Cell and tissue identification keys US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Cell and tissue identification keys. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Cell and tissue identification keys US Medical PG Question 1: A 13-year-old girl is referred to an oral surgeon after complaining of tooth pain, especially in the upper jaw. A review of her medical history reveals status post-surgical repair of a patent ductus arteriosus when she was 6 years old. At the clinic, her temperature is 37.0ºC (98.6°F), pulse is 90/min, respirations are 18/min, and blood pressure is 110/78 mm Hg. On physical examination, her height is 157.5 cm (5 ft 2 in), her weight is 50 kg (110 lb) and her arms seem disproportionately long for her trunk. She also has arachnodactyly and moderate joint laxity. Intraoral examination reveals crowded teeth and a high arched palate. Which of the following protein is most likely defective in this condition?
- A. α2-laminin (merosin)
- B. Fibrillin-1 (Correct Answer)
- C. Caveolin and the sarcoglycan proteins
- D. Lamin A
- E. Emerin
Cell and tissue identification keys Explanation: ***Fibrillin-1***
- The clinical presentation of tall stature with **disproportionately long limbs**, **arachnodactyly (long, slender fingers)**, **joint laxity**, and a **high-arched palate** is highly suggestive of **Marfan syndrome**.
- **Marfan syndrome** is an **autosomal dominant connective tissue disorder** caused by a mutation in the *FBN1* gene, which codes for **fibrillin-1**, a glycoprotein essential for the formation of elastic fibers.
- Classic cardiovascular manifestations of Marfan syndrome include **aortic root dilatation**, **mitral valve prolapse**, and **aortic dissection**. While the patient has a history of **patent ductus arteriosus** repair, this is not a typical feature of Marfan syndrome but may represent a concurrent finding or diagnostic consideration in the workup.
*α2-laminin (merosin)*
- Mutations in the gene encoding **α2-laminin** are associated with **congenital muscular dystrophy (Merosin-deficient CMD)**, a condition characterized by **muscle weakness**, hypotonia, and **white matter abnormalities** in the brain, none of which are described here.
- This condition does not typically present with the skeletal and cardiovascular features seen in the patient.
*Caveolin and the sarcoglycan proteins*
- Defects in **caveolin-3** are associated with **limb-girdle muscular dystrophy type 1C**, and defects in **sarcoglycan proteins (α, β, γ, δ)** are linked to **sarcoglycanopathies**, which are forms of **limb-girdle muscular dystrophy (LGMD)**.
- These conditions are characterized by **progressive muscle weakness and wasting**, not the connective tissue abnormalities observed in this patient.
*Lamin A*
- Mutations in the *LMNA* gene, which encodes **lamin A**, are associated with a spectrum of disorders called **laminopathies**, including **Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy**, **dilated cardiomyopathy**, and **Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome**.
- While some forms can affect cardiac function (**dilated cardiomyopathy**), they do not present with the characteristic skeletal and connective tissue features of Marfan syndrome.
*Emerin*
- **Emerin** is a protein localized to the inner nuclear membrane, and mutations in its gene (*EMD*) cause **X-linked Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy**.
- This disorder is characterized by a **clinical triad of contractures (elbow, ankles, spine)**, **progressive muscle weakness and wasting**, and **cardiac conduction defects**, which are not the primary features presented in this case.
Cell and tissue identification keys US Medical PG Question 2: Cardiac muscle serves many necessary functions, leading to a specific structure that serves these functions. The structure highlighted is an important histology component of cardiac muscle. What would be the outcome if this structure diffusely failed to function?
- A. Failure of potassium channels to appropriately open to repolarize the cell
- B. Failure of propagation of the action potential from the conduction system (Correct Answer)
- C. Ineffective excitation-contraction coupling due to insufficient calcium ions
- D. Inappropriate formation of cardiac valve leaflets
- E. Outflow tract obstruction
Cell and tissue identification keys Explanation: ***Failure of propagation of the action potential from the conduction system***
- The highlighted structure, the **intercalated disc**, contains **gap junctions** which are crucial for the rapid, synchronized spread of **action potentials** between cardiac muscle cells.
- A diffuse failure of these structures would prevent the coordinated electrical activation of the myocardium, leading to a failure of impulse propagation and **compromised cardiac contraction**.
*Failure of potassium channels to appropriately open to repolarize the cell*
- This scenario describes a problem with **ion channel function** within individual cardiomyocytes, affecting their repolarization phase.
- While critical for a single cell's electrical activity, it does not directly relate to the primary function of **intercalated discs** in *propagating* action potentials across multiple cells.
*Ineffective excitation-contraction coupling due to insufficient calcium ions*
- This outcome would result from issues with **calcium handling** mechanisms, such as problems with the **sarcoplasmic reticulum** or **calcium channels**, which are internal to the cardiomyocyte.
- It is distinct from the role of **intercalated discs** in facilitating intercellular communication and electrical spread.
*Inappropriate formation of cardiac valve leaflets*
- The formation of cardiac valve leaflets is an intricate process during **embryological development** involving specific signaling pathways and cell migration.
- This structural defect is not directly related to the function of **intercalated discs** in mature cardiac muscle, which are involved in electrical and mechanical coupling.
*Outflow tract obstruction*
- **Outflow tract obstruction** is a congenital or acquired structural defect affecting the major arteries leaving the heart (e.g., aortic or pulmonary stenosis).
- This is a macroscopic structural anomaly that is not caused by a primary failure of **intercalated disc** function.
Cell and tissue identification keys US Medical PG Question 3: An investigator is studying cellular repair mechanisms in various tissues. One of the samples being reviewed is from the anterior horn of the spinal cord of a patient who was involved in a snowboard accident. Pathologic examination of the biopsy specimen shows dispersion of the Nissl bodies, swelling of the neuronal body, and a displacement of the nucleus to the periphery in numerous cells. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for the observed findings?
- A. Neurodegenerative changes
- B. Neuronal aging
- C. Central chromatolysis (Correct Answer)
- D. Reactive astrogliosis
- E. Wallerian degeneration
Cell and tissue identification keys Explanation: ***Central chromatolysis***
- This process is a **response to axonal injury**, where the neuron undergoes characteristic morphological changes to prepare for regeneration.
- Key features include **dispersion of Nissl bodies**, **neuronal swelling**, and **nucleus displacement to the periphery**, all indicative of an attempt at cellular repair.
*Neurodegenerative changes*
- These typically involve **neuronal loss** and accumulation of **abnormal protein deposits**, rather than an attempt at cellular repair.
- The observed features (swelling, Nissl body dispersion) are part of an acute injury response, not chronic degeneration.
*Neuronal aging*
- Though aging neurons can accumulate **lipofuscin** and show some atrophy, they do not typically present with the acute, dramatic changes of cell body swelling and peripheral nucleus displacement described.
- Aging is a slow, progressive process, distinct from an acute response to injury from an accident.
*Reactive astrogliosis*
- This refers to the **proliferation and hypertrophy of astrocytes** in response to CNS injury.
- While it's a component of the injury response, it describes glial cell changes, not the neuronal body changes observed in the question.
*Wallerian degeneration*
- This process describes the **degeneration of the axon distal to the site of injury**, as well as the myelin sheath.
- It does not characterize the **changes occurring within the neuronal cell body** (soma), which are the focus of the question.
Cell and tissue identification keys US Medical PG Question 4: A 57-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by his wife 20 minutes after having had a seizure. He has had recurrent headaches and dizziness for the past 2 weeks. An MRI of the brain shows multiple, round, well-demarcated lesions in the brain parenchyma at the junction between gray and white matter. This patient's brain lesions are most likely comprised of cells that originate from which of the following organs?
- A. Kidney
- B. Skin
- C. Lung (Correct Answer)
- D. Thyroid
- E. Prostate
Cell and tissue identification keys Explanation: ***Lung (Correct Answer)***
- **Lung cancer** is the most common cause of **brain metastases** in adults, accounting for approximately **50% of all cases**
- The clinical presentation—seizure, headaches, dizziness, and **multiple, round, well-demarcated lesions at the gray-white matter junction**—is classic for metastatic lung cancer
- Both **small cell and non-small cell lung cancers** have high propensity for hematogenous spread to the brain
- The watershed areas at the gray-white junction are common sites due to lodging of tumor emboli in terminal arterioles
*Kidney (Incorrect)*
- **Renal cell carcinoma (RCC)** can metastasize to the brain but accounts for only **5-10% of brain metastases**
- While RCC metastases can appear similar on imaging, lung cancer is statistically more likely given its higher prevalence
- RCC metastases are often **highly vascular and may hemorrhage**, which is not mentioned in this case
*Skin (Incorrect)*
- **Melanoma** has the **highest propensity per case** to metastasize to the brain among all cancers
- However, the **overall incidence of melanoma is much lower** than lung cancer, making it a less probable primary source
- Melanoma brain metastases often present as **hemorrhagic lesions** and would typically have skin findings or history
*Thyroid (Incorrect)*
- **Thyroid cancer** rarely metastasizes to the brain (accounts for <1% of brain metastases)
- Brain metastases from thyroid cancer typically occur in **advanced papillary or follicular carcinoma** or in **anaplastic thyroid cancer**
- More common metastatic sites for thyroid cancer are lung and bone
*Prostate (Incorrect)*
- **Prostate cancer very rarely metastasizes to the brain** (<1% of cases)
- Prostate cancer preferentially metastasizes to **bone (especially axial skeleton), lymph nodes, and liver**
- Brain metastases from prostate cancer suggest extremely advanced, aggressive disease and are exceptionally uncommon
Cell and tissue identification keys US Medical PG Question 5: A healthy 22-year-old male participates in a research study you are leading to compare the properties of skeletal and cardiac muscle. You conduct a 3-phased experiment with the participant. In the first phase, you get him to lift up a 2.3 kg (5 lb) weight off a table with his left hand. In the second phase, you get him to do 20 burpees, taking his heart rate to 150/min. In the third phase, you electrically stimulate his gastrocnemius with a frequency of 50 Hz. You are interested in the tension and electrical activity of specific muscles as follows: Biceps in phase 1, cardiac muscle in phase 2, and gastrocnemius in phase 3. What would you expect to be happening in the phases and the respective muscles of interest?
- A. Increase of tension in experiments 2 and 3, with the same underlying mechanism
- B. Increase of tension in all phases (Correct Answer)
- C. Recruitment of large motor units followed by small motor units in experiment 1
- D. Fused tetanic contraction at the end of all three experiments
- E. Recruitment of small motor units at the start of experiments 1 and 2
Cell and tissue identification keys Explanation: ***Increase of tension in all phases***
- In **phase 1**, lifting a 2.3 kg weight requires the **biceps** to contract, generating sufficient force (**tension**) to overcome gravity.
- In **phase 2**, the **cardiac muscle** increases its contractile force (**tension**) to meet the metabolic demands of **exercise**, leading to a heart rate of 150/min.
- In **phase 3**, electrical stimulation of the **gastrocnemius** at 50 Hz triggers muscle contraction, leading to an increase in **tension**.
*Increase of tension in experiments 2 and 3, with the same underlying mechanism*
- While tension increases in phases 2 and 3, the **underlying mechanisms differ**: cardiac muscle tension increases due to increased sympathetic stimulation and preload, while skeletal muscle tension increases due to unfused or fused tetanus from electrical stimulation.
- Cardiac muscle contraction is regulated by **calcium-induced calcium release**, while skeletal muscle involves direct coupling of DHP receptor and ryanodine receptor.
*Recruitment of large motor units followed by small motor units in experiment 1*
- **Motor unit recruitment** follows the **size principle**, meaning smaller, more easily excitable motor units are activated first, followed by larger ones as more force is needed.
- Therefore, in phase 1, **small motor units** would be recruited first, not large ones.
*Fused tetanic contraction at the end of all three experiments*
- **Fused tetanic contraction** occurs in **skeletal muscle** when stimulation frequency is high enough that individual twitches summate completely, leading to sustained contraction.
- This phenomenon is **not possible in cardiac muscle** due to its long **refractory period**, which prevents sustained contraction and allows for adequate filling time.
*Recruitment of small motor units at the start of experiments 1 and 2*
- **Motor unit recruitment** applies to **skeletal muscle** (phase 1) and involves recruiting small motor units first for fine or gentle movements.
- **Cardiac muscle** (phase 2) does not have motor units; instead, it relies on the **Frank-Starling mechanism** and hormonal/nervous regulation to adjust its contractile force as a syncytium.
Cell and tissue identification keys US Medical PG Question 6: A 57-year-old man comes to the physician for a follow-up evaluation of chronic, retrosternal chest pain. The pain is worse at night and after heavy meals. He has taken oral pantoprazole for several months without any relief of his symptoms. Esophagogastroduodenoscopy shows ulcerations in the distal esophagus and a proximally dislocated Z-line. A biopsy of the distal esophagus shows columnar epithelium with goblet cells. Which of the following microscopic findings underlie the same pathomechanism as the cellular changes seen in this patient?
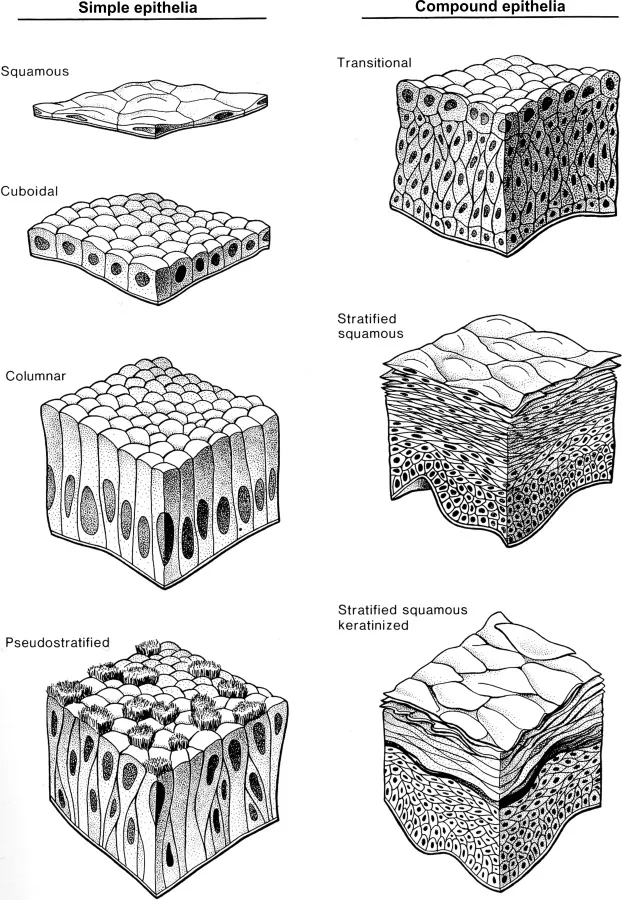
- A. Squamous epithelium in the bladder (Correct Answer)
- B. Branching muscularis mucosa in the jejunum
- C. Paneth cells in the duodenum
- D. Pseudostratified columnar epithelium in the bronchi
- E. Disorganized squamous epithelium in the endocervix
Cell and tissue identification keys Explanation: ***Squamous epithelium in the bladder***
- The patient has **Barrett's esophagus**, characterized by **columnar epithelium with goblet cells** in the distal esophagus, which is an example of **metaplasia**.
- **Squamous metaplasia in the bladder** can occur due to chronic irritation (e.g., stones, recurrent infections) and represents a similar adaptive cellular change where one differentiated cell type is replaced by another.
*Branching muscularis mucosa in the jejunum*
- **Branching muscularis mucosa** is a normal anatomical variant sometimes seen in the jejunum, not a pathological cellular change.
- This finding does not represent a change in cell type due to chronic stress or adaptation.
*Paneth cells in the duodenum*
- **Paneth cells** are a normal component of the small intestine, including the duodenum, and are responsible for antimicrobial defense through the secretion of **lysozyme** and **defensins**.
- Their presence in the duodenum is physiological and not a metaplastic change.
*Pseudostratified columnar epithelium in the bronchi*
- **Pseudostratified columnar epithelium with cilia and goblet cells** is the normal and healthy lining of the bronchi, responsible for mucociliary clearance.
- This is a normal histological finding, not an abnormal cellular adaptation like metaplasia.
*Disorganized squamous epithelium in the endocervix*
- **Disorganized squamous epithelium** in the endocervix suggests **dysplasia** or **carcinoma in situ**, which is a pre-malignant or malignant change, not simple metaplasia.
- While metaplasia (e.g., squamous metaplasia in the transformation zone of the cervix) can precede dysplasia, the term "disorganized" indicates a higher grade of cellular abnormality and a different pathomechanism.
Cell and tissue identification keys US Medical PG Question 7: A 65-year-old man with a 40-pack-year smoking history presents with hemoptysis and a persistent cough. Chest CT shows a 3.5 cm centrally located mass in the right main bronchus. Positron emission tomography confirms a malignant nodule. Bronchoscopy with transbronchial biopsy is performed and a specimen sample of the nodule is sent for frozen section analysis. The tissue sample is most likely to show which of the following tumor types?
- A. Carcinoid tumor
- B. Metastasis of colorectal cancer
- C. Small cell lung carcinoma
- D. Large cell carcinoma
- E. Squamous cell carcinoma (Correct Answer)
Cell and tissue identification keys Explanation: ***Squamous cell carcinoma***
- This is the most likely diagnosis given the **central location** in the main bronchus, **heavy smoking history**, and presentation with **hemoptysis**.
- **Squamous cell carcinoma** accounts for 25-30% of lung cancers and characteristically arises in **central/proximal airways**, making it readily accessible by **bronchoscopy**.
- Histologically, it shows **keratin pearls** and **intercellular bridges** on biopsy.
- The **central endobronchial location** and ability to obtain tissue via transbronchial biopsy strongly favor squamous cell over peripheral tumors.
*Carcinoid tumor*
- **Carcinoid tumors** are **neuroendocrine tumors** that can present as central endobronchial masses and cause hemoptysis.
- However, they are typically **slow-growing** with more indolent presentation, and PET scans show **variable uptake** (often less intense than aggressive carcinomas).
- They represent only **1-2% of lung tumors** and occur more commonly in **younger, non-smoking patients**.
*Metastasis of colorectal cancer*
- While lung is a common site for **colorectal metastases**, these typically present as **multiple peripheral nodules** rather than a solitary central endobronchial mass.
- The clinical presentation strongly suggests **primary lung cancer** rather than metastatic disease.
- Without history of colorectal cancer, this is unlikely.
*Small cell lung carcinoma*
- **Small cell lung carcinoma** (SCLC) represents 15% of lung cancers and typically presents as a **large central mass** with early mediastinal involvement.
- However, SCLC is usually **too extensive at presentation** for transbronchial biopsy alone and often requires mediastinoscopy or CT-guided biopsy.
- Histology shows **small cells with scant cytoplasm**, **salt-and-pepper chromatin**, and **oat-cell morphology**.
- While possible, the single accessible endobronchial mass is more characteristic of squamous cell.
*Large cell carcinoma*
- **Large cell carcinoma** is a **diagnosis of exclusion** made when tumors lack features of adenocarcinoma, squamous cell, or small cell differentiation.
- It typically presents as **large peripheral masses** rather than central endobronchial lesions.
- It represents only **10% of lung cancers** and is less common than squamous cell carcinoma in this clinical scenario.
Cell and tissue identification keys US Medical PG Question 8: Collagen is a very critical structural protein in many of our connective tissues. Defects in collagen produce diseases such as Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, where there is a defective lysyl hydroxylase gene, or osteogenesis imperfecta, where there is a defect in the production of type I collagen. Which of the following represents the basic repeating tripeptide of collagen?
- A. Gly-X-Y (Correct Answer)
- B. Asp-X-Y
- C. Met-X-Y
- D. Ser-X-Y
- E. Glu-X-Y
Cell and tissue identification keys Explanation: ***Gly-X-Y***
- The **basic repeating tripeptide unit of collagen** is **Glycine-X-Y**, where X and Y are often **proline** and **hydroxyproline**, respectively.
- **Glycine** is essential at every third position because its small side chain allows for the tight packing of the **collagen triple helix**.
*Asp-X-Y*
- **Aspartate (Asp)** is an **acidic amino acid** and is not typically found at the first position of the repeating tripeptide unit of collagen.
- Its bulky side chain would hinder the tight coiling of the **collagen helix**.
*Met-X-Y*
- **Methionine (Met)** is a **hydrophobic amino acid** and, while important in other proteins, it does not occupy the critical first position in the repeating collagen tripeptide.
- The unique structural requirements of collagen favor **glycine** at this position for optimal packing.
*Ser-X-Y*
- **Serine (Ser)** is a **polar, uncharged amino acid** and, like aspartate and methionine, is not the primary amino acid found at the first position of the repeating collagen tripeptide.
- The small size of **glycine** is crucial for collagen's characteristic triple helix.
*Glu-X-Y*
- **Glutamate (Glu)** is another **acidic amino acid** that is not typically found at the first position of the repeating tripeptide in collagen.
- Large or charged amino acids at this position would destabilize the **collagen secondary structure**.
Cell and tissue identification keys US Medical PG Question 9: A 52-year-old man presents to his primary care physician complaining of an ongoing cough. He reports that the cough started 1 year ago after a "bad cold" and then never resolved. He feels the cough is getting worse, sometimes the cough is dry, but often the cough will bring up a clear to white mucus, especially in the morning. The patient has hypertension and peripheral artery disease. He takes aspirin and lisinopril. He started smoking at age 16, and now smokes 2 packs of cigarettes a day. He has 1-2 beers a couple nights of the week with dinner. He denies illicit drug use. Which of the following cell types within the lung is most likely to undergo metaplasia caused by smoking?
- A. Pseudostratified columnar (Correct Answer)
- B. Simple cuboidal
- C. Transitional
- D. Simple squamous
- E. Stratified squamous
Cell and tissue identification keys Explanation: ***Pseudostratified columnar***
- The **tracheobronchial tree** is lined with **pseudostratified columnar epithelium** containing cilia and goblet cells, which are crucial for clearing mucus and inhaled particles.
- Exposure to chronic irritants like cigarette smoke causes these cells to undergo **squamous metaplasia**, transforming into more resilient but less functional stratified squamous epithelium.
*Simple cuboidal*
- **Simple cuboidal epithelium** lines the **bronchioles** and is involved in secretion and absorption, but it is not the primary site for metaplastic changes due to smoking.
- While smoking can affect bronchioles, the characteristic metaplasia seen with chronic irritation primarily occurs in the larger airways.
*Transitional*
- **Transitional epithelium** is found in the **urinary bladder** and other parts of the urinary tract, allowing for stretching.
- It is not found in the respiratory tract and thus is not affected by smoking-induced metaplasia in the lungs.
*Simple squamous*
- **Simple squamous epithelium** lines the **alveoli**, facilitating gas exchange due to its thin, flat structure.
- While smoking can damage alveolar cells, the primary metaplastic change in response to chronic irritation occurs in the conducting airways, not in the alveoli.
*Stratified squamous*
- **Stratified squamous epithelium** is the *result* of metaplasia in the airways due to smoking, not the cell type undergoing the initial change.
- **Pseudostratified columnar epithelium** transforms into stratified squamous epithelium as a protective response to chronic irritation.
Cell and tissue identification keys US Medical PG Question 10: Research is being conducted on embryoblasts. The exact date of fertilization is unknown. There is the presence of a cytotrophoblast and syncytiotrophoblast, marking the time when implantation into the uterus would normally occur. Within the embryoblast, columnar and cuboidal cells are separated by a membrane. Which of these cell layers begins to line the yolk sac cavity?
- A. Hypoblast (Correct Answer)
- B. Epiblast
- C. Syncytiotrophoblast
- D. Inner cell mass
- E. Endoderm
Cell and tissue identification keys Explanation: ***Hypoblast***
- The **hypoblast** is a layer of cuboidal cells that forms from the inner cell mass around day 8 post-fertilization.
- It plays a crucial role in forming the **primary yolk sac** by migrating to line the exocoelomic cavity.
*Epiblast*
- The **epiblast** is composed of columnar cells located dorsal to the hypoblast and forms the floor of the **amniotic cavity**.
- It is the source of the **three primary germ layers** during gastrulation (ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm), not the yolk sac lining itself.
*Syncytiotrophoblast*
- The **syncytiotrophoblast** is the outer, invasive layer of the trophoblast that facilitates implantation and forms the fetal component of the placenta.
- It is not involved in lining the yolk sac cavity but rather in **invading the uterine endometrium** and producing hCG.
*Inner cell mass*
- The **inner cell mass (ICM)** is the cluster of cells within the blastocyst that gives rise to the embryoblast (which further differentiates into epiblast and hypoblast).
- The ICM itself does not line the yolk sac; rather, its derivative, the hypoblast, does.
*Endoderm*
- The **endoderm** is one of the three primary germ layers that forms during gastrulation from the epiblast derivative.
- It ultimately forms the linings of the **gastrointestinal and respiratory tracts**, not the primary yolk sac lining.
More Cell and tissue identification keys US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.