (Sri Lanka), **supraclavicular lymphadenopathy**, and positive **interferon-gamma release assay (IGRA)** strongly suggest **tuberculosis**.
- In tuberculous lymphadenitis, **caseating granulomas** containing *Mycobacterium tuberculosis* organisms characteristically form in the **paracortex** (T-cell zone).
- The **paracortex** is where **cell-mediated immunity** occurs, with T cells interacting with infected macrophages and dendritic cells to form the **epithelioid granulomas** with **Langhans giant cells** that are pathognomonic for TB.
- The organisms are found within these **granulomas**, which predominantly occur in the paracortical (interfollicular) region.
*Mantle zone*
- The **mantle zone** primarily contains **naïve B cells** surrounding germinal centers.
- This is a B-cell area not typically involved in granuloma formation or mycobacterial infection.
*Germinal center*
- **Germinal centers** are sites of B cell proliferation, somatic hypermutation, and antibody class switching.
- TB is a disease of **cell-mediated immunity** (T cells and macrophages), not humoral immunity, so granulomas do not form in germinal centers.
*Medullary sinus*
- The **medullary sinuses** are channels in the medulla of the lymph node through which lymph flows toward the efferent lymphatic vessels.
- While macrophages line these sinuses and may contain some organisms in acute infections, the characteristic **caseating granulomas** of chronic tuberculous lymphadenitis form in the **paracortex**, not in the sinuses.
*Subcapsular sinus*
- The **subcapsular sinus** is the initial entry point for afferent lymph into the lymph node.
- While this is where pathogens first enter, chronic granulomatous infections like TB develop their characteristic pathology deeper in the node, specifically in the **paracortex** where T-cell-mediated granuloma formation occurs.
Lymphoid tissue histology US Medical PG Question 5: A syndrome caused by chromosomal anomalies is being researched in the immunology laboratory. Several congenital conditions are observed among the participating patients, mostly involving the thymus and the heart. Common facial features of affected individuals are shown in the image below. Flow cytometry analysis of patient samples reveals a CD19+ and CD3- result. What kind of congenital anomaly is generally observed in these patients, specifically in the thymus?
- A. Deformation
- B. Malformation
- C. Disruption
- D. Aplasia (Correct Answer)
- E. Agenesis
Lymphoid tissue histology Explanation: ***Aplasia***
- The scenario describes **DiGeorge syndrome**, characterized by a **22q11.2 deletion**, leading to defective development of the 3rd and 4th pharyngeal pouches.
- This results in **thymic hypoplasia or aplasia**, causing **T-cell immunodeficiency** (CD3-), and **parathyroid aplasia**, leading to hypocalcemia.
- The CD19+ (B cells present) and CD3- (T cells absent) flow cytometry result specifically points to **thymic aplasia** as the cause for the lack of mature T-cells.
*Deformation*
- A deformation refers to an **abnormality in shape or position of a normally formed body part** due to extrinsic mechanical forces, such as uterine constraint.
- This is not the primary mechanism behind the thymic and cardiac anomalies described, which are due to inherent developmental defects.
*Malformation*
- A malformation is an **intrinsic abnormality of development** occurring during the embryonic period, due to genetic or environmental factors.
- While DiGeorge syndrome involves malformations (e.g., cardiac defects, characteristic facial features), the specific term for the complete or near-complete absence of an organ like the thymus is aplasia or hypoplasia, which is a more precise description in this context.
*Disruption*
- A disruption is a **morphological defect of an organ or body part from extrinsic breakdown of, or an interference with, an originally normal developmental process**.
- Examples include **amniotic bands** causing limb defects; this does not fit the description of a primary developmental defect of the pharyngeal pouches.
*Agenesis*
- Agenesis refers to the **complete absence of an organ** due to failure of development during embryonic growth.
- While agenesis is severe, **aplasia** (failure of development resulting in a rudimentary structure or complete absence) is often used interchangeably or to describe a more specific severe lack of development, especially in conditions like DiGeorge syndrome where there can be hypoplasia or complete absence. In clinical practice for DiGeorge, aplasia or hypoplasia is more commonly used for the thymus.
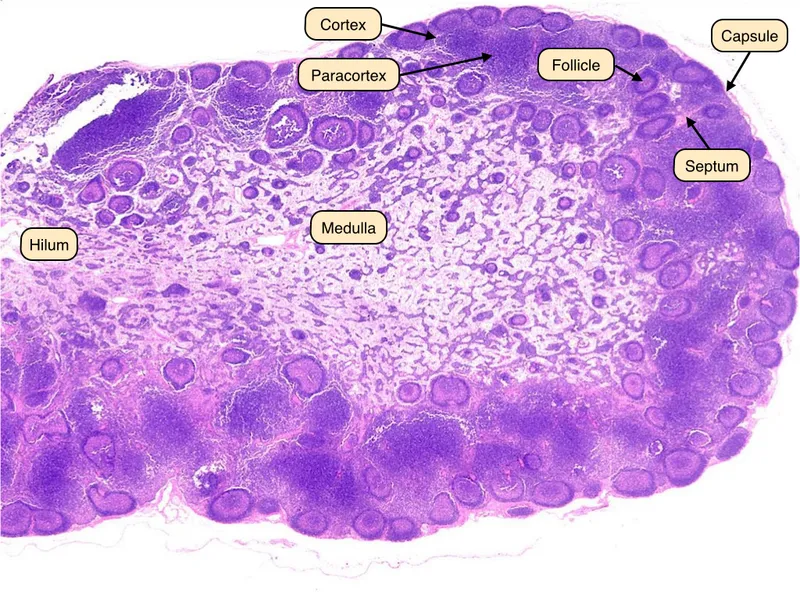
Lymphoid tissue histology US Medical PG Question 6: A study is designed to assess the functions of immune components. The investigator obtains a lymph node biopsy from a healthy subject and observes it under a microscope. A photomicrograph of the cross-section of this lymph node is shown. Which of the following immunologic processes most likely occurs in the region labeled with an arrow?
- A. Isotype switching (Correct Answer)
- B. V(D)J recombination
- C. Macrophage activation
- D. T cell activation
- E. Negative selection
Lymphoid tissue histology Explanation: ***Isotype switching***
- The arrow points to a **germinal center**, a specialized microenvironment within lymph nodes where B cells undergo **affinity maturation** and **isotype switching**.
- Isotype switching (or class switching) is the process by which B cells change the type of **antibody** they produce, e.g., from IgM to IgG, IgA, or IgE, to mediate different effector functions while retaining antigen specificity.
*V(D)J recombination*
- **V(D)J recombination** is the genetic mechanism by which the diverse repertoires of T cell receptors (TCRs) and immunoglobulins (antibodies) are generated, primarily in the **bone marrow** (for B cells) and **thymus** (for T cells) during their development.
- This process occurs much earlier in lymphocyte development and is largely completed before B cells migrate to secondary lymphoid organs like lymph nodes and form germinal centers.
*Macrophage activation*
- **Macrophage activation** is a process where macrophages acquire enhanced phagocytic and microbicidal activity, often in response to cytokines like **IFN-γ** produced by T helper cells.
- While macrophages are present in lymph nodes and play a role in antigen presentation and immune responses, their primary activation does not specifically occur within germinal centers; the germinal center is mainly a site for B cell maturation.
*T cell activation*
- **T cell activation** primarily occurs in the **T cell zones** (paracortex) of lymph nodes, where **naïve T cells** encounter antigen-presenting cells (APCs) presenting their specific antigen.
- While T follicular helper (Tfh) cells, a type of T cell, are crucial for sustaining germinal center reactions, the germinal center itself is not the primary site for the initial activation of most T cells.
*Negative selection*
- **Negative selection** is a critical process in lymphocyte development, occurring in the **thymus** for T cells and **bone marrow** for B cells, where self-reactive lymphocytes are eliminated.
- This process ensures central tolerance and occurs long before mature lymphocytes populate secondary lymphoid organs like lymph nodes.
Lymphoid tissue histology US Medical PG Question 7: A 2-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department because of fever, cough, and ear pain over the past 2 days. He has had recurrent respiratory tract infections and several episodes of giardiasis and viral gastroenteritis since he was 6 months of age. Examination shows decreased breath sounds over both lung fields and bilateral purulent otorrhea. His palatine tonsils and adenoids are hypoplastic. Quantitative flow cytometry of his blood shows decreased levels of cells that express CD19, CD20, and CD21. Which of the following is the most likely cause of this patient's condition?
- A. Mutation in NADPH oxidase gene
- B. Microdeletion on the long arm of chromosome 22
- C. Mutation in WAS gene
- D. Mutation in tyrosine kinase gene (Correct Answer)
- E. Defect in beta-2 integrin
Lymphoid tissue histology Explanation: ***Mutation in tyrosine kinase gene***
- The patient's history of **recurrent bacterial infections** (respiratory tract infections, otorrhea), **giardiasis**, and **viral gastroenteritis**, combined with **hypoplastic tonsils and adenoids**, points to a **B-cell primary immunodeficiency**.
- **Decreased levels of CD19+, CD20+, and CD21+ cells** on flow cytometry confirm a B-cell deficiency, making a mutation in the **tyrosine kinase gene (Bruton's tyrosine kinase, BTK)** the most likely cause, leading to **X-linked agammaglobulinemia (XLA)**.
*Mutation in NADPH oxidase gene*
- This mutation causes **chronic granulomatous disease (CGD)**, characterized by recurrent bacterial and fungal infections due to impaired phagocyte oxidative burst.
- Patients with CGD typically have normal numbers of B cells (CD19+, CD20+, CD21+ cells); the clinical presentation would not include hypoplastic tonsils or repeated Giardia infection as a primary hallmark.
*Microdeletion on the long arm of chromosome 22*
- This describes **DiGeorge syndrome**, which involves T-cell deficiency due to thymic hypoplasia, along with cardiac defects and hypocalcemia.
- While it can manifest with recurrent infections and sometimes lymphoid hypoplasia, the primary immune defect is in T cells, and B cell numbers would be normal unless severe secondary lymphoid tissue defects are present.
*Mutation in WAS gene*
- This causes **Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome (WAS)**, characterized by the triad of **thrombocytopenia** (small platelets), **eczema**, and **recurrent infections**.
- WAS primarily affects T cells and platelet function; it would not typically present with hypoplastic tonsils or a primary B-cell count deficiency as the main diagnostic feature.
*Defect in beta-2 integrin*
- A defect in beta-2 integrin causes **leukocyte adhesion deficiency (LAD)**, characterized by recurrent bacterial infections, **impaired wound healing**, and **delayed umbilical cord separation**.
- Patients with LAD have normal B cell numbers and do not typically present with hypoplastic lymphoid organs or a predisposition to giardiasis in the same manner as XLA.
Lymphoid tissue histology US Medical PG Question 8: A 67-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-week history of fatigue and worsening back and abdominal pain. During this period, she has also had excessive night sweats and a 4.6-kg (10-lb) weight loss. She has had swelling of the neck for 3 days. She does not smoke or drink alcohol. Vital signs are within normal limits. Physical examination shows a 4-cm, supraclavicular, nontender, enlarged and fixed lymph node. The spleen is palpated 2 cm below the left costal margin. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 10.4 g/dL
Mean corpuscular volume 87 μm3
Leukocyte count 5,200/mm3
Platelet count 190,000/mm3
Serum
Lactate dehydrogenase 310 U/L
A CT scan of the thorax and abdomen shows massively enlarged paraaortic, axillary, mediastinal, and cervical lymph nodes. Histopathologic examination of an excised cervical lymph node shows lymphocytes with a high proliferative index that stain positive for CD20. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Hairy cell leukemia
- B. Adult T-cell lymphoma
- C. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (Correct Answer)
- D. Marginal zone lymphoma
- E. Follicular lymphoma
Lymphoid tissue histology Explanation: ***Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma***
- The patient presents with **B symptoms** (fever, night sweats, weight loss), rapid progression, generalized **lymphadenopathy** (cervical, supraclavicular, paraaortic, axillary, mediastinal), **splenomegaly**, and elevated **LDH**.
- **Histopathologic examination** showing lymphocytes with a **high proliferative index** and positive **CD20 staining** confirms a B-cell lymphoma with aggressive features, highly characteristic of DLBCL.
*Hairy cell leukemia*
- This condition typically presents with **splenomegaly** and **pancytopenia**, but **lymphadenopathy** is rare and often absent.
- The characteristic "hairy cells" are identified by specific markers (CD103, CD123, CD25), and a **high proliferative index** is not a feature.
*Adult T-cell lymphoma*
- This lymphoma is associated with **HTLV-1 infection** and often presents with hypercalcemia, skin lesions, and generalized lymphadenopathy, but it is a **T-cell lymphoma**.
- The **CD20 positivity** in the histology rules out a T-cell lineage lymphoma.
*Marginal zone lymphoma*
- This is an **indolent B-cell lymphoma** that typically progresses slowly and is often associated with chronic inflammation or autoimmune diseases.
- The patient's aggressive symptoms, rapid progression, significant **B symptoms**, and **high proliferative index** are not consistent with indolent lymphoma.
*Follicular lymphoma*
- This is also an **indolent B-cell lymphoma** characterized by a follicular growth pattern and usually presents with painless lymphadenopathy.
- The rapid onset of symptoms, significant **B symptoms**, and elevated **LDH** indicate an aggressive lymphoma, which is not typical of follicular lymphoma.
Lymphoid tissue histology US Medical PG Question 9: A 38-year-old man comes to the clinic complaining of recurrent abdominal pain for the past 2 months. He reports a gnawing, dull pain at the epigastric region that improves with oral ingestion. He has been taking calcium carbonate for the past few weeks; he claims that “it used to help a lot but it’s losing its effects now.” Laboratory testing demonstrated increased gastrin levels after the administration of secretin. A push endoscopy visualized several ulcers at the duodenum and proximal jejunum. What characteristics distinguish the jejunum from the duodenum?
- A. Lack of goblet cells
- B. Crypts of Lieberkuhn
- C. Lack of submucosal Brunner glands (Correct Answer)
- D. Peyer patches
- E. Plicae circulares
Lymphoid tissue histology Explanation: ***Lack of submucosal Brunner glands***
- The **jejunum** lacks **Brunner glands**, which are characteristic of the **duodenum** and secrete alkaline mucus to neutralize acidic chyme from the stomach.
- The absence of these glands helps differentiate the jejunum from the duodenum histologically.
*Lack of goblet cells*
- **Goblet cells** are present throughout the small intestine, including both the duodenum and jejunum, though their density increases distally.
- Therefore, the **lack of goblet cells** does not distinguish the jejunum from the duodenum.
*Crypts of Lieberkuhn*
- **Crypts of Lieberkuhn** (intestinal crypts) are present throughout the entire small intestine, including both the **duodenum** and **jejunum**, where they house stem cells for epithelial renewal.
- Their presence is not a distinguishing feature between these two segments histologically.
*Peyer patches*
- **Peyer patches** are lymphoid aggregates primarily found in the **ileum**, not the jejunum or duodenum, and are involved in immune surveillance.
- They are a distinguishing feature of the ileum but not between the jejunum and duodenum.
*Plicae circulares*
- **Plicae circulares** (also known as valves of Kerckring or circular folds) are macroscopic folds of the mucosa and submucosa that are present in both the **duodenum** and **jejunum**.
- They are most prominent in the jejunum, but their mere presence does not distinguish the jejunum from the duodenum.
Lymphoid tissue histology US Medical PG Question 10: A 23-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with 3 days of fatigue and back pain after she started a drug for malaria prophylaxis. She says that her urine has also been darker over the same time period. Her past medical history is significant for allergies as well as a broken elbow that was treated in a cast 10 years ago. She does not take any medications, does not smoke, and drinks socially. Peripheral blood smear reveals both red blood cells with dark intracellular inclusions as well as abnormally shaped red blood cells. The immune cells responsible for the shape of these red blood cells are located in which of the following places?
- A. Lymph nodes
- B. Red pulp of the spleen (Correct Answer)
- C. Bone marrow
- D. White pulp of the spleen
- E. Blood vessels
Lymphoid tissue histology Explanation: ***Red pulp of the spleen***
- The patient's symptoms (fatigue, back pain, dark urine after malaria prophylaxis) and lab findings (**dark intracellular inclusions** and abnormally shaped red blood cells) suggest **G6PD deficiency**, leading to **hemolytic anemia**.
- The **red pulp of the spleen** is where old or damaged red blood cells, including those with Heinz bodies (intracellular inclusions) or abnormal shapes, are **phagocytosed** by macrophages, thus "shaping" them or removing severely affected cells.
*Lymph nodes*
- **Lymph nodes** are primarily involved in filtering lymph and are major sites for adaptive immune responses, housing B and T lymphocytes.
- They are not the primary sites for the destruction or "shaping" of red blood cells.
*Bone marrow*
- The **bone marrow** is the primary site of **hematopoiesis**, where red blood cells are produced, not where they are destroyed or undergo physical shaping due to immune cell action in hemolysis.
- While macrophages are present, their main role in marrow is related to erythropoiesis (e.g., central macrophage in erythroblastic islands) and debris clearance, not erythrocyte shaping in peripheral circulation.
*White pulp of the spleen*
- The **white pulp of the spleen** is rich in lymphocytes and is the site of immune responses, similar to lymph nodes.
- It is involved in adaptive immunity and not directly engaged in the physical destruction or "shaping" of red blood cells during hemolysis.
*Blood vessels*
- **Blood vessels** are conduits for blood transport and are not primary sites for the physical destruction or shaping of red blood cells by immune cells.
- While some hemolysis can occur intravascularly, the immune cells responsible for removing and "shaping" damaged red blood cells (like macrophages) are predominantly organ-resident.
More Lymphoid tissue histology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.