Oral cavity and pharynx US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Oral cavity and pharynx. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Oral cavity and pharynx US Medical PG Question 1: An otherwise healthy 58-year-old man comes to the physician because of a 1-year history of episodic coughing whenever he cleans his left ear. There is no history of hearing loss, tinnitus, or vertigo. Stimulating his left ear canal with a cotton swab triggers a bout of coughing. The physician informs him that these symptoms are caused by hypersensitivity of a cranial nerve. A peripheral lesion of this nerve is most likely to manifest with which of the following findings on physical examination?
- A. Ipsilateral sensorineural hearing loss
- B. Ipsilateral deviation of the tongue
- C. Inability to raise ipsilateral eyebrow
- D. Decreased secretion from ipsilateral sublingual gland
- E. Ipsilateral vocal cord palsy (Correct Answer)
Oral cavity and pharynx Explanation: ***Ipsilateral vocal cord palsy***
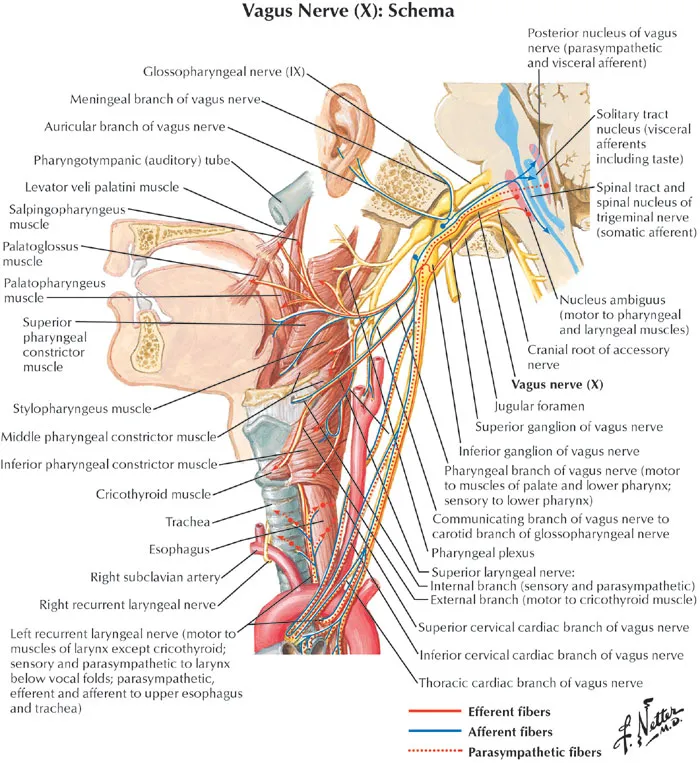
- The sensation in the external auditory canal that triggers a cough reflex is mediated by the **auricular branch of the vagus nerve (CN X)**, also known as Arnold's nerve.
- A peripheral lesion of the vagus nerve would most likely affect its motor functions, including the innervation of the **larynx**, leading to **ipsilateral vocal cord palsy** and hoarseness.
*Ipsilateral sensorineural hearing loss*
- Hearing loss is primarily associated with pathology of the **vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)**, not the vagus nerve.
- The patient's presentation does not describe any auditory symptoms.
*Ipsilateral deviation of the tongue*
- Tongue deviation is a sign of compromise of the **hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)**, which controls the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue.
- This is not a function of the vagus nerve.
*Inability to raise ipsilateral eyebrow*
- The ability to raise the eyebrow is controlled by the **facial nerve (CN VII)**, which innervates the muscles of facial expression.
- Vagus nerve lesions do not typically present with facial weakness.
*Decreased secretion from ipsilateral sublingual gland*
- Secretion from the sublingual gland is controlled by the **facial nerve (CN VII)** via the submandibular ganglion.
- While the vagus nerve has autonomic functions, it does not directly control sublingual gland secretion.
Oral cavity and pharynx US Medical PG Question 2: An otherwise healthy 45-year-old man comes to the physician because of a painful ulcer on his tongue for 3 days. Examination shows a shallow, tender 5-mm wide ulcer on the lateral aspect of the tongue, adjacent to his left first molar. There is no induration surrounding the ulcer or cervical lymphadenopathy. A lesion of the cranial nerve responsible for the transmission of pain from this ulcer would most likely result in which of the following?
- A. Loss of taste from the supraglottic region
- B. Lateral deviation of the tongue
- C. Inability to wrinkle the forehead
- D. Decreased sensation in the upper lip
- E. Loss of sensation in the anterior two-thirds of the tongue (Correct Answer)
Oral cavity and pharynx Explanation: ***Loss of sensation in the anterior two-thirds of the tongue***
- The sensation of pain from the **anterior two-thirds of the tongue** is transmitted by the **lingual nerve**, which is a branch of the mandibular division (V3) of the **trigeminal nerve**. A lesion affecting this nerve would therefore cause loss of sensation in this region.
- The ulcer is located on the **lateral aspect of the tongue**, placing it within the distribution of the lingual nerve.
*Loss of taste from the supraglottic region*
- **Taste sensation** from the **supraglottic region** and epiglottis is primarily mediated by the **superior laryngeal nerve** (a branch of the vagus nerve, CN X), not the nerve responsible for pain sensation from the anterior tongue.
- A lesion of the lingual nerve would affect taste sensation from the **anterior two-thirds of the tongue** (carried by the chorda tympani, a branch of CN VII, which joins the lingual nerve), but not the supraglottic region.
*Lateral deviation of the tongue*
- **Lateral deviation of the tongue** (towards the side of the lesion) occurs due to damage to the **hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)**, which innervates the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue.
- This is a motor deficit, whereas the question describes a sensory issue related to pain transmission from an ulcer on the tongue.
*Inability to wrinkle the forehead*
- The **inability to wrinkle the forehead** (along with other facial expressions) results from damage to the **facial nerve (CN VII)**, specifically its temporal branch.
- This is a motor deficit affecting the muscles of facial expression, unrelated to pain sensation from the tongue.
*Decreased sensation in the upper lip*
- **Sensation in the upper lip** is supplied by the **infraorbital nerve**, a branch of the maxillary division (V2) of the **trigeminal nerve**.
- A lesion affecting the nerve responsible for pain from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue (lingual nerve, V3) would not directly impact sensation in the upper lip.
Oral cavity and pharynx US Medical PG Question 3: A 45-year-old male patient presents with difficulty swallowing and hoarseness that has progressively worsened over the past month. During physical examination, the physician notices that the patient's left vocal cord is paralyzed. The paralysis is most likely due to compression of which of the following nerves?
- A. Left superior laryngeal nerve
- B. Left vagus nerve
- C. Right recurrent laryngeal nerve
- D. Left recurrent laryngeal nerve (Correct Answer)
Oral cavity and pharynx Explanation: ***Left recurrent laryngeal nerve***
- The **left recurrent laryngeal nerve** innervates all intrinsic muscles of the left larynx, except the cricothyroid muscle [1].
- Damage or compression of this nerve leads to **left vocal cord paralysis** and associated symptoms like hoarseness and difficulty swallowing (dysphagia).
*Left superior laryngeal nerve*
- The **superior laryngeal nerve** innervates the cricothyroid muscle, which is responsible for tensing the vocal cords.
- Damage to this nerve primarily affects **pitch control** and would not typically cause complete vocal cord paralysis.
*Left vagus nerve*
- The **vagus nerve** gives rise to both the superior and recurrent laryngeal nerves [1].
- While damage to the main vagus nerve would cause vocal cord paralysis, the more specific finding of isolated vocal cord paralysis points to an issue with its branch, the recurrent laryngeal nerve [1].
*Right recurrent laryngeal nerve*
- The **right recurrent laryngeal nerve** controls the intrinsic muscles of the right larynx.
- Damage to this nerve would result in **right vocal cord paralysis**, not left vocal cord paralysis as described in the patient.
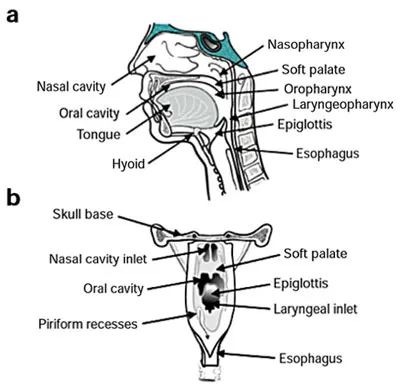
Oral cavity and pharynx US Medical PG Question 4: A 50-year-old man is brought in by ambulance to the emergency department with difficulty breathing and speaking. His wife reports that he might have swallowed a fishbone. While taking his history the patient develops a paroxysmal cough. Visualization of his oropharynx and larynx shows a fishbone lodged in the right piriform recess. After successfully removing the fishbone the patient feels comfortable, but he is not able to cough like before. Damage to which of the following nerves is responsible for the impaired cough reflex in this patient?
- A. Inferior laryngeal nerve
- B. Internal laryngeal nerve (Correct Answer)
- C. External laryngeal nerve
- D. Superior laryngeal nerve
- E. Recurrent laryngeal nerve
Oral cavity and pharynx Explanation: ***Internal laryngeal nerve***
- The internal laryngeal nerve is the **sensory nerve** of the larynx above the vocal cords, including the piriform recess. Damage to this nerve, often due to trauma from a foreign body like a fishbone, impairs the **afferent limb of the cough reflex**.
- A fishbone lodged in the **piriform recess** directly implicates the sensory function of the internal laryngeal nerve, explaining the subsequent loss of the cough reflex even after removal of the foreign body.
*Inferior laryngeal nerve*
- This nerve is primarily **motor** to almost all intrinsic laryngeal muscles and provides **sensory innervation** below the vocal folds. Damage would primarily affect phonation (hoarseness) or breathing due to vocal cord paralysis.
- It would not directly affect the sensory input initiating a cough reflex from the piriform recess, which is above the vocal folds.
*External laryngeal nerve*
- The external laryngeal nerve is a **motor nerve** supplying the **cricothyroid muscle**, which is responsible for tensing the vocal cords and altering voice pitch.
- Damage to this nerve would lead to **hoarseness** and difficulty with high-pitched sounds, not an impaired cough reflex from the piriform recess.
*Superior laryngeal nerve*
- The superior laryngeal nerve divides into the internal and external laryngeal nerves. While it contains sensory fibers that lead to the internal laryngeal nerve, stating damage to the entire superior laryngeal nerve is less specific than identifying the internal laryngeal nerve as the direct cause of the sensory deficit.
- Damage to the superior laryngeal nerve would encompass both sensory and motor deficits (internal and external branches), but the specific symptom of impaired cough reflex primarily points to the internal laryngeal branch.
*Recurrent laryngeal nerve*
- This nerve is another name for the **inferior laryngeal nerve** and is primarily **motor** to the intrinsic laryngeal muscles (except cricothyroid) and provides sensory innervation below the vocal cords.
- Damage to this nerve primarily results in **vocal cord paralysis** and voice changes (hoarseness), not the sensory loss affecting the cough reflex from the piriform recess.
Oral cavity and pharynx US Medical PG Question 5: A 45-year-old patient presents with difficulty speaking and swallowing following a stroke. MRI reveals an infarct in the medulla. Which of the following cranial nerve nuclei is most likely affected?
- A. Vestibulocochlear nucleus
- B. Trigeminal nerve nucleus
- C. Facial nerve nucleus
- D. Nucleus ambiguus (Correct Answer)
Oral cavity and pharynx Explanation: ***Nucleus ambiguus***
- The **nucleus ambiguus** is located in the **medulla** and contains motor neurons that innervate muscles involved in **speaking** and **swallowing**, specifically those of the pharynx, larynx, and soft palate via cranial nerves IX, X, and XI [1].
- An infarct in the medulla causing difficulty speaking and swallowing strongly implicates damage to this nucleus, leading to **dysarthria** and **dysphagia** [1].
*Vestibulocochlear nucleus*
- This nucleus is primarily involved in **hearing** and **balance**, which would manifest as dizziness, hearing loss, or nystagmus, not directly difficulty speaking and swallowing.
- While located in the brainstem, damage to this nucleus typically does not cause the specific symptoms of dysarthria and dysphagia described.
*Trigeminal nerve nucleus*
- The trigeminal nerve is responsible for sensory innervation of the face, and motor innervation for **mastication** (chewing).
- Damage would primarily affect facial sensation or jaw movement, not the act of deglutition or phonation.
*Facial nerve nucleus*
- This nucleus, located in the **pons**, controls the muscles of **facial expression** and taste for the anterior two-thirds of the tongue.
- Damage would lead to facial weakness or paralysis, not the profound difficulty with speaking and swallowing affecting pharyngeal and laryngeal function.
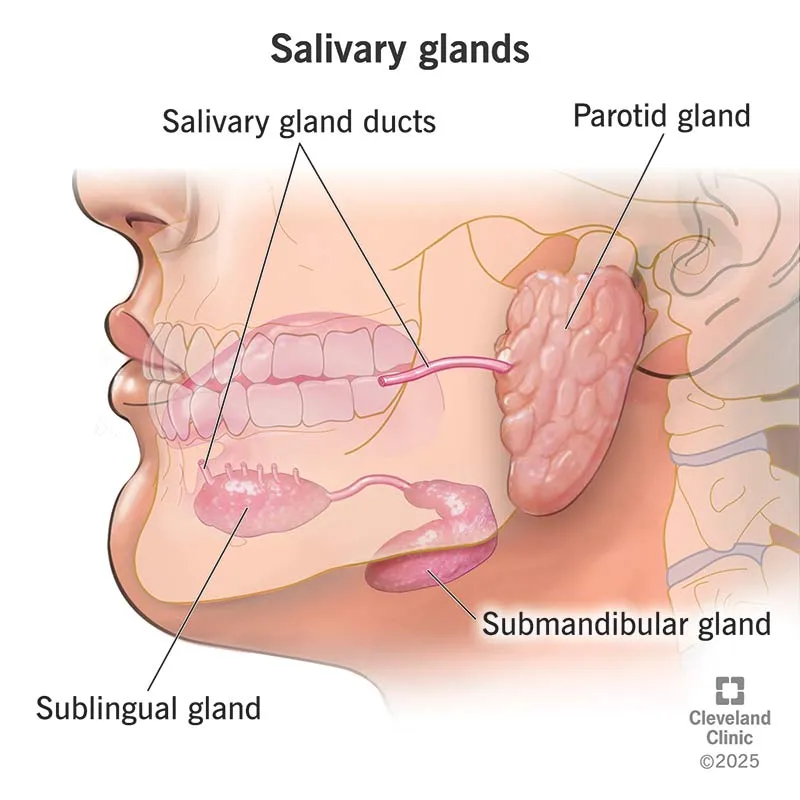
Oral cavity and pharynx US Medical PG Question 6: A 55-year-old woman with a 1-year history of left-sided tinnitus is diagnosed with a tumor at the left cerebellopontine angle affecting the glossopharyngeal nerve. Sialometry shows decreased production of saliva from the left parotid gland. The finding on sialometry is best explained by a lesion of the nerve that is also responsible for which of the following?
- A. Protrusion of the tongue
- B. Afferent limb of the cough reflex
- C. Afferent limb of the gag reflex (Correct Answer)
- D. Equilibrium and balance
- E. Taste sensation of tip of the tongue
Oral cavity and pharynx Explanation: ***Afferent limb of the gag reflex***
- The **glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)** provides **parasympathetic innervation** to the **parotid gland**, explaining the decreased saliva production on sialometry.
- CN IX is also responsible for the **afferent limb of the gag reflex** and taste sensation from the posterior one-third of the tongue.
*Protrusion of the tongue*
- **Protrusion of the tongue** is primarily controlled by the **hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)**.
- A lesion affecting the glossopharyngeal nerve would not directly impact the ability to protrude the tongue.
*Afferent limb of the cough reflex*
- The **afferent limb of the cough reflex** is primarily mediated by the **vagus nerve (CN X)**, which innervates the laryngeal and tracheobronchial mucosa.
- While there can be some overlap, the glossopharyngeal nerve is not the primary mediator for this reflex.
*Equilibrium and balance*
- **Equilibrium and balance** are primarily maintained by the **vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)**, which is responsible for transmitting vestibular information.
- A lesion of the glossopharyngeal nerve would not primarily affect these functions, although cerebellopontine angle tumors can affect CN VIII.
*Taste sensation of tip of the tongue*
- **Taste sensation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue** (including the tip) is conveyed by the **facial nerve (CN VII)** via the chorda tympani.
- The glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX) provides taste sensation to the posterior one-third of the tongue.
Oral cavity and pharynx US Medical PG Question 7: Where does the only cranial nerve without a thalamic relay nucleus enter the skull?
- A. Superior orbital fissure
- B. Internal auditory meatus
- C. Foramen rotundum
- D. Jugular foramen
- E. Cribriform plate (Correct Answer)
Oral cavity and pharynx Explanation: ***Cribriform plate***
- The **olfactory nerve (CN I)** is the only cranial nerve that does not have a thalamic relay nucleus before reaching the cerebral cortex.
- It passes through the **cribriform plate** of the ethmoid bone to reach the olfactory bulbs.
*Superior orbital fissure*
- This opening transmits the **oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), ophthalmic division of trigeminal (CN V1)**, and **abducens (CN VI)** nerves.
- These nerves all have sensory or motor components that relay through the thalamus, directly or indirectly.
*Internal auditory meatus*
- This canal transmits the **facial (CN VII)** and **vestibulocochlear (CN VIII)** nerves.
- The vestibulocochlear nerve's auditory pathway involves a thalamic relay in the **medial geniculate nucleus**.
*Foramen rotundum*
- The **maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V2)** passes through the foramen rotundum.
- Sensory information carried by CN V2 relays through the **thalamus**.
*Jugular foramen*
- This opening transmits the **glossopharyngeal (CN IX), vagus (CN X)**, and **accessory (CN XI)** nerves.
- Sensory components of these nerves, particularly taste and visceral sensation, involve thalamic nuclei.
Oral cavity and pharynx US Medical PG Question 8: A 61-year-old man sustains an intracranial injury to a nerve that also passes through the parotid gland. Which of the following is a possible consequence of this injury?
- A. Changes in hearing (Correct Answer)
- B. Horner's syndrome
- C. Paralysis of lateral rectus muscle
- D. Loss of taste from posterior 1/3 of tongue
- E. Loss of general sensation in anterior 2/3 of tongue
Oral cavity and pharynx Explanation: ***Changes in hearing***
- The **facial nerve (CN VII)** is the only cranial nerve that has both an **intracranial course** and passes **through the parotid gland**.
- The facial nerve gives off the **nerve to stapedius muscle** within the facial canal (before it exits the stylomastoid foramen).
- Damage to this nerve can lead to **hyperacusis** (increased sensitivity to sound), as the stapedius normally dampens excessive sound vibrations.
- **Note**: Facial nerve injury would also cause facial paralysis (the most prominent feature), loss of taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue via chorda tympani, and decreased lacrimation/salivation, but these are not among the answer choices.
*Horner's syndrome*
- This syndrome results from damage to the **sympathetic pathway** (hypothalamus → spinal cord → superior cervical ganglion → eye).
- Characterized by **ptosis**, **miosis**, and **anhidrosis**.
- Not related to facial nerve injury.
*Paralysis of lateral rectus muscle*
- The **lateral rectus muscle** is innervated by the **abducens nerve (CN VI)**.
- CN VI does not pass through the parotid gland.
*Loss of taste from posterior 1/3 of tongue*
- Taste from the **posterior 1/3 of the tongue** is carried by the **glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)**.
- CN IX does not pass through the parotid gland.
- **Note**: The facial nerve actually carries taste from the **anterior 2/3** of the tongue via the chorda tympani branch.
*Loss of general sensation in anterior 2/3 of tongue*
- **General sensation** (touch, pain, temperature) from the **anterior 2/3 of the tongue** is carried by the **lingual nerve** (branch of CN V3).
- The lingual nerve does not pass through the parotid gland.
Oral cavity and pharynx US Medical PG Question 9: A 28-year-old man comes to the physician because of a persistent tingling sensation in the right side of his face. The sensation began after he underwent an extraction of an impacted molar 2 weeks ago. Examination shows decreased sensation of the skin over the right side of the mandible, chin, and the anterior portion of the tongue. Taste sensation is preserved. The affected nerve exits the skull through which of the following openings?
- A. Foramen rotundum
- B. Hypoglossal canal
- C. Foramen magnum
- D. Foramen ovale (Correct Answer)
- E. Stylomastoid foramen
Oral cavity and pharynx Explanation: ***Foramen ovale***
- This patient presents with **paresthesia** in the distribution of branches of the **mandibular nerve (V3)** following molar extraction. The affected areas (mandible, chin, and anterior tongue sensation) indicate injury to the **inferior alveolar nerve** (lower teeth, chin, lower lip) and/or **lingual nerve** (general sensation to anterior 2/3 of tongue).
- Both the **inferior alveolar nerve** and **lingual nerve** are branches of the **mandibular nerve (V3)**, which exits the skull through the **foramen ovale**. These nerves run in close proximity during molar extraction and are commonly injured together.
- Taste sensation is preserved because the **chorda tympani** (taste fibers from CN VII) travels with the lingual nerve but does not exit through foramen ovale.
*Foramen rotundum*
- The **foramen rotundum** transmits the **maxillary nerve (V2)**, which innervates the midface, upper teeth, and palate.
- Injury to this nerve would cause sensory deficits in the upper lip and cheek, not the mandible or chin.
*Hypoglossal canal*
- The **hypoglossal canal** transmits the **hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)**, which is a motor nerve to the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue.
- Damage to this nerve would result in **tongue weakness** or **atrophy**, not sensory changes to the face or tongue.
*Foramen magnum*
- The **foramen magnum** is the largest opening in the skull, transmitting the **spinal cord**, vertebral arteries, and accessory nerve (CN XI).
- Damage here would likely involve severe neurological deficits, not isolated sensory loss to the lower face.
*Stylomastoid foramen*
- The **stylomastoid foramen** transmits the **facial nerve (CN VII)**, which is primarily responsible for facial expression and taste sensation to the anterior two-thirds of the tongue via the chorda tympani.
- While CN VII provides taste to the tongue, it does not provide general sensory innervation to the skin of the mandible or chin, and taste is preserved in this patient.
Oral cavity and pharynx US Medical PG Question 10: A 25-year-old man presents to the clinic with a midline swelling in his neck. He is unsure about when it appeared. He denies any difficulty with swallowing or hoarseness. His past medical history is insignificant. On physical examination, there is a 1 cm x 2 cm firm mildly tender nodule on the anterior midline aspect of the neck which moves with deglutition and elevates with protrusion of the tongue. Which of the following is the most likely embryologic origin of the nodule in this patient?
- A. Midline endoderm of the pharynx (Correct Answer)
- B. 1st and 2nd pharyngeal arch
- C. The branchial cleft
- D. 4th pharyngeal arch
- E. 4th pharyngeal pouch
Oral cavity and pharynx Explanation: ***Midline endoderm of the pharynx***
- The symptoms described, particularly a midline neck swelling that **moves with deglutition** and **elevates with tongue protrusion**, are classic for a **thyroglossal duct cyst**.
- Thyroglossal duct cysts arise from remnants of the **thyroglossal duct**, an embryonic structure that forms from the **midline endoderm of the pharyngeal floor** and descends to form the thyroid gland.
*1st and 2nd pharyngeal arch*
- The 1st and 2nd pharyngeal arches primarily contribute to the formation of structures in the **mandible**, **maxilla**, **middle ear**, and **hyoid bone**.
- Abnormalities in these arches typically lead to conditions like **Treacher Collins syndrome** or **Pierre Robin sequence**, not midline neck cysts with these specific movement characteristics.
*The branchial cleft*
- **Branchial cleft cysts** typically present as **lateral neck masses**, often anterior to the sternocleidomastoid muscle, and usually do not move with deglutition or tongue protrusion.
- They arise from incomplete obliteration of **pharyngeal clefts**, which are ectodermal structures.
*4th pharyngeal arch*
- The 4th pharyngeal arch contributes to the formation of the **cricothyroid muscle**, part of the **pharynx**, and the **laryngeal cartilages**.
- Anomalies of the 4th pharyngeal arch are rare and typically involve **vascular structures** or **recurrent laryngeal nerve** abnormalities, not midline neck cysts.
*4th pharyngeal pouch*
- The 4th pharyngeal pouch contributes to the development of the **superior parathyroid glands** and the **ultimobranchial body** (which gives rise to parafollicular C cells of the thyroid).
- Malformations of this pouch are associated with parathyroid and thyroid conditions, not midline thyroglossal duct cysts.
More Oral cavity and pharynx US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.