Endocrine gland histology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Endocrine gland histology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Endocrine gland histology US Medical PG Question 1: A 28-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician complaining of intense thirst and frequent urination for the past 2 weeks. She says that she constantly feels the urge to drink water and is also going to the bathroom to urinate frequently throughout the day and multiple times at night. She was most recently hospitalized 1 month prior to presentation following a motor vehicle accident in which she suffered severe impact to her head. The physician obtains laboratory tests, with the results shown below:
Serum:
Na+: 149 mEq/L
Cl-: 103 mEq/L
K+: 3.5 mEq/L
HCO3-: 24 mEq/L
BUN: 20 mg/dL
Glucose: 105 mg/dL
Urine Osm: 250 mOsm/kg
The patient’s condition is most likely caused by inadequate hormone secretion from which of the following locations?
- A. Adrenal cortex
- B. Anterior pituitary
- C. Preoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus
- D. Suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus
- E. Posterior pituitary (Correct Answer)
Endocrine gland histology Explanation: ***Posterior pituitary***
- The patient's symptoms of **polydipsia** and **polyuria**, coupled with **hypernatremia** and **low urine osmolality**, are classic signs of **diabetes insipidus (DI)**.
- The **posterior pituitary gland** is responsible for releasing **antidiuretic hormone (ADH)**, which, when inadequately secreted (neurogenic DI), leads to these findings. The prior **head trauma** is a common cause of damage to this region.
*Adrenal cortex*
- The adrenal cortex produces **mineralocorticoids** (e.g., **aldosterone**), **glucocorticoids** (e.g., **cortisol**), and **androgens**.
- Deficiencies or excesses of these hormones lead to conditions like **Addison's disease** (adrenal insufficiency) or **Cushing's syndrome**, which have different clinical presentations than those described.
*Anterior pituitary*
- The anterior pituitary produces hormones such as **GH, TSH, ACTH, FSH, LH**, and **prolactin**.
- Dysfunction of the anterior pituitary would lead to a range of hormonal imbalances impacting growth, metabolism, and reproduction, but not directly cause diabetes insipidus.
*Preoptic nucleus of the hypothalamus*
- The **preoptic nucleus** is involved in **thermoregulation**, **sleep**, and **hypothalamic control** of reproduction.
- While part of the hypothalamus, its primary functions do not directly involve ADH synthesis or release, thereby not causing diabetes insipidus.
*Suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus*
- The **suprachiasmatic nucleus (SCN)** is the body's primary **circadian rhythm** pacemaker.
- Damage to the SCN would disrupt the sleep-wake cycle and other circadian functions, but would not directly lead to symptoms of diabetes insipidus.
Endocrine gland histology US Medical PG Question 2: An investigator studying hormone synthesis and transport uses immunocytochemical techniques to localize a carrier protein in the central nervous system of an experimental animal. The investigator finds that this protein is synthesized together with a specific hormone from a composite precursor. The protein is involved in the transport of the hormone from the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei to its destination. The hormone transported by these carrier proteins is most likely responsible for which of the following functions?
- A. Stimulation of thyroglobulin cleavage
- B. Upregulation of renal aquaporin-2 channels (Correct Answer)
- C. Hyperplasia of the adrenal zona fasciculata
- D. Increased insulin-like growth factor 1 production
- E. Maturation of primordial germ cells
Endocrine gland histology Explanation: ***Upregulation of renal aquaporin-2 channels***
- The description of a hormone synthesized in the **supraoptic** and **paraventricular nuclei** and transported by a carrier protein refers to **antidiuretic hormone (ADH)**, also known as vasopressin.
- ADH's primary function in the kidney is to **increase water reabsorption** by upregulating **aquaporin-2 channels** in the principal cells of the collecting ducts.
*Stimulation of thyroglobulin cleavage*
- **Thyroglobulin cleavage** and subsequent release of thyroid hormones (T3, T4) are stimulated by **thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)**, which is produced by the anterior pituitary, not the hypothalamus.
- The described origin in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei is inconsistent with TSH.
*Hyperplasia of the adrenal zona fasciculata*
- **Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH)** from the anterior pituitary stimulates the adrenal cortex, including the zona fasciculata, to produce cortisol.
- The hormone described here originates in the hypothalamus and is transported to the posterior pituitary, not stimulating adrenal hyperplasia.
*Increased insulin-like growth factor 1 production*
- **Insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1)** production is stimulated primarily by **growth hormone (GH)**, which is secreted by the anterior pituitary.
- This function is not associated with hormones produced in the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei.
*Maturation of primordial germ cells*
- The maturation of **primordial germ cells** is regulated by **gonadotropins (FSH and LH)**, which are secreted by the anterior pituitary, and sex steroids.
- This process is not directly controlled by hormones originating from the supraoptic and paraventricular nuclei.
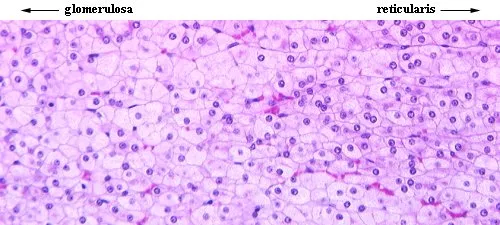
Endocrine gland histology US Medical PG Question 3: A 33-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for a wellness check-up. She states that recently she has been feeling well other than headaches that occur occasionally, which improve with ibuprofen and rest. She has a past medical history of hypertension and headaches and is currently taking hydrochlorothiazide. Her temperature is 99.2°F (37.3°C), blood pressure is 157/108 mmHg, pulse is 90/min, respirations are 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 98% on room air. Physical exam reveals a young woman who appears healthy. A normal S1 and S2 are auscultated on cardiac exam, and her lungs are clear with good air movement bilaterally. From her previous visit, it was determined that she has an elevated aldosterone and low renin level. Laboratory values are ordered as seen below.
Serum:
Na+: 139 mEq/L
Cl-: 100 mEq/L
K+: 3.7 mEq/L
HCO3-: 29 mEq/L
BUN: 20 mg/dL
Creatinine: 1.1 mg/dL
Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Benign essential hypertension
- B. Pheochromocytoma
- C. Cushing syndrome
- D. Narrowing of the renal arteries
- E. Primary hyperaldosteronism (Correct Answer)
Endocrine gland histology Explanation: ***Primary hyperaldosteronism***
- The patient presents with **hypertension**, **mild hypokalemia (K+ of 3.7 mEq/L)**, and **metabolic alkalosis (HCO3- of 29 mEq/L)**, which are classic signs of primary hyperaldosteronism.
- The elevated aldosterone and low renin levels, as noted from her previous visit, are diagnostic for primary hyperaldosteronism.
*Benign essential hypertension*
- While essential hypertension is common, the presence of **hypokalemia**, **metabolic alkalosis**, and particularly the **elevated aldosterone with low renin** points away from benign essential hypertension, which typically has normal renin-aldosterone ratios.
- This patient's hypertension is likely **secondary** due to a specific endocrine imbalance.
*Pheochromocytoma*
- This condition presents with **episodic or paroxysmal hypertension**, **tachycardia**, **sweating**, and headaches, often in a more dramatic fashion.
- The patient's blood pressure is consistently elevated, and she lacks the typical paroxysmal symptoms and signs of catecholamine excess.
*Cushing syndrome*
- Cushing syndrome is characterized by **hypertension**, central obesity, moon facies, buffalo hump, and striae, none of which are described.
- While it can cause hypertension, it is due to cortisol excess and does not typically present with the specific aldosterone-renin profile seen in this patient.
*Narrowing of the renal arteries*
- **Renal artery stenosis** causes **renovascular hypertension** and is associated with **elevated renin levels** as the kidney perceives hypoperfusion and activates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
- This patient presents with **low renin levels**, which directly contradicts the pathophysiology of renal artery stenosis.
Endocrine gland histology US Medical PG Question 4: A histological examination of the carotid body reveals glomus cells containing dense-core vesicles. These cells function primarily as chemoreceptors for which of the following?
- A. Partial pressure of oxygen (Correct Answer)
- B. Blood pH
- C. Temperature
- D. Blood glucose levels
Endocrine gland histology Explanation: ***Partial pressure of oxygen***
- Carotid body **glomus cells** are highly specialized **chemoreceptors** that primarily sense changes in the **partial pressure of oxygen (PO2)** in arterial blood.
- When PO2 decreases (e.g., hypoxia), these cells are activated and stimulate the respiratory and cardiovascular systems to increase oxygen uptake.
*Blood pH*
- While carotid body chemoreceptors can sense large changes in blood pH, their primary and most sensitive role is in detecting changes in **PO2**.
- Central chemoreceptors in the brainstem are more crucial for routine regulation of respiration in response to changes in **pH and PCO2**.
*Temperature*
- **Thermoreceptors** located in the skin, hypothalamus, and other internal organs are responsible for sensing body temperature, not the carotid body.
- The carotid body's main function is related to blood gas homeostasis, not temperature regulation.
*Blood glucose levels*
- Blood glucose levels are regulated by specialized cells in the **pancreas** (islets of Langerhans) that secrete hormones like insulin and glucagon.
- The carotid body is not directly involved in sensing or regulating glucose homeostasis.
Endocrine gland histology US Medical PG Question 5: A 36-year-old woman presents with thyroid swelling. She has been healthy until now and follows all the healthcare precautions except for missing a flu shot this year. On physical examination, the thyroid gland is diffusely enlarged and tender to palpation. Laboratory findings show a decreased serum TSH level and elevated erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Which of the following histopathologic findings would most likely be found in the thyroid gland of this patient?
- A. Extensive fibrosis of the stroma
- B. Mixed cellular infiltration with multinuclear giant cells (Correct Answer)
- C. Lymphocytic infiltration with germinal centers
- D. Orphan Annie nuclei with psammoma bodies
- E. Sheets of polygonal cells in amyloid stroma
Endocrine gland histology Explanation: ***Mixed cellular infiltration with multinuclear giant cells***
- The patient's symptoms of a **diffusely enlarged and tender thyroid**, suppressed **TSH**, elevated **ESR**, and a recent viral illness (missing flu shot) are classic for **subacute granulomatous (De Quervain's) thyroiditis**.
- Histopathologically, this condition is characterized by a **disruptive inflammatory infiltrate** with **multinucleated giant cells** engulfing colloid, surrounded by granulomatous inflammation.
*Extensive fibrosis of the stroma*
- This finding is characteristic of **Riedel's thyroiditis**, a rare form of chronic thyroiditis.
- Riedel's thyroiditis typically presents as a **hard, fixed, and painless goiter**, often leading to compressive symptoms, which does not match this patient's tender goiter.
*Lymphocytic infiltration with germinal centers*
- This pattern is typical of **Hashimoto's thyroiditis**, an **autoimmune thyroid disease**.
- Hashimoto's usually presents with a **painless goiter** and often leads to **hypothyroidism**, not the tender, hyperthyroid-like state seen here.
*Orphan Annie nuclei with psammoma bodies*
- These are hallmark features associated with **papillary thyroid carcinoma**.
- This patient's acute presentation with **tenderness, inflammation**, and temporary hyperthyroidism is inconsistent with a malignant thyroid neoplasm.
*Sheets of polygonal cells in amyloid stroma*
- This describes the histopathology of **medullary thyroid carcinoma**.
- Medullary thyroid carcinoma arises from parafollicular C-cells and is characterized by the production of **calcitonin** and often has a genetic predisposition, which is not suggested by the patient's presentation.
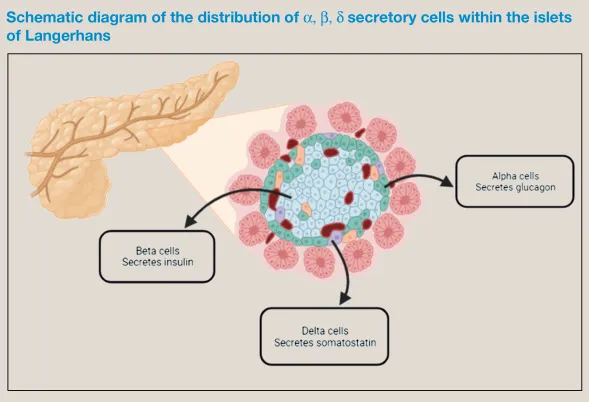
Endocrine gland histology US Medical PG Question 6: Pancreatic islets were isolated from a healthy, non-diabetic donor to perform an experiment to look at insulin secretion inhibition. Compounds would be added to separate wells containing the islets bathed in a high glucose solution for one hour. After one hour, the supernatant would be collected, and the insulin content would be measured with an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Which of the following compounds would result in the least insulin secretion when added to the islets?
- A. Isoproterenol
- B. Dobutamine
- C. Glyburide
- D. Tolbutamide
- E. Clonidine (Correct Answer)
Endocrine gland histology Explanation: ***Clonidine***
- Clonidine is an **alpha-2 adrenergic agonist**, which acts to inhibit insulin secretion from pancreatic beta cells. Alpha-2 receptors, when activated, reduce intracellular cAMP levels, thereby **suppressing insulin release**.
- In a high glucose environment, this inhibitory action of clonidine would result in the **least insulin secretion** compared to other listed compounds which either stimulate insulin secretion or have less direct inhibitory effects.
*Isoproterenol*
- Isoproterenol is a **non-selective beta-adrenergic agonist** (β1 and β2). Activation of beta-adrenergic receptors on pancreatic beta cells generally **stimulates insulin secretion** by increasing intracellular cAMP.
- Therefore, adding isoproterenol would lead to **increased insulin release**, not decreased.
*Dobutamine*
- Dobutamine is primarily a **beta-1 adrenergic agonist**, though it has some beta-2 effects. Beta-1 activation on pancreatic cells is not the primary mechanism associated with insulin regulation.
- While it may have some minor impact, its main action is on cardiac contractility and it is **not known to significantly inhibit insulin secretion** from beta cells.
*Glyburide*
- Glyburide is a **sulfonylurea drug** that works by binding to the SUR1 subunit of the **ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channel** on pancreatic beta cells, thereby closing it.
- This closure leads to **depolarization of the cell membrane**, calcium influx, and ultimately **increased insulin secretion**.
*Tolbutamide*
- Tolbutamide is another **sulfonylurea drug**, similar to glyburide, that acts by binding to and blocking the **ATP-sensitive potassium (KATP) channels** on pancreatic beta cells.
- This mechanism leads to beta cell depolarization, **calcium entry**, and **stimulation of insulin release**.
Endocrine gland histology US Medical PG Question 7: Which mechanism primarily regulates sodium reabsorption in the collecting duct?
- A. Glomerulotubular balance
- B. Atrial natriuretic peptide
- C. Antidiuretic hormone
- D. Aldosterone (Correct Answer)
Endocrine gland histology Explanation: ***Aldosterone***
- **Aldosterone** is the primary hormone that stimulates **sodium reabsorption** and **potassium secretion** in the principal cells of the collecting duct.
- It acts by increasing the synthesis and activity of **ENaC channels** on the apical membrane and **Na+/K+-ATPase pumps** on the basolateral membrane.
*Glomerulotubular balance*
- **Glomerulotubular balance** refers to the mechanism by which the **proximal tubule** reabsorbs a constant fraction of the filtered load, regardless of changes in glomerular filtration rate (GFR).
- This mechanism maintains a relatively constant delivery of fluid and solutes to downstream segments but does not primarily regulate sodium in the collecting duct.
*Atrial natriuretic peptide*
- **Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP)** primarily **inhibits sodium reabsorption** in the collecting duct, leading to **natriuresis** and **diuresis**, which is the opposite of sodium reabsorption.
- ANP is released in response to atrial stretch, indicating increased blood volume.
*Antidiuretic hormone*
- **Antidiuretic hormone (ADH)** primarily regulates **water reabsorption** in the collecting duct by increasing the insertion of **aquaporin-2 channels** into the apical membrane, making the collecting duct permeable to water.
- While ADH can indirectly affect sodium concentration by influencing water movement, it does not directly regulate sodium transport to the same extent as aldosterone.
Endocrine gland histology US Medical PG Question 8: A 38-year-old man comes to the clinic complaining of recurrent abdominal pain for the past 2 months. He reports a gnawing, dull pain at the epigastric region that improves with oral ingestion. He has been taking calcium carbonate for the past few weeks; he claims that “it used to help a lot but it’s losing its effects now.” Laboratory testing demonstrated increased gastrin levels after the administration of secretin. A push endoscopy visualized several ulcers at the duodenum and proximal jejunum. What characteristics distinguish the jejunum from the duodenum?
- A. Lack of goblet cells
- B. Crypts of Lieberkuhn
- C. Lack of submucosal Brunner glands (Correct Answer)
- D. Peyer patches
- E. Plicae circulares
Endocrine gland histology Explanation: ***Lack of submucosal Brunner glands***
- The **jejunum** lacks **Brunner glands**, which are characteristic of the **duodenum** and secrete alkaline mucus to neutralize acidic chyme from the stomach.
- The absence of these glands helps differentiate the jejunum from the duodenum histologically.
*Lack of goblet cells*
- **Goblet cells** are present throughout the small intestine, including both the duodenum and jejunum, though their density increases distally.
- Therefore, the **lack of goblet cells** does not distinguish the jejunum from the duodenum.
*Crypts of Lieberkuhn*
- **Crypts of Lieberkuhn** (intestinal crypts) are present throughout the entire small intestine, including both the **duodenum** and **jejunum**, where they house stem cells for epithelial renewal.
- Their presence is not a distinguishing feature between these two segments histologically.
*Peyer patches*
- **Peyer patches** are lymphoid aggregates primarily found in the **ileum**, not the jejunum or duodenum, and are involved in immune surveillance.
- They are a distinguishing feature of the ileum but not between the jejunum and duodenum.
*Plicae circulares*
- **Plicae circulares** (also known as valves of Kerckring or circular folds) are macroscopic folds of the mucosa and submucosa that are present in both the **duodenum** and **jejunum**.
- They are most prominent in the jejunum, but their mere presence does not distinguish the jejunum from the duodenum.
Endocrine gland histology US Medical PG Question 9: A 32-year-old woman presents with amenorrhea and galactorrhea. MRI shows a pituitary adenoma. Histological examination of the surgical specimen shows cells arranged in cords and nests with sinusoidal capillaries. Special staining reveals three distinct cell types: chromophobes (50%), acidophils (40%), and basophils (10%). Immunohistochemistry shows the tumor cells staining strongly for prolactin. Evaluate the relationship between normal pituitary architecture and tumor development to determine which cell type most likely gave rise to this neoplasm.
- A. Somatotrophs (acidophils producing growth hormone)
- B. Lactotrophs (acidophils producing prolactin) (Correct Answer)
- C. Corticotrophs (basophils producing ACTH)
- D. Gonadotrophs (basophils producing FSH/LH)
- E. Chromophobes (null cells with no secretory granules)
Endocrine gland histology Explanation: ***Lactotrophs (acidophils producing prolactin)***
- These cells are classified as **acidophils** based on their staining characteristics and are responsible for the secretion of **prolactin**, consistent with the patient's **amenorrhea** and **galactorrhea**.
- Although the tumor specimen contains various cell types, the **immunohistostaining** specifically identifying **prolactin** confirms these cells as the source of the neoplasm.
*Somatotrophs (acidophils producing growth hormone)*
- While these are also **acidophilic** cells, they secrete **Growth Hormone (GH)**, and a tumor of this type would present with **acromegaly** or gigantism rather than galactorrhea.
- They do not typically stain for **prolactin**, unless the tumor is a rare plurihormonal adenoma, which is not indicated here.
*Corticotrophs (basophils producing ACTH)*
- These cells are **basophils** and produce **ACTH**; an adenoma arising from them would lead to **Cushing's disease** due to hypercortisolism.
- Histologically, they would not correspond to the strong **prolactin** staining observed in this immunohistochemical evaluation.
*Gonadotrophs (basophils producing FSH/LH)*
- These are **basophilic** cells that produce **FSH** and **LH**, and tumors originating from them are usually non-functional or present with mass effects rather than hormonal excess.
- They are clinically and histologically distinct from **prolactin-producing** lactotrophs.
*Chromophobes (null cells with no secretory granules)*
- **Chromophobes** lack significant cytoplasmic staining due to a lack of hormone granules; they often represent cells that have depleted their secretory stores.
- While they occupy 50% of the specimen, the **strong prolactin staining** identifies the active neoplastic process as originating from the hormone-producing lineage.
Endocrine gland histology US Medical PG Question 10: A 65-year-old man with progressive shortness of breath undergoes transbronchial biopsy. Microscopy shows thickened alveolar septa with increased collagen deposition. Type I pneumocytes are decreased, and there is proliferation of type II pneumocytes. Alveolar macrophages are present. The patient has a history of environmental asbestos exposure 30 years ago. Evaluate the histological progression and synthesize the most likely diagnosis considering the temporal relationship and cellular changes.
- A. Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis with granulomas
- B. Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with usual interstitial pneumonia pattern
- C. Asbestosis with interstitial fibrosis and ferruginous bodies (Correct Answer)
- D. Sarcoidosis with non-caseating granulomas
- E. Acute respiratory distress syndrome with diffuse alveolar damage
Endocrine gland histology Explanation: ***Asbestosis with interstitial fibrosis and ferruginous bodies***
- The histological findings of **thickened alveolar septa**, **type I pneumocyte loss**, and **type II pneumocyte hyperplasia** characterize chronic **interstitial fibrosis** consistent with **asbestosis** in the context of exposure.
- Asbestos fibers are ingested by **alveolar macrophages**, triggering a fibrogenic response that typically manifests after a **latency period** of 20 to 30 years.
*Chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis with granulomas*
- This condition is an immunologic reaction to inhaled organic antigens, characterized by **poorly formed non-caseating granulomas**.
- While it causes **interstitial fibrosis**, it lacks the specific association with **asbestos exposure** and the long-term temporal progression described.
*Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis with usual interstitial pneumonia pattern*
- **IPF** presents with a **Usual Interstitial Pneumonia (UIP)** pattern, featuring **fibroblastic foci** and **honeycombing** with temporal heterogeneity.
- While similar in appearance, this diagnosis is reserved for cases of **unknown etiology** where occupational exposures like asbestos are absent.
*Sarcoidosis with non-caseating granulomas*
- **Sarcoidosis** typically presents with **well-formed non-caseating granulomas** distributed along **lymphatic pathways** and bronchovascular bundles.
- It is a systemic disease that primarily affects **hilar lymph nodes**, which is not the pathology described in this biopsy.
*Acute respiratory distress syndrome with diffuse alveolar damage*
- **ARDS** is characterized by an acute onset with **hyaline membranes** lining the alveolar spaces during the **diffuse alveolar damage (DAD)** phase.
- The scenario describes a **chronic, progressive** clinical course rather than the acute, critical illness seen in respiratory failure.
More Endocrine gland histology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.