Respiratory system overview US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Respiratory system overview. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Respiratory system overview US Medical PG Question 1: A 3-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department by her parents with sudden onset shortness of breath. They tell the emergency physician that their daughter was lying on the bed watching television when she suddenly began gasping for air. They observed a bowl of peanuts lying next to her when they grabbed her up and brought her to the emergency department. Her respirations are 25/min, the pulse is 100/min and the blood pressure is 90/65 mm Hg. The physical findings as of now are apparently normal. She is started on oxygen and is sent in for a chest X-ray. Based on her history and physical exam findings, the cause of her current symptoms would be seen on the X-ray at which of the following sites?
- A. The superior segment of the right lower lobe
- B. The posterior segment of the right lower lobe (Correct Answer)
- C. The lingula of the left upper lobe
- D. The apical segment of the right upper lobe
- E. The apical segment of the left upper lobe
Respiratory system overview Explanation: ***The posterior segment of the right lower lobe***
- This is the **most common site for foreign body aspiration in a supine or lying down position** due to gravity and anatomical orientation.
- The history explicitly states the child was **"lying on the bed watching television"** when aspiration occurred, making the **posterior segment of the right lower lobe** the most gravity-dependent and therefore most likely location.
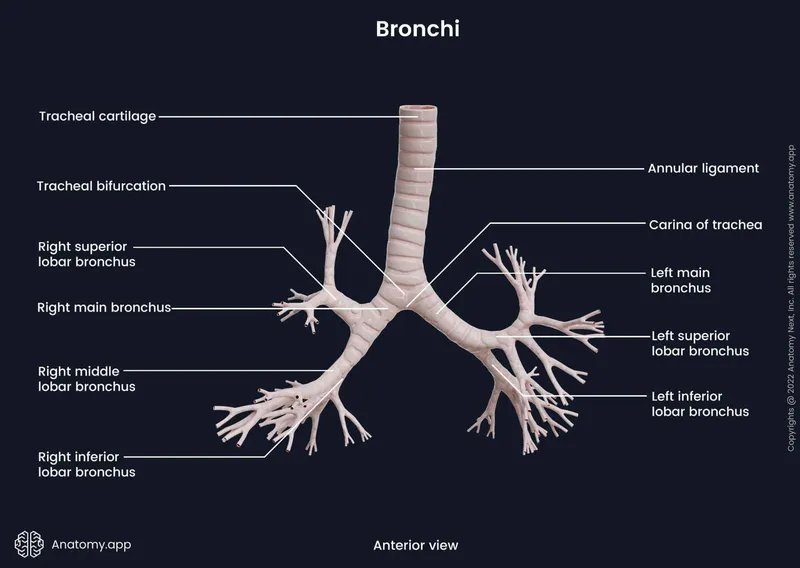
- The **right main bronchus** is wider, shorter, and more vertical than the left, making the right lung the predominant site for aspiration, and in supine position, the posterior segment is most dependent [1, 2].
*The superior segment of the right lower lobe*
- The **superior segment of the right lower lobe** is the most common site for aspiration in **upright, standing, or semi-upright positions**, not in a supine position.
- Since the child was lying down (supine), gravity would direct the aspirated peanut to the **posterior segment** rather than the superior segment.
- This would be correct if the child had aspirated while sitting upright.
*The lingula of the left upper lobe*
- The **lingula** is an uncommon site for aspiration because the **left main bronchus** has a sharper angle and smaller diameter compared to the right bronchus [2].
- The anatomical differences make aspiration into the right lung significantly more common than the left lung [2].
- The lingula is not a gravity-dependent area in the supine position.
*The apical segment of the right upper lobe*
- The **apical segment of the right upper lobe** is associated with aspiration when the patient is in **Trendelenburg position** (head lower than feet) or in extreme head-down positions.
- The described scenario of lying flat on the bed does not favor aspiration into apical segments, which are non-gravity-dependent in supine position.
- This location would be contra-gravity in the supine position.
*The apical segment of the left upper lobe*
- Aspiration into the **left upper lobe** is less frequent than the right lung due to the sharper angle of the left main bronchus [2].
- The **apical segment** would require head-down positioning (Trendelenburg) that is not described in this clinical scenario.
- This is the least likely location given both the supine position and left-sided anatomy.
Respiratory system overview US Medical PG Question 2: A 60-year-old man comes to the clinic complaining of a persistent cough for the last few months. His cough started gradually about a year ago, and it became more severe and persistent despite all his attempts to alleviate it. During the past year, he also noticed some weight loss and a decrease in his appetite. He also complains of progressive shortness of breath. He has a 40-pack-year smoking history but is a nonalcoholic. Physical examination findings are within normal limits. His chest X-ray shows a mass in the right lung. A chest CT shows a 5 cm mass with irregular borders near the lung hilum. A CT guided biopsy is planned. During the procedure, just after insertion of the needle, the patient starts to feel pain in his right shoulder. Which of the following nerves is responsible for his shoulder pain?
- A. Thoracic spinal nerves
- B. Phrenic nerve (Correct Answer)
- C. Vagus nerve
- D. Pulmonary plexus
- E. Intercostal nerves
Respiratory system overview Explanation: **Phrenic nerve**
- The **phrenic nerve** innervates the diaphragm and also carries sensory fibers from the **mediastinal and diaphragmatic pleura**, as well as the **pericardium**.
- Irritation of the phrenic nerve, due to its **C3-C5 cervical origin**, can cause **referred pain to the ipsilateral shoulder** or neck.
*Thoracic spinal nerves*
- These nerves primarily serve the **intercostal muscles** and skin of the chest wall.
- While they can transmit pain from the chest wall, they are not typically associated with **referred shoulder pain** from intrathoracic structures.
*Vagus nerve*
- The **vagus nerve** provides parasympathetic innervation to many thoracic and abdominal organs and carries visceral afferents.
- It plays a role in regulating lung function but does not transmit sensory information that would be perceived as **shoulder pain** from diaphragmatic irritation.
*Pulmonary plexus*
- The **pulmonary plexus** is formed by branches of the vagus and sympathetic nerves, primarily involved in regulating **bronchial and vascular tone** in the lungs.
- It does not transmit sensory input that would cause referred pain to the shoulder.
*Intercostal nerves*
- These nerves run along the ribs and innervate the **intercostal muscles** and skin of the **thoracic wall**.
- Pain from these nerves would typically be felt along the **rib cage** or chest wall, not as referred shoulder pain.
Respiratory system overview US Medical PG Question 3: A 45-year-old male alcoholic presents with fever, productive cough, and foul-smelling sputum for the past two weeks. Vital signs are T 38.3 C, HR 106, BP 118/64 and RR 16. Oxygen saturation on room air is 90%. Given a diagnosis of aspiration pneumonia, initial chest radiograph findings would most likely include:
- A. Mediastinal abscess located between vertebral levels T1-T3
- B. Left lung abscess due to increased ventilation-perfusion ratio of the left lung
- C. Right lung abscess due to the right main bronchus being wider and more vertically oriented (Correct Answer)
- D. Right lung abscess due to increased anterior-posterior diameter of the right lung
- E. Left lung abscess due to the left main bronchus being located superior to the right main bronchus
Respiratory system overview Explanation: ***Right lung abscess due to the right main bronchus being wider and more vertically oriented***
- Aspiration pneumonia most commonly affects the **right lower lobe** because the **right main bronchus** is wider, shorter, and more vertically oriented than the left, making it a straighter path for aspirated material.
- Alcoholism is a significant risk factor for aspiration, and the clinical presentation of fever, productive cough, and foul-smelling sputum is classic for **post-aspiration bacterial infection** leading to an abscess.
*Mediastinal abscess located between vertebral levels T1-T3*
- A mediastinal abscess is a collection of pus in the **mediastinum**, usually resulting from esophageal perforation, infection spread from neck/pharynx, or surgery.
- While serious, it is not the typical initial radiographic finding in aspiration pneumonia, which primarily affects lung parenchyma.
*Left lung abscess due to increased ventilation-perfusion ratio of the left lung*
- While a lung abscess can occur in any lobe, aspiration preferentially affects the **right lung** due to anatomical differences in the bronchi, not primarily due to ventilation-perfusion ratios.
- An increased ventilation-perfusion ratio (V/Q) typically indicates areas of the lung are well-ventilated but poorly perfused (e.g., pulmonary embolism), which is not the primary mechanism leading to an aspiration abscess.
*Right lung abscess due to increased anterior-posterior diameter of the right lung*
- The anterior-posterior (AP) diameter of the lung is not a significant anatomical factor determining the preferential aspiration into the right lung.
- The key anatomical features are the **width and vertical orientation** of the bronchi.
*Left lung abscess due to the left main bronchus being located superior to the right main bronchus*
- This statement is anatomically incorrect; both main bronchi originate at the carina at approximately the same level, but the **right main bronchus** is wider, shorter, and more vertical in its orientation.
- The left main bronchus is actually longer and more horizontally oriented, making aspiration into it less common.
Respiratory system overview US Medical PG Question 4: During a thoracotomy procedure, a surgeon needs to access the posterior mediastinum. Which of the following structures forms the anterior boundary of the posterior mediastinum?
- A. Descending thoracic aorta
- B. Pericardial sac (Correct Answer)
- C. Azygos vein
- D. Thoracic vertebrae
- E. Sternum
Respiratory system overview Explanation: ***Pericardial sac***
- The **pericardial sac** (and the diaphragm, inferiorly) forms the anterior boundary of the **posterior mediastinum** [1].
- This anatomical relationship is crucial for surgeons during thoracotomy to distinguish between the middle and posterior mediastinal compartments [1].
*Descending thoracic aorta*
- The **descending thoracic aorta** is a large vessel located *within* the posterior mediastinum itself, typically running along its left side [2].
- Therefore, it is a content of the posterior mediastinum, not a boundary.
*Azygos vein*
- The **azygos vein** is also a major structure *within* the posterior mediastinum, running along the right side of the vertebral column.
- It is a content, not a boundary, of this compartment.
*Thoracic vertebrae*
- The **thoracic vertebrae** form the *posterior* boundary of the posterior mediastinum [1].
- This anatomical landmark gives the posterior mediastinum its name and defines its dorsal limit.
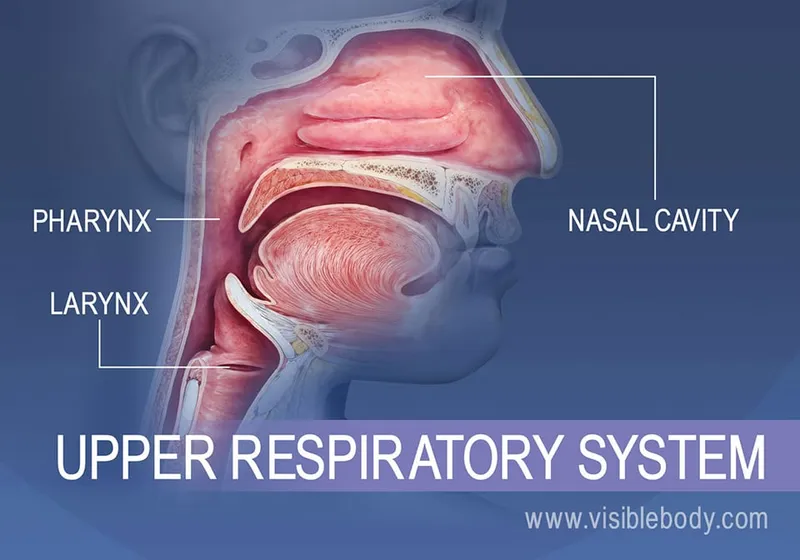
Respiratory system overview US Medical PG Question 5: A 3-year-old girl is brought to the physician by her parents because of a barking cough, a raspy voice, and noisy breathing for the last 3 days. Five days ago, she had a low-grade fever and runny nose. She attends daycare. Her immunizations are up-to-date. Her temperature is 37.8°C (100°F) and respirations are 33/min. Physical examination shows supraclavicular retractions. There is a high-pitched sound present on inspiration. Examination of the throat shows erythema without exudates. Which of the following is the most likely location of the anatomic narrowing causing this patient's symptoms?
- A. Bronchioles
- B. Pharynx
- C. Subglottic larynx (Correct Answer)
- D. Distal trachea
- E. Epiglottis
Respiratory system overview Explanation: ***Subglottic larynx***
- The patient's symptoms of **barking cough**, **raspy voice**, **stridor** (high-pitched inspiratory sound), and **supraclavicular retractions** are classic for **croup** (laryngotracheobronchitis), which is caused by inflammation and narrowing of the subglottic region of the larynx.
- The preceding low-grade fever and runny nose are typical of a viral upper respiratory infection, which commonly precedes croup.
*Bronchioles*
- Narrowing in the bronchioles typically causes **wheezing** (a high-pitched whistling sound on expiration) and **respiratory distress**, often seen in conditions like **bronchiolitis** or **asthma**.
- A barking cough and raspy voice are not characteristic symptoms of bronchiolar obstruction.
*Pharynx*
- Inflammation and narrowing of the pharynx primarily cause **sore throat**, **difficulty swallowing** (dysphagia), and sometimes **muffled voice**.
- It would not typically lead to a barking cough, stridor, or severe inspiratory distress.
*Distal trachea*
- While tracheal narrowing can cause stridor, the classic **barking cough** and **hoarseness** (raspy voice) are more specifically localized to the laryngeal area.
- Obstruction in the distal trachea would be less likely to affect voice quality as significantly as subglottic narrowing.
*Epiglottis*
- **Epiglottitis** presents as a rapidly progressive, life-threatening condition with **high fever**, **dysphagia**, **drooling**, and a **muffled "hot potato" voice**.
- The patient would typically appear toxic and prefer to sit in the **tripod position**, which is not described in this case, and her symptoms are less acute.
Respiratory system overview US Medical PG Question 6: In which of the following pathological states would the oxygen content of the trachea resemble the oxygen content in the affected alveoli?
- A. Emphysema
- B. Exercise
- C. Pulmonary embolism (Correct Answer)
- D. Pulmonary fibrosis
- E. Foreign body obstruction distal to the trachea
Respiratory system overview Explanation: ***Pulmonary embolism***
- A pulmonary embolism blocks **blood flow** to a portion of the lung, creating **dead space ventilation** (high V/Q ratio).
- In the affected alveoli, **no blood perfusion** means no oxygen extraction occurs, so the alveolar oxygen content remains **high and similar to tracheal/inspired air**.
- This is the classic physiological state where ventilation continues but perfusion is absent, preventing gas exchange.
*Foreign body obstruction distal to the trachea*
- A complete obstruction **prevents fresh air** from reaching the affected alveoli.
- The trapped gas undergoes **resorption atelectasis**: oxygen is absorbed into capillary blood, CO2 diffuses in, and alveolar gas equilibrates with **venous blood** composition.
- Alveolar oxygen content becomes **very low**, not similar to tracheal air.
*Emphysema*
- Emphysema involves destruction of **alveolar walls** and enlargement of airspaces with impaired gas exchange.
- While V/Q mismatch occurs, oxygen is still extracted by perfusing blood.
- Alveolar oxygen content is **lower than tracheal air** due to ongoing (though inefficient) gas exchange.
*Exercise*
- During exercise, **oxygen consumption increases** dramatically with enhanced cardiac output and oxygen extraction.
- Alveolar oxygen content is **significantly lower** than tracheal air due to increased oxygen uptake by blood.
*Pulmonary fibrosis*
- Pulmonary fibrosis causes **thickening of the alveolar-capillary membrane**, impairing oxygen diffusion.
- Despite diffusion limitation, blood still perfuses the alveoli and extracts oxygen.
- Alveolar oxygen content is **lower than tracheal air**, though the A-a gradient is increased.
Respiratory system overview US Medical PG Question 7: A 2-year-old girl is brought to the emergency department by her mother because the girl has had a cough and shortness of breath for the past 2 hours. Her symptoms began shortly after she was left unattended while eating watermelon. She appears anxious and mildly distressed. Examination shows intercostal retractions and unilateral diminished breath sounds with inspiratory wheezing. Flexible bronchoscopy is most likely to show a foreign body in which of the following locations?
- A. Left upper lobe bronchus
- B. Left lower lobe bronchus
- C. Right middle lobe bronchus
- D. Left main bronchus
- E. Right intermediate bronchus (Correct Answer)
Respiratory system overview Explanation: ***Right intermediate bronchus***
- Due to the **anatomy of the tracheobronchial tree**, aspirated foreign bodies preferentially enter the **right bronchial tree** because the right main bronchus is wider, shorter, and more vertically oriented than the left.
- In the right bronchial tree, foreign bodies most commonly lodge in the **right lower lobe bronchus or right intermediate bronchus region** (the intermediate bronchus is the segment between the right upper lobe takeoff and the middle/lower lobe bifurcation).
- Among the options provided, the **right intermediate bronchus** is the most anatomically accurate location, as it represents the pathway through which most aspirated foreign bodies travel in the right lung.
- Classic presentation includes sudden onset **cough, shortness of breath, inspiratory wheezing**, and **unilateral diminished breath sounds**.
*Left upper lobe bronchus*
- The **left main bronchus** is narrower and branches at a more acute angle (40-60°) from the trachea compared to the right (20-30°), making aspiration into the left side significantly less common.
- The left upper lobe bronchus branches superiorly and is even less likely to receive aspirated material due to its upward trajectory.
*Left lower lobe bronchus*
- While the **left lower lobe bronchus** is more vertically oriented than the left upper lobe, the entire left bronchial tree receives aspirated foreign bodies much less frequently than the right side.
- If aspiration occurs on the left, this would be the more likely site than the upper lobe, but right-sided aspiration predominates (approximately 60-80% of cases).
*Right middle lobe bronchus*
- The **right middle lobe bronchus** branches anterolaterally from the intermediate bronchus and takes a horizontal course, making it less likely to receive aspirated foreign bodies compared to the more vertical right lower lobe pathway.
- Foreign bodies following gravity tend to bypass this horizontal branch and continue into the lower lobe.
*Left main bronchus*
- While a foreign body could lodge in the **left main bronchus**, this is much less common than right-sided aspiration due to the **more acute angle** (40-60°) at which the left main bronchus branches from the trachea.
- The right main bronchus is the preferential pathway in approximately 60-80% of aspiration cases in young children.
Respiratory system overview US Medical PG Question 8: Where does the only cranial nerve without a thalamic relay nucleus enter the skull?
- A. Superior orbital fissure
- B. Internal auditory meatus
- C. Foramen rotundum
- D. Jugular foramen
- E. Cribriform plate (Correct Answer)
Respiratory system overview Explanation: ***Cribriform plate***
- The **olfactory nerve (CN I)** is the only cranial nerve that does not have a thalamic relay nucleus before reaching the cerebral cortex.
- It passes through the **cribriform plate** of the ethmoid bone to reach the olfactory bulbs.
*Superior orbital fissure*
- This opening transmits the **oculomotor (CN III), trochlear (CN IV), ophthalmic division of trigeminal (CN V1)**, and **abducens (CN VI)** nerves.
- These nerves all have sensory or motor components that relay through the thalamus, directly or indirectly.
*Internal auditory meatus*
- This canal transmits the **facial (CN VII)** and **vestibulocochlear (CN VIII)** nerves.
- The vestibulocochlear nerve's auditory pathway involves a thalamic relay in the **medial geniculate nucleus**.
*Foramen rotundum*
- The **maxillary division of the trigeminal nerve (CN V2)** passes through the foramen rotundum.
- Sensory information carried by CN V2 relays through the **thalamus**.
*Jugular foramen*
- This opening transmits the **glossopharyngeal (CN IX), vagus (CN X)**, and **accessory (CN XI)** nerves.
- Sensory components of these nerves, particularly taste and visceral sensation, involve thalamic nuclei.
Respiratory system overview US Medical PG Question 9: A 29-year-old mother brings in her 2-week-old baby boy to a pediatrician because he has been having difficulty feeding. The mother reveals that she had no prenatal care during her pregnancy and gave birth at home without complications. She says that her son seems to be having difficulty sucking, and she occasionally sees breast milk coming out of the infant’s nose. Physical exam reveals that this patient has a gap between his oral and nasal cavities behind the incisive foramen. He is therefore prescribed specialized bottles and his mom is taught positional techniques to ensure better feeding. Failure to fuse which of the following structures is most likely responsible for this patient's disorder?
- A. Maxillary and medial nasal prominences
- B. Nasal septum with primary plates
- C. Maxillary and lateral nasal prominences
- D. Palatine shelves with primary plates
- E. Palatine shelves with nasal septum (Correct Answer)
Respiratory system overview Explanation: ***Palatine shelves with nasal septum***
- A **cleft palate** results from the **failure of fusion of the palatine shelves** with each other and/or with the **nasal septum**, creating an abnormal communication between the oral and nasal cavities.
- This anatomical defect explains the infant's **feeding difficulties** and the leakage of breast milk into the nose, as well as the observed **gap behind the incisive foramen**.
*Maxillary and medial nasal prominences*
- The failure of fusion between the maxillary and medial nasal prominences results in a **cleft lip**, which is an anterior defect and does not explain the posterior gap described.
- While cleft lip can coexist with cleft palate, the symptoms here specifically point to a palatal defect, not primarily a lip defect.
*Nasal septum with primary plates*
- The primary palate forms from the fusion of the medial nasal prominences, anterior to the incisive foramen.
- While crucial for normal development, the specific clinical presentation (gap *behind* the incisive foramen and feeding difficulties) is more characteristic of a secondary palate defect involving the palatine shelves.
*Maxillary and lateral nasal prominences*
- The fusion of these structures contributes to the formation of the **nasolacrimal groove** and parts of the cheek, not the palate.
- Deficiencies in this fusion would lead to defects in the lateral facial region, not an oro-nasal communication related to feeding.
*Palatine shelves with primary plates*
- The **primary palate** fuses with the anterior part of the secondary palate (formed by the palatine shelves) at the incisive foramen.
- However, the more common and clinically relevant defect leading to an open communication between the oral and nasal cavities, especially *behind* the incisive foramen, involves the failure of fusion of the **palatine shelves** with each other and the **nasal septum**.
Respiratory system overview US Medical PG Question 10: A 35-year-old man is brought to the trauma bay by ambulance after sustaining a gunshot wound to the right arm. The patient is in excruciating pain and states that he can't move or feel his hand. The patient states that he has no other medical conditions. On exam, the patient's temperature is 98.4°F (36.9°C), blood pressure is 140/86 mmHg, pulse is 112/min, and respirations are 14/min. The patient is alert and his Glasgow coma scale is 15. On exam, he has a single wound on his right forearm without continued bleeding. The patient has preserved motor and sensation in his right elbow; however, he is unable to extend his wrist or extend his fingers further. He is able to clench his hand, but this is limited by pain. On sensory exam, the patient has no sensation to the first dorsal web space but has preserved sensation on most of the volar surface. Which of the following structures is most likely injured?
- A. Recurrent motor branch of the median nerve
- B. Main median nerve
- C. Lower trunk
- D. Ulnar nerve
- E. Radial nerve (Correct Answer)
Respiratory system overview Explanation: ***Radial nerve***
- The inability to **extend the wrist and fingers** (wrist drop) is a classic sign of **radial nerve injury**, as it innervates the extensors of the forearm and hand.
- **Loss of sensation in the first dorsal web space** is also characteristic of radial nerve damage, as this area is supplied by the superficial radial nerve.
*Recurrent motor branch of the median nerve*
- This nerve primarily innervates the **thenar muscles** (flexor pollicis brevis, abductor pollicis brevis, opponens pollicis), affecting **thumb opposition**.
- Injury would primarily lead to **weakness in thumb movements**, not wrist or finger extension, and would spare sensation in the first dorsal web space.
*Main median nerve*
- The median nerve primarily innervates the **flexors of the forearm and hand**, and contributes to sensation on the **volar aspect of the thumb**, index, middle, and radial half of the ring finger.
- Injury would cause difficulty with **flexion of the wrist and fingers**, and loss of sensation on the volar surface, which is largely preserved in this patient.
*Lower trunk*
- The lower trunk of the brachial plexus (C8-T1) gives rise to the ulnar nerve and part of the median nerve, affecting **flexion of the wrist and fingers**, and intrinsic hand muscles.
- Injury would result in more widespread weakness affecting the **intrinsic hand muscles** and flexion, and would include sensory loss in the **ulnar nerve distribution**, which is not described.
*Ulnar nerve*
- The ulnar nerve primarily innervates the **intrinsic hand muscles** (excluding the thenar group) and the **flexor carpi ulnaris** and **medial half of flexor digitorum profundus**.
- Injury would typically cause **weakness in intrinsic hand functions** (e.g., finger abduction/adduction, ring and little finger flexion) and sensory loss on the **ulnar side of the hand**, not the dorsal web space.
More Respiratory system overview US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.