Skull and cranial cavity US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Skull and cranial cavity. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Skull and cranial cavity US Medical PG Question 1: During an examination of the cranial nerves, a patient shows inability to move their eye laterally past the midline. Which of the following structures in the cavernous sinus is most likely affected?
- A. Oculomotor nerve
- B. Trochlear nerve
- C. Ophthalmic nerve
- D. Abducens nerve (Correct Answer)
Skull and cranial cavity Explanation: ***Abducens nerve***
- The **abducens nerve (CN VI)** innervates the **lateral rectus muscle**, responsible for **abduction** (lateral movement) of the eye [1].
- Inability to move the eye laterally past the midline indicates paralysis or weakness of the lateral rectus muscle, directly implicating the abducens nerve [1].
*Oculomotor nerve*
- The **oculomotor nerve (CN III)** controls most **extraocular muscles** (superior, inferior, medial rectus, inferior oblique) and the levator palpebrae superioris, as well as pupillary constriction [1], [2].
- Damage to this nerve would primarily affect **adduction**, elevation, depression, and eyelid opening, not isolated lateral gaze.
*Trochlear nerve*
- The **trochlear nerve (CN IV)** innervates the **superior oblique muscle**, which depresses and internally rotates the eye [1].
- A lesion here typically presents with **vertical diplopia**, particularly when reading or descending stairs, due to impaired eye depression and intorsion.
*Ophthalmic nerve*
- The **ophthalmic nerve (V1)** is one of the three divisions of the trigeminal nerve and is purely **sensory**.
- It provides sensation to the forehead, upper eyelid, cornea, and nose, and does not control any eye movements.
Skull and cranial cavity US Medical PG Question 2: A 28-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after developing an altered mental state following blunt trauma to the head. The patient was competing at a local mixed martial arts competition when he was struck in the head and lost consciousness. A few minutes later, upon regaining consciousness, he had a progressive decline in mental status. Past medical history is noncontributory. Upon arrival at the hospital, the temperature is 37.0°C (98.6°F), the blood pressure is 145/89 mm Hg, the pulse is 66/min, the respiratory rate is 14/min, and the oxygen saturation is 99% on room air. He is alert now. A noncontrast CT scan is performed, and the result is provided in the image. Which of the following structures is most likely affected in this patient?
- A. Subarachnoid space
- B. Suprasellar cistern
- C. Middle Meningeal artery (Correct Answer)
- D. Ventricular system
- E. Bridging veins
Skull and cranial cavity Explanation: ***Middle Meningeal artery***
- The CT scan shows a **lenticular** or **biconvex** shaped hemorrhage, characteristic of an **epidural hematoma**. This type of hematoma is typically caused by trauma leading to rupture of the middle meningeal artery.
- The history of blunt head trauma followed by a **lucid interval** and then progressive neurological decline strongly points to an epidural hematoma, which results from arterial bleeding.
*Subarachnoid space*
- Hemorrhage in the subarachnoid space (subarachnoid hemorrhage) typically appears as **blood filling the sulci and basal cisterns** on CT, not a localized collection like seen in the image.
- While subarachnoid hemorrhage can be traumatic, the classic presentation of an epidural hematoma (lucid interval, lenticular shape) is not consistent with primary subarachnoid bleeding.
*Suprasellar cistern*
- The suprasellar cistern is located at the base of the brain, superior to the sella turcica, and typically contains cerebrospinal fluid.
- While it can be affected by subarachnoid hemorrhage, the image clearly shows a hematoma in the temporal-parietal region, not specifically within the suprasellar cistern.
*Ventricular system*
- The ventricular system contains CSF and is an internal structure of the brain. Hemorrhage within the ventricles (intraventricular hemorrhage) would appear as blood filling the ventricular spaces.
- The image shows an extra-axial hematoma, meaning outside the brain parenchyma and ventricles.
*Bridging veins*
- Rupture of bridging veins typically causes a **subdural hematoma**, which appears as a **crescent-shaped** collection of blood along the surface of the brain, conforming to the contours of the cerebral hemisphere.
- The hematoma in the image has a **lenticular (biconvex)** shape, which is characteristic of an epidural hematoma, not a subdural hematoma.
Skull and cranial cavity US Medical PG Question 3: A 7-year-old boy is brought to the emergency department by his mother 1 hour after falling off his bike and landing head-first on the pavement. His mother says that he did not lose consciousness but has been agitated and complaining about a headache since the event. He has no history of serious illness and takes no medications. His temperature is 37.1°C (98.7°F), pulse is 115/min, respirations are 20/min, and blood pressure is 100/65 mm Hg. There is a large bruise on the anterior scalp. Examination, including neurologic examination, shows no other abnormalities. A noncontrast CT scan of the head shows a non-depressed linear skull fracture with a 2-mm separation. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in management?
- A. Inpatient observation (Correct Answer)
- B. Contact child protective services
- C. CT angiography
- D. Discharge home
- E. MRI of the brain
Skull and cranial cavity Explanation: ***Inpatient observation***
- A **nondepressed linear skull fracture** with mild separation and persistent symptoms (headache, agitation) after head trauma warrants **inpatient observation**.
- This allows for close neurological monitoring for potential complications like **intracranial hemorrhage** or worsening of symptoms.
*Contact child protective services*
- The history of falling off a bike, a visible bruise, and a fracture consistent with trauma does not suggest **child abuse**.
- There are no other suspicious signs or inconsistencies in the mother's account to raise immediate concerns about neglect or abuse.
*CT angiography*
- **CT angiography** is used to evaluate the cerebral vasculature and is not indicated in this case, as there is no evidence of vascular injury or dissection.
- The primary concern here is the potential for **intracranial bleeding** or evolving neurological compromise, which is best monitored with serial neurological exams and potentially repeat noncontrast CT scans.
*Discharge home*
- The presence of a **skull fracture**, even if linear and nondepressed, combined with persistent symptoms like headache and agitation makes immediate discharge home unsafe.
- There is an increased risk of **epidural hematoma** or other delayed complications that require professional medical monitoring.
*MRI of the brain*
- **MRI** is more sensitive for detecting subtle brain parenchymal injuries but is not the initial or primary imaging modality for acute head trauma, especially in a child who may require sedation.
- An **MRI** would be considered if there were persistent or evolving neurological deficits despite a normal or stable CT scan, or if there is concern for specific soft tissue or white matter injuries that CT cannot adequately assess.
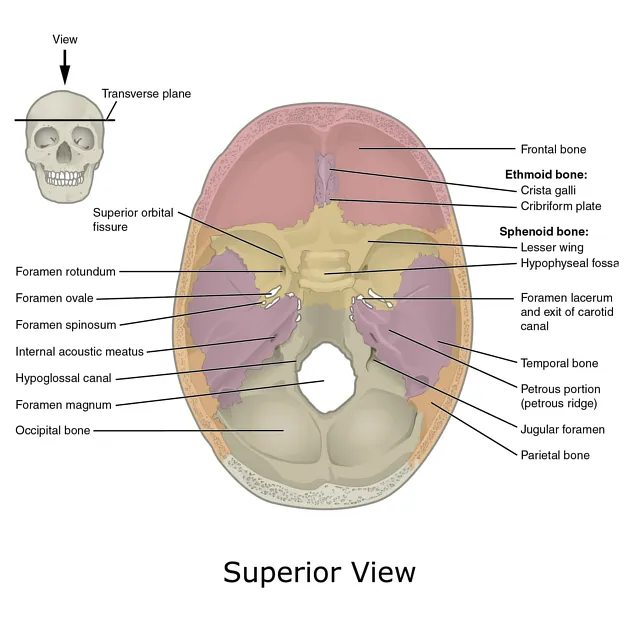
Skull and cranial cavity US Medical PG Question 4: A 47-year-old man presents to you with gradual loss of voice and difficulty swallowing for the past couple of months. The difficulty of swallowing is for both solid and liquid foods. His past medical history is insignificant except for occasional mild headaches. Physical exam also reveals loss of taste sensation on the posterior third of his tongue and palate, weakness in shrugging his shoulders, an absent gag reflex, and deviation of the uvula away from the midline. MRI scanning was suggested which revealed a meningioma that was compressing some cranial nerves leaving the skull. Which of the following openings in the skull transmit the affected cranial nerves?
- A. Jugular foramen (Correct Answer)
- B. Foramen rotundum
- C. Foramen spinosum
- D. Foramen ovale
- E. Foramen lacerum
Skull and cranial cavity Explanation: ***Jugular foramen***
- The symptoms described—loss of voice, difficulty swallowing, loss of taste on the posterior third of the tongue, absent gag reflex, and uvula deviation—point to impairment of **cranial nerves IX (glossopharyngeal), X (vagus), XI (accessory)**, which all exit the skull via the **jugular foramen**.
- The **vagus nerve** (CN X) is responsible for voice and swallowing (via innervation of the pharynx and larynx), the **glossopharyngeal nerve** (CN IX) for taste from the posterior third of the tongue and the gag reflex, and the **accessory nerve** (CN XI) for shoulder shrugging (trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles).
- Note: Loss of taste on the palate may involve CN VII (facial nerve) fibers, but the dominant clinical picture with absent gag reflex, uvula deviation, dysphagia, and dysphonia clearly indicates jugular foramen pathology.
*Foramen rotundum*
- The **foramen rotundum** transmits the **maxillary nerve (V2)**, a branch of the trigeminal nerve.
- Damage to V2 would primarily cause sensory deficits in the midface and upper teeth, which are not described in this patient.
*Foramen spinosum*
- The **foramen spinosum** transmits the **middle meningeal artery** and the **meningeal branch of the mandibular nerve (V3)**.
- Injury here would not explain the constellation of symptoms related to voice, swallowing, taste, or shoulder movement.
*Foramen ovale*
- The **foramen ovale** transmits the **mandibular nerve (V3)**, the **accessory meningeal artery**, and occasionally the superficial petrosal nerve.
- Damage to V3 would result in sensory loss to the lower face and motor deficits in the muscles of mastication, which are not reported.
*Foramen lacerum*
- The **foramen lacerum** is filled with cartilage in vivo and does not typically transmit major neurovascular structures directly through its aperture.
- The **internal carotid artery** passes superior to it, and some small nerves may traverse its vicinity, but not the specific cranial nerves indicated by the patient's symptoms.
Skull and cranial cavity US Medical PG Question 5: A 27-year-old man presents to a physician for evaluation of 3 months of increased vertigo. He says that occasionally he will experience several seconds of intense vertigo that makes him lose his balance. He came in for evaluation because this symptom is affecting his ability to drive to work. He has also been occasionally experiencing tinnitus. Physical exam reveals rotatory nystagmus that is delayed in onset and stops with visual fixation. The nerve that is most likely causing these symptoms exits the skull at which of the following locations?
- A. Internal auditory meatus (Correct Answer)
- B. Cribriform plate
- C. Foramen ovale
- D. Jugular foramen
- E. Foramen rotundum
Skull and cranial cavity Explanation: ***Internal auditory meatus***
- The symptoms described, particularly **vertigo** and **tinnitus**, are indicative of an issue with the **vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)**.
- The **vestibulocochlear nerve** exits the skull through the **internal auditory meatus**, which is also the pathway for the **facial nerve (CN VII)**.
*Cribriform plate*
- The **cribriform plate** is associated with the passage of the **olfactory nerves (CN I)**, which are responsible for the sense of smell.
- Damage to this area would typically cause **anosmia**, not vertigo or tinnitus.
*Foramen ovale*
- The **foramen ovale** is the exit point for the **mandibular nerve (V3)**, a branch of the trigeminal nerve.
- Dysfunction here would lead to problems with **mastication** or altered sensation in the lower face, not vertigo.
*Jugular foramen*
- The **jugular foramen** transmits several cranial nerves: the **glossopharyngeal (CN IX)**, **vagus (CN X)**, and **accessory (CN XI)** nerves.
- Issues in this region would manifest as difficulties with **swallowing**, **speech**, or **shoulder/neck movement**, not balance or hearing.
*Foramen rotundum*
- The **foramen rotundum** transmits the **maxillary nerve (V2)**, another branch of the trigeminal nerve.
- Damage to this nerve would primarily affect **sensation in the middle third of the face**, not balance or hearing.
Skull and cranial cavity US Medical PG Question 6: A 25-year-old pregnant woman, at 18 weeks of gestation, undergoes a routine ultrasound scan. The ultrasound images provided show below. Based on the imaging findings, what is the most likely diagnosis?
- A. Spina bifida (Correct Answer)
- B. Anencephaly
- C. Encephalocele
- D. Holoprosencephaly
- E. Iniencephaly
Skull and cranial cavity Explanation: ***Spina bifida***
- The ultrasound image shows a **defect in the posterior elements of the fetal spine**, with characteristic splaying or widening of the vertebral arches.
- This is a **neural tube defect** resulting from incomplete closure of the spinal column during embryonic development.
- Associated findings on prenatal ultrasound may include the **"lemon sign"** (scalloping of frontal bones) and **"banana sign"** (abnormal cerebellar shape).
- Spina bifida is typically detected on **second-trimester anatomy scan** (18-20 weeks).
*Anencephaly*
- This condition involves the **absence of a major portion of the brain, skull, and scalp** due to failure of anterior neural tube closure.
- On ultrasound, anencephaly presents with **absent calvarium above the orbits** and absent cerebral hemispheres, which is distinctly different from a spinal defect.
- This would be a **cranial abnormality**, not a spinal column defect.
*Encephalocele*
- An **encephalocele** is a protrusion of brain tissue and meninges through a defect in the skull, most commonly at the **occipital region**.
- On ultrasound, this appears as a **cranial mass** extending beyond the skull contour, not a spinal defect.
*Holoprosencephaly*
- This condition results from **failure of forebrain (prosencephalon) to divide properly** into two hemispheres.
- Ultrasound findings include **single ventricle**, fused thalami, and absent midline structures, often with associated **facial anomalies**.
- The imaging would show **brain abnormalities**, not spinal column defects.
*Iniencephaly*
- This is a rare **neural tube defect** characterized by extreme retroflexion of the head with severe spinal defects in the cervical and thoracic regions.
- On ultrasound, iniencephaly shows the fetal head in extreme **hyperextension** with the face looking upward, creating a characteristic "stargazing" appearance.
- This differs from the typical spinal defect pattern seen in spina bifida.
Skull and cranial cavity US Medical PG Question 7: A 32-year-old man presents to the emergency department with a severe headache. He says that the pain has been getting progressively worse over the last 24 hours and is located primarily in his left forehead and eye. The headaches have woken him up from sleep and it is not relieved by over-the-counter medications. He has been recovering from a sinus infection that started 1 week ago. His past medical history is significant for type 1 diabetes and he has a 10 pack-year history of smoking. Imaging shows thrombosis of a sinus above the sella turcica. Which of the following findings would most likely also be seen in this patient?
- A. Anosmia
- B. Mandibular pain
- C. Vertigo
- D. Ophthalmoplegia (Correct Answer)
- E. Vision loss
Skull and cranial cavity Explanation: ***Ophthalmoplegia***
- **Cavernous sinus thrombosis** (thrombosis of a sinus above the sella turcica) most commonly causes palsy of cranial nerves III, IV, and VI, which pass through the cavernous sinus, leading to **ophthalmoplegia**
- The patient's severe headache, particularly in the eye and forehead, progressive worsening, and history of recent sinus infection are all classic features of cavernous sinus thrombosis
- The cavernous sinus contains CN III (oculomotor), CN IV (trochlear), CN VI (abducens), and branches of CN V (V1 and V2), making ophthalmoplegia the most characteristic finding
*Anosmia*
- While a sinus infection can lead to temporary **anosmia** (loss of smell), it is not a direct consequence of cavernous sinus thrombosis
- The **olfactory nerve (CN I)** is located in the roof of the nasal cavity and passes through the cribriform plate, not through the cavernous sinus
- Anosmia would be related to the preceding sinus infection itself, not the cavernous sinus thrombosis
*Mandibular pain*
- **Mandibular pain** would typically be associated with issues affecting the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve **(CN V3)**, which does not pass through the cavernous sinus
- Although CN V1 (ophthalmic) and CN V2 (maxillary) do pass through the cavernous sinus and could cause facial pain, the predominant pain pattern in cavernous sinus thrombosis is orbital and frontal, not mandibular
- V3 exits the skull via foramen ovale and bypasses the cavernous sinus entirely
*Vertigo*
- **Vertigo** is a sensation of spinning or dizziness typically associated with vestibular dysfunction (inner ear or CN VIII/brainstem pathology)
- It is not a common or direct symptom of **cavernous sinus thrombosis**, which primarily affects structures passing through or adjacent to the cavernous sinus
- CN VIII (vestibulocochlear nerve) does not pass through the cavernous sinus
*Vision loss*
- While severe complications such as **optic nerve compression** from orbital swelling or **retinal venous congestion** can occur, direct **vision loss** is not the most common or earliest finding in cavernous sinus thrombosis
- The **optic nerve (CN II)** does not pass through the cavernous sinus itself, though it runs nearby
- Ophthalmoplegia (extraocular movement dysfunction) is far more characteristic than visual acuity loss as an initial presentation
Skull and cranial cavity US Medical PG Question 8: A patient was admitted with skull base trauma. The doctor was testing the marked structure in the pharyngeal region. Which of the following nerves was being tested?
- A. Trigeminal nerve
- B. Facial nerve
- C. Glossopharyngeal nerve (Correct Answer)
- D. Vagus
- E. Hypoglossal nerve
Skull and cranial cavity Explanation: ***Glossopharyngeal nerve***
- The image shows a probe stimulating the posterior part of the **pharynx**, which elicits the **gag reflex**.
- The afferent limb of the **gag reflex** is mediated primarily by the **glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)**, which detects sensation from the posterior tongue and pharynx.
*Trigeminal nerve*
- The **trigeminal nerve (CN V)** primarily mediates sensation from the face, teeth, and anterior two-thirds of the tongue, and motor control of the **muscles of mastication**.
- It does not have a primary role in the sensation or reflex of the posterior pharyngeal wall.
*Facial nerve*
- The **facial nerve (CN VII)** is responsible for the **muscles of facial expression**, taste from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, and parasympathetic innervation to several glands.
- While it contributes to some aspects of swallowing, it is not the main sensory nerve for the gag reflex from the posterior pharynx.
*Vagus*
- The **vagus nerve (CN X)** provides the efferent limb of the gag reflex, causing pharyngeal muscle contraction.
- However, the sensory input from the posterior pharynx (the afferent limb being tested by the probe) is primarily carried by the **glossopharyngeal nerve**.
*Hypoglossal nerve*
- The **hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)** provides motor innervation to the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue.
- While it is relevant in skull base trauma, it does not mediate sensation from the pharynx or the gag reflex being tested in the image.
Skull and cranial cavity US Medical PG Question 9: A 28-year-old man comes to the physician because of a persistent tingling sensation in the right side of his face. The sensation began after he underwent an extraction of an impacted molar 2 weeks ago. Examination shows decreased sensation of the skin over the right side of the mandible, chin, and the anterior portion of the tongue. Taste sensation is preserved. The affected nerve exits the skull through which of the following openings?
- A. Foramen rotundum
- B. Hypoglossal canal
- C. Foramen magnum
- D. Foramen ovale (Correct Answer)
- E. Stylomastoid foramen
Skull and cranial cavity Explanation: ***Foramen ovale***
- This patient presents with **paresthesia** in the distribution of branches of the **mandibular nerve (V3)** following molar extraction. The affected areas (mandible, chin, and anterior tongue sensation) indicate injury to the **inferior alveolar nerve** (lower teeth, chin, lower lip) and/or **lingual nerve** (general sensation to anterior 2/3 of tongue).
- Both the **inferior alveolar nerve** and **lingual nerve** are branches of the **mandibular nerve (V3)**, which exits the skull through the **foramen ovale**. These nerves run in close proximity during molar extraction and are commonly injured together.
- Taste sensation is preserved because the **chorda tympani** (taste fibers from CN VII) travels with the lingual nerve but does not exit through foramen ovale.
*Foramen rotundum*
- The **foramen rotundum** transmits the **maxillary nerve (V2)**, which innervates the midface, upper teeth, and palate.
- Injury to this nerve would cause sensory deficits in the upper lip and cheek, not the mandible or chin.
*Hypoglossal canal*
- The **hypoglossal canal** transmits the **hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)**, which is a motor nerve to the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue.
- Damage to this nerve would result in **tongue weakness** or **atrophy**, not sensory changes to the face or tongue.
*Foramen magnum*
- The **foramen magnum** is the largest opening in the skull, transmitting the **spinal cord**, vertebral arteries, and accessory nerve (CN XI).
- Damage here would likely involve severe neurological deficits, not isolated sensory loss to the lower face.
*Stylomastoid foramen*
- The **stylomastoid foramen** transmits the **facial nerve (CN VII)**, which is primarily responsible for facial expression and taste sensation to the anterior two-thirds of the tongue via the chorda tympani.
- While CN VII provides taste to the tongue, it does not provide general sensory innervation to the skin of the mandible or chin, and taste is preserved in this patient.
Skull and cranial cavity US Medical PG Question 10: Where does the only cranial nerve without a thalamic relay nucleus enter the skull?
- A. Superior orbital fissure
- B. Internal auditory meatus
- C. Foramen rotundum
- D. Jugular foramen
- E. Cribriform plate (Correct Answer)
Skull and cranial cavity Explanation: ***Cribriform plate***
- The **olfactory nerve (CN I)** is the only cranial nerve that does not have a thalamic relay nucleus before reaching the cerebral cortex.
- It passes through the **cribriform plate** of the ethmoid bone to reach the olfactory bulbs.
*Superior orbital fissure*
- This opening transmits the **oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), ophthalmic division of trigeminal (CN V1)**, and **abducens (CN VI)** nerves.
- These nerves all have sensory or motor components that relay through the thalamus, directly or indirectly.
*Internal auditory meatus*
- This canal transmits the **facial (CN VII)** and **vestibulocochlear (CN VIII)** nerves.
- The vestibulocochlear nerve's auditory pathway involves a thalamic relay in the **medial geniculate nucleus**.
*Foramen rotundum*
- The **maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V2)** passes through the foramen rotundum.
- Sensory information carried by CN V2 relays through the **thalamus**.
*Jugular foramen*
- This opening transmits the **glossopharyngeal (CN IX), vagus (CN X)**, and **accessory (CN XI)** nerves.
- Sensory components of these nerves, particularly taste and visceral sensation, involve thalamic nuclei.
More Skull and cranial cavity US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.