Cardiovascular system overview US Medical PG Practice Questions and MCQs
Practice US Medical PG questions for Cardiovascular system overview. These multiple choice questions (MCQs) cover important concepts and help you prepare for your exams.
Cardiovascular system overview US Medical PG Question 1: During a clinical study examining the diffusion of gas between the alveolar compartment and the pulmonary capillary blood, men between the ages of 20 and 50 years are evaluated while they hold a sitting position. After inhaling a water-soluble gas that rapidly combines with hemoglobin, the concentration of the gas in the participant's exhaled air is measured and the diffusion capacity is calculated. Assuming that the concentration of the inhaled gas remains the same, which of the following is most likely to increase the flow of the gas across the alveolar membrane?
- A. Deep exhalation
- B. Entering a cold chamber
- C. Treadmill exercise (Correct Answer)
- D. Standing straight
- E. Assuming a hunched position
Cardiovascular system overview Explanation: ***Correct: Treadmill exercise***
- **Treadmill exercise** increases cardiac output and pulmonary blood flow, which in turn recruits and distends more **pulmonary capillaries**. This increases the **surface area** available for gas exchange and reduces the diffusion distance, thereby enhancing the flow of gas across the alveolar membrane.
- Exercise also typically leads to deeper and more frequent breaths, increasing the **ventilation-perfusion matching** and overall efficiency of gas exchange.
- According to Fick's law of diffusion (Vgas = A/T × D × ΔP), increasing the surface area (A) directly increases gas flow.
*Incorrect: Deep exhalation*
- **Deep exhalation** would empty the lungs more completely, potentially leading to alveolar collapse in some regions and thus **decreasing the alveolar surface area** available for gas exchange.
- This would also reduce the **driving pressure** for gas diffusion by lowering the alveolar concentration of the inhaled gas.
*Incorrect: Entering a cold chamber*
- Exposure to a **cold chamber** can cause **bronchoconstriction** in some individuals, particularly those with reactive airways, which would increase airway resistance and potentially reduce alveolar ventilation.
- While metabolic rate may slightly increase in the cold, the primary effect on the lungs is unlikely to promote increased gas diffusion in a healthy individual.
*Incorrect: Standing straight*
- **Standing straight** is a normal physiological posture and does not significantly alter the **pulmonary capillary recruitment** or the alveolar surface area in a way that would dramatically increase gas flow compared to a seated position.
- There might be minor gravitational effects on blood flow distribution, but these are generally less impactful than dynamic changes like exercise.
*Incorrect: Assuming a hunched position*
- **Assuming a hunched position** can restrict chest wall expansion and diaphragm movement, leading to **reduced tidal volume** and overall alveolar ventilation.
- This posture, by reducing lung volumes and potentially compressing the lungs, would likely **decrease the effective surface area** for gas exchange and therefore reduce gas flow.
Cardiovascular system overview US Medical PG Question 2: A 40-year-old female volunteers for an invasive study to measure her cardiac function. She has no previous cardiovascular history and takes no medications. With the test subject at rest, the following data is collected using blood tests, intravascular probes, and a closed rebreathing circuit:
Blood hemoglobin concentration 14 g/dL
Arterial oxygen content 0.22 mL O2/mL
Arterial oxygen saturation 98%
Venous oxygen content 0.17 mL O2/mL
Venous oxygen saturation 78%
Oxygen consumption 250 mL/min
The patient's pulse is 75/min, respiratory rate is 14/ min, and blood pressure is 125/70 mm Hg. What is the cardiac output of this volunteer?
- A. Body surface area is required to calculate cardiac output.
- B. Stroke volume is required to calculate cardiac output.
- C. 250 mL/min
- D. 5.0 L/min (Correct Answer)
- E. 50 L/min
Cardiovascular system overview Explanation: ***5.0 L/min***
- Cardiac output can be calculated using the **Fick principle**: Cardiac Output $(\text{CO}) = \frac{{\text{Oxygen Consumption}}}{{\text{Arterial } \text{O}_2 \text{ Content} - \text{Venous O}_2 \text{ Content}}}$.
- Given Oxygen Consumption = 250 mL/min, Arterial O$_2$ Content = 0.22 mL/mL, and Venous O$_2$ Content = 0.17 mL/mL. Thus, CO = $\frac{{250 \text{ mL/min}}}{{(0.22 - 0.17) \text{ mL } \text{O}_2/\text{mL blood}}} = \frac{{250 \text{ mL/min}}}{{0.05 \text{ mL } \text{O}_2/\text{mL blood}}} = 5000 \text{ mL/min } = 5.0 \text{ L/min}$.
*Body surface area is required to calculate cardiac output.*
- **Body surface area (BSA)** is used to calculate **cardiac index**, which is cardiac output normalized to body size, but not cardiac output directly.
- While a normal cardiac output might be compared to a patient's BSA for context, it is not a necessary component for calculating the absolute cardiac output.
*Stroke volume is required to calculate cardiac output.*
- Cardiac output can be calculated as **Stroke Volume (SV) x Heart Rate (HR)**. However, stroke volume is not provided directly in this question.
- The Fick principle allows for the calculation of cardiac output **without explicit knowledge of stroke volume** or heart rate, using oxygen consumption and arteriovenous oxygen difference.
*250 mL/min*
- 250 mL/min represents the **oxygen consumption**, not the cardiac output.
- Cardiac output is the volume of blood pumped by the heart per minute, which is influenced by both oxygen consumption and the difference in oxygen content between arterial and venous blood.
*50 L/min*
- A cardiac output of 50 L/min is an **extremely high and physiologically impossible** value for a resting individual.
- This value is 10 times higher than the calculated cardiac output and typically represents a calculation error.
Cardiovascular system overview US Medical PG Question 3: Cardiac muscle serves many necessary functions, leading to a specific structure that serves these functions. The structure highlighted is an important histology component of cardiac muscle. What would be the outcome if this structure diffusely failed to function?
- A. Failure of potassium channels to appropriately open to repolarize the cell
- B. Failure of propagation of the action potential from the conduction system (Correct Answer)
- C. Ineffective excitation-contraction coupling due to insufficient calcium ions
- D. Inappropriate formation of cardiac valve leaflets
- E. Outflow tract obstruction
Cardiovascular system overview Explanation: ***Failure of propagation of the action potential from the conduction system***
- The highlighted structure, the **intercalated disc**, contains **gap junctions** which are crucial for the rapid, synchronized spread of **action potentials** between cardiac muscle cells.
- A diffuse failure of these structures would prevent the coordinated electrical activation of the myocardium, leading to a failure of impulse propagation and **compromised cardiac contraction**.
*Failure of potassium channels to appropriately open to repolarize the cell*
- This scenario describes a problem with **ion channel function** within individual cardiomyocytes, affecting their repolarization phase.
- While critical for a single cell's electrical activity, it does not directly relate to the primary function of **intercalated discs** in *propagating* action potentials across multiple cells.
*Ineffective excitation-contraction coupling due to insufficient calcium ions*
- This outcome would result from issues with **calcium handling** mechanisms, such as problems with the **sarcoplasmic reticulum** or **calcium channels**, which are internal to the cardiomyocyte.
- It is distinct from the role of **intercalated discs** in facilitating intercellular communication and electrical spread.
*Inappropriate formation of cardiac valve leaflets*
- The formation of cardiac valve leaflets is an intricate process during **embryological development** involving specific signaling pathways and cell migration.
- This structural defect is not directly related to the function of **intercalated discs** in mature cardiac muscle, which are involved in electrical and mechanical coupling.
*Outflow tract obstruction*
- **Outflow tract obstruction** is a congenital or acquired structural defect affecting the major arteries leaving the heart (e.g., aortic or pulmonary stenosis).
- This is a macroscopic structural anomaly that is not caused by a primary failure of **intercalated disc** function.
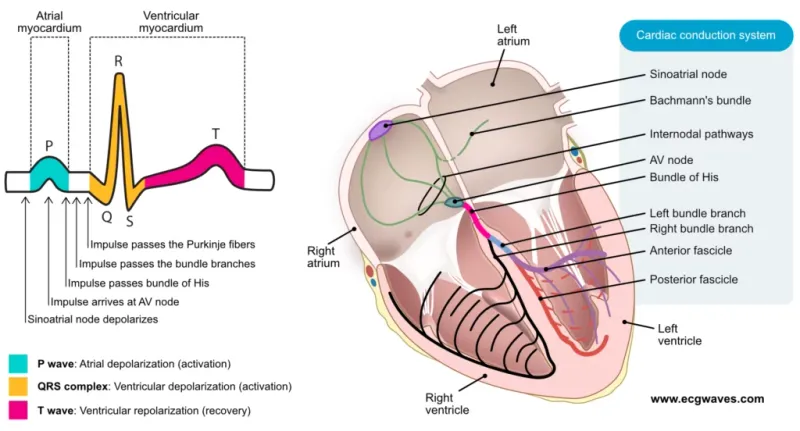
Cardiovascular system overview US Medical PG Question 4: A researcher measures action potential propagation velocity in various regions of the heart in a 42-year-old Caucasian female. Which of the following set of measurements corresponds to the velocities found in the atrial muscle, AV Node, Purkinje system, and ventricular muscle, respectively?
- A. 0.05 m/s, 1.1 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 3.3 m/s
- B. 2.2 m/s, 0.3 m/s, 0.05 m/s, 1.1 m/s
- C. 0.3 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 0.05 m/s, 1.1 m/s
- D. 0.5 m/s, 1.1 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 3 m/s
- E. 1.1 m/s, 0.05 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 0.3 m/s (Correct Answer)
Cardiovascular system overview Explanation: ***1.1 m/s, 0.05 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 0.3 m/s***
- This option correctly lists the approximate conduction velocities for the **atrial muscle (1.1 m/s)**, **AV node (0.05 m/s)**, **Purkinje system (2.2 m/s)**, and **ventricular muscle (0.3 m/s)**, respectively.
- The **AV node has the slowest conduction velocity (~0.05 m/s)**, which is crucial for delaying ventricular contraction and allowing complete ventricular filling.
- The **Purkinje system has the fastest conduction velocity (~2-4 m/s)**, ensuring rapid and coordinated ventricular depolarization.
- **Atrial muscle (~1 m/s)** and **ventricular muscle (~0.3-0.5 m/s)** have intermediate velocities.
*0.05 m/s, 1.1 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 3.3 m/s*
- This sequence is incorrect because it places the **AV node's velocity (0.05 m/s)** first (as atrial muscle) and significantly overestimates ventricular muscle velocity (3.3 m/s).
- Atrial muscle conducts faster than 0.05 m/s, and ventricular muscle velocity should be approximately 0.3-0.5 m/s, not 3.3 m/s.
*2.2 m/s, 0.3 m/s, 0.05 m/s, 1.1 m/s*
- This option incorrectly assigns the **highest velocity (2.2 m/s)** to atrial muscle, which is characteristic of the Purkinje system, and misplaces the **slowest velocity (0.05 m/s)** in the Purkinje system instead of the AV node.
- The values do not align with known physiological conduction speeds across cardiac tissues.
*0.3 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 0.05 m/s, 1.1 m/s*
- This sequence incorrectly places the **slowest velocity (0.05 m/s)** in the Purkinje system, which is known for the most rapid conduction, and assigns an unrealistically high velocity (2.2 m/s) to the AV node.
- The arrangement directly contradicts the physiological function and relative speeds within the cardiac conduction system.
*0.5 m/s, 1.1 m/s, 2.2 m/s, 3 m/s*
- This option underestimates the **atrial muscle velocity** (0.5 m/s instead of ~1 m/s) and significantly overestimates the **ventricular muscle velocity** (3 m/s instead of ~0.3-0.5 m/s).
- The provided values do not accurately represent the typical ranges of conduction velocities for each specified cardiac region.
Cardiovascular system overview US Medical PG Question 5: A 65-year-old woman comes to the physician because of a 3-month history of intermittent palpitations and shortness of breath. Cardiopulmonary examination shows no other abnormalities. An ECG shows an absence of P waves, an oscillating baseline, and irregular RR intervals at a rate of approximately 95 beats per minute. The difference between atrial and ventricular rates in this patient is most likely due to which of the following?
- A. Prolonged influx through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in the bundle of His
- B. Transient activation of K+ current in Purkinje fibers
- C. Inhibition of the Na+/K+-ATPase pump in ventricular cells
- D. Limited speed of conduction through the left bundle branch
- E. Temporary inactivation of Na+ channels in the AV node (Correct Answer)
Cardiovascular system overview Explanation: ***Temporary inactivation of Na+ channels in the AV node***
- The ECG findings are classic for **atrial fibrillation**, characterized by a rapid, irregular atrial rhythm (oscillating baseline with no P waves) and an irregularly irregular ventricular response.
- The **AV node's refractory period** and the number of sodium channels available for conduction dictate the rate at which atrial impulses can pass to the ventricles, preventing a dangerously fast ventricular rate.
*Prolonged influx through voltage-gated Ca2+ channels in the bundle of His*
- The **bundle of His** primarily conducts impulses rather than primarily regulating the rate difference between atria and ventricles through calcium channel kinetics.
- Prolonged calcium influx would generally **slow conduction** or decrease excitability, but it's not the primary mechanism explaining the ventricular rate control in atrial fibrillation.
*Transient activation of K+ current in Purkinje fibers*
- **Purkinje fibers** are involved in rapid ventricular depolarization, but their primary role is not to mediate the rate difference between atria and ventricles in atrial fibrillation.
- Activation of K+ current typically leads to **repolarization**, affecting action potential duration, not the overall filtering of atrial impulses.
*Inhibition of the Na+/K+-ATPase pump in ventricular cells*
- Inhibition of the **Na+/K+-ATPase pump** would lead to intracellular sodium accumulation and depolarization, potentially causing arrhythmias, not regulating the ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation.
- This is the mechanism of action for **digoxin**, which can slow AV nodal conduction but through a different primary pathway affecting the pump.
*Limited speed of conduction through the left bundle branch*
- While conduction system abnormalities can occur, a **limited speed of conduction** specifically in the left bundle branch would cause a wide QRS complex or bundle branch block, not the inherent rate-limiting seen in atrial fibrillation.
- The AV node is the primary regulator of ventricular response rate in atrial fibrillation due to its inherent physiological properties.
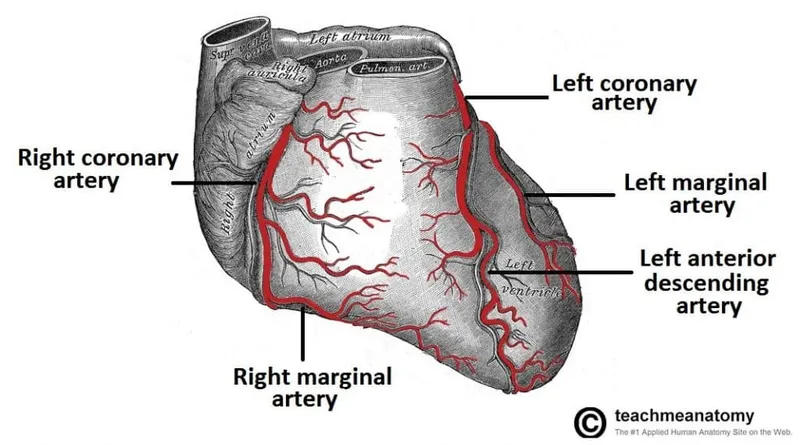
Cardiovascular system overview US Medical PG Question 6: A 41-year-old man with a history of hypertension and hyperlipidemia is brought to the emergency department by his wife for difficulty breathing after choking on food at dinner. He is unconscious and pulseless on arrival. Despite appropriate life-saving measures, he dies. Examination of the heart shows a necrotic, pale yellow plaque in the left circumflex artery. Similar lesions are most likely to be found in which of the following locations?
- A. Thoracic aorta
- B. Superficial temporal artery
- C. Internal carotid artery (Correct Answer)
- D. Abdominal aorta
- E. Pulmonary artery
Cardiovascular system overview Explanation: ***Internal carotid artery***
- The description of a "necrotic, pale yellow plaque" in the **left circumflex artery** is characteristic of an **atherosclerotic plaque** that has likely led to a **myocardial infarction (MI)**.
- **Atherosclerosis** is a **systemic disease** that preferentially affects **medium-sized muscular arteries** at bifurcations and areas of turbulent flow.
- Given the patient's history of **hypertension** and **hyperlipidemia**, similar lesions are most likely to be found in the **internal carotid artery**, which is:
- A **medium-sized muscular artery** (like coronary arteries)
- A common site for **atherosclerotic plaque formation** leading to **thrombotic stroke**
- Subject to the same risk factors and pathophysiology as coronary arteries
- Prone to similar acute complications (plaque rupture, thrombosis, vessel occlusion)
*Thoracic aorta*
- While the **thoracic aorta** can develop **atherosclerotic plaques**, it is an **elastic artery** rather than a muscular artery.
- Atherosclerosis in the aorta is typically less obstructive and less prone to acute thrombotic events compared to medium-sized muscular arteries.
- The thoracic aorta is less frequently the site for clinically significant acute occlusive events like MI or stroke.
*Superficial temporal artery*
- The **superficial temporal artery** is typically involved in diseases like **giant cell arteritis**, an inflammatory vasculitis, rather than widespread **atherosclerosis**.
- It is a smaller, more distal artery and not a typical site for the type of clinically significant **atherosclerotic plaques** described in this case.
- Atherosclerotic disease causing acute events preferentially affects larger, proximal vessels.
*Abdominal aorta*
- The **abdominal aorta** is indeed a very common site for **atherosclerosis** and **aneurysm formation**.
- However, like the thoracic aorta, it is an **elastic artery** rather than a muscular artery, so the lesions may differ in character and clinical behavior.
- While atherosclerosis here is common, it is less directly linked to acute thrombotic occlusive events (like acute MI or stroke) compared to medium-sized muscular arteries supplying the heart and brain.
*Pulmonary artery*
- The **pulmonary artery** system is a **low-pressure system** and is generally spared from systemic **atherosclerosis**.
- **Atherosclerotic plaques** are exceedingly rare in the pulmonary arteries unless there is severe pre-existing **pulmonary hypertension**.
- This is not a typical site for systemic atherosclerotic disease.
Cardiovascular system overview US Medical PG Question 7: Which factor most strongly influences coronary blood flow during exercise?
- A. Endothelin release
- B. Metabolic demand (Correct Answer)
- C. Myogenic response
- D. Neural regulation
- E. Baroreceptor reflex
Cardiovascular system overview Explanation: **Metabolic demand**
- During exercise, increased **myocardial activity** leads to a higher demand for oxygen and nutrients, prompting a significant increase in coronary blood flow.
- Local release of **metabolites** such as adenosine, nitric oxide, and hydrogen ions causes powerful vasodilation of coronary arteries, closely matching blood supply to demand.
*Endothelin release*
- **Endothelin** is a potent vasoconstrictor and plays a role in regulating vascular tone, but its primary influence is not the immediate or strongest factor dictating increased coronary flow during exercise.
- While it can modulate flow, metabolic changes are the dominant driver for the rapid and substantial increases needed during exertion.
*Myogenic response*
- The **myogenic response** is an intrinsic property of vascular smooth muscle cells to contract when stretched (due to increased pressure) and relax when pressure decreases, helping to maintain relatively constant blood flow.
- This mechanism primarily contributes to **autoregulation** and flow stability, but it does not account for the massive increase in flow required by the heart during exercise.
*Neural regulation*
- **Neural regulation**, primarily sympathetic stimulation, increases heart rate and contractility, which indirectly increases metabolic demand.
- However, direct neural effects on coronary arteries can be complex (both vasodilation and vasoconstriction depending on receptor type), and the overriding control during exercise is typically metabolic.
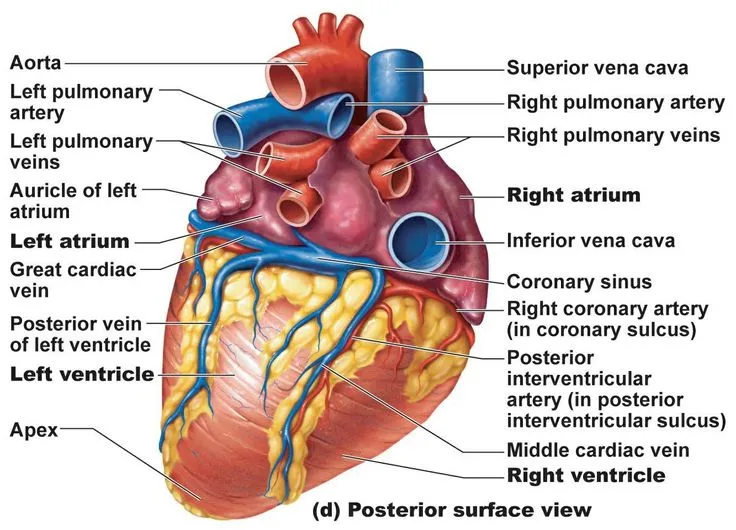
Cardiovascular system overview US Medical PG Question 8: In a patient with acute myocardial ischemia, which of the following cardiovascular structures is at greatest risk of damage?
- A. Pulmonary valve
- B. Cardiac conduction system (Correct Answer)
- C. Coronary artery
- D. Cardiac septum
- E. Temporal artery
Cardiovascular system overview Explanation: ***Cardiac conduction system***
- The **cardiac conduction system** is highly dependent on a constant oxygen supply, and its disruption by ischemia can lead to serious **arrhythmias** and **heart blocks**.
- Ischemia in critical areas like the **AV node** (supplied by the RCA) or the **bundle branches** can severely impair the heart's electrical activity.
*Pulmonary valve*
- The **pulmonary valve** is primarily a passive structure and is generally not directly damaged by acute myocardial ischemia.
- Its function is more affected by changes in **pulmonary artery pressure** or **ventricular remodeling**, not immediate ischemic injury.
*Coronary artery*
- While **coronary artery disease (CAD)** is the *cause* of myocardial ischemia, the coronary artery itself is not the structure *damaged* in the sense of functional impairment due to lack of blood flow in acute ischemia.
- The damage occurs downstream in the **myocardium** that the artery supplies.
*Cardiac septum*
- The **cardiac septum** can be damaged by myocardial ischemia, particularly the **interventricular septum**, leading to complications like **septal rupture**.
- However, the conduction system is at *greatest* immediate risk of functional damage leading to life-threatening events due to its critical role in rhythm generation.
*Temporal artery*
- The **temporal artery** is a blood vessel located in the head, entirely separate from the heart.
- It is not involved in myocardial ischemia and is not at risk of damage from a cardiac event.
Cardiovascular system overview US Medical PG Question 9: A 42-year-old Caucasian woman is enrolled in a randomized controlled trial to study cardiac function in the setting of several different drugs. She is started on verapamil and instructed to exercise at 50% of her VO2 max while several cardiac parameters are being measured. During this experiment, which of the following represents the relative conduction speed through the heart from fastest to slowest?
- A. Purkinje fibers > ventricles > atria > AV node
- B. Purkinje fibers > atria > ventricles > AV node (Correct Answer)
- C. Atria > Purkinje fibers > ventricles > AV node
- D. AV node > ventricles > atria > Purkinje fibers
- E. Purkinje fibers > AV node > ventricles > atria
Cardiovascular system overview Explanation: ***Purkinje fibers > atria > ventricles > AV node***
- The **Purkinje fibers** have the fastest conduction velocity, ensuring rapid and synchronous ventricular depolarization.
- The **atria** conduct impulses faster than the ventricles, but slower than the Purkinje fibers, allowing for atrial contraction before ventricular systole.
*Purkinje fibers > ventricles > atria > AV node*
- This option correctly identifies the **Purkinje fibers** and **AV node** at the fastest and slowest ends, respectively, but incorrectly orders the atria and ventricles.
- While Purkinje fibers are fastest, cardiac muscle cells (atria then ventricles) conduct slower than Purkinje fibers.
*Atria > Purkinje fibers > ventricles > AV node*
- This option incorrectly places the **atria** as having the fastest conduction speed, which is not true as Purkinje fibers are significantly faster.
- It also misorders the Purkinje fibers relative to the atria in terms of speed.
*AV node > ventricles > atria > Purkinje fibers*
- This option is incorrect as it places the **AV node** as the fastest conductor and the **Purkinje fibers** as the slowest, which is the exact opposite of their actual conduction speeds.
- The AV node is known for its slow conduction to allow for ventricular filling.
*Purkinje fibers > AV node > ventricles > atria*
- This option incorrectly places the **AV node** as the second fastest conductor, and the ventricles as slower than the atria.
- The AV node is specifically designed to slow the impulse to allow for proper ventricular filling.
Cardiovascular system overview US Medical PG Question 10: A 55-year-old man comes to the emergency department because of left-sided chest pain and difficulty breathing for the past 30 minutes. His pulse is 88/min. He is pale and anxious. Serum studies show increased cardiac enzymes. An ECG shows ST-elevations in leads I, aVL, and V5-V6. A percutaneous coronary intervention is performed. In order to localize the site of the lesion, the catheter must pass through which of the following structures?
- A. Left coronary artery → left circumflex artery (Correct Answer)
- B. Right coronary artery → posterior descending artery
- C. Left coronary artery → left anterior descending artery
- D. Right coronary artery → right marginal artery
- E. Left coronary artery → posterior descending artery
Cardiovascular system overview Explanation: ***Left coronary artery → left circumflex artery***
- **ST-elevations** in leads I, aVL, and V5-V6 are indicative of a **lateral myocardial infarction**.
- The **left circumflex artery** primarily supplies the lateral wall of the left ventricle.
*Right coronary artery → posterior descending artery*
- The **posterior descending artery** (PDA) typically supplies the inferior wall and posterior interventricular septum.
- An occlusion here would cause **ST-elevations** in leads II, III, and aVF, which is not seen in this case.
*Left coronary artery → left anterior descending artery*
- The **left anterior descending** (LAD) artery supplies the anterior wall and apex of the left ventricle.
- Occlusion of the LAD would typically cause **ST-elevations** in leads V1-V4, indicating an anterior MI.
*Right coronary artery → right marginal artery*
- The **right marginal artery** is a branch of the right coronary artery and supplies part of the right ventricle.
- Occlusion here would primarily affect the **right ventricle**, and is not typically associated with the given ECG changes.
*Left coronary artery → posterior descending artery*
- While the **posterior descending artery** can sometimes originate from the left circumflex artery (**left dominant circulation**), it primarily supplies the inferior wall.
- The observed ECG changes in leads I, aVL, and V5-V6 are characteristic of a **lateral wall infarct**, which is supplied by the left circumflex artery.
More Cardiovascular system overview US Medical PG questions available in the OnCourse app. Practice MCQs, flashcards, and get detailed explanations.