Common radiologic findings in pathology US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Common radiologic findings in pathology. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Common radiologic findings in pathology US Medical PG Question 1: A 57-year-old man presents to his family physician for a routine exam. He feels well and reports no new complaints since his visit last year. Last year, he had a colonoscopy which showed no polyps, a low dose chest computerized tomography (CT) scan that showed no masses, and routine labs which showed a fasting glucose of 93 mg/dL. He is relatively sedentary and has a body mass index (BMI) of 24 kg/m^2. He has a history of using methamphetamines, alcohol (4-5 drinks per day since age 30), and tobacco (1 pack per day since age 18), but he joined Alcoholics Anonymous and has been in recovery, not using any of these for the past 7 years. Which of the following is indicated at this time?
- A. Colonoscopy
- B. Chest computerized tomography (CT) scan (Correct Answer)
- C. Abdominal ultrasound
- D. Chest radiograph
- E. Fasting glucose
Common radiologic findings in pathology Explanation: ***Chest computerized tomography (CT) scan***
- This patient has a significant **smoking history** (1 pack per day since age 18 = **39 pack-years**) and is 57 years old, placing him in a high-risk group for **lung cancer**.
- Annual low-dose CT screening for lung cancer is recommended for individuals aged 50-80 with a 20 pack-year smoking history who currently smoke or have quit within the past 15 years.
- He meets all criteria: age 57, 39 pack-years, and quit only 7 years ago (within the 15-year window).
- Since he had screening **last year** with no masses, this year's visit represents the appropriate time for his **annual follow-up screening**.
*Colonoscopy*
- The patient had a colonoscopy last year with **no polyps**, suggesting he is at average risk for colorectal cancer.
- For individuals at average risk with normal findings, repeat screening colonoscopy is typically recommended every **10 years** (or every 5 years for flexible sigmoidoscopy), not annually.
*Abdominal ultrasound*
- One-time abdominal ultrasound screening for **abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA)** is recommended for men aged 65-75 who have ever smoked.
- This patient is only 57 years old and does not yet meet the age criteria for AAA screening.
*Chest radiograph*
- While a chest radiograph can identify some lung abnormalities, a **low-dose CT scan** is far more sensitive and specific for detecting early-stage lung cancer in high-risk populations.
- Chest radiography is **not recommended** as a screening tool for lung cancer due to its lower sensitivity and lack of mortality benefit in trials.
*Fasting glucose*
- The patient had a **normal fasting glucose** of 93 mg/dL last year, and there are no new symptoms suggestive of diabetes.
- For asymptomatic adults with normal glucose, diabetes screening is typically repeated every **3 years**.
- Annual re-screening is not indicated without new risk factors or symptoms.
Common radiologic findings in pathology US Medical PG Question 2: A mother brings her 7-year-old son to the pediatrician because she is worried about his sleep. She reports that the child has repeatedly woken up in the middle of the night screaming and thrashing. Although she tries to reassure the child, he does not respond to her or acknowledge her presence. Soon after she arrives, he stops screaming and appears confused and lethargic before falling back asleep. When asked about these events, the child reports that he cannot recall ever waking up or having any bad dreams. These events typically occur within four hours of the child going to sleep. The child’s past medical history is notable for asthma and type I diabetes mellitus. He uses albuterol and long-acting insulin. There have been no recent changes in this patient’s medication regimen. His family history is notable for obesity and obstructive sleep apnea in his father. Physical examination reveals a healthy male at the 40th and 45th percentiles for height and weight, respectively. Which of the following EEG waveforms is most strongly associated with this patient’s condition?
- A. Delta waves (Correct Answer)
- B. Theta waves
- C. Sleep spindles
- D. Beta waves
- E. Alpha waves
Common radiologic findings in pathology Explanation: ***Delta waves***
- The child's symptoms (screaming, thrashing, unresponsiveness during waking, confusion afterward, and no recall) are characteristic of **sleep terror (pavor nocturnus)**, which is a **non-REM parasomnia**.
- Sleep terrors typically occur during **slow-wave sleep (NREM stage 3/4 sleep)**, which is predominantly characterized by the presence of **delta waves** on an EEG.
*Theta waves*
- **Theta waves** are characteristic of **NREM stage 1 and 2 sleep**, which are lighter stages of sleep.
- Sleep terrors are arousal disorders that originate from the deep stages of non-REM sleep, not the lighter stages where theta waves are prominent.
*Sleep spindles*
- **Sleep spindles** and **K-complexes** are characteristic EEG findings of **NREM stage 2 sleep**.
- While stage 2 is part of NREM sleep, sleep terrors are specifically associated with the deeper NREM stage 3/4, which is dominated by delta waves, not sleep spindles.
*Beta waves*
- **Beta waves** are high-frequency, low-amplitude waves associated with **awake, alert, and active mental states**.
- Their presence indicates wakefulness or active mental engagement and is not associated with any stage of sleep.
*Alpha waves*
- **Alpha waves** are characteristic of a state of **relaxed wakefulness**, often with closed eyes, and are a precursor to sleep onset.
- They are not associated with the deep sleep stages where sleep terrors occur.
Common radiologic findings in pathology US Medical PG Question 3: A 81-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with a 4-month history of shortness of breath. He says that he has slowly lost the ability to do things due to fatigue and now gets winded after walking around the house. He also says that his cough has been getting worse and seems to be producing more sputum. He has gained about 5 pounds over the last 6 months. His past medical history is significant for hypertension and diabetes. He has a 40 pack-year smoking history and drinks about 3 drinks per week. Physical exam reveals a cyanotic appearing man with 1+ edema in his legs bilaterally. He also has wheezing on lung auscultation with a prolonged expiratory phase. Which of the following would most likely be seen on a chest radiograph in this patient?
- A. Perihilar mass with unilateral hilar enlargement
- B. Cardiomegaly and increased bronchial markings
- C. Subpleural cystic enlargement
- D. Calcified pleural plaques surrounding the diaphragm
- E. Hyperinflated lungs and loss of lung markings (Correct Answer)
Common radiologic findings in pathology Explanation: ***Hyperinflated lungs and loss of lung markings***
- The patient's symptoms (shortness of breath, cough with sputum, fatigue, wheezing, prolonged expiratory phase, cyanosis, and 40 pack-year smoking history) are highly suggestive of **severe COPD, particularly emphysema**.
- **Emphysema** is characterized by the destruction of alveolar walls, leading to enlarged air spaces, **hyperinflation of the lungs**, and a **loss of normal lung markings** due to decreased vascularity.
*Perihilar mass with unilateral hilar enlargement*
- This finding is suspicious for a **bronchogenic carcinoma**, which is possible in a heavy smoker.
- However, the overall clinical picture, including bilateral wheezing, prolonged expiration, and signs of chronic hypoxemia (cyanosis, edema from potential right heart failure), points more strongly to widespread obstructive lung disease rather than a localized mass as the primary radiologic finding.
*Cardiomegaly and increased bronchial markings*
- **Cardiomegaly** can be seen in heart failure, and while the patient has leg edema (suggesting right heart strain due to lung disease or independent heart failure), his primary respiratory symptoms are more indicative of obstructive lung disease.
- **Increased bronchial markings** suggest bronchial wall thickening, which can be seen in chronic bronchitis or asthma, but does not fully capture the diffuse destructive changes of emphysema that better fit the clinical presentation.
*Subpleural cystic enlargement*
- **Subpleural cystic enlargement** can be seen in conditions like **pulmonary fibrosis** (e.g., usual interstitial pneumonia), which presents with restrictive lung disease.
- This pattern is inconsistent with the patient's obstructive symptoms of wheezing and prolonged expiratory phase, which are characteristic of airflow limitation.
*Calcified pleural plaques surrounding the diaphragm*
- **Calcified pleural plaques** are a hallmark sign of **asbestos exposure**.
- While possible given his age, there is no history of asbestos exposure, and these plaques are typically asymptomatic, not explaining the acute worsening of respiratory symptoms.
Common radiologic findings in pathology US Medical PG Question 4: A 42-year-old man presents to the emergency department with abdominal pain. The patient was at home watching television when he experienced sudden and severe abdominal pain that prompted him to instantly call emergency medical services. The patient has a past medical history of obesity, smoking, alcoholism, hypertension, and osteoarthritis. His current medications include lisinopril and ibuprofen. His temperature is 98.5°F (36.9°C), blood pressure is 120/97 mmHg, pulse is 130/min, respirations are 22/min, and oxygen saturation is 97% on room air. The patient is in an antalgic position on the stretcher. His abdomen is rigid and demonstrates rebound tenderness and hypoactive bowel sounds. What is the next best step in management?
- A. CT of the abdomen
- B. Urgent laparoscopy
- C. NPO, IV fluids, and analgesics
- D. Urgent laparotomy (Correct Answer)
- E. Abdominal radiograph
Common radiologic findings in pathology Explanation: ***Urgent laparotomy***
- The patient's presentation with **sudden, severe abdominal pain**, a **rigid abdomen**, **rebound tenderness**, and **hypoactive bowel sounds** indicates **acute peritonitis**, most likely from a **perforated viscus**.
- In a patient with **frank peritonitis** and clinical signs of perforation, the diagnosis is **made clinically** based on physical examination findings.
- **Urgent laparotomy** (exploratory surgery) is the definitive management and should not be delayed for imaging when peritonitis is obvious.
- The patient's risk factors (NSAID use, alcoholism) further support peptic ulcer perforation as the likely etiology.
*CT of the abdomen*
- While CT scan is highly sensitive for identifying perforation and can provide anatomic detail, it is **not necessary when the diagnosis of peritonitis is clinically evident**.
- In a patient with **obvious peritonitis**, obtaining a CT scan would **delay definitive surgical treatment** without changing management.
- CT is more appropriate for stable patients with **uncertain diagnosis** or equivocal physical findings, not for those with frank peritonitis.
*Urgent laparoscopy*
- **Laparoscopy** can be used diagnostically and therapeutically in selected cases of abdominal emergencies.
- However, in a patient with diffuse peritonitis and suspected perforation, **laparotomy** is generally preferred over laparoscopy as it provides better exposure, faster source control, and easier peritoneal lavage.
- Laparoscopy may be considered in stable patients with localized findings, but this patient has signs of diffuse peritonitis.
*NPO, IV fluids, and analgesics*
- These are **essential supportive measures** and should be initiated immediately as part of resuscitation.
- However, they are **adjunctive** to definitive surgical management and do not constitute the "next best step" in a patient requiring emergency surgery.
- These measures should be initiated concurrently while preparing for urgent laparotomy.
*Abdominal radiograph*
- An **upright chest X-ray** or **abdominal radiograph** can show **free air under the diaphragm** (pneumoperitoneum) in cases of perforation.
- However, it is **only 50-70% sensitive**, meaning it misses many perforations.
- In a patient with **clinical peritonitis**, the absence of free air on X-ray does **not rule out perforation** and should not delay surgery.
- Imaging should not delay surgical intervention when peritonitis is clinically evident.
Common radiologic findings in pathology US Medical PG Question 5: A 72-year-old man presents to his primary care physician for his annual exam. He has a very stoic personality and says that he is generally very healthy and has "the normal aches and pains of old age." On further probing, you learn that he does have pretty significant back and hip pain that worsens throughout the day. On physical exam you note bony enlargement of the distal interphalangeal joints bilaterally. Which of the following is the likely cause of his symptoms?
- A. Rheumatoid arthritis
- B. Osteoarthritis (Correct Answer)
- C. Gout
- D. Pseudogout
- E. Osteopenia
Common radiologic findings in pathology Explanation: ***Osteoarthritis***
- The patient's age (72 years), back and hip pain that **worsens throughout the day** (classic for *wear-and-tear*), and **bony enlargement of the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints** (Heberden's nodes) are highly characteristic of osteoarthritis.
- This condition involves the progressive **degeneration of articular cartilage**, leading to bone-on-bone friction and osteophyte formation.
*Osteopenia*
- **Osteopenia** is a precursor to osteoporosis, characterized by **reduced bone mineral density**, making bones weaker.
- It typically presents with **no symptoms** until it progresses to osteoporosis and causes fractures; it does not cause pain that worsens throughout the day or bony enlargements of joints.
*Rheumatoid arthritis*
- **Rheumatoid arthritis** typically affects the **small joints of the hands and feet symmetrically**, but it predominantly involves the **proximal interphalangeal (PIP) and metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints**, sparing the distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints.
- Pain and stiffness associated with rheumatoid arthritis are usually **worse in the morning** and *improve with activity*, in contrast to the patient's symptoms.
*Gout*
- **Gout** is an inflammatory arthritis caused by the deposition of **urate crystals**, typically presenting as *acute, severe attacks* of pain, swelling, and redness in a single joint, most commonly the **big toe**.
- While it can affect other joints over time, it does not typically cause gradual onset, activity-related pain, or bony enlargement of DIP joints as described.
*Pseudogout*
- **Pseudogout**, or **calcium pyrophosphate deposition disease (CPPD)**, is caused by the deposition of **calcium pyrophosphate crystals** in joints.
- Similar to gout, it causes *acute inflammatory arthritis*, often affecting larger joints like the knee or wrist, and is not characterized by the chronic, activity-related pain and DIP joint bony changes seen in this patient.
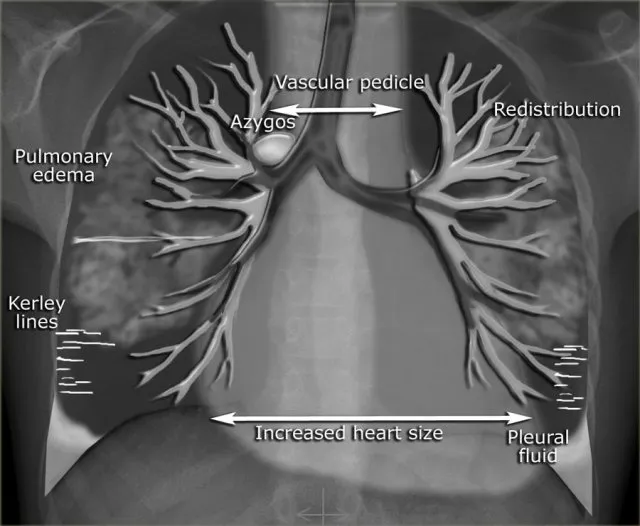
Common radiologic findings in pathology US Medical PG Question 6: A 68-year-old female presents to the emergency room with acute onset of dyspnea and hemoptysis. Her past medical history is unremarkable and she has had no prior surgeries. A ventilation-perfusion scan demonstrates a large perfusion defect that is not matched by a ventilation defect in the left lower lobe. Which of the following would you also expect to find in this patient:
- A. Bradycardia
- B. Increased inspiratory capacity
- C. Claudication
- D. Aortic dilation
- E. Pleuritic chest pain (Correct Answer)
Common radiologic findings in pathology Explanation: ***Pleuritic chest pain***
- The presented symptoms (dyspnea, hemoptysis, V/Q scan showing unmatched perfusion defect) are highly suggestive of **pulmonary embolism (PE)**. **Pleuritic chest pain** is a common symptom of PE, resulting from inflammation of the pleura often associated with a pulmonary infarct.
- **Pleuritic chest pain** is classically described as sharp, localized pain that worsens with deep inspiration or coughing, which aligns with the potential for pleural irritation in PE.
*Bradycardia*
- **Tachycardia**, not bradycardia, is a common finding in pulmonary embolism, often due to the body's compensatory response to hypoxemia and increased cardiovascular strain.
- Bradycardia would be atypical and likely unrelated to the acute presentation of PE in a previously healthy individual.
*Increased inspiratory capacity*
- In a patient with an acute pulmonary embolism, the inspiratory capacity is more likely to be normal or **decreased** due to discomfort from pleuritic chest pain, dyspnea, and potential V/Q mismatch affecting lung mechanics.
- Increased inspiratory capacity is not a typical physiological response to an acute PE; instead, patients often experience **restrictive breathing patterns**.
*Claudication*
- **Claudication** refers to pain, usually in the legs, caused by too little blood flow during exercise; it typically indicates **peripheral artery disease**.
- While PE is a thrombotic event, claudication is a symptom of chronic arterial insufficiency and is not directly related to acute pulmonary embolism.
*Aortic dilation*
- **Aortic dilation** is associated with conditions like aortic aneurysm or Marfan syndrome and is not a direct consequence or expected finding in acute pulmonary embolism.
- There is no pathophysiological link between acute PE and the immediate development or presence of aortic dilation.
Common radiologic findings in pathology US Medical PG Question 7: A previously healthy 66-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-day history of fever, cough, and right-sided chest pain. Her temperature is 38.8°C (101.8°F) and respirations are 24/min. Physical examination shows dullness to percussion, increased tactile fremitus, and egophony in the right lower lung field. The remainder of the examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely cause of these findings?
- A. Fluid in the interstitial space
- B. Air in the pleural space
- C. Consolidation of a lung segment (Correct Answer)
- D. Fluid in the pleural space
- E. Collapse of a lung segment
Common radiologic findings in pathology Explanation: ***Consolidation of a lung segment***
- The combination of **fever**, **cough**, and **chest pain** along with physical exam findings of **dullness to percussion**, **increased tactile fremitus**, and **egophony** in a specific lung field is classic for **lobar pneumonia**, which involves consolidation.
- **Consolidation** occurs when the normally air-filled alveoli become filled with inflammatory exudate (fluid, cells, and fibrin), leading to increased density of the lung tissue.
*Fluid in the interstitial space*
- **Interstitial fluid** typically causes **crackles** on auscultation and can be associated with conditions like **pulmonary edema**, but it does not usually cause **increased tactile fremitus** or **egophony**.
- **Dullness to percussion** would be less localized and tactile fremitus would not be increased as the sound transmission is not enhanced.
*Air in the pleural space*
- **Air in the pleural space (pneumothorax)** would lead to **hyperresonance** to percussion, **decreased or absent breath sounds**, and **decreased tactile fremitus**, which are opposite to the findings described.
- There would be no egophony, as sound transmission is diminished.
*Fluid in the pleural space*
- **Fluid in the pleural space (pleural effusion)** would cause **dullness to percussion** and **decreased or absent breath sounds** over the effusion.
- It would also typically result in **decreased tactile fremitus** due to the fluid separating the lung from the chest wall, unlike the increased fremitus seen with consolidation.
*Collapse of a lung segment*
- **Collapse of a lung segment (atelectasis)** would result in **dullness to percussion** and **decreased or absent breath sounds**.
- **Tactile fremitus** would be **decreased** over the affected area, not increased, because the collapsed lung tissue does not transmit vibrations as effectively.
Common radiologic findings in pathology US Medical PG Question 8: An 8-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her parents for a 10-month history of disturbing dreams and daytime sleepiness. She has difficulty falling asleep and says she sometimes sees ghosts just before falling asleep at night. She has had a 7-kg (15-lb) weight gain during this period despite no changes in appetite. She is alert and oriented, and neurologic examination is unremarkable. During physical examination, she spontaneously collapses after the physician drops a heavy book, producing a loud noise. She remains conscious after the collapse. Polysomnography with electroencephalogram is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Slow spike-wave pattern
- B. Periodic sharp waves
- C. Decreased delta wave sleep duration
- D. Diffuse slowing of waves
- E. Rapid onset of REM sleep (Correct Answer)
Common radiologic findings in pathology Explanation: ***Rapid onset of REM sleep***
- The patient's symptoms of **daytime sleepiness**, **hallucinations** (seeing ghosts before sleep, i.e., **hypnagogic hallucinations**), **sleep-onset difficulty**, and the spontaneous collapse (likely **cataplexy** triggered by strong emotion/surprise) are characteristic of **narcolepsy**.
- **Narcolepsy** is often associated with a disinhibition of REM sleep, leading to its occurrence at sleep onset or within 15 minutes of falling asleep, which would be detected by **polysomnography** with **EEG**.
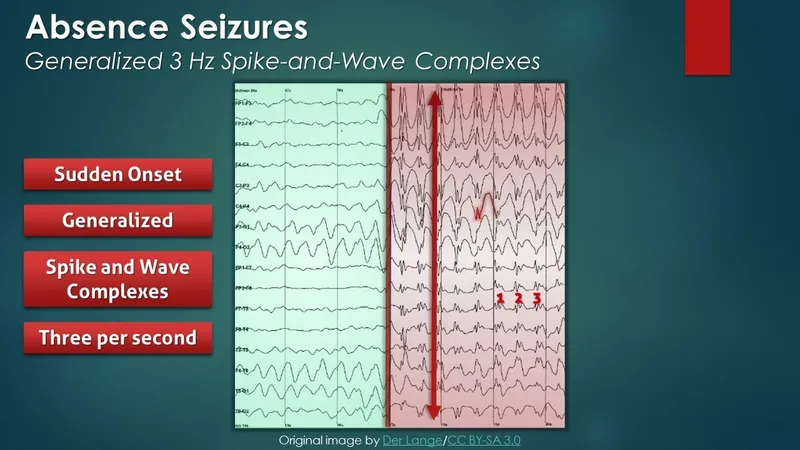
*Slow spike-wave pattern*
- This pattern is characteristic of **absence seizures** (petit mal seizures), which involve brief staring spells and loss of consciousness, not the constellation of sleep disturbances and cataplexy seen here.
- Absence seizures typically do not cause significant **daytime sleepiness** or **hallucinations**.
*Periodic sharp waves*
- **Periodic sharp wave complexes** are pathognomonic for **Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease** (CJD), a rapidly progressive neurodegenerative disorder.
- CJD presents with dementia, myoclonus, and other neurological signs, which are distinct from the patient's symptoms.
*Decreased delta wave sleep duration*
- **Delta wave sleep** (slow-wave sleep or N3 sleep) is a stage of deep non-REM sleep, which is important for restorative sleep.
- While sleep architecture can be disturbed in various sleep disorders, a primary decrease in delta wave sleep duration is not the most specific or hallmark finding for narcolepsy; rather, narcolepsy is defined by its REM sleep abnormalities.
*Diffuse slowing of waves*
- **Diffuse slowing of brain waves** on EEG is a non-specific finding often associated with **encephalopathy**, metabolic disturbances, or diffuse brain dysfunction.
- It does not specifically account for the unique constellation of symptoms seen in this patient, particularly the abrupt onset of sleep-related phenomena and **cataplexy**.
Common radiologic findings in pathology US Medical PG Question 9: A 27-year-old man presents to the emergency department with back pain. The patient states that he has back pain that has been steadily worsening over the past month. He states that his pain is worse in the morning but feels better after he finishes at work for the day. He rates his current pain as a 7/10 and says that he feels short of breath. His temperature is 99.5°F (37.5°C), blood pressure is 130/85 mmHg, pulse is 80/min, respirations are 14/min, and oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. On physical exam, you note a young man who does not appear to be in any distress. Cardiac exam is within normal limits. Pulmonary exam is notable only for a minor decrease in air movement bilaterally at the lung bases. Musculoskeletal exam reveals a decrease in mobility of the back in all four directions. Which of the following is the best initial step in management of this patient?
- A. MRI of the sacroiliac joint (Correct Answer)
- B. CT scan of the chest
- C. Pulmonary function tests
- D. Ultrasound
- E. Radiography of the lumbosacral spine
Common radiologic findings in pathology Explanation: ***MRI of the sacroiliac joint***
- The patient's symptoms of **worsening back pain**, morning stiffness that improves with activity, and decreased back mobility are highly suggestive of **ankylosing spondylitis**.
- **MRI** is the most sensitive imaging modality for detecting early inflammatory changes in the **sacroiliac joints** and spine, which are characteristic of ankylosing spondylitis, even before radiographic changes are visible.
*CT scan of the chest*
- While the patient reports feeling **short of breath**, his vital signs and oxygen saturation are normal, and he does not appear in acute distress.
- A CT scan of the chest would be a more appropriate step if there were clearer signs of acute pulmonary pathology, such as significant hypoxemia, fever, or adventitious lung sounds, which are not present here.
*Pulmonary function tests*
- **Shortness of breath** could eventually be a complication of severe ankylosing spondylitis due to restricted chest wall expansion.
- However, PFTs are generally not the *initial* diagnostic step given the primary presentation of back pain and the need to confirm the underlying rheumatologic condition first.
*Ultrasound*
- **Ultrasound** is not a primary imaging modality for evaluating the sacroiliac joints or the spine in the context of suspected ankylosing spondylitis.
- It could be useful for assessing peripheral joint inflammation in other arthropathies, but not for axial involvement.
*Radiography of the lumbosacral spine*
- **X-rays of the lumbosacral spine** might show changes in advanced ankylosing spondylitis (e.g., squaring of vertebrae, syndesmophytes), but they are often normal in the early stages of the disease.
- **MRI** is superior for detecting early inflammatory changes and is often used to diagnose the condition before radiographic damage is evident.
Common radiologic findings in pathology US Medical PG Question 10: A 71-year-old man with type 2 diabetes mellitus comes to the physician because of a 9-month history of pain and stiffness in the right knee. He reports that the stiffness lasts approximately 10 minutes after waking up and that the pain is worse in the evening. There is no history of trauma. He is 175 cm (5 ft 9 in) tall and weighs 102 kg (225 lb); BMI is 33 kg/m2. Examination of the right knee shows tenderness in the anteromedial joint line and crepitus during knee movement. Laboratory studies show an erythrocyte sedimentation rate of 15 mm/h and a serum uric acid concentration of 6.9 mg/dL. Which of the following is the most likely finding on imaging of the right knee?
- A. Osteophytes and narrowing of the joint-space (Correct Answer)
- B. Loculated epiphyseal cyst with thinning of the overlying cortex
- C. Bony ankylosis and bone proliferation at the entheses
- D. Marginal bony erosions and opacification of periarticular soft tissue
- E. Periarticular osteopenia and pannus formation
Common radiologic findings in pathology Explanation: ***Osteophytes and narrowing of the joint-space***
- The patient's symptoms (age, knee pain worse in evening, short morning stiffness, obesity, crepitus, anteromedial tenderness) are classic for **osteoarthritis (OA)**.
- **Osteoarthritis** is characterized by the breakdown of articular cartilage, leading to bone-on-bone friction, resulting in **joint space narrowing** and the formation of **osteophytes** (bone spurs) at the joint margins, which are readily visible on imaging.
*Loculated epiphyseal cyst with thinning of the overlying cortex*
- This finding is more characteristic of a **chondroblastoma** or an **aneurysmal bone cyst**, which are typically seen in younger individuals and present with localized pain, swelling, and sometimes pathologic fractures, rather than the chronic, activity-related pain of OA.
- While subchondral cysts can occur in severe OA, a large, loculated epiphyseal cyst with cortical thinning is not the primary or most characteristic radiographic finding and would suggest a different etiology.
*Bony ankylosis and bone proliferation at the entheses*
- **Bony ankylosis** (fusion of joints) and **enthesitis** (inflammation and ossification at tendon/ligament insertions) are hallmark features of **spondyloarthropathies** like ankylosing spondylitis, not osteoarthritis.
- The patient's symptoms do not suggest an inflammatory arthritis (e.g., morning stiffness is 10 minutes, not hours, and ESR is normal).
*Marginal bony erosions and opacification of periarticular soft tissue*
- **Marginal bony erosions** (rat-bite erosions) and **periarticular soft tissue opacification** (due to monosodium urate crystal deposition) are characteristic findings of **gout**.
- While the patient has an elevated serum uric acid (6.9 mg/dL), this level is within the normal range for some labs and not definitively diagnostic of gout, especially without acute inflammatory flares or tophi. The chronic, activity-related nature of the pain is inconsistent with acute gout.
*Periarticular osteopenia and pannus formation*
- **Periarticular osteopenia** (bone thinning around the joint) and **pannus formation** (granulation tissue that erodes cartilage and bone) are characteristic features of **rheumatoid arthritis**.
- The patient's presentation (older age, pain worse with activity, short morning stiffness, no systemic inflammatory signs) is inconsistent with rheumatoid arthritis.
More Common radiologic findings in pathology US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.