Pelvic lymphatic drainage US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Pelvic lymphatic drainage. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Pelvic lymphatic drainage US Medical PG Question 1: A 30-year-old woman who is 24-weeks pregnant presents to the emergency department with fever, painful urination, and headache. The patient's blood pressure is 111/67 mm Hg, the pulse is 95/min, the respiratory rate is 16/min, and the temperature is 38.3°C (101.1°F). Physical examination reveals bilateral tender inguinal lymphadenopathy and painful genital lesions. On closer inspection, the patient’s genital lesions contain clear fluid and measure 5–6 mm in diameter. What is the appropriate description of these lesions?
- A. Pustule
- B. Ulcer
- C. Papule
- D. Bulla
- E. Vesicle (Correct Answer)
Pelvic lymphatic drainage Explanation: ***Vesicle***
- A **vesicle** is defined as a **circumscribed, elevated lesion** (macule/papule) containing **clear fluid** and measuring less than 1 cm in diameter.
- The patient's lesions, which are 5-6 mm in diameter and contain clear fluid, perfectly fit the description of vesicles, characteristic of **herpes simplex virus (HSV)** infection.
*Pustule*
- A **pustule** is a small, elevated lesion similar to a vesicle but filled with **pus**, not clear fluid.
- Examples include acne or folliculitis, which are typically opaque and yellowish, unlike the described lesions.
*Ulcer*
- An **ulcer** is a defect or excavation of the skin past the **epidermis**, resulting in the loss of tissue.
- The patient's lesions are described as fluid-filled and elevated, not as an open wound with tissue loss.
*Papule*
- A **papule** is a **solid, elevated lesion** measuring less than 1 cm in diameter.
- While elevated and small, a papule does **not contain fluid**, which is a key characteristic of the described lesions.
*Bulla*
- A **bulla** is a **fluid-filled lesion** that is **larger than 1 cm** in diameter.
- The lesions described are 5-6 mm, making them smaller than the definition of a bulla.
Pelvic lymphatic drainage US Medical PG Question 2: A 26-year-old woman presents to her primary care physician for 5 days of increasing pelvic pain. She says that the pain has been present for the last 2 months; however, it has become increasingly severe recently. She also says that the pain has been accompanied by unusually heavy menstrual periods in the last few months. Physical exam reveals a mass in the right adnexa, and ultrasonography reveals a 9 cm right ovarian mass. If this mass is surgically removed, which of the following structures must be diligently protected?
- A. External iliac artery
- B. Ureter (Correct Answer)
- C. Ovarian ligament
- D. Cardinal ligament of the uterus
- E. Internal iliac artery
Pelvic lymphatic drainage Explanation: ***Ureter***
- During **oophorectomy** (removal of an ovarian mass), the **ureter** is particularly vulnerable to injury due to its close proximity to the **ovary** and its blood supply.
- The right ureter courses directly posterior to the **right ovarian vessels** within the infundibulopelvic ligament, making it susceptible to **ligation** or **transection** during surgical maneuvers.
*External iliac artery*
- The external iliac artery is located more laterally within the **pelvis** and supplies the lower extremity; it is generally not in the immediate surgical field for ovarian mass removal.
- While injury to major pelvic vessels is always a concern, the **anatomical relationship** of the external iliac artery makes it less directly vulnerable compared to the ureter during this specific procedure.
*Ovarian ligament*
- The **ovarian ligament** connects the ovary to the **uterus** and is typically dissected or ligated during oophorectomy.
- Although it is cut during the procedure, it is not a structure that requires meticulous protection in the same way as the **ureter**, as its injury primarily impacts **ovarian removal** rather than causing significant morbidity.
*Cardinal ligament of the uterus*
- The **cardinal ligament** provides support to the **cervix** and **upper vagina** but is generally not directly involved in the removal of an **isolated ovarian mass**.
- Injury to this ligament is more typically associated with **hysterectomy** or procedures involving the **uterus**.
*Internal iliac artery*
- The **internal iliac artery** supplies blood to the **pelvic organs** and is situated deeper within the pelvis, making it less prone to direct injury during an oophorectomy compared to the **ureter**.
- While it gives off branches to the uterus and vagina, its main trunk is not as immediately adjacent to the **ovary** as the ureter.
Pelvic lymphatic drainage US Medical PG Question 3: A 35-year-old man presents to his primary care provider complaining of dull pain in his scrotum and lower back pain over the last 3 months. He is a computer engineer working in a private IT company. He had an uncomplicated appendectomy at the age of 22 years, but is otherwise without a significant past medical history. He smokes 2–3 cigarettes on weekends and drinks alcohol occasionally. He is sexually active with his wife. Today his heart rate is 90/min and blood pressure is 132/76 mm Hg. Scrotal examination reveals a firm, small and painless nodule on the left testicle. Scrotal ultrasound reveals a 0.9 x 0.5 cm irregular, non-cystic mass. He undergoes a left radical orchiectomy and histopathological examination reveals uniform tumor cells with abundant clear cytoplasm and distinct cell borders, consistent with a seminoma. Subsequent PET/CT scans show supraclavicular and para-aortic lymph node involvement. Which is the next and most appropriate step in the management of this patient?
- A. Immunotherapy
- B. Radiotherapy
- C. Chemotherapy (Correct Answer)
- D. Observation
- E. Surgery
Pelvic lymphatic drainage Explanation: ***Chemotherapy***
- The patient has **metastatic seminoma** (supraclavicular and para-aortic lymph node involvement) following orchiectomy, which requires **systemic treatment**.
- **Chemotherapy** is the primary treatment for metastatic seminoma due to its high cure rates, especially with regimens like BEP (bleomycin, etoposide, cisplatin).
*Immunotherapy*
- **Immunotherapy** is generally not a first-line treatment for seminoma and is primarily used in refractory or metastatic cases of other solid tumors, not typically germ cell tumors.
- While research is ongoing, current guidelines do not recommend immunotherapy as the initial treatment for this stage of seminoma.
*Radiotherapy*
- **Radiotherapy** can be effective for localized seminoma involving lymph nodes, but it is typically reserved for local control and not for widespread metastatic disease involving both supraclavicular and para-aortic nodes.
- Systemic disease with involvement of distant lymph nodes (like supraclavicular) necessitates a systemic approach like chemotherapy rather than localized radiation.
*Observation*
- **Observation** is only appropriate for Stage I seminoma following orchiectomy, where there is no evidence of metastatic spread.
- In this case, the patient has clear evidence of **metastasis** to supraclavicular and para-aortic lymph nodes, making observation an inappropriate and dangerous choice.
*Surgery*
- **Surgery** (radical orchiectomy) has already been performed to remove the primary tumor.
- While surgical resection of residual masses after chemotherapy may be considered in some cases, it is not the primary next step for initial management of widespread lymph node metastases.
Pelvic lymphatic drainage US Medical PG Question 4: A 76-year-old woman comes to the physician for evaluation of a 3-month history of vulvar itching and pain. She was diagnosed with lichen sclerosus 4 years ago. She has smoked 1 pack of cigarettes daily for 35 years. Physical examination shows a 2.5-cm nodular, ulcerative lesion on the vaginal introitus and left labia minora with surrounding erythema. Punch biopsy shows squamous cell carcinoma. A CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis shows enlarged lymph nodes concerning for metastatic disease. Which of the following lymph node regions is the most likely primary site of metastasis?
- A. Superficial inguinal (Correct Answer)
- B. Internal iliac
- C. External iliac
- D. Inferior mesenteric
- E. Para-aortic
Pelvic lymphatic drainage Explanation: ***Superficial inguinal***
- The **vulva** drains primarily into the **superficial inguinal lymph nodes**, making them the most likely first site for metastatic spread from vulvar squamous cell carcinoma.
- The lesion's location on the **vaginal introitus** and **labia minora** directly correlates with this lymphatic drainage pathway.
*Internal iliac*
- **Internal iliac nodes** receive drainage mainly from deep pelvic structures like the cervix, upper vagina, and uterus, not directly from the vulva.
- Metastasis to these nodes usually occurs after involvement of more superficial nodes or in advanced disease with deeper invasion.
*External iliac*
- **External iliac nodes** generally drain the lower extremities and deeper pelvic structures (e.g., bladder, distal ureter), not the vulva as a primary site.
- Involvement here would typically indicate more advanced local spread or secondary metastasis from other pelvic nodes.
*Inferior mesenteric*
- **Inferior mesenteric nodes** drain the hindgut and its derivatives, including the distal colon and rectum, which are distant from the vulva.
- This region is not involved in the lymphatic drainage of the vulva.
*Para-aortic*
- **Para-aortic nodes** drain structures like the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and upper uterus; they are too superior for primary vulvar lymphatic drainage.
- Metastasis to these nodes from vulvar cancer would signify widespread, very advanced disease and not a primary site of spread.
Pelvic lymphatic drainage US Medical PG Question 5: A 28-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 2-week history of testicular swelling and dull lower abdominal discomfort. Physical examination shows a firm, nontender left testicular nodule. Ultrasonography of the scrotum shows a well-defined hypoechoic lesion of the left testicle. Serum studies show an elevated β-hCG concentration and a normal α-fetoprotein concentration. The patient undergoes a radical inguinal orchiectomy. Histopathologic examination of the surgical specimen shows a mixed germ cell tumor with invasion of adjacent lymphatic vessels. Further evaluation is most likely to show malignant cells in which of the following lymph node regions?
- A. External iliac
- B. Deep inguinal
- C. Para-aortic (Correct Answer)
- D. Mediastinal
- E. Internal iliac
Pelvic lymphatic drainage Explanation: ***Para-aortic***
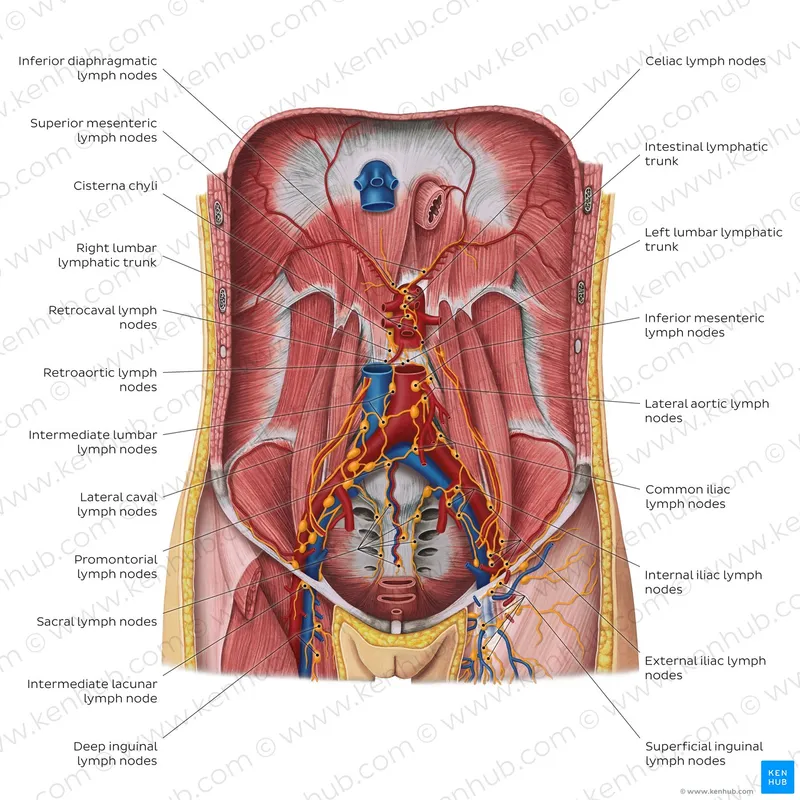
- Testicular lymphatic drainage primarily follows the **gonadal vessels** back to the para-aortic lymph nodes (also known as retroperitoneal lymph nodes).
- This is the **most common site** for metastatic spread of testicular germ cell tumors.
*External iliac*
- The external iliac lymph nodes primarily drain structures in the pelvis and lower limbs, such as the bladder and vagina, not the testes.
- While they can be involved in advanced pelvic malignancies, they are not the primary drainage site for testicular cancer.
*Deep inguinal*
- The deep inguinal lymph nodes primarily drain the superficial inguinal lymph nodes, which receive lymphatic drainage from the penis, scrotum (superficial layers), and perineum.
- Testicular lymphatics bypass the inguinal nodes unless there is scrotal invasion or prior surgery involving the scrotum.
*Mediastinal*
- Mediastinal lymph nodes are involved in the lymphatic drainage of thoracic organs and can be affected in later stages of testicular cancer if there is widespread metastatic disease, particularly to the lungs.
- However, they are not the initial or primary site of lymphatic spread from testicular tumors.
*Internal iliac*
- The internal iliac lymph nodes primarily drain pelvic organs and the deep perineum.
- While they may be involved in some pelvic cancers, they are not the primary lymphatic drainage site for the testes.
Pelvic lymphatic drainage US Medical PG Question 6: A 62-year-old female presents to her primary care physician complaining of bloody stool. She reports several episodes of bloody stools over the past two months as well as a feeling of a mass near her anus. She has one to two non-painful bowel movements per day. She has a history of alcohol abuse and hypertension. Anoscopy reveals engorged vessels. Which of the following vessels most likely drains blood from the affected region?
- A. Internal pudendal vein
- B. Left colic vein
- C. Inferior rectal vein (Correct Answer)
- D. Middle rectal vein
- E. Superior rectal vein
Pelvic lymphatic drainage Explanation: ***Inferior rectal vein***
- The patient's symptoms (bloody stool, anal mass, engorged vessels on anoscopy) are classic for **external hemorrhoids**.
- **External hemorrhoids** are distended veins located **below the dentate line** in the anal canal, which are drained by the **inferior rectal veins**.
- The inferior rectal veins drain into the **internal pudendal vein**, then to the **internal iliac vein** (part of the **systemic venous circulation**).
*Internal pudendal vein*
- The **internal pudendal vein** drains structures in the perineum and external genitalia, but it is not the **primary/direct drainage** for hemorrhoids.
- It receives blood from the inferior rectal veins but is one step removed from the hemorrhoidal plexus itself.
*Left colic vein*
- The **left colic vein** typically drains the distal transverse colon and descending colon.
- It is part of the **inferior mesenteric venous system** and is anatomically distant from the anorectal region, not involved in draining hemorrhoids.
*Middle rectal vein*
- The **middle rectal vein** drains the middle part of the rectum and connects both portal and systemic circulations.
- It drains the **muscularis layer** of the rectum but is not the primary drainage for the external hemorrhoidal plexus below the dentate line.
*Superior rectal vein*
- The **superior rectal vein** drains the upper part of the rectum and anal canal **above the dentate line**.
- Distention of these veins leads to **internal hemorrhoids**, which are typically painless unless prolapsed or thrombosed.
- It drains into the **inferior mesenteric vein** (part of the **portal venous circulation**).
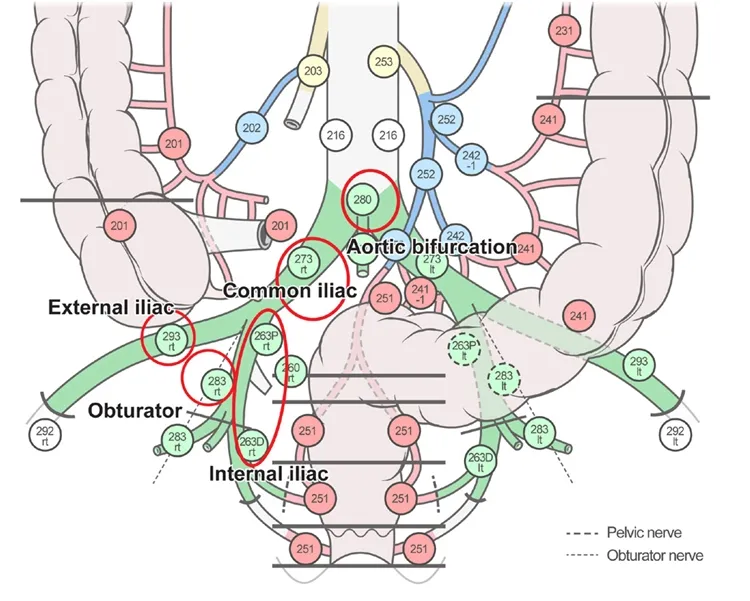
Pelvic lymphatic drainage US Medical PG Question 7: A 44-year-old woman undergoes radical hysterectomy for stage IB2 cervical cancer. During surgery, the gynecologic oncologist notes aberrant lymphatic drainage patterns possibly related to the patient's history of pelvic inflammatory disease and previous cesarean section. Frozen section of a lymph node from the obturator fossa shows metastatic disease. Synthesizing knowledge of primary and collateral cervical lymphatic drainage, which nodal group represents the most critical next level of drainage that would impact surgical decision-making?
- A. Presacral nodes via uterosacral ligament pathway
- B. Common iliac and para-aortic nodes via external iliac pathway (Correct Answer)
- C. Internal iliac nodes only
- D. Inguinal nodes via deep femoral pathway
- E. Superficial inguinal nodes via round ligament pathway
Pelvic lymphatic drainage Explanation: ***Common iliac and para-aortic nodes via external iliac pathway***
- The **common iliac nodes** serve as the primary drainage destination from both the **external iliac** and **obturator nodes**, making them the critical next level when **obturator metastasis** is confirmed.
- Lymphatic spread in cervical cancer typically follows a regular pattern: primary pelvic nodes (obturator, external/internal iliacs) move toward the **common iliac** and then **para-aortic** regions.
*Superficial inguinal nodes via round ligament pathway*
- Drainage to these nodes occurs primarily from the **uterine horns** or the **vulva**, not typically the cervix unless the tumor involves the lower vagina.
- These nodes are not part of the standard cephalad **retroperitoneal spread** pathway for stage IB2 cervical cancer.
*Presacral nodes via uterosacral ligament pathway*
- These nodes provide a minor primary drainage route via the **uterosacral ligaments**, but they are anatomically distinct from the lateral **obturator fossa** chain.
- They do not represent the "next level" of drainage that would indicate **systemic progression** beyond the pelvic basin.
*Internal iliac nodes only*
- The **internal iliac nodes** are primary pelvic nodes and are considered on the **same drainage tier** as the obturator nodes already found to be positive.
- Assessing these nodes only would not provide enough information regarding the **cephalad extent** of the disease required for surgical modification.
*Inguinal nodes via deep femoral pathway*
- The **deep femoral pathway** primarily drains the lower limb and vulva rather than the **cervical stroma** and parametrium.
- Involvement of these nodes would be an exception and would not help in determining the transition to **extended-field radiation** for retroperitoneal disease.
Pelvic lymphatic drainage US Medical PG Question 8: A 67-year-old man with squamous cell carcinoma of the anal canal presents for staging. Physical examination reveals a 3 cm tumor at the dentate line extending both above and below it. Inguinal lymphadenopathy is palpable bilaterally. CT shows both inguinal and pelvic lymph node enlargement. Evaluating the lymphatic drainage of the anal canal, which treatment approach best addresses the dual drainage patterns of this tumor location?
- A. Chemoradiation targeting both inguinal and pelvic nodal basins (Correct Answer)
- B. Pelvic lymph node dissection only, following inferior mesenteric pathways
- C. Sequential surgery: abdominoperineal resection then inguinal dissection
- D. Radiation to inguinal nodes only with surgical resection of pelvic nodes
- E. Inguinal lymph node dissection only, as anal tumors drain superficially
Pelvic lymphatic drainage Explanation: ***Chemoradiation targeting both inguinal and pelvic nodal basins***
- Tumors at the **dentate line** exhibit dual lymphatic drainage: the area above drains to **internal iliac** and **perirectal nodes**, while the area below drains to **superficial inguinal nodes**.
- The standard of care for anal **squamous cell carcinoma** (SCC) is the **Nigro protocol**, which uses **definitive chemoradiotherapy** to treat both the primary tumor and all involved regional nodal basins.
*Inguinal lymph node dissection only, as anal tumors drain superficially*
- While the area below the dentate line drains to **inguinal nodes**, the area above drains into the **pelvis**, meaning a dissection limited to the groin would miss half of the drainage pathway.
- Surgical dissection is not the primary treatment for anal SCC, as **chemoradiation** offers high rates of cure while preserving anal sphincter function.
*Pelvic lymph node dissection only, following inferior mesenteric pathways*
- This approach neglects the **superficial inguinal nodes**, which are already palpably enlarged in this patient and are the primary drainage route for the inferior anal canal.
- **Pelvic lymph node dissection** is technically difficult and carries high morbidity; it has been largely superseded by targeted **radiotherapy** in the management of this malignancy.
*Sequential surgery: abdominoperineal resection then inguinal dissection*
- **Abdominoperineal resection (APR)** is now considered **salvage therapy** for persistent or recurrent disease after definitive chemoradiotherapy rather than a first-line treatment.
- Sequential surgeries increase the risk of **wound complications** and **lymphedema** without offering a survival benefit over conservative chemoradiation in SCC.
*Radiation to inguinal nodes only with surgical resection of pelvic nodes*
- Splitting treatment between radiation for one basin and surgery for another increases **treatment toxicity** and delays the start of systemic chemotherapy.
- Both **inguinal and pelvic nodal basins** are exquisitely **radiosensitive** in anal SCC, so the entire region is standardly managed with integrated radiation fields.
Pelvic lymphatic drainage US Medical PG Question 9: A 38-year-old woman presents with a firm, fixed thyroid mass. Fine needle aspiration suggests papillary thyroid carcinoma. Ultrasound reveals suspicious lymph nodes in multiple cervical levels. She has a history of total laryngectomy for laryngeal cancer 5 years ago, which altered her cervical lymphatic drainage. Synthesizing knowledge of both normal and altered lymphatic pathways, which nodal station would be LEAST likely to be involved by direct thyroid lymphatic spread in this patient?
- A. Level IV (lower jugular) nodes
- B. Level III (mid-jugular) nodes
- C. Level II (upper jugular) nodes (Correct Answer)
- D. Level VII (superior mediastinal) nodes
- E. Level VI (central compartment) nodes
Pelvic lymphatic drainage Explanation: ***Level II (upper jugular) nodes***
- **Level II nodes** are the least likely to be involved by direct lymphatic spread because the thyroid gland primarily drains into the **Level VI central compartment** and the **mid-to-lower jugular chain** (Level III and IV).
- Although **altered lymphatic flow** after laryngectomy can occur, Level II involvement is typically a secondary or late event, as it is anatomically distant from the thyroid's primary drainage pathways compared to Level III and IV.
*Level VI (central compartment) nodes*
- These are the **sentinel nodes** for thyroid drainage and are the most common site for metastasis in **papillary thyroid carcinoma**.
- Even after a laryngectomy, any residual nodes in the **pretracheal and paratracheal** space remain the most direct route for thyroid lymphatics.
*Level III (mid-jugular) nodes*
- These nodes are part of the **lateral cervical drainage** pathway that receives direct flow from the thyroid gland, especially the upper poles.
- They are common sites for **regional metastasis** and are frequently involved when central nodes are overwhelmed or bypassed.
*Level IV (lower jugular) nodes*
- Level IV nodes receive significant lymphatic drainage from the **lower thyroid poles** and the recurrent laryngeal nerve chain.
- They represent a direct **lateral pathway** for spread and are consistently involved in cases of lateral neck metastasis from thyroid cancer.
*Level VII (superior mediastinal) nodes*
- These nodes are a direct inferior extension of the **Level VI central compartment** and receive drainage via the tracheoesophageal groove.
- **Papillary thyroid carcinoma** frequently spreads to this area, particularly if the primary tumor is located in the inferior aspect of the thyroid lobes.
Pelvic lymphatic drainage US Medical PG Question 10: A 48-year-old woman presents with a pigmented lesion on the plantar surface of her right heel. Biopsy reveals melanoma with a Breslow depth of 2.5 mm. Sentinel lymph node biopsy is planned. However, during lymphoscintigraphy, tracer uptake is seen in two separate nodal basins. Which anatomic explanation best accounts for this dual drainage pattern from the heel?
- A. Primary drainage to deep inguinal nodes with secondary popliteal drainage
- B. Bidirectional drainage to both popliteal and superficial inguinal nodes due to watershed area (Correct Answer)
- C. Drainage to external iliac nodes with retrograde flow to popliteal nodes
- D. Aberrant lymphatic channels due to the melanoma altering normal drainage
- E. The heel drains exclusively to popliteal nodes with scan artifact showing inguinal uptake
Pelvic lymphatic drainage Explanation: ***Bidirectional drainage to both popliteal and superficial inguinal nodes due to watershed area***
- The **heel and lateral aspect of the foot** are unique as they represent a **lymphatic watershed** where drainage can follow the **medial bundle** (following the great saphenous vein) or the **lateral bundle** (following the small saphenous vein).
- The medial bundle leads directly to the **superficial inguinal nodes**, while the lateral bundle leads to the **popliteal nodes**, resulting in the dual drainage pattern observed on **lymphoscintigraphy**.
*The heel drains exclusively to popliteal nodes with scan artifact showing inguinal uptake*
- Modern **lymphoscintigraphy** is highly sensitive and a dual pattern represents true **radioisotope** accumulation in distinct nodes rather than a technical artifact.
- It is anatomically incorrect to say the heel drains exclusively to one basin, as most of the foot drains to the **inguinal nodes** via the medial lymphatic system.
*Primary drainage to deep inguinal nodes with secondary popliteal drainage*
- Skin and subcutaneous tissues typically drain into the **superficial lymphatics** first; drainage to **deep inguinal nodes** usually occurs after passing through superficial nodes or via deep subfascial vessels.
- Popliteal nodes are located proximal to the heel but are considered a **primary nodal basin** for lateral foot drainage, not a secondary site following inguinal drainage.
*Drainage to external iliac nodes with retrograde flow to popliteal nodes*
- Lymphatic flow is **unidirectional** due to the presence of **valves**; retrograde flow is pathological (usually seen in advanced lymphedema) and would not occur in standard sentinel mapping.
- Drainage to **external iliac nodes** is tertiary (after inguinal nodes), and it would not explain how the tracer reached the **popliteal fossa**.
*Aberrant lymphatic channels due to the melanoma altering normal drainage*
- While some tumors can induce **lymphangiogenesis**, they rarely create entirely new macro-anatomic pathways to a different **regional basin** unless there is total obstruction of normal channels.
- The dual drainage from the heel is a **normal anatomical variant** of the lower extremity lymphatic system rather than a tumor-induced pathology.
More Pelvic lymphatic drainage US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.