Cervical sympathetic chain US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Cervical sympathetic chain. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Cervical sympathetic chain US Medical PG Question 1: A 69-year-old man undergoes modified radical neck dissection for an oropharyngeal tumor. During the procedure, he requires multiple blood transfusions. Four hours after the surgery, examination shows that the right and left pupils do not constrict when a light is shone into the left eye. When light is shone into the right eye, both pupils constrict. Fundoscopic examination shows no abnormalities. Which of the following is the most likely location of the lesion?
- A. Ciliary ganglion
- B. Pretectal nuclei
- C. Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- D. Optic nerve (Correct Answer)
- E. Superior cervical ganglion
Cervical sympathetic chain Explanation: ***Optic nerve***
- The finding that pupils **do not constrict** when light is shone into the left eye (afferent defect) but both pupils constrict when light is shone into the right eye (intact efferent pathway) indicates a lesion in the **afferent limb** of the pupillary light reflex on the left side.
- The **optic nerve** (cranial nerve II) transmits afferent signals from the retina to the brainstem. A lesion here prevents the signal from reaching the pretectal nuclei, thus bilateral pupillary constriction does not occur when the affected eye is stimulated.
*Ciliary ganglion*
- A lesion in the **ciliary ganglion** would affect the **efferent pathway** of pupillary constriction, typically leading to a dilated, unreactive pupil (e.g., Adie's tonic pupil).
- This would mean that the affected pupil would not constrict when *either* eye is stimulated, which is not consistent with the described findings.
*Pretectal nuclei*
- The **pretectal nuclei** receive afferent input from both optic tracts and project to the Edinger-Westphal nuclei, mediating the consensual light reflex.
- A lesion here would typically affect both direct and consensual light reflexes, or cause selective deficits not limited to a single afferent pathway.
*Edinger-Westphal nucleus*
- The **Edinger-Westphal nucleus** is the parasympathetic nucleus of the oculomotor nerve (CN III) and controls pupillary constriction.
- A lesion would disrupt the **efferent pathway** unilaterally or bilaterally, leading to a fixed, dilated pupil.
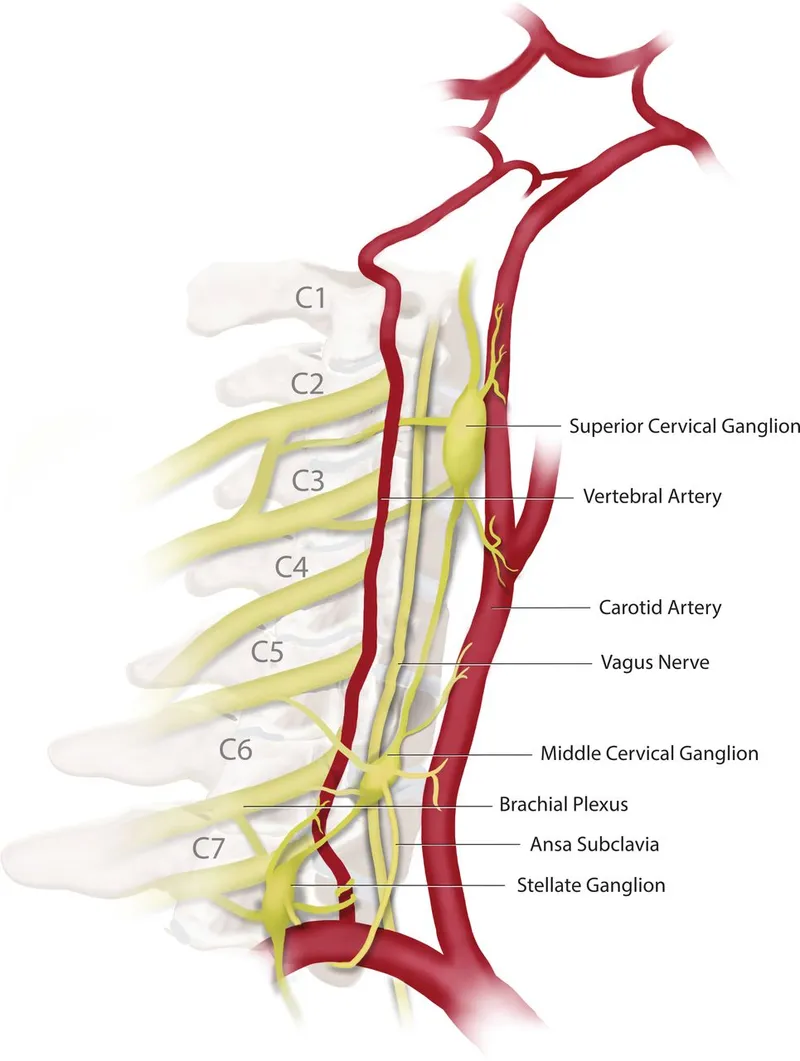
*Superior cervical ganglion*
- Lesions of the **superior cervical ganglion** affect the **sympathetic pathway** to the eye, resulting in **Horner's syndrome** (miosis, ptosis, anhidrosis).
- This would cause a miotic (constricted) pupil, not the failure of constriction described in the scenario.
Cervical sympathetic chain US Medical PG Question 2: A 45-year-old man is brought to the emergency department by ambulance after a motor vehicle collision. He is not responsive to verbal commands and is unable to provide any history. His pulse is 108/min and regular. Physical examination shows ecchymoses over the neck and back. Neurological examination indicates damage to the spinal cord at the level shown in the illustration. This patient's injury is most likely located at which of the following levels of the spinal cord?
- A. C2
- B. S2
- C. L4
- D. T6 (Correct Answer)
- E. S4
Cervical sympathetic chain Explanation: ***T6***
- The correct answer depends on identifying the spinal cord level shown in the illustration (cross-sectional anatomy).
- Injury at **T6** (mid-thoracic level) can present with:
- **Paraplegia** with loss of lower extremity function
- **Sensory level** at approximately the xiphoid process (T6 dermatome)
- Risk of **autonomic dysreflexia** if injury is complete (occurs with injuries at or above T6)
- Preserved upper extremity function and respiratory capacity
- The mid-thoracic spinal cord cross-section would show the characteristic butterfly-shaped gray matter with surrounding white matter tracts.
*C2*
- **C2** injury is a high cervical lesion that would result in:
- **Quadriplegia** (tetraplegia) affecting all four extremities
- Severe **respiratory compromise** requiring mechanical ventilation (phrenic nerve C3-C5)
- High mortality if untreated
- Cross-sectional anatomy at C2 shows enlarged gray matter for upper limb innervation.
*S2*
- **S2** injury is at the level of the conus medullaris/cauda equina and would cause:
- **Bowel and bladder dysfunction** (loss of parasympathetic control)
- **Saddle anesthesia** (loss of perineal sensation)
- Possible lower extremity weakness
- No significant autonomic instability
- Would not explain the clinical presentation in the upper body.
*L4*
- **L4** injury affects the lumbar enlargement and would cause:
- **Lower extremity weakness** (quadriceps, tibialis anterior)
- **Diminished patellar reflex**
- Sensory loss in the medial leg and foot
- Bowel/bladder may be affected
- Cross-section shows prominent gray matter for lower limb innervation.
*S4*
- **S4** is the lowest sacral level and injury would cause:
- Very limited dysfunction: **anal sphincter weakness**
- **Loss of anocutaneous reflex**
- Minimal motor or sensory deficits elsewhere
- Would not cause systemic neurological compromise.
Cervical sympathetic chain US Medical PG Question 3: A 72-year-old man presents to his primary care physician because he feels like his vision has been changing over the last 6 months. In particular, he feels that he cannot see as well out of his right eye as previously. His past medical history is significant for myocardial infarction as well as Lyme disease. On presentation, he is found to have a droopy right eyelid as well as persistent constriction of his right pupil. Additionally, the skin on his right half of his face is found to be cracked and dry. Which of the following is most likely associated with this patient's symptoms?
- A. Oculomotor nerve damage
- B. Drug use
- C. Syphilis
- D. Facial nerve damage
- E. Pancoast tumor (Correct Answer)
Cervical sympathetic chain Explanation: ***Pancoast tumor***
- The patient's symptoms (droopy eyelid, constricted pupil, and dry skin on one side of the face) are classic for **Horner's syndrome**, which results from damage to the **sympathetic nerves** to the eye and face.
- A **Pancoast tumor** (a tumor in the apex of the lung) can compress the **sympathetic chain** in the neck/chest, leading to Horner's syndrome.
*Oculomotor nerve damage*
- Oculomotor nerve damage would typically cause a **dilated pupil** (due to unopposed sympathetic innervation) and **ptosis** (drooping eyelid), but not miosis (constricted pupil) or anhidrosis (dry skin).
- The patient's **constricted pupil** points away from oculomotor nerve involvement.
*Drug use*
- While certain drugs can affect pupil size (e.g., opiates cause miosis), drug use alone is unlikely to explain the entire triad of **Horner's syndrome** (ptosis, miosis, anhidrosis) in combination with the focal neurological findings.
- No other information in the vignette suggests drug use.
*Syphilis*
- **Neurosyphilis** can cause pupillary abnormalities, such as **Argyll Robertson pupils** (small, irregular pupils that accommodate but do not react to light).
- However, it typically does not present with the specific combination of ptosis, miosis, and anhidrosis characteristic of Horner's syndrome.
*Facial nerve damage*
- **Facial nerve damage** (e.g., Bell's palsy) affects the muscles of **facial expression** and could cause ipsilateral facial weakness or droop.
- It would not cause pupillary changes or anhidrosis, as these symptoms are related to the sympathetic nervous system and superior cervical ganglion, not the facial nerve.
Cervical sympathetic chain US Medical PG Question 4: A 65-year-old female with a past medical history of hypertension presents to her primary care doctor with a 3 month history of spasmodic facial pain. The pain is located in her right cheek and seems to be triggered when she smiles, chews, or brushes her teeth. The pain is sharp and excruciating, lasts for a few seconds, and occurs up to twenty times per day. She denies headaches, blurry vision, facial weakness, or changes in her memory. She feels rather debilitated and has modified much of her daily activities to avoid triggering the spasms. In the clinic, her physical exam is within normal limits. Her primary care doctor prescribes carbamazepine and asks her to follow up in a few weeks. Which cranial nerve is most likely involved in the patient's disease process?
- A. CN III
- B. CN V (Correct Answer)
- C. CN VI
- D. CN VII
- E. CN IV
Cervical sympathetic chain Explanation: ***CN V***
- The patient's presentation of **recurrent, sharp, excruciating, unilateral facial pain** triggered by movements like chewing, smiling, or brushing teeth is classic for **trigeminal neuralgia**.
- **Trigeminal neuralgia** specifically affects the **trigeminal nerve (CN V)**, which has sensory branches covering the face, and is often treated with **carbamazepine**.
*CN III*
- The **oculomotor nerve (CN III)** is primarily involved in **eye movement** and **pupillary constriction**.
- Damage to CN III typically causes **diplopia, ptosis,** and **pupil dilation**, which are not present in this patient's symptoms.
*CN VI*
- The **abducens nerve (CN VI)** controls the **lateral rectus muscle**, responsible for **abducting the eye** (moving it outward).
- Dysfunction typically results in **diplopia** and an inability to move the eye laterally, not facial pain.
*CN VII*
- The **facial nerve (CN VII)** controls **facial expressions**, taste sensation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue, and lacrimation/salivation.
- While it innervates facial muscles, its involvement typically presents as **facial weakness** or **paralysis** (e.g., Bell's palsy), not sharp, spasmodic pain.
*CN IV*
- The **trochlear nerve (CN IV)** innervates the **superior oblique muscle**, which is involved in rotating and depressing the eye.
- Lesions usually lead to **vertical diplopia**, particularly when looking down and inward, which is unrelated to the described facial pain.
Cervical sympathetic chain US Medical PG Question 5: A 28-year-old man comes to the physician because of a persistent tingling sensation in the right side of his face. The sensation began after he underwent an extraction of an impacted molar 2 weeks ago. Examination shows decreased sensation of the skin over the right side of the mandible, chin, and the anterior portion of the tongue. Taste sensation is preserved. The affected nerve exits the skull through which of the following openings?
- A. Foramen rotundum
- B. Hypoglossal canal
- C. Foramen magnum
- D. Foramen ovale (Correct Answer)
- E. Stylomastoid foramen
Cervical sympathetic chain Explanation: ***Foramen ovale***
- This patient presents with **paresthesia** in the distribution of branches of the **mandibular nerve (V3)** following molar extraction. The affected areas (mandible, chin, and anterior tongue sensation) indicate injury to the **inferior alveolar nerve** (lower teeth, chin, lower lip) and/or **lingual nerve** (general sensation to anterior 2/3 of tongue).
- Both the **inferior alveolar nerve** and **lingual nerve** are branches of the **mandibular nerve (V3)**, which exits the skull through the **foramen ovale**. These nerves run in close proximity during molar extraction and are commonly injured together.
- Taste sensation is preserved because the **chorda tympani** (taste fibers from CN VII) travels with the lingual nerve but does not exit through foramen ovale.
*Foramen rotundum*
- The **foramen rotundum** transmits the **maxillary nerve (V2)**, which innervates the midface, upper teeth, and palate.
- Injury to this nerve would cause sensory deficits in the upper lip and cheek, not the mandible or chin.
*Hypoglossal canal*
- The **hypoglossal canal** transmits the **hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)**, which is a motor nerve to the intrinsic and extrinsic muscles of the tongue.
- Damage to this nerve would result in **tongue weakness** or **atrophy**, not sensory changes to the face or tongue.
*Foramen magnum*
- The **foramen magnum** is the largest opening in the skull, transmitting the **spinal cord**, vertebral arteries, and accessory nerve (CN XI).
- Damage here would likely involve severe neurological deficits, not isolated sensory loss to the lower face.
*Stylomastoid foramen*
- The **stylomastoid foramen** transmits the **facial nerve (CN VII)**, which is primarily responsible for facial expression and taste sensation to the anterior two-thirds of the tongue via the chorda tympani.
- While CN VII provides taste to the tongue, it does not provide general sensory innervation to the skin of the mandible or chin, and taste is preserved in this patient.
Cervical sympathetic chain US Medical PG Question 6: A 68-year-old man comes to the physician because of double vision and unilateral right eye pain that began this morning. His vision improves when he covers either eye. He has hypertension, mild cognitive impairment, and type 2 diabetes mellitus. The patient has smoked two packs of cigarettes daily for 40 years. His current medications include lisinopril, donepezil, metformin, and insulin with meals. His temperature is 37°C (98.6°F), pulse is 85/minute, respirations are 12/minute, and blood pressure is 132/75 mm Hg. His right eye is abducted and depressed with slight intorsion. He can only minimally adduct the right eye. Visual acuity is 20/20 in both eyes. Extraocular movements of the left eye are normal. An MRI of the head shows no abnormalities. His fingerstick blood glucose concentration is 325 mg/dL. Further evaluation is most likely to show which of the following?
- A. Ptosis (Correct Answer)
- B. Dilated and fixed pupil
- C. Bitemporal hemianopsia
- D. Miosis and anhidrosis
- E. Positive swinging-flashlight test
Cervical sympathetic chain Explanation: ***Ptosis***
- The patient's presentation of an **abducted and depressed right eye with minimal adduction** is highly suggestive of an **ischemic (diabetic) third nerve palsy**.
- Ischemic third nerve palsies characteristically **spare the pupillary fibers** (pupil remains normal in size and reactive) but affect the **somatomotor fibers** that innervate the extraocular muscles and the **levator palpebrae superioris**, leading to **ptosis**.
- The key clinical feature distinguishing ischemic from compressive CN III palsy is **pupil-sparing**, which is present in this case.
*Dilated and fixed pupil*
- A dilated and fixed pupil would indicate **compression of the oculomotor nerve**, often by an aneurysm (e.g., posterior communicating artery aneurysm).
- Compressive lesions affect the superficial **pupillomotor fibers** first, while ischemic third nerve palsies, as seen in patients with **diabetes**, typically affect the inner somatomotor fibers while **sparing the pupil**.
*Bitemporal hemianopsia*
- This visual field defect is characteristic of **optic chiasm compression**, commonly caused by a **pituitary adenoma**.
- This patient's symptoms are localized to a single eye and involve extraocular muscle dysfunction, not visual field loss.
*Miosis and anhidrosis*
- **Miosis** (constricted pupil) and **anhidrosis** (decreased sweating) on one side of the face, accompanied by **ptosis**, are classic signs of **Horner syndrome**.
- Horner syndrome results from a lesion in the **sympathetic pathway**, which is inconsistent with the extraocular muscle deficits observed in this patient.
*Positive swinging-flashlight test*
- A positive swinging-flashlight test (Marcus Gunn pupil) indicates an **afferent pupillary defect**, often seen in conditions affecting the **optic nerve** (e.g., optic neuritis, severe retinal disease).
- This patient's symptoms point to a **cranial nerve III palsy**, which affects efferent ocular movements and typically does not cause an afferent pupillary defect.
Cervical sympathetic chain US Medical PG Question 7: A 39-year-old woman is brought to the emergency department following a stab wound to the neck. Per the patient, she was walking her dog when she got robbed and was subsequently stabbed with a knife. Vitals are stable. Strength examination reveals 2/5 right-sided elbow flexion and extension, wrist extension, and finger motions. Babinski sign is upward-going on the right. There is decreased sensation to light touch and vibration on the patient's right side up to her shoulder. She also reports decreased sensation to pinprick and temperature on her left side, including her lower extremities, posterior forearm, and middle finger. The patient's right pupil is 2 mm smaller than the left with drooping of the right upper eyelid. Which of the following is the most likely cause of the patient’s presentation?
- A. Hemisection injury (Correct Answer)
- B. Syringomyelia
- C. Anterior cord syndrome
- D. Posterior cord syndrome
- E. Central cord syndrome
Cervical sympathetic chain Explanation: ***Hemisection injury***
- The combination of **ipsilateral motor weakness** and **dorsal column deficits** (vibration, light touch) along with **contralateral loss of pain and temperature sensation** (spinothalamic tract) is the hallmark of a Brown-Séquard syndrome, which results from a hemisection injury to the spinal cord.
- The presence of **ipsilateral Horner's syndrome** (miosis and ptosis) indicates sympathetic nerve damage, further localizing the injury to the cervical spinal cord and supporting a hemisection.
*Syringomyelia*
- This condition is characterized by a **cavity (syrinx)** within the spinal cord, typically leading to a **cape-like distribution of pain and temperature loss** due to damage to the decussating spinothalamic fibers.
- It usually spares the dorsal columns and motor tracts in early stages, which contradicts the described ipsilateral motor and dorsal column deficits.
*Anterior cord syndrome*
- Results from damage to the **anterior spinal artery**, leading to **bilateral loss of motor function** (corticospinal tracts) and **pain/temperature sensation** (spinothalamic tracts) below the level of injury.
- **Proprioception and vibration sensation** (dorsal columns) are typically preserved in this syndrome, which is inconsistent with the patient's presentation.
*Posterior cord syndrome*
- Involves damage primarily to the **dorsal columns**, resulting in **loss of proprioception, vibration, and light touch** below the level of injury.
- **Motor function, pain, and temperature sensation** are generally preserved, which is not consistent with the motor deficits and contralateral pain/temperature loss described.
*Central cord syndrome*
- Most commonly seen after **hyperextension injuries**, leading to greater **motor weakness in the upper extremities** than the lower extremities.
- It typically causes varying degrees of **sensory loss** and can preserve sacral sensation, but the specific pattern of ipsilateral motor/dorsal column deficits and contralateral spinothalamic loss is not characteristic of central cord syndrome.
Cervical sympathetic chain US Medical PG Question 8: Impaired gag reflex is seen due to a lesion in which cranial nerves?
- A. CN V&VI
- B. CN X & XI
- C. CN IX & X (Correct Answer)
- D. CN VII & VIII
- E. CN XI & XII
Cervical sympathetic chain Explanation: ***Correct: CN IX & X***
The **gag reflex (pharyngeal reflex)** is a protective reflex involving two cranial nerves:
- **Afferent limb**: **CN IX (Glossopharyngeal nerve)** provides sensory innervation to the posterior third of the tongue, oropharynx, and pharyngeal walls
- **Efferent limb**: **CN X (Vagus nerve)** provides motor innervation to the pharyngeal muscles (via the pharyngeal plexus) that contract during the reflex
**Clinical correlation**: Testing the gag reflex helps assess brainstem function and the integrity of CN IX and X. Impairment suggests lesions affecting these nerves or their nuclei in the medulla.
*Incorrect: CN V & VI*
- CN V (Trigeminal) provides facial sensation and motor to muscles of mastication, not involved in gag reflex
- CN VI (Abducens) controls lateral rectus muscle for eye abduction
*Incorrect: CN X & XI*
- While CN X is involved, CN XI (Accessory nerve) innervates sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles, not pharyngeal muscles
*Incorrect: CN VII & VIII*
- CN VII (Facial) controls facial expression and taste from anterior 2/3 of tongue
- CN VIII (Vestibulocochlear) is involved in hearing and balance, not the gag reflex
*Incorrect: CN XI & XII*
- CN XI (Accessory) innervates SCM and trapezius
- CN XII (Hypoglossal) provides motor to intrinsic and extrinsic tongue muscles, not pharyngeal muscles involved in gag reflex
Cervical sympathetic chain US Medical PG Question 9: Which tongue papillae do not have taste buds?
- A. Fungiform
- B. Filiform (Correct Answer)
- C. Circumvallate
- D. Foliate
- E. Conical
Cervical sympathetic chain Explanation: ***Filiform***
- **Filiform papillae** are the most abundant type of papillae on the tongue and are responsible for the **mechanical action of gripping food**, due to their cone-shaped, abrasive structure of keratinized epithelium.
- Unlike other papillae, they **lack taste buds** and thus do not play a role in taste sensation.
*Fungiform*
- **Fungiform papillae** are mushroom-shaped and are scattered among the filiform papillae, primarily on the tip and sides of the tongue.
- These papillae **contain taste buds** on their superior surface and are involved in sensing taste stimuli.
*Circumvallate*
- **Circumvallate papillae** are large, dome-shaped structures arranged in a V-shape at the back of the tongue.
- They are surrounded by a trench into which salivary glands empty, and their walls contain a **large number of taste buds**.
*Foliate*
- **Foliate papillae** are leaf-like folds located on the lateral margins of the posterior tongue.
- They are **well-developed in young children** and contain taste buds, though they tend to degenerate with age.
*Conical*
- **Conical** is not a recognized classification of tongue papillae. While filiform papillae have a conical (cone-shaped) structure, "conical papillae" is not an anatomical term used to describe a distinct type of papilla.
Cervical sympathetic chain US Medical PG Question 10: Match the following nerves to their respective areas of supply to the auricle
- A. A - Auriculotemporal, B - Greater auricular, C - Vagus, D - Lesser occipital (Correct Answer)
- B. A - Greater auricular, B - Auriculotemporal, C - Lesser occipital, D - Vagus
- C. A - Auriculotemporal, B - Lesser occipital, C - Greater auricular, D - Vagus
- D. A - Auriculotemporal, B - Lesser occipital, C - Vagus, D - Greater auricular
- E. A - Vagus, B - Greater auricular, C - Auriculotemporal, D - Lesser occipital
Cervical sympathetic chain Explanation: ***A - Auriculotemporal, B - Greater auricular, C - Vagus, D - Lesser occipital***
- **A points to the anterior-superior part of the auricle**, which is supplied by the **auriculotemporal nerve**, a branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3).
- **B points to the posterolateral surface of the auricle and the lobule**, primarily supplied by the **greater auricular nerve**, a branch of the cervical plexus (C2-C3).
- **C (the concha)** is innervated by the **vagus nerve** (CN X).
- **D, the superior posterior part of the auricle**, is supplied by the **lesser occipital nerve** (C2-C3).
*A - Auriculotemporal, B - Lesser occipital, C - Vagus, D - Greater auricular*
- This option incorrectly swaps the **lesser occipital** and **greater auricular** nerve distributions.
- The **greater auricular nerve** supplies the prominent posterolateral auricle (area B), not area D.
*A - Vagus, B - Greater auricular, C - Auriculotemporal, D - Lesser occipital*
- This option incorrectly assigns the **vagus nerve** to area A (anterosuperior auricle), which is innervated by the **auriculotemporal nerve**.
- The **auriculotemporal nerve** is incorrectly placed at C; the vagus nerve primarily innervates the concha (area C).
*A - Greater auricular, B - Auriculotemporal, C - Lesser occipital, D - Vagus*
- This option reverses the **greater auricular** and **auriculotemporal** distributions and misplaces the vagus and lesser occipital nerves.
- The **auriculotemporal nerve** supplies the anterosuperior region (A), not the posterolateral region (B).
*A - Auriculotemporal, B - Lesser occipital, C - Greater auricular, D - Vagus*
- This option incorrectly places the **lesser occipital nerve** at B and misidentifies the concha's innervation.
- The **greater auricular nerve** supplies area B (posterolateral auricle and lobule), not the concha (C).
More Cervical sympathetic chain US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.