Cardiovascular histology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Cardiovascular histology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
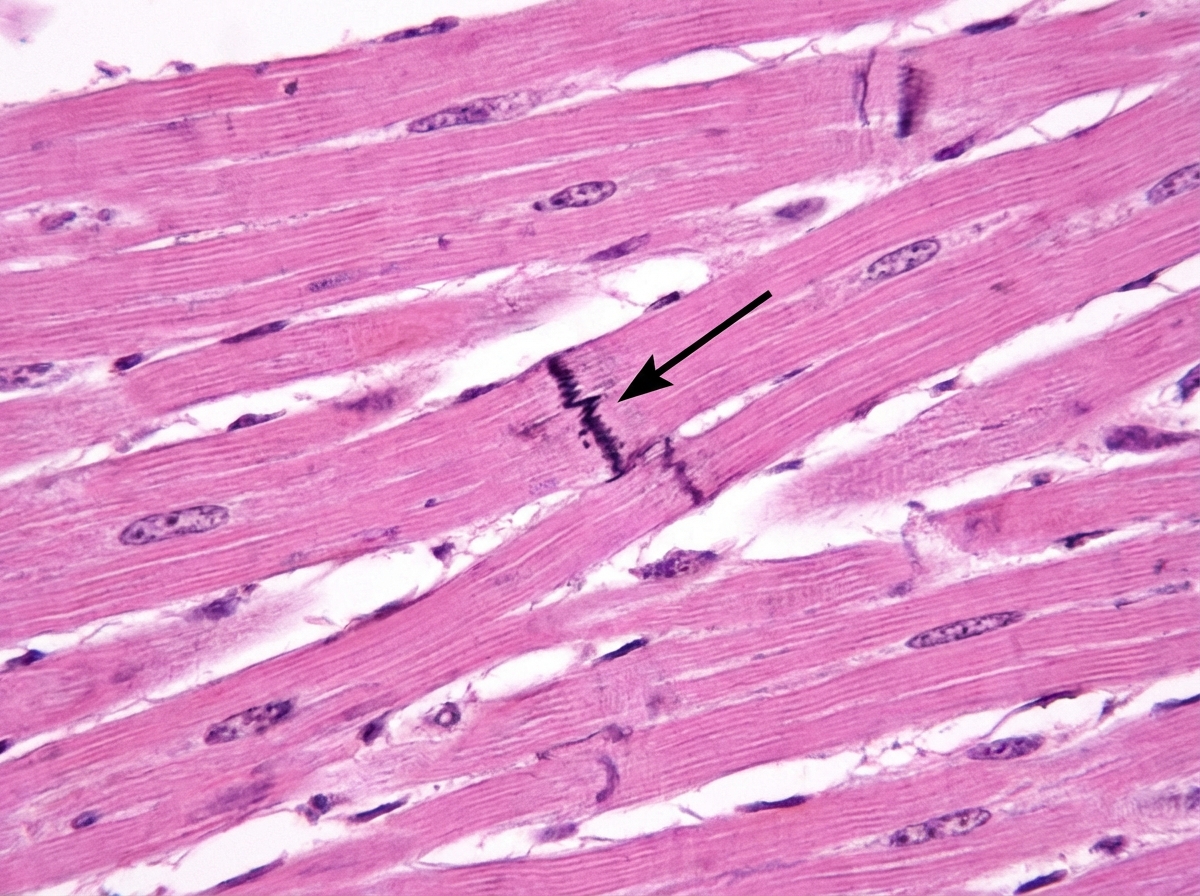
Cardiovascular histology US Medical PG Question 1: Cardiac muscle serves many necessary functions, leading to a specific structure that serves these functions. The structure highlighted is an important histology component of cardiac muscle. What would be the outcome if this structure diffusely failed to function?
- A. Failure of potassium channels to appropriately open to repolarize the cell
- B. Failure of propagation of the action potential from the conduction system (Correct Answer)
- C. Ineffective excitation-contraction coupling due to insufficient calcium ions
- D. Inappropriate formation of cardiac valve leaflets
- E. Outflow tract obstruction
Cardiovascular histology Explanation: ***Failure of propagation of the action potential from the conduction system***
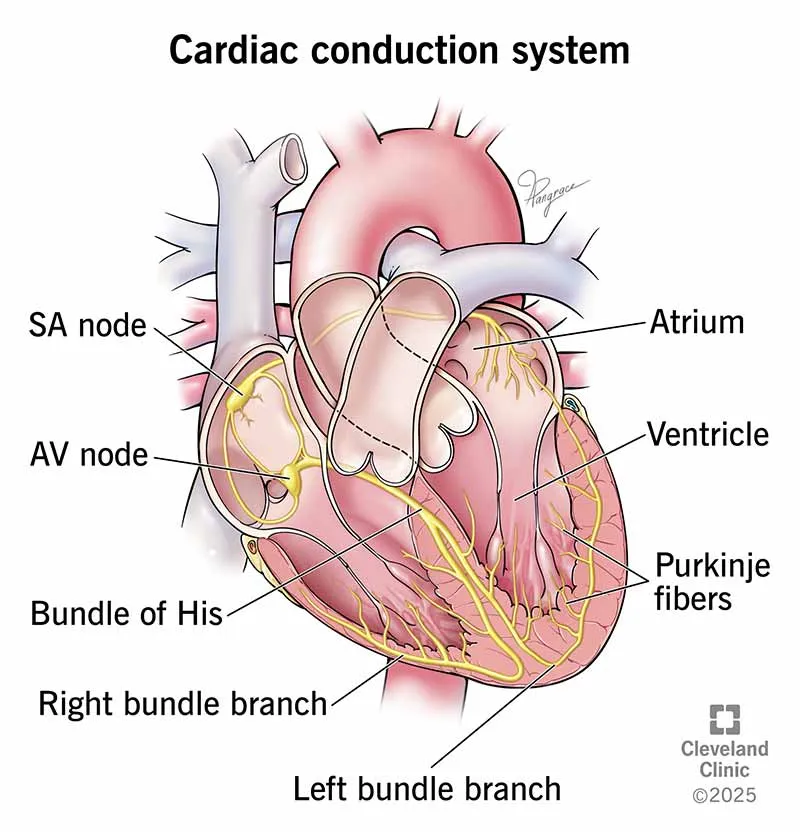
- The highlighted structure, the **intercalated disc**, contains **gap junctions** which are crucial for the rapid, synchronized spread of **action potentials** between cardiac muscle cells.
- A diffuse failure of these structures would prevent the coordinated electrical activation of the myocardium, leading to a failure of impulse propagation and **compromised cardiac contraction**.
*Failure of potassium channels to appropriately open to repolarize the cell*
- This scenario describes a problem with **ion channel function** within individual cardiomyocytes, affecting their repolarization phase.
- While critical for a single cell's electrical activity, it does not directly relate to the primary function of **intercalated discs** in *propagating* action potentials across multiple cells.
*Ineffective excitation-contraction coupling due to insufficient calcium ions*
- This outcome would result from issues with **calcium handling** mechanisms, such as problems with the **sarcoplasmic reticulum** or **calcium channels**, which are internal to the cardiomyocyte.
- It is distinct from the role of **intercalated discs** in facilitating intercellular communication and electrical spread.
*Inappropriate formation of cardiac valve leaflets*
- The formation of cardiac valve leaflets is an intricate process during **embryological development** involving specific signaling pathways and cell migration.
- This structural defect is not directly related to the function of **intercalated discs** in mature cardiac muscle, which are involved in electrical and mechanical coupling.
*Outflow tract obstruction*
- **Outflow tract obstruction** is a congenital or acquired structural defect affecting the major arteries leaving the heart (e.g., aortic or pulmonary stenosis).
- This is a macroscopic structural anomaly that is not caused by a primary failure of **intercalated disc** function.
Cardiovascular histology US Medical PG Question 2: A 72-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 6-month history of intermittent dull abdominal pain that radiates to the back. He has smoked one pack of cigarettes daily for 50 years. His blood pressure is 145/80 mm Hg. Abdominal examination shows generalized tenderness and a pulsatile mass in the periumbilical region on deep palpation. Further evaluation of the affected blood vessel is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Obliterative inflammation of the vasa vasorum
- B. Formation of giant cells in the tunica media
- C. Necrotizing inflammation of the entire vessel wall
- D. Fragmentation of elastic tissue in the tunica media (Correct Answer)
- E. Accumulation of foam cells in the tunica intima
Cardiovascular histology Explanation: ***Fragmentation of elastic tissue in the tunica media***
- This patient's presentation with **intermittent dull abdominal pain radiating to the back**, a **pulsatile periumbilical mass**, and a history of **heavy smoking** is highly suggestive of an **abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)**.
- The pathological hallmark of AAA is **degradation and fragmentation of elastic tissue in the tunica media**, caused by chronic inflammation and increased activity of **matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs)**.
- This medial degeneration leads to **weakening of the vessel wall** and progressive **dilation**, ultimately forming an aneurysm.
- While atherosclerosis initiates the process, the actual aneurysm formation is characterized by this elastic tissue destruction in the media.
*Accumulation of foam cells in the tunica intima*
- This describes the **early lesion of atherosclerosis**, which is a **risk factor** for AAA development.
- However, when examining an **established AAA**, the predominant finding is not intimal foam cells but rather **medial degeneration** with elastic tissue fragmentation.
- Atherosclerosis is the underlying cause, but the question asks about findings in the affected vessel (the aneurysm itself).
*Obliterative inflammation of the vasa vasorum*
- This is characteristic of **syphilitic aortitis** (tertiary syphilis), which typically affects the **ascending thoracic aorta**.
- While syphilis can cause aneurysms, the patient's presentation and demographics are more consistent with atherosclerotic AAA.
*Formation of giant cells in the tunica media*
- This finding is associated with **giant cell arteritis** (temporal arteritis), which affects large and medium-sized arteries, particularly the temporal and ophthalmic arteries.
- It presents with headache, jaw claudication, and visual disturbances—features absent in this case.
*Necrotizing inflammation of the entire vessel wall*
- This describes **necrotizing vasculitis** such as **polyarteritis nodosa**, which affects medium-sized muscular arteries.
- While vasculitis can cause aneurysms, the clinical picture of AAA in an elderly smoker with atherosclerotic risk factors points to atherosclerotic pathogenesis, not primary vasculitis.
Cardiovascular histology US Medical PG Question 3: An 80-year-old man is admitted to the hospital after the sudden onset of sub-sternal chest pain and shortness of breath while sitting in a chair. He has hypertension and type 2 diabetes mellitus. He has smoked 1 pack of cigarettes daily for 42 years. Four days after admission, he becomes tachycardic and then loses consciousness; the cardiac monitor shows irregular electrical activity. Cardiac examination shows a new systolic murmur at the apex. Despite appropriate measures, he dies. Microscopic evaluation of the myocardium is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Wavy myocardial fibers without inflammatory cells
- B. Coagulative necrosis with dense neutrophilic infiltrate
- C. Low cellularity with dense, non-contractile scar tissue
- D. Dense granulation tissue with collagenous scar formation
- E. Hyperemic granulation tissue with abundance of macrophages (Correct Answer)
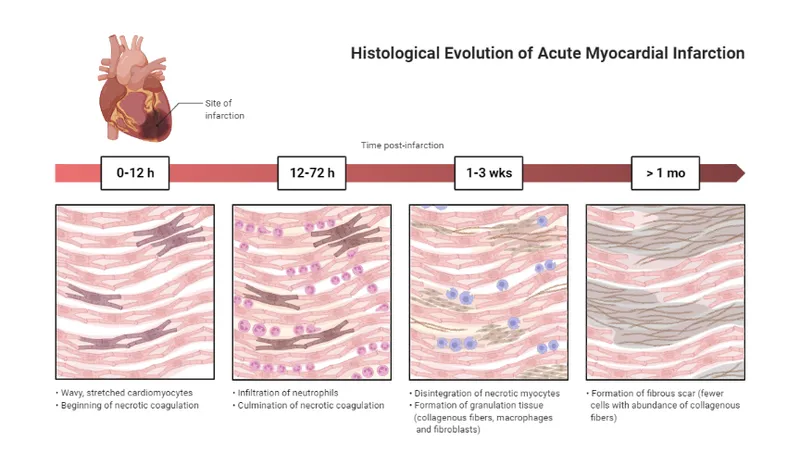
Cardiovascular histology Explanation: ***Hyperemic granulation tissue with abundance of macrophages***
- The patient experienced an **acute myocardial infarction (MI)** with subsequent complications, including sudden death occurring 4 days after the initial event.
- At 4 days post-MI, the characteristic microscopic finding is **hyperemic granulation tissue**, where **macrophages** are prominent in clearing necrotic debris, and new blood vessels start to form.
*Wavy myocardial fibers without inflammatory cells*
- This finding is typically seen within the first few hours (0-4 hours) after an MI, representing early irreversible ischemic injury before significant inflammation begins.
- The patient died 4 days later; therefore, more advanced changes would be expected.
*Coagulative necrosis with dense neutrophilic infiltrate*
- This stage is observed between 12 hours and 3 days post-MI, as neutrophils infiltrate the necrotic tissue to initiate breakdown and removal of dead cells.
- While neutrophil infiltration is important, the primary characteristic at 4 days would shift towards macrophage predominance and early granulation tissue.
*Low cellularity with dense, non-contractile scar tissue*
- This describes the **final stage of MI healing**, typically observed several weeks to months after the event, when the necrotic tissue has been completely replaced by a mature collagenous scar.
- At 4 days, the process is still actively inflammatory and reparative.
*Dense granulation tissue with collagenous scar formation*
- This stage represents a later phase of healing, usually from 1 to 2 weeks post-MI, where the granulation tissue becomes more dense and collagen deposition increases.
- While granulation tissue is present at 4 days, it would be described as more hyperemic with a prominent macrophage presence rather than dense collagenous scar formation.
Cardiovascular histology US Medical PG Question 4: A 3175-g (7-lb) male newborn is delivered at 39 weeks' gestation to a 29-year-old primigravid woman following a spontaneous vaginal delivery. Apgar scores are 8 and 9 at 1 and 5 minutes, respectively. Cardiac examination in the delivery room shows a continuous machine-like murmur. An echocardiogram shows a structure with blood flow between the pulmonary artery and the aorta. This structure is most likely a derivate of which of the following?
- A. 4th aortic arch
- B. 1st aortic arch
- C. 6th aortic arch (Correct Answer)
- D. 2nd aortic arch
- E. 3rd aortic arch
Cardiovascular histology Explanation: ***6th aortic arch***
- The description of a "continuous machine-like murmur" and a structure with blood flow between the pulmonary artery and the aorta is characteristic of a **patent ductus arteriosus (PDA)**.
- The **ductus arteriosus** is a remnant of the **6th aortic arch**, connecting the pulmonary artery to the aorta in fetal life.
*4th aortic arch*
- The **4th aortic arch** contributes to the formation of the **aortic arch** itself on the left side and the proximal **right subclavian artery** on the right.
- Abnormalities of the 4th arch can lead to conditions like **coarctation of the aorta** or **vascular rings**, which do not typically present as a PDA.
*1st aortic arch*
- The **1st aortic arch** largely disappears, but its remnants contribute to the formation of the **maxillary artery** and the **external carotid artery**.
- It is not involved in developmental anomalies of the major vessels between the pulmonary artery and aorta.
*2nd aortic arch*
- The **2nd aortic arch** also largely regresses, but its remnants contribute to the **stapedial artery** and part of the **hyoid artery**.
- It does not play a role in the formation of the ductus arteriosus or other major arteries of the heart.
*3rd aortic arch*
- The **3rd aortic arch** develops into the common carotid arteries and the proximal internal carotid arteries.
- Genetic disorders and malformations involving this arch typically affect the carotid system, not the connection between the pulmonary artery and aorta.
Cardiovascular histology US Medical PG Question 5: A 60-year-old male presents for a routine health check-up. The patient complains of reduced exercise tolerance for the past 2 years. Also, in the past year, he has noticed chest pain after climbing the stairs in his home. He has no significant past medical history or current medications. The patient reports a 45-pack-year smoking history. The vital signs include temperature 37.0°C (98.6°F), blood pressure 160/100 mm Hg, pulse 72/min, respiratory rate 15/min, and oxygen saturation 99% on room air. His body mass index (BMI) is 34 kg/m2. Physical examination is unremarkable. Laboratory studies show:
Serum total cholesterol 265 mg/dL
HDL 22 mg/dL
LDL 130 mg/dL
Triglycerides 175 mg/dL
HDL: high-density lipoprotein; LDL: low-density lipoprotein
Which of the following vascular pathologies is most likely present in this patient?
- A. Medial calcific sclerosis
- B. Deep venous thrombosis
- C. Lymphedema
- D. Atherosclerosis (Correct Answer)
- E. Hyperplastic arteriosclerosis
Cardiovascular histology Explanation: ***Atherosclerosis***
- This patient presents with multiple **risk factors for atherosclerosis**, including **hyperlipidemia** (elevated total cholesterol, LDL, and triglycerides with low HDL), **hypertension**, **obesity**, and a significant **smoking history**.
- His symptoms of **reduced exercise tolerance** and **exertional chest pain** are classic manifestations of **angina pectoris**, which is caused by narrowed coronary arteries due to atherosclerosis.
*Medial calcific sclerosis*
- Also known as **Mönckeberg arteriosclerosis**, involves calcification of the **tunica media** of muscular arteries, without significant luminal narrowing.
- While it can lead to **artery hardening**, it typically does not obstruct blood flow or cause angina, and is more common in **elderly** and **diabetic** individuals.
*Deep venous thrombosis*
- This condition involves the formation of a **blood clot in a deep vein**, usually in the legs, leading to symptoms like **leg swelling, pain, and redness**.
- The patient's symptoms of chest pain and reduced exercise tolerance are not characteristic of DVT.
*Lymphedema*
- Characterized by **swelling** in one or more limbs due to an impaired **lymphatic drainage system**.
- It does not present with chest pain or reduced exercise tolerance and is distinct from vascular pathologies affecting blood flow.
*Hyperplastic arteriosclerosis*
- This is a form of **arteriolar sclerosis** primarily seen in severe **hypertension**, characterized by **concentric thickening of arteriolar walls** due to smooth muscle cell proliferation and basement membrane duplication.
- While the patient has hypertension, his symptoms point towards obstruction of larger coronary arteries rather than widespread arteriolar changes, and his lipid profile is more indicative of atherosclerosis.
Cardiovascular histology US Medical PG Question 6: A 72-year-old male presents to a cardiac surgeon for evaluation of severe aortic stenosis. He has experienced worsening dyspnea with exertion over the past year. The patient also has a history of poorly controlled hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and hyperlipidemia. An echocardiogram revealed a thickened calcified aortic valve. The surgeon is worried that the patient will be a poor candidate for open heart surgery and decides to perform a less invasive transcatheter aortic valve replacement. In order to perform this procedure, the surgeon must first identify the femoral pulse just inferior to the inguinal ligament and insert a catheter into the vessel in order to gain access to the arterial system. Which of the following structures is immediately lateral to this structure?
- A. Lymphatic vessels
- B. Femoral vein
- C. Sartorius muscle
- D. Pectineus muscle
- E. Femoral nerve (Correct Answer)
Cardiovascular histology Explanation: ***Femoral nerve***
- The **femoral nerve** lies lateral to the **femoral artery** within the **femoral triangle**.
- The order of structures from **lateral to medial** under the inguinal ligament is remembered by the mnemonic **NAVEL**: **N**erve, **A**rtery, **V**ein, **E**mpty space, **L**ymphatics.
*Lymphatic vessels*
- **Lymphatic vessels** and nodes are located most medially within the femoral triangle, medial to the femoral vein.
- This position is not immediately lateral to the femoral artery.
*Femoral vein*
- The **femoral vein** is located immediately medial to the **femoral artery**.
- It would not be found immediately lateral to the femoral artery.
*Sartorius muscle*
- The **sartorius muscle** forms the lateral boundary of the **femoral triangle** but is not immediately adjacent and lateral to the femoral artery within the triangle itself.
- The femoral nerve is enclosed within the iliopsoas fascial compartment, which runs deep to the sartorius.
*Pectineus muscle*
- The **pectineus muscle** forms part of the floor of the **femoral triangle**, but it is deep to the neurovascular structures.
- It is not immediately lateral to the femoral artery.
Cardiovascular histology US Medical PG Question 7: An 18-year-old man presents with a sudden loss of consciousness while playing college football. There was no history of a concussion. Echocardiography shows left ventricular hypertrophy and increased thickness of the interventricular septum. Which is the most likely pathology underlying the present condition?
- A. Autoimmunity of myocardial fibers
- B. Drug abuse
- C. Viral infection
- D. Mutation in the myosin heavy chain (Correct Answer)
- E. Streptococcal infection
Cardiovascular histology Explanation: ***Mutation in the myosin heavy chain***
- The presentation of **sudden loss of consciousness** (syncope) in a young athlete with **left ventricular hypertrophy** and **interventricular septal thickening** is classic for **hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM)**.
- HCM is most commonly caused by **autosomal dominant mutations in genes** encoding sarcomeric proteins, with **beta-myosin heavy chain mutations** being the most frequent.
*Autoimmunity of myocardial fibers*
- Autoimmune conditions affecting the heart, such as **myocarditis** or **lupus carditis**, typically present with symptoms like **chest pain**, **dyspnea**, or signs of **heart failure**, which are not described here.
- While they can lead to cardiac dysfunction, they are less likely to cause isolated severe hypertrophy and sudden syncope in a young asymptomatic individual as the initial presentation.
*Drug abuse*
- **Stimulant drug abuse** (e.g., cocaine, amphetamines) can cause cardiomyopathy and arrhythmias, potentially leading to syncope.
- However, the specific echocardiographic findings of **marked septal hypertrophy** are not characteristic of drug-induced cardiomyopathy, which often manifests as **dilated cardiomyopathy** or global ventricular dysfunction.
*Viral infection*
- **Viral myocarditis** can cause cardiac inflammation, leading to **dilated cardiomyopathy** or arrhythmias, and can present with sudden cardiac death.
- While viral myocarditis can lead to some degree of hypertrophy, the prominent and isolated **asymmetric septal hypertrophy** and the chronic nature implied by the structural changes are less typical of acute or resolving viral infection.
*Streptococcal infection*
- **Rheumatic heart disease**, a sequela of **Streptococcus pyogenes infection**, primarily causes **valvular damage** (especially mitral stenosis or regurgitation) and less commonly diffuse myocardial involvement.
- It does not typically present with isolated severe **left ventricular hypertrophy** and **interventricular septal thickening** as the primary cardiac pathology leading to sudden syncope.
Cardiovascular histology US Medical PG Question 8: A 55-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of left-sided chest pain and difficulty breathing for the past 30 minutes. His pulse is 88/min. He is pale and anxious. Serum studies show increased cardiac enzymes. An ECG shows ST-elevations in leads I, aVL, and V5-V6. A percutaneous coronary intervention is performed. In order to localize the site of the lesion, the catheter must pass through which of the following structures?
- A. Left coronary artery → left circumflex artery (Correct Answer)
- B. Right coronary artery → posterior descending artery
- C. Left coronary artery → left anterior descending artery
- D. Right coronary artery → right marginal artery
- E. Left coronary artery → posterior descending artery
Cardiovascular histology Explanation: ***Left coronary artery → left circumflex artery***
- **ST-elevations** in leads I, aVL, and V5-V6 are indicative of a **lateral myocardial infarction**.
- The **left circumflex artery** primarily supplies the lateral wall of the left ventricle.
*Right coronary artery → posterior descending artery*
- The **posterior descending artery** (PDA) typically supplies the inferior wall and posterior interventricular septum.
- An occlusion here would cause **ST-elevations** in leads II, III, and aVF, which is not seen in this case.
*Left coronary artery → left anterior descending artery*
- The **left anterior descending** (LAD) artery supplies the anterior wall and apex of the left ventricle.
- Occlusion of the LAD would typically cause **ST-elevations** in leads V1-V4, indicating an anterior MI.
*Right coronary artery → right marginal artery*
- The **right marginal artery** is a branch of the right coronary artery and supplies part of the right ventricle.
- Occlusion here would primarily affect the **right ventricle**, and is not typically associated with the given ECG changes.
*Left coronary artery → posterior descending artery*
- While the **posterior descending artery** can sometimes originate from the left circumflex artery (**left dominant circulation**), it primarily supplies the inferior wall.
- The observed ECG changes in leads I, aVL, and V5-V6 are characteristic of a **lateral wall infarct**, which is supplied by the left circumflex artery.
Cardiovascular histology US Medical PG Question 9: A 23-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician with 3 days of fatigue and back pain after she started a drug for malaria prophylaxis. She says that her urine has also been darker over the same time period. Her past medical history is significant for allergies as well as a broken elbow that was treated in a cast 10 years ago. She does not take any medications, does not smoke, and drinks socially. Peripheral blood smear reveals both red blood cells with dark intracellular inclusions as well as abnormally shaped red blood cells. The immune cells responsible for the shape of these red blood cells are located in which of the following places?
- A. Lymph nodes
- B. Red pulp of the spleen (Correct Answer)
- C. Bone marrow
- D. White pulp of the spleen
- E. Blood vessels
Cardiovascular histology Explanation: ***Red pulp of the spleen***
- The patient's symptoms (fatigue, back pain, dark urine after malaria prophylaxis) and lab findings (**dark intracellular inclusions** and abnormally shaped red blood cells) suggest **G6PD deficiency**, leading to **hemolytic anemia**.
- The **red pulp of the spleen** is where old or damaged red blood cells, including those with Heinz bodies (intracellular inclusions) or abnormal shapes, are **phagocytosed** by macrophages, thus "shaping" them or removing severely affected cells.
*Lymph nodes*
- **Lymph nodes** are primarily involved in filtering lymph and are major sites for adaptive immune responses, housing B and T lymphocytes.
- They are not the primary sites for the destruction or "shaping" of red blood cells.
*Bone marrow*
- The **bone marrow** is the primary site of **hematopoiesis**, where red blood cells are produced, not where they are destroyed or undergo physical shaping due to immune cell action in hemolysis.
- While macrophages are present, their main role in marrow is related to erythropoiesis (e.g., central macrophage in erythroblastic islands) and debris clearance, not erythrocyte shaping in peripheral circulation.
*White pulp of the spleen*
- The **white pulp of the spleen** is rich in lymphocytes and is the site of immune responses, similar to lymph nodes.
- It is involved in adaptive immunity and not directly engaged in the physical destruction or "shaping" of red blood cells during hemolysis.
*Blood vessels*
- **Blood vessels** are conduits for blood transport and are not primary sites for the physical destruction or shaping of red blood cells by immune cells.
- While some hemolysis can occur intravascularly, the immune cells responsible for removing and "shaping" damaged red blood cells (like macrophages) are predominantly organ-resident.
Cardiovascular histology US Medical PG Question 10: A 32-year-old woman presents with amenorrhea and galactorrhea. MRI shows a pituitary adenoma. Histological examination of the surgical specimen shows cells arranged in cords and nests with sinusoidal capillaries. Special staining reveals three distinct cell types: chromophobes (50%), acidophils (40%), and basophils (10%). Immunohistochemistry shows the tumor cells staining strongly for prolactin. Evaluate the relationship between normal pituitary architecture and tumor development to determine which cell type most likely gave rise to this neoplasm.
- A. Somatotrophs (acidophils producing growth hormone)
- B. Lactotrophs (acidophils producing prolactin) (Correct Answer)
- C. Corticotrophs (basophils producing ACTH)
- D. Gonadotrophs (basophils producing FSH/LH)
- E. Chromophobes (null cells with no secretory granules)
Cardiovascular histology Explanation: ***Lactotrophs (acidophils producing prolactin)***
- These cells are classified as **acidophils** based on their staining characteristics and are responsible for the secretion of **prolactin**, consistent with the patient's **amenorrhea** and **galactorrhea**.
- Although the tumor specimen contains various cell types, the **immunohistostaining** specifically identifying **prolactin** confirms these cells as the source of the neoplasm.
*Somatotrophs (acidophils producing growth hormone)*
- While these are also **acidophilic** cells, they secrete **Growth Hormone (GH)**, and a tumor of this type would present with **acromegaly** or gigantism rather than galactorrhea.
- They do not typically stain for **prolactin**, unless the tumor is a rare plurihormonal adenoma, which is not indicated here.
*Corticotrophs (basophils producing ACTH)*
- These cells are **basophils** and produce **ACTH**; an adenoma arising from them would lead to **Cushing's disease** due to hypercortisolism.
- Histologically, they would not correspond to the strong **prolactin** staining observed in this immunohistochemical evaluation.
*Gonadotrophs (basophils producing FSH/LH)*
- These are **basophilic** cells that produce **FSH** and **LH**, and tumors originating from them are usually non-functional or present with mass effects rather than hormonal excess.
- They are clinically and histologically distinct from **prolactin-producing** lactotrophs.
*Chromophobes (null cells with no secretory granules)*
- **Chromophobes** lack significant cytoplasmic staining due to a lack of hormone granules; they often represent cells that have depleted their secretory stores.
- While they occupy 50% of the specimen, the **strong prolactin staining** identifies the active neoplastic process as originating from the hormone-producing lineage.
More Cardiovascular histology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.