Liver and gallbladder histology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Liver and gallbladder histology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Liver and gallbladder histology US Medical PG Question 1: A 34-year-old patient presents with severe pain in the right upper quadrant that radiates to the right shoulder. During laparoscopic cholecystectomy, which of the following anatomical spaces must be carefully identified to prevent bile duct injury?
- A. Foramen of Winslow
- B. Lesser sac
- C. Calot's triangle (Correct Answer)
- D. Morrison's pouch
Liver and gallbladder histology Explanation: ***Calot's triangle***
- **Calot's triangle** is the critical anatomical landmark containing the **cystic artery** and **cystic duct**, whose proper identification is essential to prevent injury to the hepatic artery or bile ducts during cholecystectomy.
- Its boundaries are the **cystic duct** (lateral), the **common hepatic duct** (medial), and the **inferior border of the liver** (superior, sometimes described as the cystic artery).
*Foramen of Winslow*
- The **Foramen of Winslow** (epiploic foramen) is an opening connecting the **greater and lesser sacs** of the peritoneal cavity.
- It is not directly relevant to identifying structures during cholecystectomy, but rather to accessing the lesser sac or for surgical procedures involving structures like the portal triad.
*Lesser sac*
- The **lesser sac** (omental bursa) is a peritoneal cavity posterior to the stomach and lesser omentum.
- It is explored in procedures involving the pancreas, posterior gastric wall, or for assessing fluid collections, but not for direct identification of cystic structures during standard cholecystectomy.
*Morrison's pouch*
- **Morrison's pouch** is the **hepatorenal recess**, a potential space between the posterior aspect of the liver and the right kidney and adrenal gland.
- It is a common site for **fluid accumulation** (e.g., ascites, blood) but is not directly incised or dissected for preventing bile duct injury during cholecystectomy.
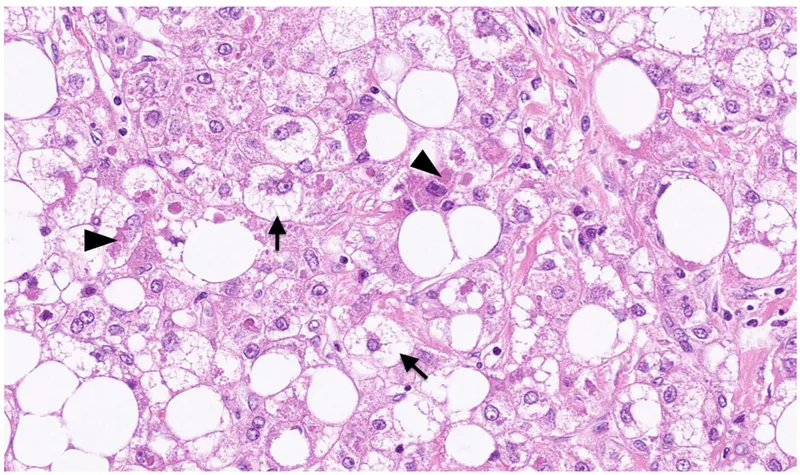
Liver and gallbladder histology US Medical PG Question 2: A 45-year-old man comes to the physician for a routine health maintenance examination. He feels well. He has type 2 diabetes mellitus. There is no family history of serious illness. He works as an engineer at a local company. He does not smoke. He drinks one glass of red wine every other day. He does not use illicit drugs. His only medication is metformin. He is 180 cm (5 ft 11 in) tall and weighs 100 kg (220 lb); BMI is 31 kg/m2. His vital signs are within normal limits. Examination shows a soft, nontender abdomen. The liver is palpated 2 to 3 cm below the right costal margin. Laboratory studies show an aspartate aminotransferase concentration of 100 U/L and an alanine aminotransferase concentration of 130 U/L. Liver biopsy shows hepatocyte ballooning degeneration, as well as inflammatory infiltrates with scattered lymphocytes, neutrophils, and Kupffer cells. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (Correct Answer)
- B. Autoimmune hepatitis
- C. Viral hepatitis
- D. Primary biliary cholangitis
- E. Alcoholic fatty liver disease
Liver and gallbladder histology Explanation: ***Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis***
- The patient's **obesity (BMI 31)**, **type 2 diabetes mellitus**, and elevated liver enzymes (ALT > AST) in the absence of significant alcohol intake or other causes of liver disease are highly suggestive of **nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)**, with the biopsy findings of **hepatocyte ballooning degeneration** and **inflammatory infiltrates** confirming progression to **nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)**.
- **NASH** is a severe form of NAFLD characterized by **steatosis**, **inflammation**, and hepatocyte injury (ballooning degeneration), which can progress to cirrhosis and liver failure.
*Autoimmune hepatitis*
- This condition is typically characterized by high levels of **autoantibodies** (e.g., ANA, anti-smooth muscle antibodies), which are not mentioned and would be an important diagnostic clue.
- Although it can cause elevated transaminases and inflammatory infiltrates, the biopsy typically shows **interface hepatitis** and prominent plasma cell infiltrates, rather than significant steatosis and ballooning degeneration.
*Viral hepatitis*
- While viral hepatitis (e.g., hepatitis B or C) causes elevated transaminases and inflammatory changes, the biopsy findings of **hepatocyte ballooning** are not characteristic.
- The patient's presentation does not include risk factors or symptoms typically associated with acute or chronic viral hepatitis, and serological markers would be required for diagnosis.
*Primary biliary cholangitis*
- This is a chronic autoimmune cholestatic liver disease primarily affecting **interlobular bile ducts**, usually seen in middle-aged women.
- It is characterized by elevated **alkaline phosphatase** levels and positive **antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA)**, which are not described in this patient, and the biopsy would show granulomatous destruction of bile ducts.
*Alcoholic fatty liver disease*
- Although the biopsy findings of **steatosis**, **hepatocyte ballooning**, and **inflammation** can be seen in alcoholic liver disease, the patient's reported alcohol consumption of "one glass of red wine every other day" is well below the threshold for causing significant alcoholic liver damage.
- **Alcoholic hepatitis** typically involves an AST:ALT ratio of >2 and a history of heavy, prolonged alcohol use.
Liver and gallbladder histology US Medical PG Question 3: A 57-year-old man presents with fever and yellow discoloration of the skin for the past 4 days. He denies any recent weight loss or changes in urine or stool color. His past medical history is unremarkable. He admits to drinking about 130 g/day of alcohol and says he has been doing so for the past 25 years. His wife who is accompanying him during this visit adds that once her husband drank 15 cans of beer at a funeral. The patient also reports a 10-pack-year smoking history. His vital signs include: pulse 98/min, respiratory rate 13/min, temperature 38.2°C (100.8°F) and blood pressure 120/90 mm Hg. On physical examination, the patient appears jaundiced and is ill-appearing. Sclera is icteric. Abdominal examination reveals tenderness to palpation in the right upper quadrant with no rebound or guarding. Percussion reveals significant hepatomegaly extending 3 cm below the right costal margin. Laboratory studies are significant for the following:
Sodium 135 mEq/L
Potassium 3.5 mEq/L
ALT 240 U/L
AST 500 U/L
A liver biopsy is obtained but the results are pending. Which of the following would most likely be seen in this patient's biopsy?
- A. Steatosis alone
- B. Hürthle cells
- C. 'Florid' bile duct lesion
- D. Gaucher cells
- E. Mallory-Denk bodies (Correct Answer)
Liver and gallbladder histology Explanation: ***Mallory-Denk bodies***
- The patient's history of heavy alcohol consumption, fever, **jaundice**, elevated AST and ALT with an **AST:ALT ratio > 2:1**, and hepatomegaly are highly indicative of **alcoholic hepatitis**.
- **Mallory-Denk bodies (MDBs)**, or alcoholic hyaline, are characteristic histological findings in alcoholic liver disease, representing damaged intermediate filaments within hepatocytes.
*Steatosis alone*
- While **steatosis (fatty liver)** is the earliest and most common response to alcohol, the presence of fever, jaundice, and marked transaminitis (especially the **AST:ALT ratio**) suggests a more severe, active inflammatory process like alcoholic hepatitis rather than isolated steatosis.
- **Simple steatosis** typically yields milder symptoms and less pronounced liver enzyme elevations.
*Hürthle cells*
- **Hürthle cells** are typically found in the **thyroid gland** and are associated with thyroid conditions like Hashimoto's thyroiditis or Hürthle cell carcinoma.
- They are not a feature of liver biopsies or alcoholic liver disease.
*'Florid' bile duct lesion*
- A **"florid" bile duct lesion** is characteristic of **primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)**, an autoimmune liver disease affecting small bile ducts.
- The patient's clinical presentation (heavy alcohol use, AST:ALT ratio > 2) does not align with PBC.
*Gaucher cells*
- **Gaucher cells** are **lipid-laden macrophages** found in individuals with **Gaucher disease**, a lysosomal storage disorder.
- They are typically seen in the bone marrow, spleen, and liver in the context of this specific genetic disorder, not alcoholic hepatitis.
Liver and gallbladder histology US Medical PG Question 4: A 49-year-old woman presents to the primary care physician with complaints of recurrent episodes of right upper abdominal pain for the past 2 years. She is currently symptom-free. She mentions that the pain often occurs after a heavy fatty meal and radiates to her right shoulder. On examination, the patient has no tenderness in the abdomen and all other systemic examination is normal. Blood work shows:
Leukocyte count 8,000/mm³
Total bilirubin 1.2 mg/dL
Prothrombin time 12 s
Aspartate transaminase 58 IU/L
Alanine transaminase 61 IU/L
Serum albumin 4.1 g/dL
Stool occult blood negative
Ultrasonography of the abdomen shows a thickened gallbladder wall with few gallstones. A hydroxy iminodiacetic acid (HIDA) scan was done which demonstrated non-filling of the gallbladder and a minimal amount of tracer in the common bile duct. Which of the following best describes a histopathological feature in the gallbladder described in this case?
- A. Minimal lymphoid aggregates
- B. Hyalinized collagen and dystrophic calcification in the submucosal layer
- C. Abnormal deposits of cholesterol ester in macrophages in the lamina propria
- D. Entrapped epithelial crypts seen as pockets of epithelium in the wall of the gallbladder (Correct Answer)
- E. Neutrophilic infiltration with vascular congestion and fibrin deposition in the gallbladder
Liver and gallbladder histology Explanation: ***Entrapped epithelial crypts seen as pockets of epithelium in the wall of the gallbladder***
- The clinical presentation (recurrent right upper abdominal pain after fatty meals, radiating to the right shoulder, thickened gallbladder wall, and non-filling on HIDA scan) strongly suggests **chronic cholecystitis**.
- **Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses**, which are outpouchings of the gallbladder mucosa through the muscular layer, are a characteristic histopathological feature of chronic cholecystitis. These appear as entrapped epithelial crypts or pockets of epithelium within the gallbladder wall.
*Minimal lymphoid aggregates*
- While **lymphoid aggregates** can be seen in chronic inflammation as a general response, they are not specific or a hallmark feature distinguishing chronic cholecystitis from other conditions, nor do they represent a specific pathological structure like Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses.
- Their presence alone does not best describe the expected histopathology given the classic clinical and imaging findings pointing towards chronic cholecystitis.
*Hyalinized collagen and dystrophic calcification in the submucosal layer*
- **Hyalinized collagen** and **dystrophic calcification** in the gallbladder wall can occur in late-stage chronic inflammation, particularly in conditions like a porcelain gallbladder.
- While these might be present in severe or long-standing cases, they are not the primary or most characteristic histopathological feature that underpins the development of chronic cholecystitis, especially when Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses are a more direct consequence of chronic inflammation.
*Abnormal deposits of cholesterol ester in macrophages in the lamina propria*
- This description refers to **cholesterolosis (strawberry gallbladder)**, characterized by cholesterol-laden macrophages within the lamina propria.
- While cholesterolosis is associated with gallstones and can cause similar pain, it is a distinct condition and does not specifically involve the architectural changes in the gallbladder wall (like Rokitansky-Aschoff sinuses) that are highly characteristic of chronic cholecystitis.
*Neutrophilic infiltration with vascular congestion and fibrin deposition in the gallbladder*
- This describes **acute cholecystitis**, which involves an active inflammatory process with neutrophils and signs of acute tissue damage.
- The patient is currently symptom-free and has a history of *recurrent* pain, indicating a chronic rather than acute process. The blood work (normal WBC count) also does not support an acute inflammatory state.
Liver and gallbladder histology US Medical PG Question 5: A 40-year-old man presents to his primary care provider complaining of abdominal pain. The patient reports a dull pain that has been present for 4 weeks now. The patient states that the pain is located to his right upper quadrant and does not change with eating. The patient denies any alcohol or illicit substance use, stating that he is meticulous about eating healthy since he is a professional bodybuilder. The patient reports no history of malignancy. On exam, the patient's temperature is 98.2°F (36.8°C), blood pressure is 130/86 mmHg, pulse is 60/min, and respirations are 12/min. The patient has an athletic build, and his exam is unremarkable for any palpable mass or abdominal tenderness. On further questioning, the patient does endorse a 5-year history of using anabolic steroids for bodybuilding. Imaging demonstrates an enhancing liver nodule. Which of the following is the most likely histopathologic finding of this patient’s disease?
- A. Hemorrhagic nests with atypical endothelial cells
- B. Multifocal tumor with multiple layers of hepatocytes with hemorrhage and necrosis
- C. Columnar cells with acinar structures
- D. Hypervascular lesion lined by normal endothelial cells
- E. Sheets of normal hepatocytes without portal tracts or central veins (Correct Answer)
Liver and gallbladder histology Explanation: ***Sheets of normal hepatocytes without portal tracts or central veins***
- This describes **hepatic adenoma**, which is strongly associated with **anabolic steroid use** and can present as an enhancing liver nodule.
- The absence of portal tracts and central veins within the nodule, composed of sheets of normal-appearing hepatocytes, is a key histologic feature.
*Hemorrhagic nests with atypical endothelial cells*
- This description is characteristic of **angiosarcoma of the liver**, a rare and aggressive tumor.
- While it can be hemorrhagic, the presence of **atypical endothelial cells** points to a malignant vascular tumor, which is not suggested by anabolic steroid use alone.
*Multifocal tumor with multiple layers of hepatocytes with hemorrhage and necrosis*
- This description aligns more with **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)**, especially if multifocal.
- In HCC, hepatocytes are **atypical** and arranged in thickened layers, often with areas of hemorrhage and necrosis, which is not directly caused by anabolic steroids but rather from chronic liver disease.
*Columnar cells with acinar structures*
- This histopathological finding is more suggestive of an **adenocarcinoma**, possibly metastatic to the liver, or rarely, a primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma.
- While adenocarcinomas can occur in the liver, they typically do not arise from anabolic steroid use and are not primarily composed of hepatic cellular elements.
*Hypervascular lesion lined by normal endothelial cells*
- This description most closely fits a **hepatic hemangioma**, the most common benign liver tumor.
- Although hemangiomas are hypervascular and lined by normal endothelial cells, they are typically incidental findings and not directly associated with anabolic steroid use or specific symptoms like the dull RUQ pain described.
Liver and gallbladder histology US Medical PG Question 6: A previously healthy 75-year-old woman comes to the physician because of fatigue and decreasing exercise tolerance over the past 6 weeks. She also has intermittent episodes of dizziness. She has never smoked and does not drink alcohol. She takes a daily multivitamin. She appears pale. Physical examination shows a smooth liver that is palpable 1 cm below the costal margin. The spleen is not palpable. Laboratory studies show:
Hemoglobin 9.8 g/dL
MCV 104 fL
Reticulocyte count 0.2 %
Folate 21 ng/mL (N = 2–20)
Vitamin B12 789 pg/mL (N = 200–900)
A peripheral blood smear shows anisocytosis and bone marrow aspirate shows ringed sideroblasts. This patient is most likely to develop which of the following?
- A. Hairy cell leukemia
- B. Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- C. Burkitt lymphoma
- D. Acute myelocytic leukemia (Correct Answer)
- E. Sézary syndrome
Liver and gallbladder histology Explanation: ***Acute myelocytic leukemia***
- The presence of **fatigue**, **anemia** (Hb 9.8 g/dL), **macrocytosis** (MCV 104 fL), **low reticulocyte count** (0.2%), and specifically **ringed sideroblasts** in the bone marrow aspirate points to a myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) with ringed sideroblasts.
- A significant portion of patients with **myelodysplastic syndromes** (MDS), especially those with ringed sideroblasts, are at an elevated risk of transforming to **acute myelocytic leukemia (AML)**, making this the most likely future complication.
*Hairy cell leukemia*
- This typically presents with **splenomegaly**, **pancytopenia**, and characteristic **'hairy' lymphocytes** on peripheral smear, none of which are described here.
- The patient's presentation with **ringed sideroblasts** is not a feature of hairy cell leukemia.
*Chronic lymphocytic leukemia*
- Characterized by **lymphocytosis** (>5000 clonal B lymphocytes/µL), often with **lymphadenopathy** and **splenomegaly**, and typically presenting in older adults.
- The current findings of **macrocytic anemia** and **ringed sideroblasts** do not align with the typical features of CLL.
*Burkitt lymphoma*
- This is an aggressive B-cell lymphoma often associated with specific **translocations (e.g., t(8;14))** and rapidly growing tumors, especially in endemic regions.
- The patient's signs of **anemia** and **ringed sideroblasts** are not suggestive of Burkitt lymphoma.
*Sézary syndrome*
- This is a **leukemic variant of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma**, characterized by generalized erythroderma, lymphadenopathy, and circulating malignant T-cells (Sézary cells).
- The patient's anemic presentation and **ringed sideroblasts** are not consistent with Sézary syndrome.
Liver and gallbladder histology US Medical PG Question 7: A 28-year-old male presents to his primary care physician with complaints of intermittent abdominal pain and alternating bouts of constipation and diarrhea. His medical chart is not significant for any past medical problems or prior surgeries. He is not prescribed any current medications. Which of the following questions would be the most useful next question in eliciting further history from this patient?
- A. "Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?"
- B. "Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?"
- C. "Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life"
- D. "Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?"
- E. "Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?" (Correct Answer)
Liver and gallbladder histology Explanation: ***Can you tell me more about the symptoms you have been experiencing?***
- This **open-ended question** encourages the patient to provide a **comprehensive narrative** of their symptoms, including details about onset, frequency, duration, alleviating/aggravating factors, and associated symptoms, which is crucial for diagnosis.
- In a patient presenting with vague, intermittent symptoms like alternating constipation and diarrhea, allowing them to elaborate freely can reveal important clues that might not be captured by more targeted questions.
*Does the diarrhea typically precede the constipation, or vice-versa?*
- While knowing the sequence of symptoms can be helpful in understanding the **pattern of bowel dysfunction**, it is a very specific question that might overlook other important aspects of the patient's experience.
- It prematurely narrows the focus without first obtaining a broad understanding of the patient's overall symptomatic picture.
*Is the diarrhea foul-smelling?*
- Foul-smelling diarrhea can indicate **malabsorption** or **bacterial overgrowth**, which are important to consider in some gastrointestinal conditions.
- However, this is a **specific symptom inquiry** that should follow a more general exploration of the patient's symptoms, as it may not be relevant if other crucial details are missed.
*Please rate your abdominal pain on a scale of 1-10, with 10 being the worst pain of your life*
- Quantifying pain intensity is useful for assessing the **severity of discomfort** and monitoring changes over time.
- However, for a patient with intermittent rather than acute, severe pain, understanding the **character, location, and triggers** of the pain is often more diagnostically valuable than just a numerical rating initially.
*Are the symptoms worse in the morning or at night?*
- Diurnal variation can be relevant in certain conditions, such as inflammatory bowel diseases where nocturnal symptoms might be more concerning, or functional disorders whose symptoms might be stress-related.
- This is another **specific question** that should come after gathering a more complete initial picture of the patient's symptoms to ensure no key information is overlooked.
Liver and gallbladder histology US Medical PG Question 8: Two weeks after returning from vacation in Mexico, a 21-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of malaise, nausea, vomiting, fever, and abdominal pain. He has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. Physical examination shows scleral icterus and right upper quadrant tenderness. The liver is palpated 1.5 cm below the right costal margin. A biopsy specimen of this patient's liver would most likely show which of the following findings?
- A. Piecemeal necrosis and fatty changes
- B. Lymphocytic infiltration and progressive ductopenia
- C. Ballooning degeneration and bridging necrosis (Correct Answer)
- D. Ground glass hepatocytes and apoptotic bodies
- E. Dysplastic hepatocytes with intracellular bile
Liver and gallbladder histology Explanation: ***Ballooning degeneration and bridging necrosis***
- The patient presents with symptoms and signs of **acute viral hepatitis**, characterized by malaise, nausea, vomiting, fever, abdominal pain, scleral icterus, and right upper quadrant tenderness following travel to an endemic area (Mexico). **Ballooning degeneration** of hepatocytes and **bridging necrosis** (necrosis extending between portal tracts and central veins) are classic histological features of severe acute viral hepatitis.
- These findings reflect the **cytopathic effect of the virus** and the host's immune response, leading to hepatocyte injury and extensive liver damage.
*Piecemeal necrosis and fatty changes*
- **Piecemeal necrosis** (also known as interface hepatitis) is characteristic of **chronic hepatitis**, where inflammation at the portal-parenchymal interface leads to destruction of periportal hepatocytes, not typical for acute resolving hepatitis.
- **Fatty changes** (steatosis) are commonly seen in conditions like **alcoholic liver disease** or **non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)**, and are not primary features of acute viral hepatitis.
*Lymphocytic infiltration and progressive ductopenia*
- **Lymphocytic infiltration** is a general feature of many forms of hepatitis, but **progressive ductopenia** (loss of bile ducts) is highly suggestive of **primary biliary cholangitis (PBC)**, an autoimmune condition, or **primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC)**, which does not fit the acute presentation or travel history.
- These conditions are typically chronic and have different clinical manifestations.
*Ground glass hepatocytes and apoptotic bodies*
- **Ground-glass hepatocytes** are a hallmark feature of **chronic hepatitis B infection**, indicating the accumulation of HBsAg in the endoplasmic reticulum. This is not typical for acute viral hepatitis where the virus may still be replicating rapidly.
- While **apoptotic bodies** (Councilman bodies) can be seen in acute hepatitis, they are not the predominant or most specific finding to describe the widespread damage seen with ballooning degeneration and necrosis.
*Dysplastic hepatocytes with intracellular bile*
- **Dysplastic hepatocytes** are indicative of **precancerous changes** or **hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC)**, usually occurring in the context of chronic liver disease, not acute self-limiting hepatitis.
- While **intracellular bile** might be seen in cholestatic conditions, the combination of dysplastic hepatocytes points away from acute viral hepatitis.
Liver and gallbladder histology US Medical PG Question 9: A 32-year-old woman presents with amenorrhea and galactorrhea. MRI shows a pituitary adenoma. Histological examination of the surgical specimen shows cells arranged in cords and nests with sinusoidal capillaries. Special staining reveals three distinct cell types: chromophobes (50%), acidophils (40%), and basophils (10%). Immunohistochemistry shows the tumor cells staining strongly for prolactin. Evaluate the relationship between normal pituitary architecture and tumor development to determine which cell type most likely gave rise to this neoplasm.
- A. Somatotrophs (acidophils producing growth hormone)
- B. Lactotrophs (acidophils producing prolactin) (Correct Answer)
- C. Corticotrophs (basophils producing ACTH)
- D. Gonadotrophs (basophils producing FSH/LH)
- E. Chromophobes (null cells with no secretory granules)
Liver and gallbladder histology Explanation: ***Lactotrophs (acidophils producing prolactin)***
- These cells are classified as **acidophils** based on their staining characteristics and are responsible for the secretion of **prolactin**, consistent with the patient's **amenorrhea** and **galactorrhea**.
- Although the tumor specimen contains various cell types, the **immunohistostaining** specifically identifying **prolactin** confirms these cells as the source of the neoplasm.
*Somatotrophs (acidophils producing growth hormone)*
- While these are also **acidophilic** cells, they secrete **Growth Hormone (GH)**, and a tumor of this type would present with **acromegaly** or gigantism rather than galactorrhea.
- They do not typically stain for **prolactin**, unless the tumor is a rare plurihormonal adenoma, which is not indicated here.
*Corticotrophs (basophils producing ACTH)*
- These cells are **basophils** and produce **ACTH**; an adenoma arising from them would lead to **Cushing's disease** due to hypercortisolism.
- Histologically, they would not correspond to the strong **prolactin** staining observed in this immunohistochemical evaluation.
*Gonadotrophs (basophils producing FSH/LH)*
- These are **basophilic** cells that produce **FSH** and **LH**, and tumors originating from them are usually non-functional or present with mass effects rather than hormonal excess.
- They are clinically and histologically distinct from **prolactin-producing** lactotrophs.
*Chromophobes (null cells with no secretory granules)*
- **Chromophobes** lack significant cytoplasmic staining due to a lack of hormone granules; they often represent cells that have depleted their secretory stores.
- While they occupy 50% of the specimen, the **strong prolactin staining** identifies the active neoplastic process as originating from the hormone-producing lineage.
Liver and gallbladder histology US Medical PG Question 10: A 65-year-old man with progressive shortness of breath undergoes transbronchial biopsy. Microscopy shows thickened alveolar septa with increased collagen deposition. Type I pneumocytes are decreased, and there is proliferation of type II pneumocytes. Alveolar macrophages are present. The patient has a history of environmental asbestos exposure 30 years ago. Evaluate the histological progression and synthesize the most likely diagnosis considering the temporal relationship and cellular changes.
- A. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis with granulomas
- B. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with usual interstitial pneumonia pattern
- C. Asbestosis with interstitial fibrosis and ferruginous bodies (Correct Answer)
- D. Sarcoidosis with non-caseating granulomas
- E. Acute respiratory distress syndrome with diffuse alveolar damage
Liver and gallbladder histology Explanation: ***Asbestosis with interstitial fibrosis and ferruginous bodies***
- The histological findings of **thickened alveolar septa**, **type I pneumocyte loss**, and **type II pneumocyte hyperplasia** characterize chronic **interstitial fibrosis** consistent with **asbestosis** in the context of exposure.
- Asbestos fibers are ingested by **alveolar macrophages**, triggering a fibrogenic response that typically manifests after a **latency period** of 20 to 30 years.
*Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis with granulomas*
- This condition is an immunologic reaction to inhaled organic antigens, characterized by **poorly formed non-caseating granulomas**.
- While it causes **interstitial fibrosis**, it lacks the specific association with **asbestos exposure** and the long-term temporal progression described.
*Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with usual interstitial pneumonia pattern*
- **IPF** presents with a **Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP)** pattern, featuring **fibroblastic foci** and **honeycombing** with temporal heterogeneity.
- While similar in appearance, this diagnosis is reserved for cases of **unknown etiology** where occupational exposures like asbestos are absent.
*Sarcoidosis with non-caseating granulomas*
- **Sarcoidosis** typically presents with **well-formed non-caseating granulomas** distributed along **lymphatic pathways** and bronchovascular bundles.
- It is a systemic disease that primarily affects **hilar lymph nodes**, which is not the pathology described in this biopsy.
*Acute respiratory distress syndrome with diffuse alveolar damage*
- **ARDS** is characterized by an acute onset with **hyaline membranes** lining the alveolar spaces during the **diffuse alveolar damage (DAD)** phase.
- The scenario describes a **chronic, progressive** clinical course rather than the acute, critical illness seen in respiratory failure.
More Liver and gallbladder histology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.